Olive groves under no-tillage operations [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Deborah Niggli
Ακαλλιέργεια (Greek)
technologies_1035 - ប្រទេសក្រិក
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Ioannis Mentzidakis
+30 28210 - 83410
imetzis@nagref-cha.gr
National Agricultural Research Foundation - NAGREF - Institute for Olive Tree and Subtropical Plants of Chania
Agrokipio, 73100 Chania, Crete
ប្រទេសក្រិក
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - ប្រទេសក្រិកឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Agricultural Research Foundation (NAGREF) - ប្រទេសក្រិក1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
11/05/2011
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Sustainable development of olive groves I [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas

Sustainable development of olive groves II [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations and plastic nets on the soil surface
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
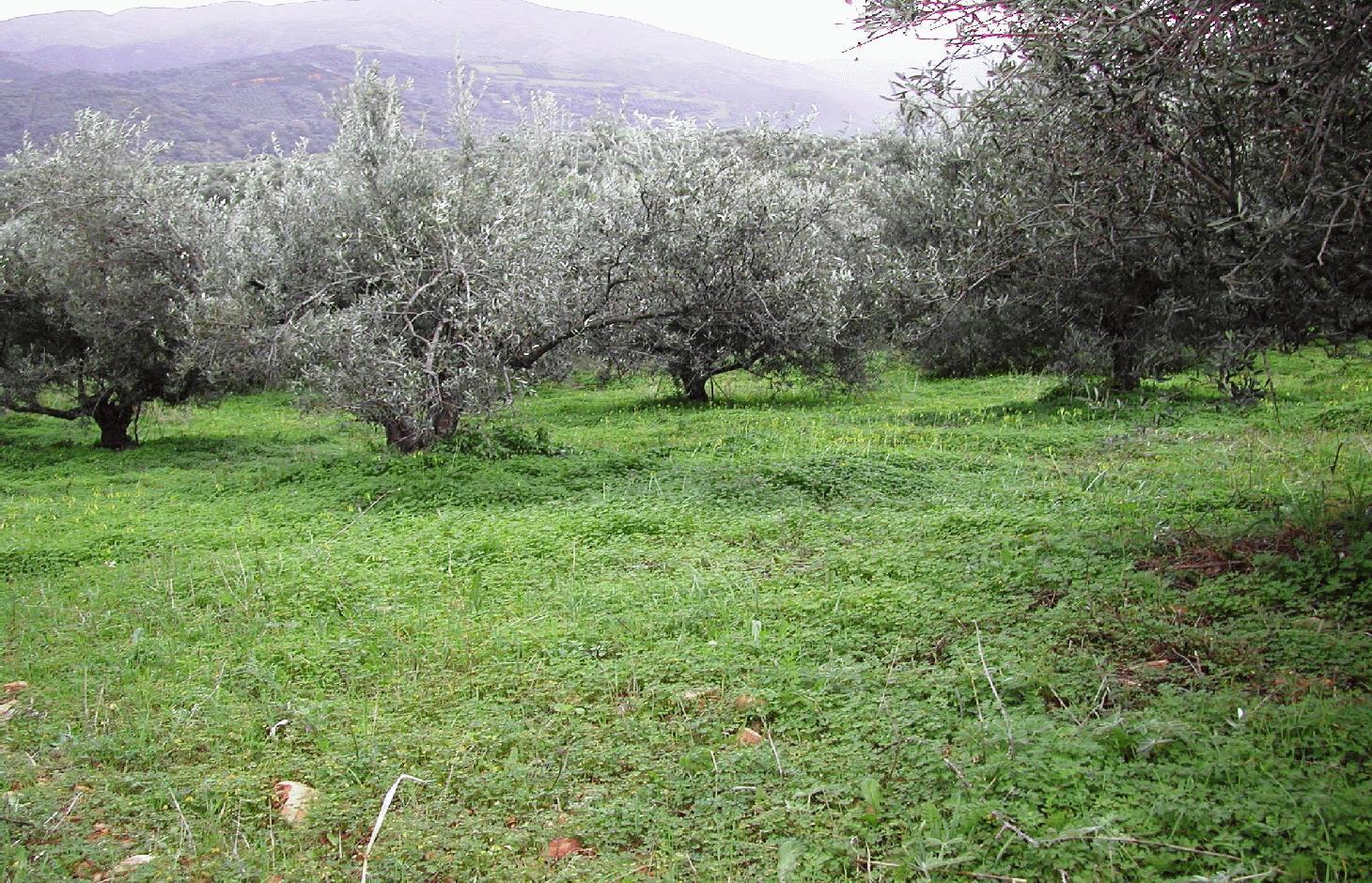
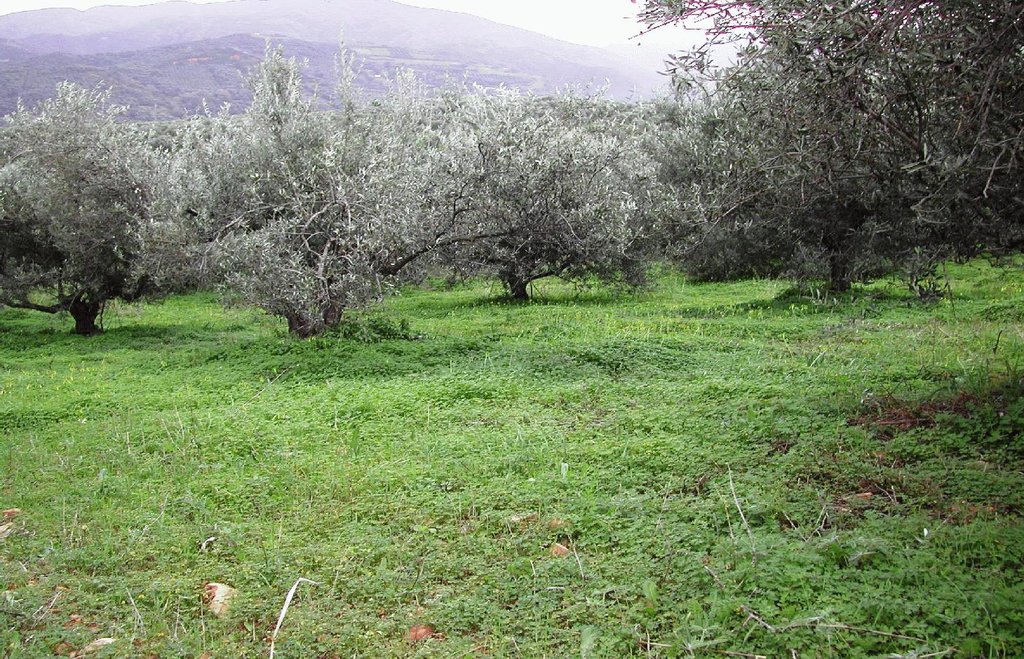
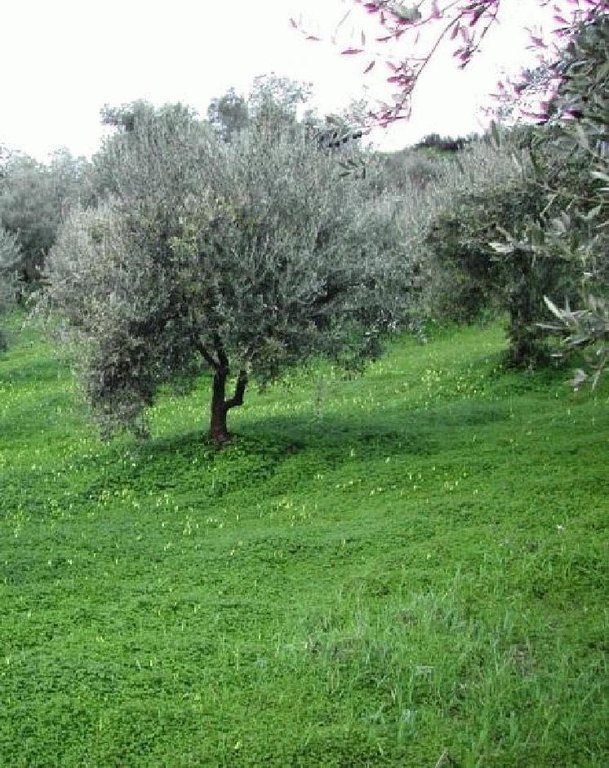
Olive groves under no tillage and no herbicide application.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Sustainable farming may include several measures for protecting natural resources. One measure, that of no-tillage, relates to reduced soil erosion. This may have favourable effects on soil aggregation and protection from soil crusting and soil erosion. In a no-tillage system, the residues are concentrated on the surface of the soil, which enhances aggregate stability and protects the soil from erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: Sustainable farming may include several measures for protecting natural resources. One of the applied measures in the context of sustainable farming, related to reduction of soil erosion, is minimum tillage or no tillage operations. No tillage may have favourable effects on soil aggregation and protection of soil crusting and soil erosion. Maximum soil degradation occurs when soil is tilled with a mouldboard plough, followed by disking. In no-tillage system, the residues are concentrated on the surface of the soil enhancing aggregate stability and protecting the soil from erosion.There is no any extra cost for application of the Technology. In the opposite, farm income increases since cost production is decreased without any decrease in olive oil production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The most frequently used cover crop is Oxalis pescaprae, a species considered as a weed but with a positive effect on soil and water conservation. It is left to grow during winter to improve water infiltration into the soil and to help prevent soil erosion. Owing to its high sensitivity to drought, Oxalis tends to reach wilting point in late spring due to lack of water in the upper soil layer. Disc-ploughing once every four to five years is necessary to destroy the perennial vegetation and incorporate fertilizers and plant residues into the soil. There is no extra cost involved in applying the technology. In fact, farm income increases, since production costs decrease without any reduction in olive oil production.
Natural / human environment: This practice is common locally and was established 30 years ago by the collaboration of national specialists and land users. It has been applied in a variety of natural and human environmental conditions typical of the Mediterranean region.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសក្រិក
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kissamos province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Chania-Crete
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Major cash crop: Olives

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high soil erosion rates and a decrease in groundwater recharge
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increasing production costs when the technique is not applied
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: November to April
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
- បញ្ចូលការគ្រប់គ្រងសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺតាមបែបចម្រុះ (រួមទាំង កសិកម្មសរីរាង្គ)
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 532 m2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M4: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរចម្បងៗក្នុងការកំណត់ ពេលអនុវត្តសកម្មភាព
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (displacement of soil by ploughing)
Secondary causes of degradation: labour availability
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
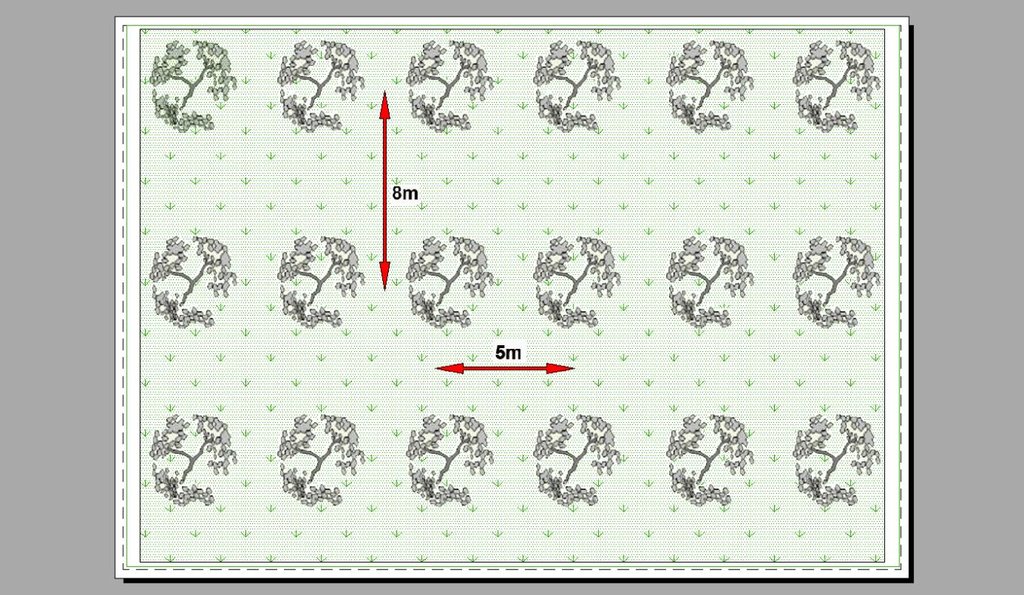
Olive groves occur widely throughout Crete (Greece). One of the main cultivation practices adopted recently is minimum or no tillage. Under this land management practice, weeds are allowed to grow, covering and protecting the soil surface from raindrop impact. The most widely distributed weed is Oxalis pescaprae, a plant species that has positive effects on soil and water conservation. Oxalis grows during winter improving water infiltration into the soil and helping to prevent soil erosion. Owing to its high sensitivity to drought, Oxalis reaches wilting point during late spring due to a lack of soil water in the upper soil layer. The plant is indigenous to South Africa and highly invasive. The plant has a reputation for being very difficult to eradicate once it has become established. Olive trees, planted close together, partially prevent the growth of understorey vegetation. In the Crete study area, rows of olive trees are spaced at intervals of 8 m and trees are planted 5 m apart in the rows
Location: Voukolies. Chania
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness
Mulching
Material/ species: oxalis sp
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of weeds if they interfere significantly with the collection of the olive crop | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 5 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | no maintenance | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: no machinery needed
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
No factors affect costs since Oxalis grows in the area under natural conditions
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ក្រុមហ៊ុន
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
2200-2500€/ha
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Hindered farm operations
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase in farmers income and reduction the off-site effects
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ដី
សំណើមដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនស្គាល់ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| arid climatic conditions | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
2650
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 50-90%
មតិយោបល់:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1850 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
800 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Production costs can be cut, but may create problems for olive harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? the necessity to cut weeds during harvesting |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Technologies for conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete mainly relate to land management. Olive groves are widespread on the island as a result of the importance of olive oil for everyday cooking. Furthermore, olive groves can survive adverse weather and soil conditions providing a significant income for farmers for a relatively low labour input. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and knowledge transfer by local institutes and specialists. No-tillage land management practice with olives can be considered as an important technique to protect against land degradation and desertification and increase farmers’ incomes How can they be sustained / enhanced? education of farmers |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The field is ‘clean’ in readiness for harvesting | the necessity to cut weeds during harvesting |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| A slight decrease in water availability for the growing trees | no solution to this problem |
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Sustainable development of olive groves I [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas

Sustainable development of olive groves II [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations and plastic nets on the soil surface
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល