Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Michael Herger
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_2990 - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 1 ខែ កុម្ភៈ ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 22 ខែ កុម្ភៈ ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 3 ខែ កញ្ញា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 9 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2019 (public)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Sepeika Milton
+254 (0) 723870987
olenape@yahoo.com
Makurian Group Ranch
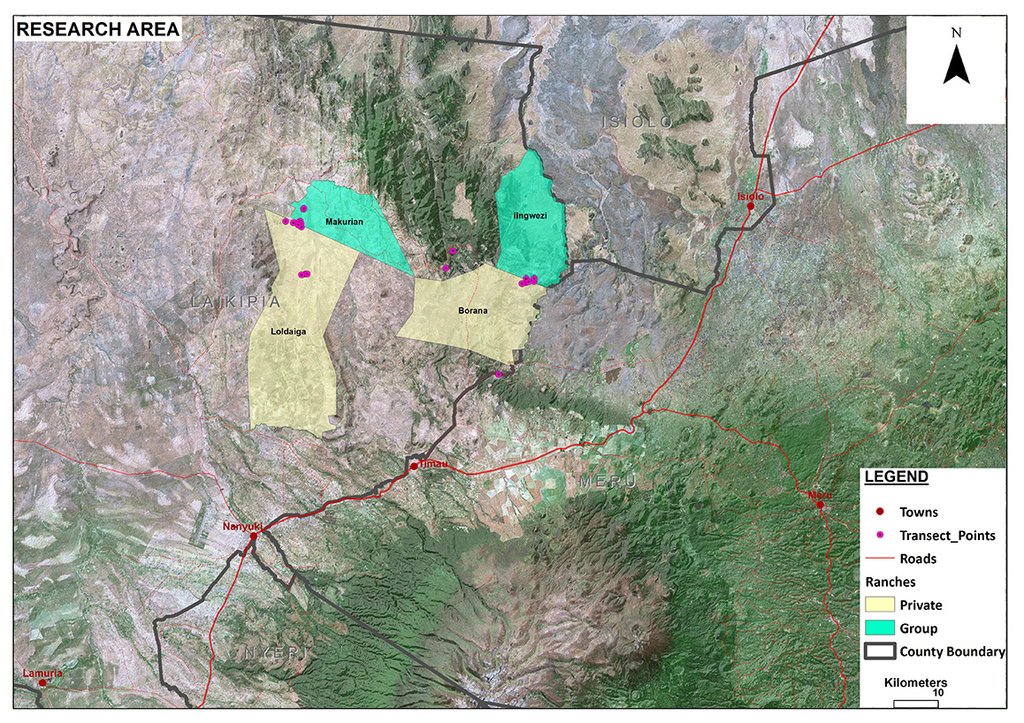
Mukogodo Division, Laikipia North District, Kenya
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
22/01/2017
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
Makurian rangeland is in bad condition. The land is largely degraded and dominated by the invasive species "Opuntia". Makurian Group Ranch has abandoned the in 2007 implemented "Holistic Management" principles. However, one has to take into account that Masai pastoralists have historically been squeezed from all sides into smaller areas. Compare Herger (2018).
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
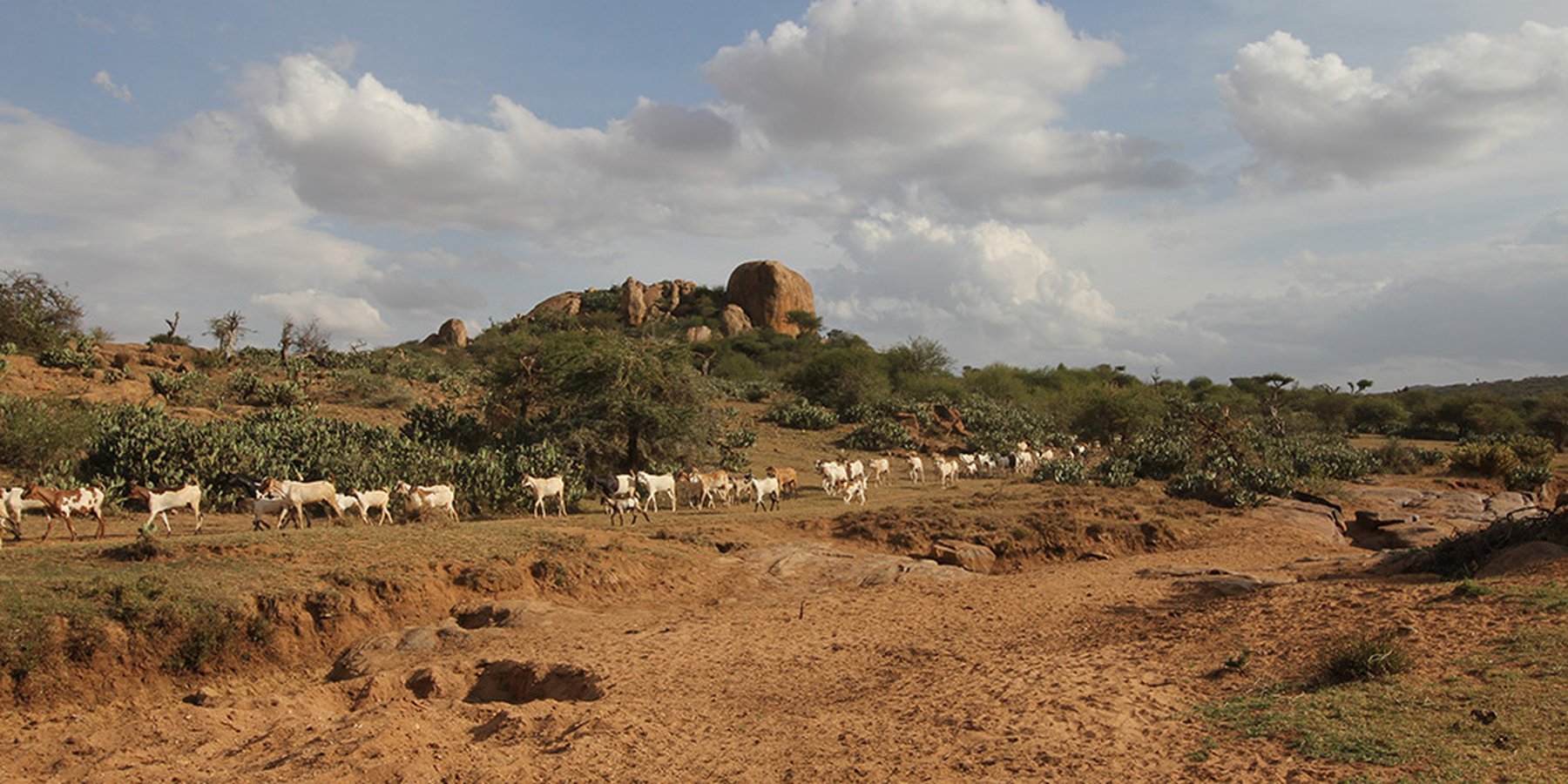
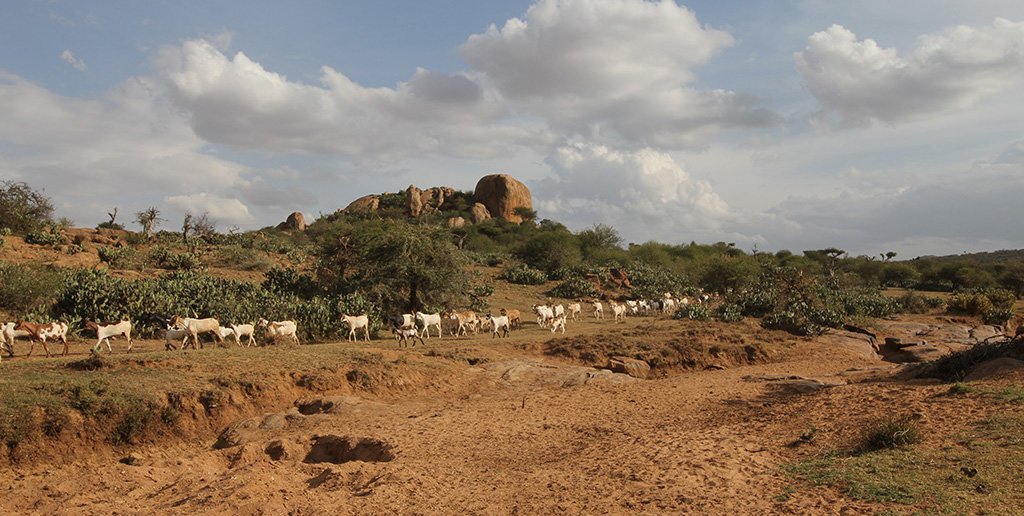
The grazing principles of a Masai group ranch (pastoralists) deal with high numbers of livestock in semi-arid lands with very limited water resources. Makurian has abandoned "Holistic Management" principles and applies a more traditional management system today. There is a grazing plan for the rains, while during the dry season everybody seeks for water and pasture individually. Bare land is recovered by "Boma” technology (strategic corralling of animals overnight) and reseeding. The rangeland is due to high stocking rates severely degraded with lots of erosion, bare ground, and invasive species. High stocking rates have on the one hand historical and political reasons and on the other hand socioeconomic rationales.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
On Makurian Masai Group Ranch, livestock production management is through a combination of traditional livestock keeping practices and newly introduced management principles. Livestock production at Makurian is for subsistence and local use, and has very high cultural significance.
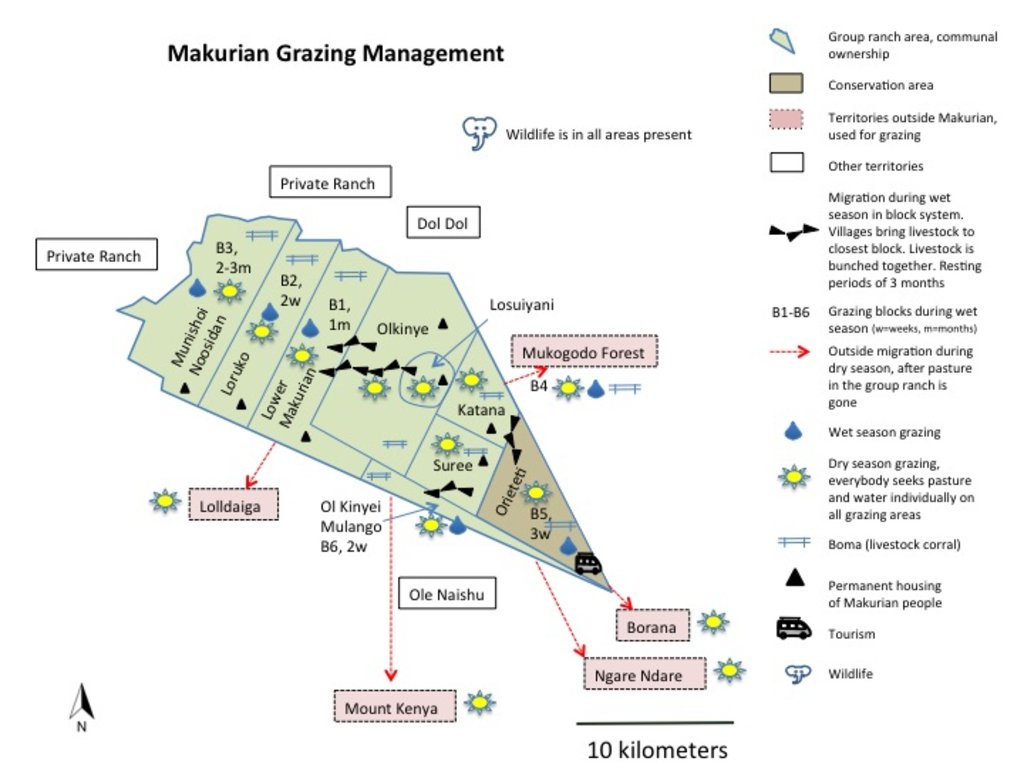
During the wet season, livestock are “bunched” together and rotational grazing in blocks is practiced. The management team group all livestock from each village (16 villages) and each uses the block next to their village. Livestock are hardly separated (cows, heifers, steers, bulls all herded together).
o Block 1: Lower Makurian - 1 month
o Block 2: Makurian Loruko - 2 weeks (next to Lolldaiga Northern Gate)
o Block 3: Munishoi Noosidan - 2-3 months
o Block 4: Mukogodo Forest - 1-2 months
o Block 5: Orieteti Conservation Area - 3 weeks. Soft grass, runs out quickly.
o Block 6: Ol Kinyei Mulango - 2 weeks. Next to Olenaisho
They apply resting periods of three months after usage (if this rule is broken, the owner is punished by a fine of one livestock unit).
When it becomes dry, everyone is responsible for their own livestock. Owners of livestock want to maintain and decide about their livestock individually, this is why "Holistic Management" and specific grazing plans for the dry season did not work.
In comparison to earlier days when the whole family moved, and livestock was herded by morans (young warriors), they hire external herders nowadays (800 herders in total). Herders seek whatever water and pasture remains on the group ranch, then move on to:
(a) Ngare Ndare forest: 1,000 cattle and 1,000 sheep and goats (shoats) per year on average, for 1-2 months, over an area of 250 km2;
(b) Mukogodo forest: 3,000 cattle and 4,000 shoats per year on average, for 3-4 weeks, over 250 km2, and
(c) Mount Kenya: 12,000 cattle and 5,000 shoats on average per year, for 1-2 months, on an undefined area.
In Mukogodo forest, Makurian Masai have also officially settled, in Ngare Ndare forest on the other hand they graze on the basis of an informal agreement and on Mount Kenya it is not official pasture - but grazing is tolerated). They are also assisted by private ranches to graze during droughts (Lolldaiga and Borana; for every 1,000 units, they usually pay 5 Ksh per cow per month: a token amount). On one private ranch (Borana) they also graze steers and cows for fattening and selling.
Furthermore, Laikipia rangelands support some of the highest densities of wildlife in Kenya, however, group ranches less so than private ranches. The wild herbivore biomass density on group ranches is by Georgiadis et al. (2007) estimated at 205 ha /TLU.
Bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) for the livestock are constructed in traditional style, where animals are kept closely bunched together in enclosures overnight. Bomas are strategically located on denuded land to rehabilitate the land (through dung accumulation and breaking the soil crust by hoof action). Every homestead has one boma (approximately 1,500 in total in the whole Group Ranch). When herders are moving with livestock, temporary bomas are constructed.
Sales are usually need-driven (e.g. for school fees) within a family. They sell to the nearest local markets (in DolDol and Nanyuki) or directly to butchers. Makurian is also part of the "Dung Market" in Mukogodo District, where livestock dung is sold as manure for crop production. Moreover, Makurian makes additional income by harvesting sand and selling it for construction.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Laikipia
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Mukogodo Division
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory was implemented in 2007, which was abandoned after a few years. This documentation focuses on the traditional system and new management principles they introduced since then. For Holistic Management see "Il Ngwesi" and "Borana" documentations.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ប្រភេទសត្វ និងផលិតផលចម្បងៗ:
Livestock: Cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, camels. Meat and milk production (also blood) and as a bank/ value asset. Subsistence and local production. Livestock: 13,500 TLU, Stocking Rate 0.6 ha/TLU calculating the total area used by livestock (78 km2). Pressure on land (including wildlife density of 205 ha/TLU): 0.6 ha/TLU Livestock numbers: 15,000 cattle, 30,000 shoats (ratio goats - sheep 2:1) Livestock fluctuations (per year): -500 cattle sales, -4,000 shoats sales, +100 cattle purchase, +350 shoats purchase, -3,500 shoats slaughtered. +6,000 cattle, + 15,000 shoats due to natural breeding. On average, 2200 steers on Borana rangeland for fattening purpose. During droughts, livestock move to neighbouring private ranches (1,000 cows each on Lolldaiga and Borana on average) Wildlife: Giraffe, antelope/gazelle (e.g. gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle), baboons, zebras, dikdik, hares, elephants, and more.

លំនៅដ្ឋាន ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
- ដីលំនៅស្ថាន អគារ
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
Villages, bomas, manyattas.
8'000 inhabitans.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
ដង់ស៊ីតេនៃសត្វចិញ្ចឹម (បើពាក់ព័ន្ធ):
13’500 TLU, Stocking Rate 0.6 ha/TLU
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- 10-100 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
The area size of the group ranch is 68 km2, however, the total area affected by livestock is 78 km2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
- M4: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរចម្បងៗក្នុងការកំណត់ ពេលអនុវត្តសកម្មភាព
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pi: ការគ្របផ្ទៃដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី
មតិយោបល់:
Across the grasslands and rangelands, an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems caused (partly) by livestock production in the research area are: major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species (Makurian is heavily affected by the invasion of Opuntia strica species). The current major problem on rangelands is the invasive species Opuntia stricta, which, however, only could spread that widely because of degraded land in the first place. The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land.
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
Herders, animals treatment (for the total area affected by livestock = 78km2)
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1.5
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grazing planning for bunched animals (livestock from all households) | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | |
| 2. | Hiring herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ការគ្រប់គ្រង |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | unknown |
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ||
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | ||
| 3. | Planning activites | ||
| 4. | Boma Management (mainly movement of Bomas) |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Herders, watchmen, supervisors | Person-days | 260000,0 | 1,5 | 390000,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Engaged population in livestock production | 720000,0 | 1,5 | 1080000,0 | ||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Animals treatments | Per TLU | 13500,0 | 3,5 | 47250,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 1517250,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Every family hires their own herder during the dry season. The family is staying put. Inhabitants are also considered as labor since they are usually all engaged in livestock production. However, milk and blood production are not considered.
Animal treatments consist of vaccination, spraying (ticks), injections.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Herders
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
378,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes. Makurian generally drier than Lolldaiga.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Rainfall gauge Lolldaiga Northern Gate (neighbouring ranch)
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol
SOC 0.8 %
pH: 6.4
Clay: 9 %
Silt: 41 %
Sand: 50 %
Fore more data on rangeland health see Herger (2018)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Grassed acacia bushland. Bare land up to 70% during dry season. Loss of (native) vegetation. Invasive species coming in. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Opuntia, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies. Dominant trees: Acacia drepanolobium, Acacia etbaica. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (see Herger 2018).
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Masai people. 8'000 Masai living in Makurian. Traditional livestyle. Livestock with very high cultural value.
Have been historically "squeezed" from all sides into smaller areas for livestock keeping. Future of pastoralism is in question.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
This applies for households that are staying put. Herders trek livestock on a total area of over 10'000 ha.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Lack of rain. Impact analysis is comparing the current state vs. some 10 years ago when they applied Holistic Management. This is why improvements are indicated according to the land user, even though the land is severely degraded.
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
less salt
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Compared to HM it has decreased, because of higher numbers of livestock it has increased though
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
More traditional knowledge than with Holistic Management
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Other communities
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Opuntia
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
រំហួត
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Opuntia (an invasive cactus) is chasing out native plants and consuming water. Elephants are destroying trees (high density of elephants, Opuntia is additionally attracting elephants)
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Opuntia
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
More wildlife coming in, roaming even in villages. Elephants problematic; breaking fences
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Wildlife numbers are declining drastically. Indigenous vegetation is being driven out by invasive species like Opuntia.
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Resilience has worsened
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមការវាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់:
All listed impacts are as perceived by land users according to Milton Sepeika, Chief of Makurian. In his opinion, abandoning Holistic Management principles had many advantages. According to him, animal production has increased. Though he recognices the bad condition of the land and poor conditon of livestock. He mainly blames the drought and the Opuntia invasion for these problems. Results from a rangeland health assessment (only ecological conditions) show heavily degraded ecological conditions (dry season up to 70% bare soil, poor soil and vegetation, erosions features, inability of producing annual and perennial grasses after rains etc) (compare Herger 2018). A
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុផ្សេងៗ | Greater variation of seasonal rainfall, more intense rainfalls, change in rainfall regimes in general (see Schmocker 2013 and Imfeld 2016). | កើនឡើង | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រលកកម្តៅ | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Masai people have changed their livestock composition towards owning more smallstock (goats and sheep) than cattle. Goats are tolerant to drought, and as browsers they don't need grass. They can be turned into money much quicker than a cow in times of need. Their faster reproductive cycle means they can rebuild numbers faster than cattle after losses through drought.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Everybody makes their own decision about their livestock (during the dry season). Owners stay in charge. |
| Grazing principles and plans lead to community control. |
| Traditional knowledge |
| Fewer costs |
| Less of effort (during the dry season no bunching of animals) |
| Fewer trees cut. During Holistic Management times many trees had to be cut to create two big bomas every month. |
| Can enrich land, livestock is tilling ground (seeds don't go away - kept in ground due to "tilling") |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Brings in conflicts. If you start to protect and maintain your grass, thieves come in. | |
| Spread of diseases when animals from different places with different diseases are brought together during the wet season |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Makurian (mostly next to Lolldaiga Northern Gate) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Several meetings with chief, rangeland specialist and botanist of Makurian.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Imfeld, N. (2016). Modeling Seasonal and Annual Precipitation using long-term Climate Records and Topography. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Online
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
University of Bern
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Georgiadis, N.J., Olivero, I.N., Romanach, S.S. (2007). Savanna herbivore dynamics in a livestock-dominated landscape: I. Dependence on land use, rainfall, density, and time. Biology Conservation 137(3): 461-472.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Online
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល