Wire Mesh Maize Storage Crib [អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ PRISCILLA VIVIAN KYOSABA
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Jalia Namakula, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Udo Höggel
Akaju k'obutimba akubarabikamu ebikyoli
technologies_3375 - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Musinguzi Garuga
Kamwenge District, South Western Uganda
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
15/11/2017
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
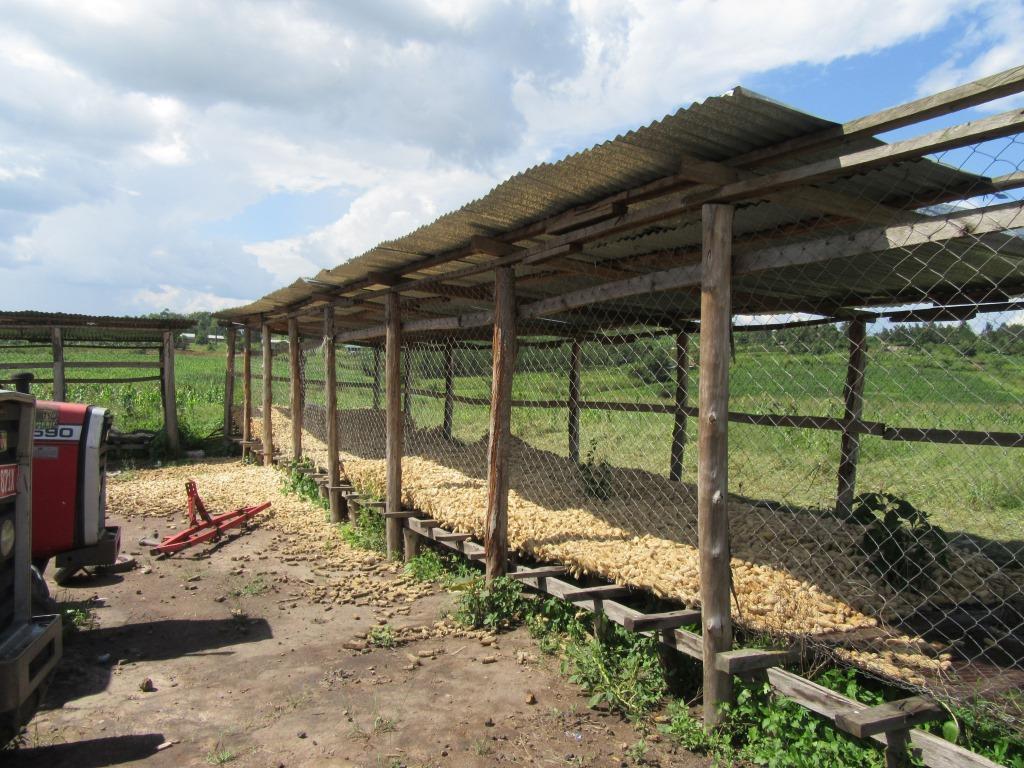
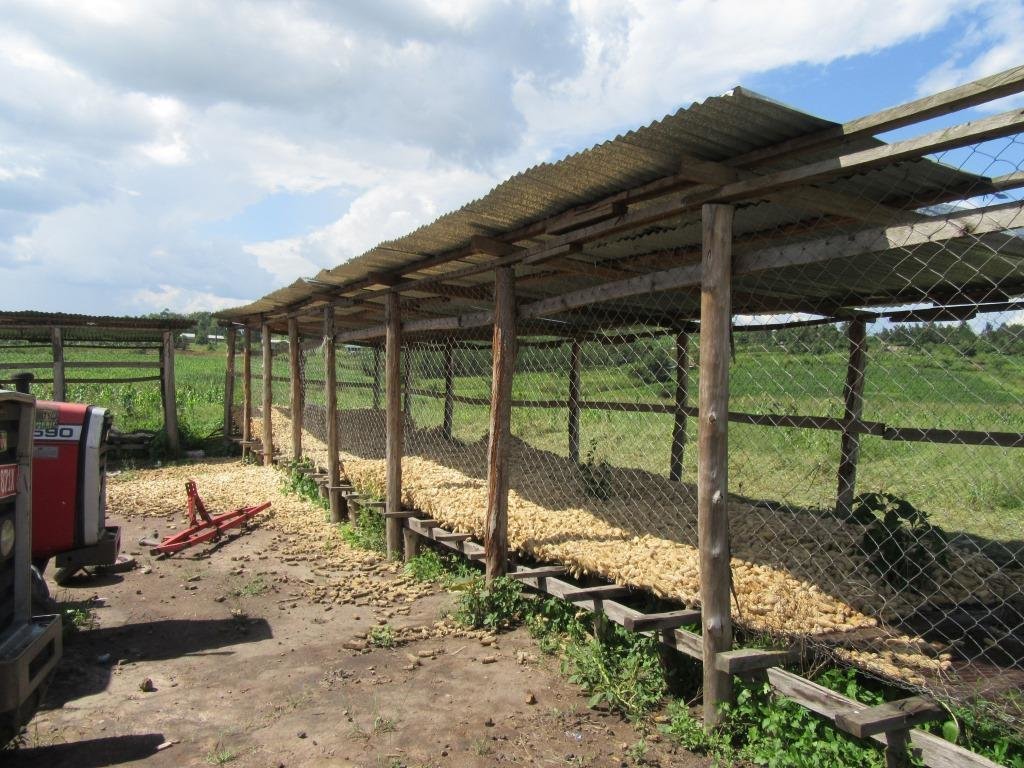
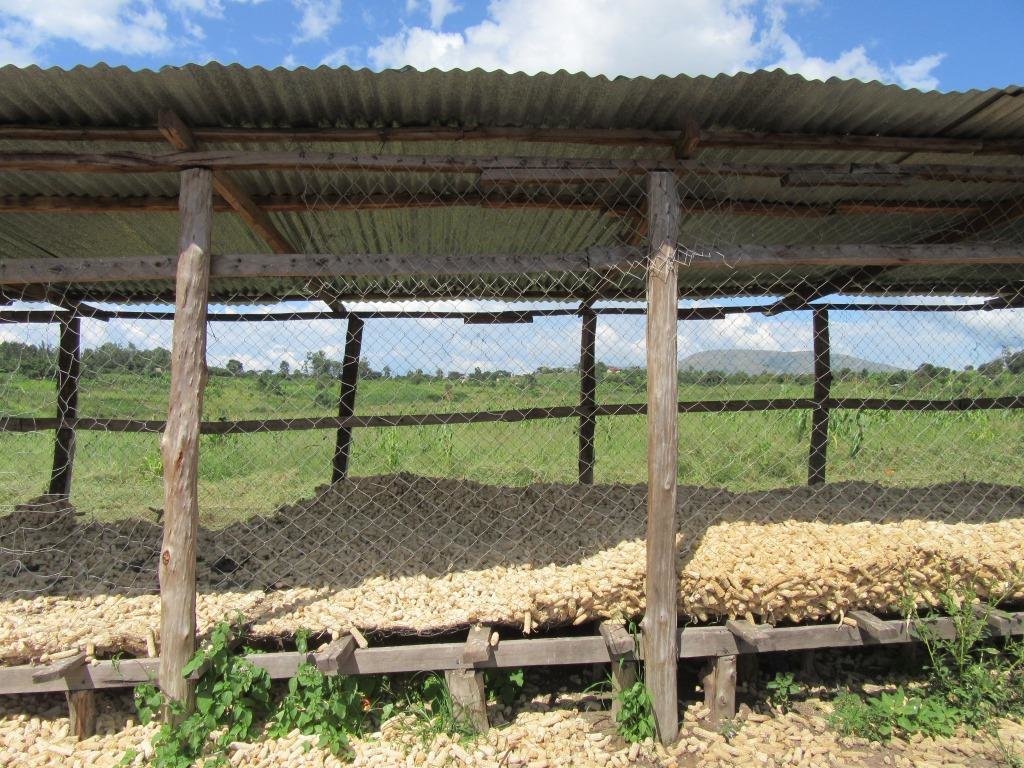
Wire mesh maize storage crib technology is a medium to large scale technology promoted by a farmer in Kamwenge District in South Western Uganda to prevent maize grains from being affected by rainfall. The technology allows for good air circulation which is essential for drying out the maize grains. In this way the grain quality is improved.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The technology is suitable for farmers growing maize on medium to large scale for commercial purposes. It was adopted from Europe by a farmer in Kamwenge District to help in handling large quantities of maize harvests from a 50-acre farm, which is the largest piece of land under maize farming in the area. Most operations on the farm e.g. land preparation, planting, weeding, spraying and harvesting are semi mechanized. Maize harvest from the farm averages about 2,000 tons per season. This requires a reliable post- harvest handling system that can store the large volumes of maize grain safely with good quality for the market.
The storage cribs are constructed with a wire mesh which is bent to form a rectangular shape to allow more space for storage. The wire mesh structure is then placed on a wooden platform raised a 1 meter above the ground. The whole system is then protected from elements of weather by an iron sheet roof raised 3 meters away from the platform. In front of the structure is a floor space where the harvested maize is first spread on a tarpaulin for sun drying to reduce the moisture content that may be a source of mould leading to grain spoilage and reduces grain quality.
The crib is suitable for storage of maize cobs in both the humid and dry seasons in the Kamwenge area. The structure is well positioned with the longer side in a direction perpendicular to the prevailing wind direction thus facilitating natural ventilation. This allows the drying process to continue even during storage and minimises the possibility of post harvest losses through spoilage.
The storage life greatly depends on the prevailing ambient temperature and relative humidity, and other factors like the inherent moisture pests and diseases. The rectangular shape allows for more space for storage and the material used is durable to beyond 7 years if repairs are done in time. Yet, despite these advantages, the wide open wire mesh allows in birds which feed on the maize which brings about losses.
Establishment cost of the maize storage crib is mainly determined by the construction materials and size. The farmer reported using US$ 4,191.7 in total to establish the structural size of 30 m length, 12 m height and 3 m width . Maintenance activities included repairing the damaged patches on the crib plus also fumigating the units to prevent insects from damaging the poles and eating harvested maize which costs the farmer about US$ 54.8 per season.The costs involved in establishing the technology are slightly higher in the short run while in the long run the net benefits surpass the initial costs. This system is best suited for farmers practising commercial maize farming. However, small scale farmers may be able to construct small size storage cribs using cheaper materials like reeds, bamboo and wood.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
Photo clearly shows the usefulness of the maize crib as a post handling technique
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
A video for the Wire Mesh Maize Storage Crib
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
15/11/2017
ទីតាំង:
Kamwenge District, South Western Uganda
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Aine Amon
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
South Western Region
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kamwenge District, South Western Uganda
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2007
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Through exchange visit from established farmers from other locations
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- Reduction of post harvest lossses
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Maize
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- វិធានការក្រោយការប្រមូលផល
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Cribs constructed in the middle of the maize field.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការផ្សេងៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Maize storage construction
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ផ្សេងៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Reduction of post harvest losses which contributes to saving resources e.g soil
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ដែលមិនអាចអនុវត្តបាន
មតិយោបល់:
Reduction of post harvest losses which contributes to saving resources e.g soil
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Prossy Kaheru
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
15/11/2017
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Crib structure dimension
-Length is 30 meters, height 4 meters and width is 3 meters
-Spacing between crib units is 2 meters
-Wire mesh size is measure depending on the size of structure in this case 30 by 4 meters
-Timber used is eucalyptus variety, pole size is 16 centimeters diameter, pole height 5.5 meters
-Gentle sloping
-Construction materials used are wire mesh, nails, timber, poles and iron sheets
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
Crip: 30m*4m*3m
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3600,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
50,000 Uganda shillings
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction labor | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
| 2. | Wire Mesh | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
| 3. | Iron sheets | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
| 4. | Nails | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
| 5. | Timber | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | once |
| 6. | Poles | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once |
មតិយោបល់:
Establishing activities as reported by farmer
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction labor | Days | 30,0 | 13,8 | 414,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Wire Mesh | Meters | 150,0 | 7,9 | 1185,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Poles | Pieces | 268,0 | 0,6 | 160,8 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Nails | Kilograms | 105,0 | 1,2 | 126,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Timber | Pieces | 420,0 | 1,0 | 420,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Iron sheets | Pieces (2.5mX0.5m) | 120,0 | 6,2 | 744,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 3049,8 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
All the costs were met the farmers
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing damaged patches of the crib | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once a year |
| 2. | Fumigating the crib units to prevent pests | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | During harvesting periods |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
បើអាច បំបែកថ្លៃដើមនៃការថែទាំទៅតាមតារាងខាងក្រោម បញ្ជាក់ធាតុចូលលម្អិត និងថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា។ បើអ្នកមិនអាចបំបែកបាន សូមផ្តល់នូវតម្លៃប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសសរុប:
166,0
មតិយោបល់:
Maintenance cost calculated on a yearly basis
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Construction materials
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Individual owning a company that runs all the farm activities
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
It is a large scale because the size of the farm area is 50 acres with a production of 2000 tones of maize / year
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased crop production since a farmer has a secure safe storage system hence he can produce more as it is stored
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Being it the grains are kept properly and in a favorable environment for the grains
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The technology has promoted income increase simply because with the storage system a farmer can get to sell his produce
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
This has helped in solving a problem of food insecurity since the maize grains can be stored for a relatively long period. Hence, at any time grains can be processed into maize flour.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់:
None has adopted the technology because of the high establishment cost and most farmers sell their farm produce immediately after harvesting.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Maintains the maize grains in good conditions |
| Allows drying process to continue even during storage time |
| The farmer generates more income since he sells when the market prices are favorable |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Quite a good innovation practice especially for those farmers growing maize on large scale for commercial purposes |
| Reliable post harvesting technique |
| Reliable storage system |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Crib establishment is relatively costly | Farmers opt for cheap system like the traditional granaries |
| Best for farmers growing maize on a very large scale for commercial purposes | To be adopted by farmers growing maize on commercial scale |
| Fumigating the units during harvest period is relatively expensive |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Only favors farmers who can handle the establishment cost | Farmer organisations and government should come in to help middle farmers by providing them with establishment materials at a relatively lower price, this will enable them adopt the system. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
one
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
One person in this case the farm manager
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Economic importance of different maize storage structures in Kenya
វេបសាយ:
https://www.slideshare.net/pchenevixtrench/economic-importance-of-different-maize-storage-structures-in-kenya
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Does Improved Storage Technology modern input use and food security? Evidence of randomized trial in Uganda
វេបសាយ:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030438781830926X
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល