Hand-dug trenches [ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dieter Nill
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ David Streiff
Tranchées manuelles (French)
technologies_1625 - ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)
Niamey
ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Misereor - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/07/2012
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Hand-dug trenches contribute to the restoration of tree cover and prevention of water erosion on slopes.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
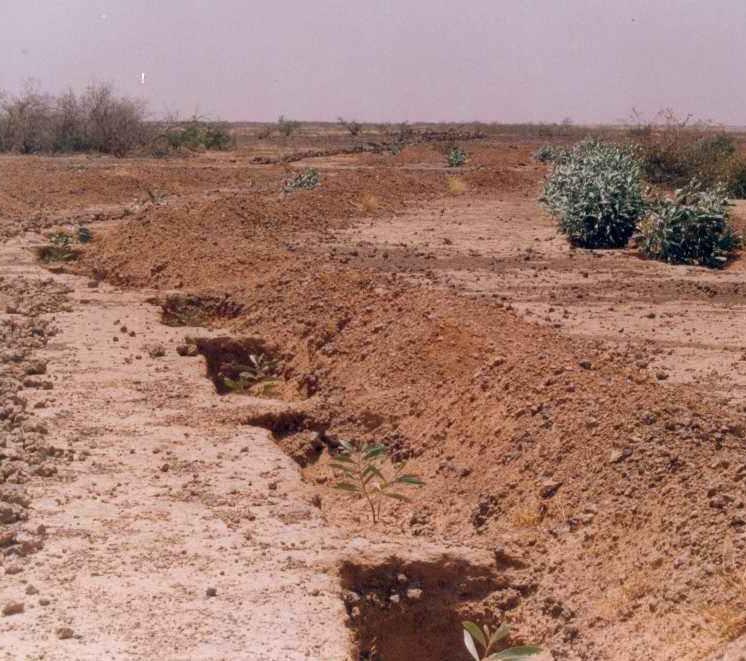
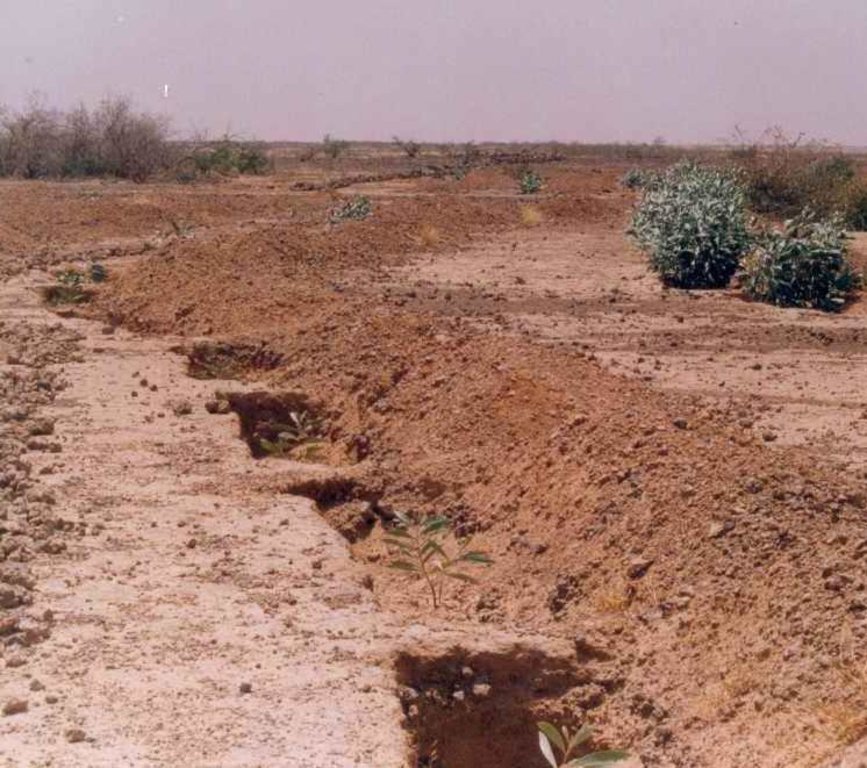
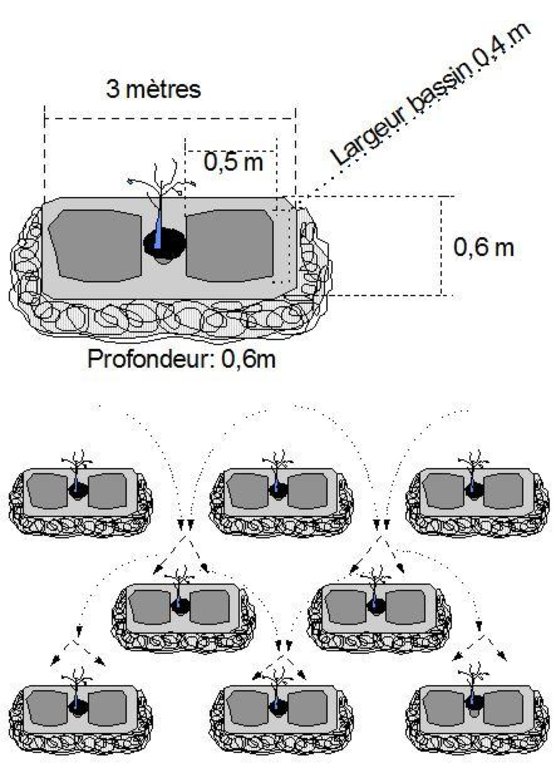
This technique is designed to restore communal land on slopes and highland pediments. It involves manually excavating trenches 3 to 3.5 m long and 0.6 m deep, spaced 4 m apart in staggered rows. This results in around 625 trenches per hectare. The excavated earth is piled downhill of the trenches, which are aligned perpendicular to the slope. In the middle of each trench, a 0.40 m high step is left on which the tree seedling is planted. The tree receives the water it needs from the trench where it collects.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this technique is to restore tree cover on degraded, unfertile land and prevent water erosion on slopes by reducing the flow of water that threatens land downstream. The trenches reduce gully erosion and pedimentation of areas with a fragile soil structure. Like all afforestation measures, in the medium term, this technique is effective in protecting the land against water and wind erosion. The shade provided by the trees also lowers the temperature of the soil and the infiltration of water in the hand-dug trenches contributes to groundwater recharge.
Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technique is very labour intensive. Work must begin immediately after harvesting when the soil is still moist and workable. A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees. The mortality of trees after planting is relatively high (survival rate is about 60%), and dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years. Good community organisation is required.
Natural / human environment: Hand-dug trenches are particularly useful when rainfall is low, as they retain water and make it available to the trees growing in them. In years when rainfall is abundant or there are violent downpours, the young trees are protected, as they are planted on a raised step within the trench, although there is a risk of flooding in the event of very heavy rain.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Niger
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by German Development Cooperation (BMZ, GIZ, KfW) in Niger by projects e.g. PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project)
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow peas and mangoes

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ដីដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water erosion (gully, sheet), wind erosion, degraded and infertile land
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: armers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S3: កម្ពស់ភ្លឺ ប្រឡាយ ផ្លូវទឹក
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted land use methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rains), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
មតិយោបល់:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Trenches are manually excavated 3 to 3.5 m long and 0.6 m deep, spaced 4 m apart in staggered rows. This results in around 625 trenches per hectare. The excavated earth is piled downhill of the trenches, which are aligned perpendicular to the slope. In the middle of each trench, a 0.40 m high step is left on which the tree seedling is planted. The tree benefits from the water collected in the trench.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Vegetative measure: planted in trench
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 4
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the contour line | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 2. | laying out the trenches in staggered rows | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 3. | digging two rectangular microcatchments separated horizontally by a flat surface | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 4. | making a hole in the central area | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | |
| 5. | planting the seedlings | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | |
| 6. | sowing grass on the ridges | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | All the Labour | unit | 1,0 | 220,76 | 220,76 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seedlings | unit | 1,0 | 41,55 | 41,55 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Transport of seedlings | unit | 1,0 | 1,93 | 1,93 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 264,24 | |||||
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | |
| 2. | dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ |
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Other costs
• equipment, such as jumper bars, shovels and axes
• 625 tree seedlings
• 15 kg of grass seed
• cost of transporting 2 cartloads of seedlings
• 120 seedlings to replace dead trees.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also footslopes and valley floors
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor - medium
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: > 10m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អខ្លាំង
- មិនល្អ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence , but surplus is sold on the market. Some vegetable growing is just for commercial/ market.
Level of mechanization: Oxes and donkeys used for animal traction.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ភូមិ
- not titled
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់:
Traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
This technique permits the reintroduction of trees on degraded, unfertile land. Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
មតិយោបល់:
Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
Establishment of the trenches involves considerable labour and growth of trees takes a couple of years.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology has been applied by PDRT on common land using food/cash for work in order to inject money and food into the local communities.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There was no spontaneous adoption. The technology is designed for common lands and takes considerable labour that only very well organised communities are able to mobilise.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The young trees are protected of flooding, as they are planted on a raised step within the trench |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Hand-dug trenches retain water and make it available to the trees growing in them. Although the trenches are progressively filled with sediment, which reduces their capacity to retain water, at the same time, the trees develop and become less dependent on stored water. |
| This technique has proved effective in restoring forest/rangeland sites. The progressive development of grass and tree cover continues on the improved sites, where the tree population is up to 20 years old. After around ten years, the average annual production of wood is 1.3 steres per hectare. |
| The shade provided by the trees also lowers the temperature of the soil. |
|
In the medium term, this technique is effective in protecting the land against water and wind erosion. |
| Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The technique is very labour intensive. Work must begin immediately after harvesting when the soil is still moist and workable. | Good community organisation is required. |
| A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees. The mortality of trees after planting is relatively high (survival rate is about 60%), and dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
វេបសាយ:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល