Conservation agriculture [ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Alastaire Leake
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
non-inversion tillage, incorporation of crop residues, non-selective herbicides
technologies_987 - ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust - ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/10/2004
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Improved soil management based on non-inversion tillage for cost-effective and timely crop establishment.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
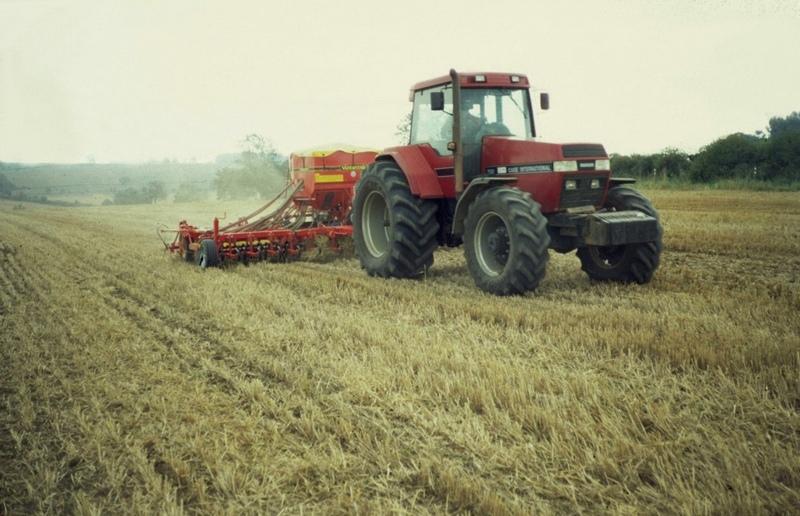
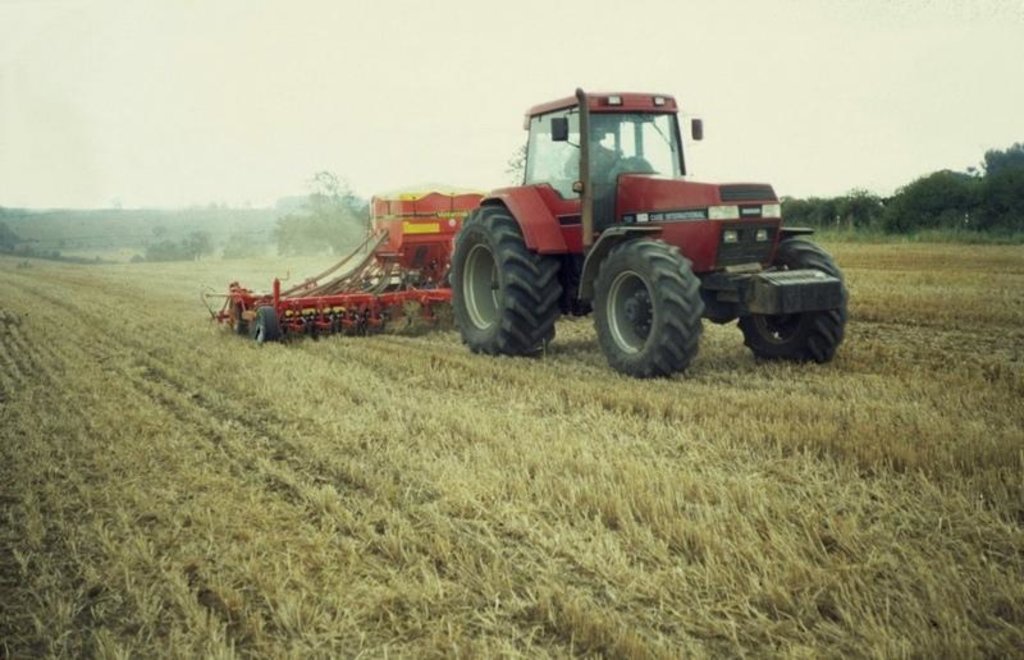
Conservation agriculture (CA), involving superficial non-inversion tillage, began to be widely taken up in England following advances in seed drill technology, non-selective herbicides and straw-chopping combine harvesters in the late 1980s.
This case focuses on the Game Conservancy Trust’s Allerton Project at Loddington, which in 2000 pooled resources with its neighbour to purchase a single set of cultivation equipment, and replaced conventional mouldboard ploughing (with its multiple cultivations) by state-of-the-art CA. Contract services offered by the joint venture means that 1,000 ha are now covered each year. The main winter crops are wheat, oats, and oilseed rape. Beans are sown in the spring. The heavy clay loam is vulnerable to excessive surface moisture, restricting crop establishment
‘windows’.
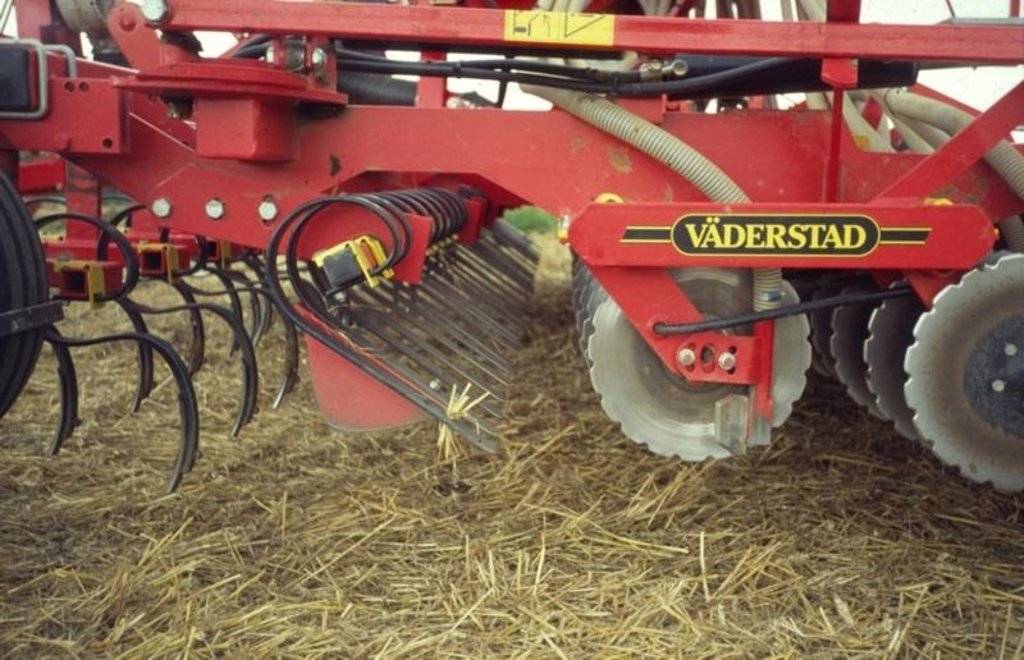
Immediately after harvest the soil is loosened and straw incorporated, and then soil is consolidated (using a ‘cultivation train’ combining two machines: the ‘Simba Solo’ and the ‘Cultipress’). This encourages up to 60% of the weeds to emerge in a ‘stale seedbed’. Spraying then removes all the weeds and volunteer plants of previous crops. This is followed by a light surface tillage, using the ‘Väderstad Rapid Cultivator Drill’, before sowing into the seedbed created. Equipment comprises implements with tines and/or discs which create a tilth to around 10 cm
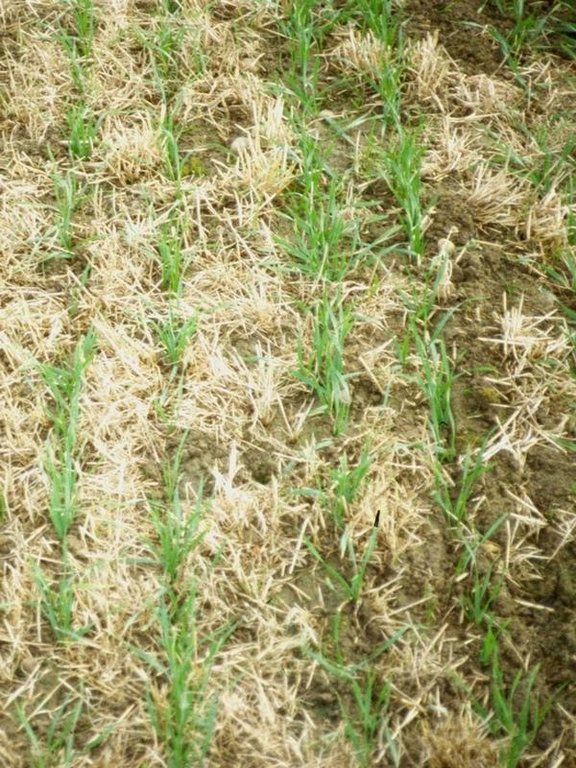
without inverting the soil. Cambridge rollers are then used to consolidate the sown land. After crop maturity, combine harvesting takes place - with simultaneous chopping of straw/crop residues. A trash rake is used to disperse the chopped straw. This way excessive trash is incorporated rapidly into the soil. Compaction may arise in the transition phase, because of the lack of soil loosening through ploughing: minimising traffic, keeping to tramlines and headlands can all help. In time, increases in soil organic matter content and earthworm biomass make compaction less of a problem. The problem of slugs can be reduced by improving seed-to-soil contact, and by drilling deeper.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of conservation agriculture is cost effective, timely and rapid crop establishment, under good soil conditions. High-speed operations are the key. Compared with conventional ploughing, labour is saved and fuel costs lowered. However, an additional application of herbicides represents an extra expenditure. Yields per hectare haven’t risen but the key difference is that about four times as many hectares can be prepared in time for autumn planting under conservation tillage, thus improving overall production. Incorporation of crop residues improves soil structure and leads to a more friable, less erodible topsoil.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Leicestershire
Map
×2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Major cash crop: Wheat, oats,oilseed rape
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Traditional inversion tillage is slow and costly. By moving to high speed non-inversion conservation tillage farmers can
spread costs over a larger area and maximise the area under winter crops. The speed at which ground can be worked in the autumn is critical: one month earlier planting can mean an extra ton in cereal yield.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 330Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Dec
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10 m2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Loosen the soil and incorporate the straw using the ‘Simba Solo’; soil consolidation, using the 'Cultipress' | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | immediately post-harvest / |
| 2. | Spray the stale seedbed to remove all the weeds/volunteer plants of previous crops | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | mid September |
| 3. | Light surface tillage and sowing into the seedbed; using the 'Väderstad Rapid Cultivator Drill' | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | usually end September, just after spraying |
| 4. | Consolidation of the sown land | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | using Cambridge rollers |
| 5. | After crop maturity, combine harvesting - with simultaneous chopping of straw | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | |
| 6. | Disperse the chopped straw, using a trash rake. | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 180,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 180,0 | |||||
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
No establishment costs for purchase of special conservation tillage equipment are included here – though this
investment is considerable. Tractors of sufficient horsepower and a couple of special machines (see above) are needed. The investment in this case was shared by two neighbouring farms, who implemented conservation agriculture on a joint venture basis. The only costs presented in the table above are total recurrent annual costs for tillage operations. This total, US$ 180, compares with US$ 260 for conventional tillage operations. While drilling is not included in the above conventional tillage calculation, subsequent application of additional herbicides represents an extra cost of conservation tillage of about US$ 80/ha. In balance the costs per hectare are broadly similar. Labour inputs however are reduced considerably as a proportion: the Allerton farm with its 260 ha of arable land is operated by a farm manager and just one farm worker.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Off-farm income specification: contract work on other farms is an important source of additional revenue for the ‘joint venture’ of the two neighbouring farms
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ក្រុមហ៊ុន
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
- ឯកជន
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced yields in the early years (due to initial compaction)
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
Carbon sequestration
Loss of nutrients (through leaching)
Biodiversity enhancement
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Above and below ground
Soil structure
Organic matter depletion (in certain sandy soils)
Reliance on herbicides
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Extent of adoption depends on farm size, enterprise & soil type. From 10% in 95, approx 40% of arable land in Eng is currently (04) under conservation agriculture/cultivation tillage.
Additional info: Farmers involved adopted the system without incentives other than those of timeliness, lower cost, speedier crop establishment, reduced soil erosion & benefits to wildlife. There is significant growing spontaneous adoption: the extent of adoption depends on farm size, enterprise & soil type. Editors’ comments: Conservation agriculture is rapidly catching on throughout the world. While most attention has been focussed on the Americas, a revolution is taking place in Europe also. In England, for example, around 40% of the large scale arable area is now under CA – a rise from just 10% a decade ago. CA helps to minimise costs and reduce local, and global, environmental impacts. This is a case from a leading proponent of CA in England. Comparative case studies are documented from Morocco, Australia and Kenya.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Increases soil biota (more than doubling earthworm mass) and biodiversity generally (nearly doubling the number of different organisms) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain system over time to maximise these benefits. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Lowers recurrent soil tillage costs – mainly due to reduction in fuel use (down by about one third) and labour (saving around one person day per hectare) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread over greater area to maximise cost reduction. |
|
ncreases overall farm yield (and income) by speeding up land preparation in autumn, allowing a larger area to be planted as winter crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto. |
|
Improves soil structure and physical properties in various ways How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain system over time to maximise these benefits. |
|
Reduces runoff (by a half), soil erosion (by two thirds), and leaching of nutrients (by three quarters) thus decreasing movement of phosphates and nitrates to streams and rivers How can they be sustained / enhanced? To improve further, combine with other measures such as adding organic matter or growing green manures and cover crops. |
|
Increases soil buffering capacity against climatic extremes (especially rainfall) through maintaining surface cover and building up soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain system over time to maximise these benefits. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Increased growth of grass weeds and thus greater cost of herbicides | Use ‘stale seedbeds’ – surface tillage immediately post-harvest to induce weed germination – followed by spraying. Crop rotation, spring cropping, occasional ploughing (every few years as necessary). |
| Not suitable for all soil types (not appropriate on some sandy soils) | Don’t introduce/promote CA indiscriminately. |
| Excessive surface trash/crop residues | Good chopping, then spreading and incorporation. |
| Problems with slugs | Drill seed deeper, ensure good seed-to-soil |
| Surface compaction in the early stages of conversion to conservation agriculture | Appropriate loosening of soil, using tined implement. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Soil Management Initiative/Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) A guide to managing crop
establishment.. (undated).
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
SMI, UK (www.smi.org.uk)
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Soil Management Initiative Improved soil management for agronomic and environmental
gain.. (undated).
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
SMI, UK(www.smi.org.uk)
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Soil Management Initiative/Väderstad Target on establishment: innovation for the future of farming.. (undated).
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
SMI, UK(www.smi.org.uk)
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល