Area enclosure : Invasive species management through physical removal and grassland restoration [ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Beatrice Otieno
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Urs Baumgartner, Christian Hergarten
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Rene Eschen
Reseeding
technologies_3454 - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Meigiri Esther
+254 712387590
NA
Local community member of Marigat Sub-County, Kenya
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Grace Chemutai
+254 700865828
NA
Local community member of Marigat Sub-County, Kenya
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
R4D Woody Weedsឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Centre for Training and Integrated Research in ASAL Development (CETRAD) - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
15/11/2019
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
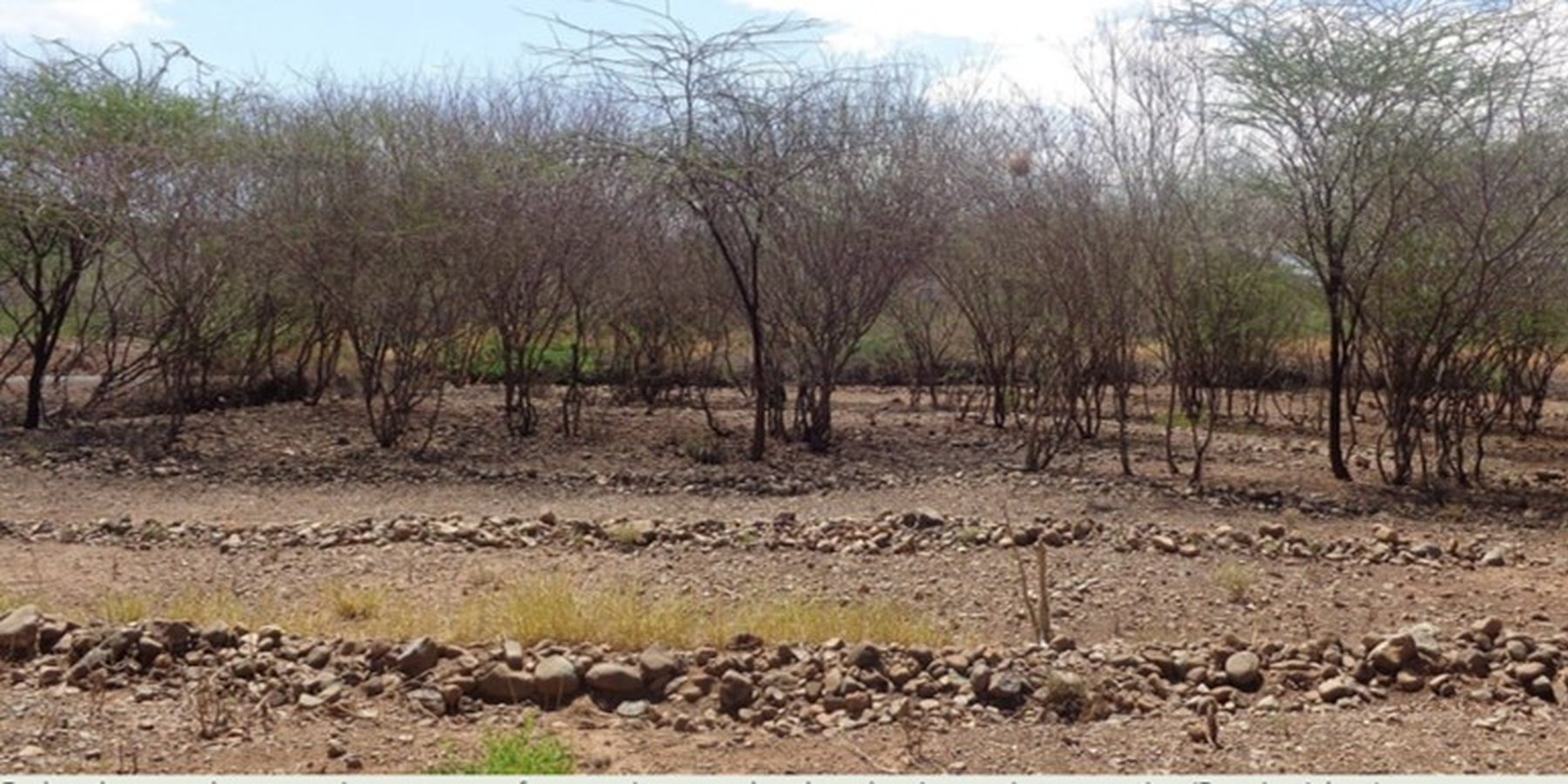
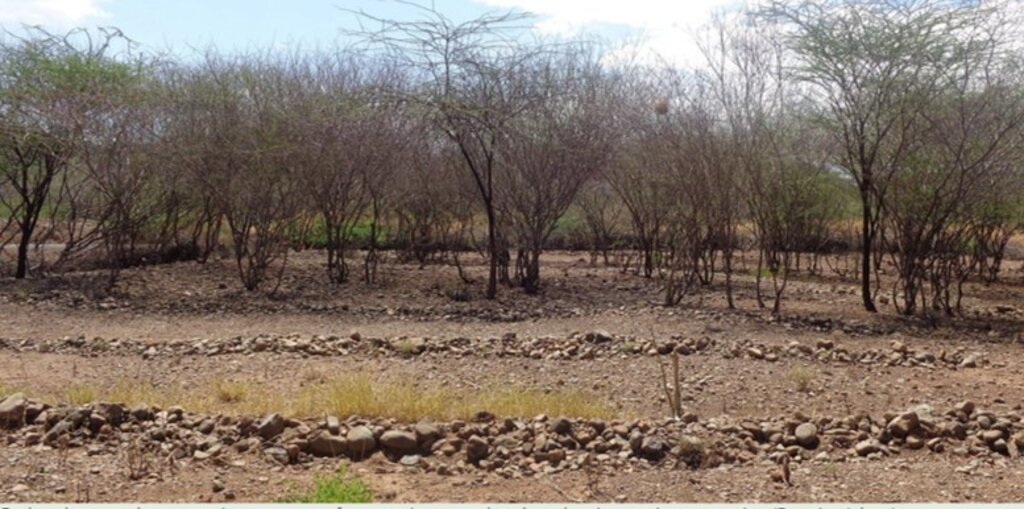
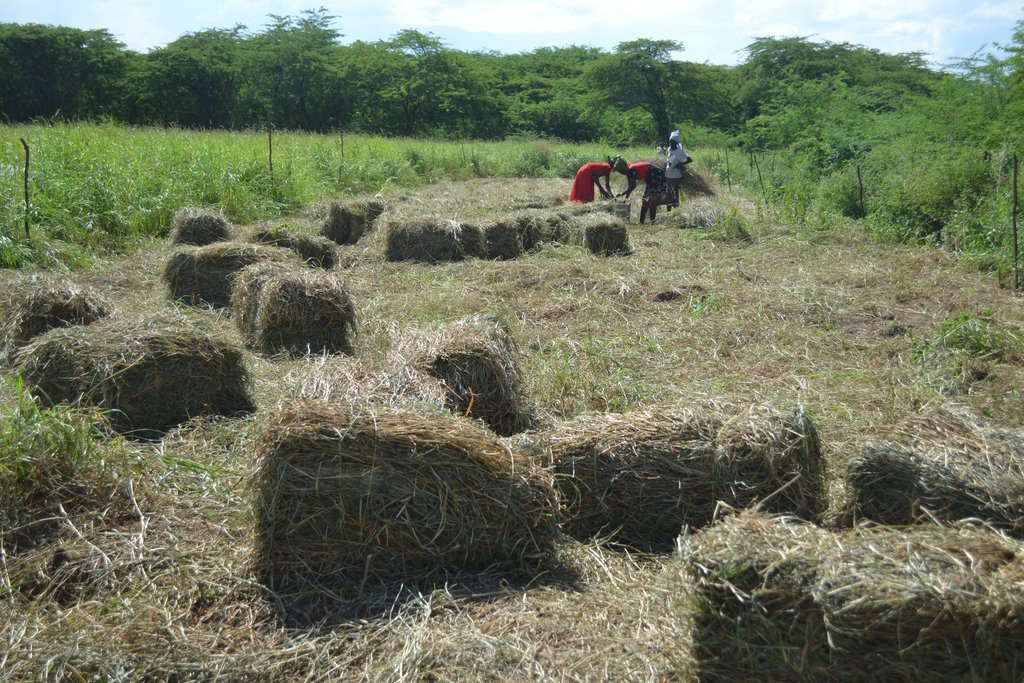
Area enclosures are a set of restoration strategies through which land is cleared of invasive species, restored using a combination of agronomic, structural, and vegetative measures, and surrounded by barriers to restrict unauthorized entry and minimize disturbance.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
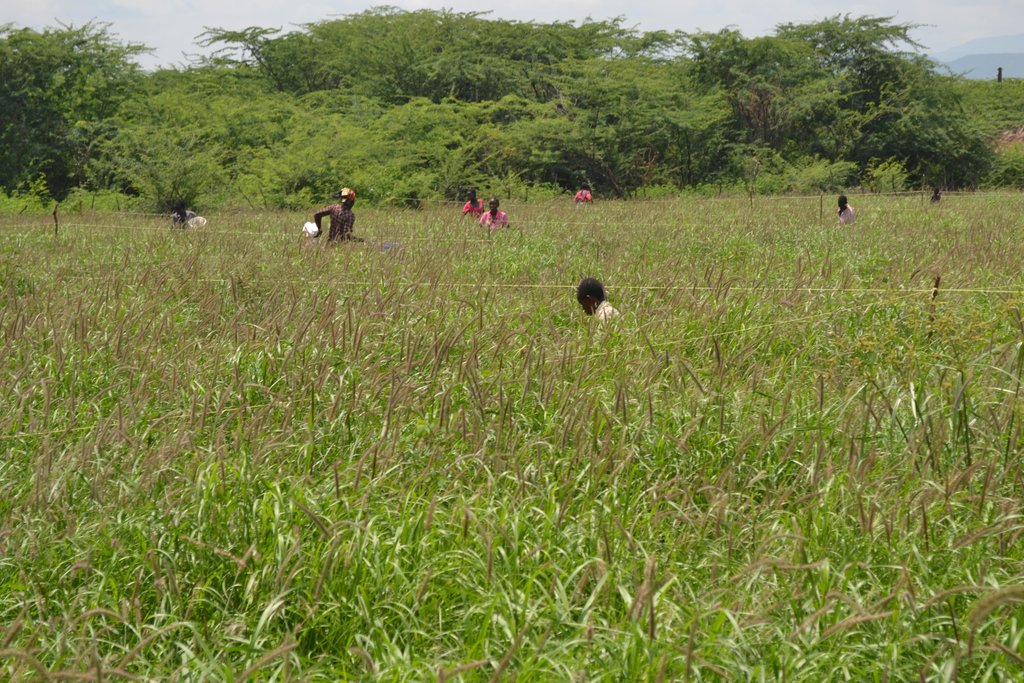
Area enclosures are sustainable land management (SLM) technologies implemented locally to rehabilitate land invaded by species such as Prosopis juliflora and prevent further re-invasion. They are crucial in preventing, controlling, and restoring of Prosopis management and are preferred for their cost-effectiveness, offering significant financial, environmental, and social benefits. Enclosures improve land aesthetics, diversify income sources in pastoral economies—such as through the sale of grass seeds and fodder—and help reduce conflicts over grazing land. In Baringo, several women have reported improved livelihoods and livestock acquisition from income generated by selling grass products.
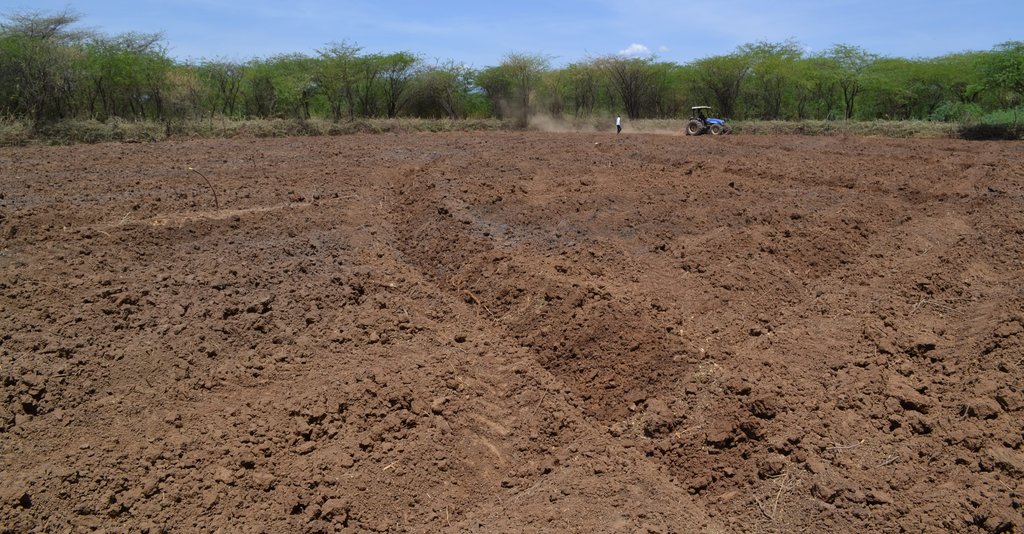
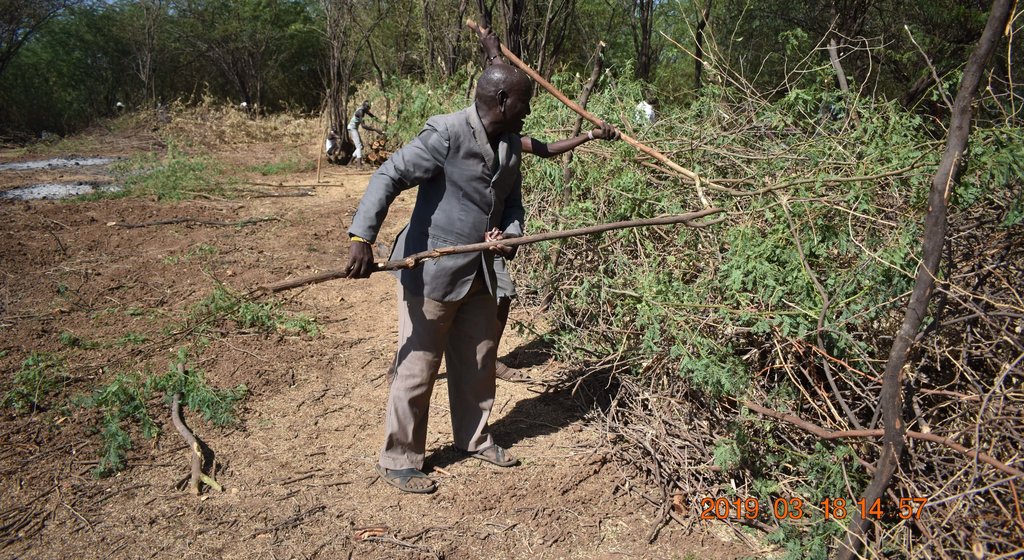
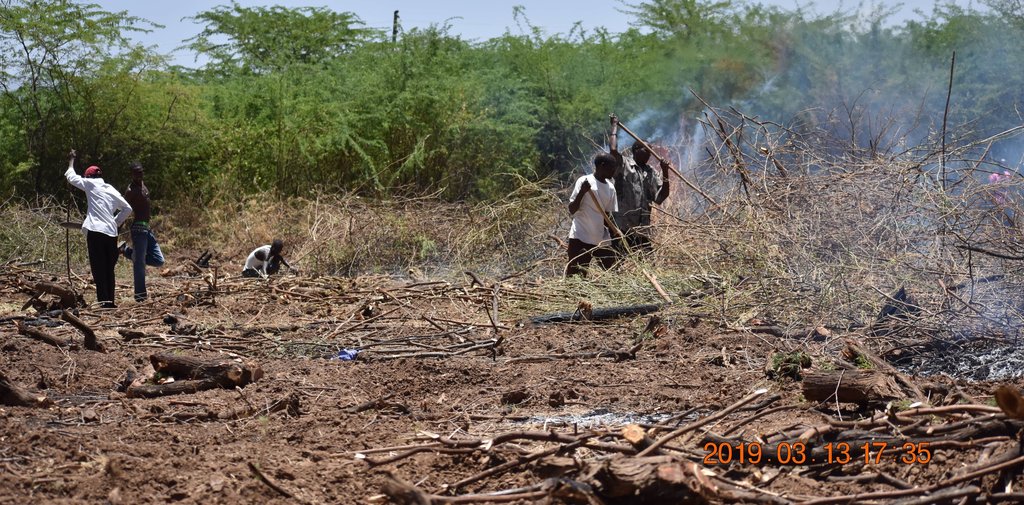
The implementation of this SLM technology involves several steps: Established Prosopis trees are manually cut and uprooted using simple tools like machetes and hoes, with roots removed about 30 cm below the soil surface to prevent coppicing. This labor-intensive process can be hindered by inefficient equipment, potentially increasing costs. Barriers are then erected around the cleared land to restrict access by livestock and unauthorized individuals, often using tree branches for fencing. A tractor plows and ridges the land to create ridges that enhance water infiltration, with stone bunds placed along the edges to slow water flow and reduce soil erosion. Grass seeds are sown on ridge risers to form grass strips, with sowing timed for the rainy season to ensure optimal germination. While the Ministry of Agriculture provides seeds, local farmers may also sell them, as supply can sometimes fall short of demand. Additionally, native plants like acacia are intercropped with grass to offer extra ground cover and shade, reducing soil water evaporation.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Baringo County
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ngambo Sub-Location, Marigat Sub- County
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2019
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The project was established by an NGO, the Rehabilitation of Arid Environments Charitable Trust (RAE) in collaboration with the community to restore degraded land and enhance human livelihoods in Baringo by providing alternative sources of income. Local participants in the Woody Weeds project adopted the technology for implementation so as to evaluate its effect in managing invasive species while at the same time, enhancing human livelihoods.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Grasses for fodder and grass seeds

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- កាត់ និងជញ្ជូន/ គ្មានវាលស្មៅសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- បង្កើនវាលស្មៅ
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Before Prosopis invasion, the area was part of the Perkerra irrigation scheme. Due to climate changes, the streams progressively dried making the land unsuitable for crop production and vulnerable to Prosopis invasion. Likewise, frequent flooding of the area forced community members to abandon flooded parcels, which were subsequently invaded
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
The grass is grown once at the beginning of the restoration and is continuously harvested for 4 to 5 years before re-planting as it naturally re-vegetates after harvesting.
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- តំបន់ទ្រនាប់ (បិទការប្រើប្រាស់ គាំទ្រដល់ការស្តារឡើងវិញ)
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
The technology is applied by households in small scale covering an average of between 1 to 5 ha per household.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
- A5: ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រាប់ពូជ បង្កើនប្រភេទពូជ

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ
- V4: ការជំនួស ឬការយកចេញនៃប្រភេទរុក្ខជាតិក្រៅស្រុក/ ការរាតត្បាត

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
- M5: គ្រប់គ្រង/ ការប្លាស់ប្តូរសមាសភាពពូជ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
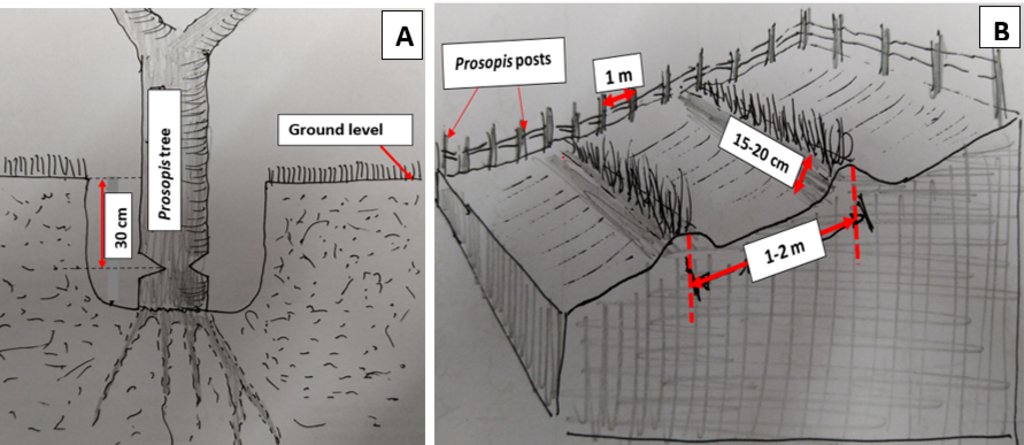
To uproot Prosopis trees, the soil around the stem is dug 30 cm deep, matching the maximum plowing depth of a tractor (Figure A). Depending on the stem's diameter, handheld tools like axes may be used to create a 90-degree notch on two opposite sides of the stem before cutting it with a chainsaw. A notch is a V-shaped cut or groove made on opposite sides of the tree's stem. This notch is created with an axe to weaken the tree and guide the direction in which it will fall when the tree is cut down with a chainsaw. The notch helps ensure that the tree falls in a controlled manner, reducing the risk of accidents and making the uprooting process more efficient.
Ridges are formed by a light tractor at a depth of 15 to 20 cm to minimize soil displacement and reduce erosion, with the depth adjusted according to the slope gradient. Shallower depths are often recommended for steeper slopes. The resulting furrows are spaced 1 to 2 meters apart and run parallel to the slope (Figure B) to help retain water and improve infiltration. Additionally, live fence poles are placed 1 meter apart to strengthen the enclosure. These live posts, made from tree stems, can grow roots and continue to thrive after being planted, helping to stabilize the soil, provide shade, and enhance the overall resilience of the enclosure.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1 ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
KES
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
110,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
KES 500
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearance of land | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Once |
| 2. | Fencing/ Enclosure | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once a year |
| 3. | Ploughing | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Once at the beginning of the project |
| 4. | Ridging | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Once at the beginning of the project |
| 5. | Stone bund development | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Once at the beginning of the project |
| 6. | Sowing | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Once at the beginning of the project in 4 to 5 years |
| 7. | Removal of all Prosopis seedlings while small | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Repeatedly, but mostly during early stage of technology |
| 8. | "Common" weeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Twice a year, with more frequent removal of seedlings recommended while they are still small in the early stages, until the seed bank is depleted. |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Uprooting of Prosopis trees | Man-days | 96,0 | 500,0 | 48000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Fencing | Man-days | 38,0 | 500,0 | 19000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Planting | Man-days | 30,0 | 100,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Ploughing tractor | Hours | 6,0 | 420,0 | 2520,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Ridging | Hours | 6,0 | 420,0 | 2520,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Chain-saw hire | Fuel-tank used | 13,0 | 600,0 | 7800,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Grass seeds | kg | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 85840,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
The woody weeds project
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Twice a year, but at the initial stages, there may be need for more frequent removal of young seedlings until the Prosopis seedbank in the soil is depleted. |
| 2. | Ridging | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | once or twice a year depending on the status of the ridges |
| 3. | Harvesting | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Three times a year |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Weeding | Man-hour | 90,0 | 100,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Ridging | Man-hour | 60,0 | 100,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Harvesting | Man-hour | 50,0 | 100,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Stone bunds | Man-hour | 6,0 | 100,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 20600,0 | |||||
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
1. Density of Prosopis invasion
2. Size of the farm area
3. Size of Prosopis trees
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
The area is in a semi-arid zone, with temperatures ranging from 16 to 36 degrees Celsius. The average annual rainfall is 670 mm and highly erratic. Annual evaporation rates are much higher and ranging from 2000 mm to 2800 mm.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ភាពទៀងទាត់:
ញឹកញាប់
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 bales of fodder/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
32 bales of fodder/ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Income from fodder: 32 x 300 KES = 9600 KES
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Enhanced livestock productivity due to availability of high quality fodder across seasons
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 products
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
3 products (fodder, grass seeds, and charcoal, the latter being optional)
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Charcoal production only during establishment, when prosopis trees are removed
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Grassland restoration ensures improved ground cover which reduces soil erosion
ការបង្កើតថាមពល
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 bags of charcoal
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
37 bags of charcoal
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Prosopis trees uprooted during land preparation are used for charcoal production.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 KES
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
95,300 KES
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
KES 45,600
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 sources of income
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
3 income sources from sale of fodder, grass seeds, and charcoal
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Activities involved in this technology are tedious especially during land preparation and harvesting
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
A number of women groups have been established, whose members collectively support each other during implementation of the SLM.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Most of the practicing households have learnt of the SLM from their neighbors and community group members, e.g., women groups. This enhances awareness creation on land degradation and respective management options.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Grassland restoration results into self sufficient household minimizing competition for communally shared grazing land hence minimizing conflicts.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Restored lands are often covered by grass which lowers the impact of rain water on the soil hence reducing soil erosion.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mbaabu et al. 2020 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77126-7) have demonstrated that carbon sequestration by grasslands is comparable to that of Prosopis. Therefore, substituting Prosopis with grass is unlikely to significantly affect carbon sequestration benefits. This suggests that replacing Prosopis with grass can maintain carbon sequestration benefits while reducing the negative impacts of Prosopis, resulting in a net positive gain.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមការវាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់:
In the very short term, surface soil ersosion and downstream deposition may increase due to clearing work, while in the longer term, if properly managed, erosion is expected to decrease due to vegetation cover management.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 10-50%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 50-90%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Diversification of income sources hence improving human livelihoods and well being. |
| Economic benefits are derived from extra related activities such as charcoal burning from cleared Prosopis trees during land preparation. |
| Less physical activities in subsequent years after initial planting season making it less tedious and easy to maintain. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Improved vegetation regeneration and enhanced recovery of restored degraded land due to restricted human and livestock disturbances . |
| Enhanced land management measures speeds up rehabilitation strategy as well as mitigating soil erosion. |
| Suitable for management of invasive species such as Prosopis since land is not left idle for re-invasion. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Market exploitation by middlemen | Price regulation and enhancing equitable access to market |
| Associated high cost of initial land clearance | Land users should constantly maintain their farms to prevent re-invasion by Prosopis and hence lower the cost of land preparation. |
| Harvesting grass seeds is tedious and costly | Land users should adopt mechanized harvesting |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The technology is susceptible to environmental shocks and in particular, floods | The implementation of the SLM technology should be compliant with land use plans and disaster prone areas should be avoided. In cases where this is inevitable, suitable structures such as dykes, dams, and canals should be constructed to enhance the resilience of the technology. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
3
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
3
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
3
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Jones, M.B and Donnelly, A. (2004). Carbon sequestration in temperate grassland ecosystems and the influence of management, climate and elevated CO 2; Botany Department, Trinity College, University of Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01201.x
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Gebrehiwot T, Veen AVD (2014) The Effect of Enclosures in Rehabilitating Degraded Vegetation: A Case of Enderta District, Northern Ethiopia. Forest Res 3:128. doi: 10.4172/2168-9776.1000128
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/the-effect-of-enclosures-in-rehabilitating-degraded-vegetation-2168-9776.1000128.php?aid=33063
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Eschen, R., Bekele, K., Jumanne, Y., Kibet, S., Makale, F., Mbwambo, J.R., Megersa, B., Mijay, M., Moyo, F., Munishi, L., Mwihomeke, M., Nunda, W., Nyangito, M., Witt, A., Schaffner, U., ‘Experimental prosopis management practices and grassland restoration in three Eastern African countries,’ CABI Agriculture and Bioscience, 13 July 2023.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
DOI: 10.1186/s43170-023-00163-5
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Restoration of degraded grasslands, but not invasion by Prosopis juliflora, avoids trade-offs between climate change mitigation and other ecosystem services Purity Rima Mbaabu, Daniel Olago, Maina Gichaba, Sandra Eckert, René Eschen, Silas Oriaso, Simon Kosgei Choge, Theo Edmund Werner Linders, Urs Schaffner
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-77126-7
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Towards estimating the economic cost of invasive alien species to African crop and livestock production. Eschen, R., Beale, T., Bonnin, J. M., Taylor, B., & 10 additional authors (2021) CABI Agriculture and Bioscience, 2(1).
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43170-021-00038-7, Free
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Prosopis juliflora management and grassland restoration in Baringo County, Kenya: Opportunities for soil carbon sequestration and local livelihoods. Eschen, R., Bekele, K., Mbaabu, P. R., Eckert, S., (2021) Journal of Applied Ecology, 58(6), 1234-1245.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13854, Free
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Nutrient and Sediment Discharge from Southern Plains Grasslands
វេបសាយ:
https://journals.uair.arizona.edu/index.php/jrm/article/download/7560/7172
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល