Landslip and stream bank stabilisation [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dileep Kumar Karna
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Bans ko bhatta, Manra bandhi (Nepali)
technologies_1491 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Singh Bijendra
bijendra25@hotmail.com
DSCO
Kabhrepalanchok, Nepal
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Basnet Druba P.
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Chittagong Hill Tracts Development Board (CHTDB) - ប្រទេសបង់ក្លាដែសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development (G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development) - ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌាឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CSKHPKV Palampur (CSKHPKV Palampur) - ប្រទេសឥណ្ឌា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
12/02/2003
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Integrated watershed management for landslip and stream bank … [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
Integrated watershed management as an example for landslip and stream bank stabilisation based on fostering a partnership between community institutions, line agencies, district authorities and consultants
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dileep Kumar Karna
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
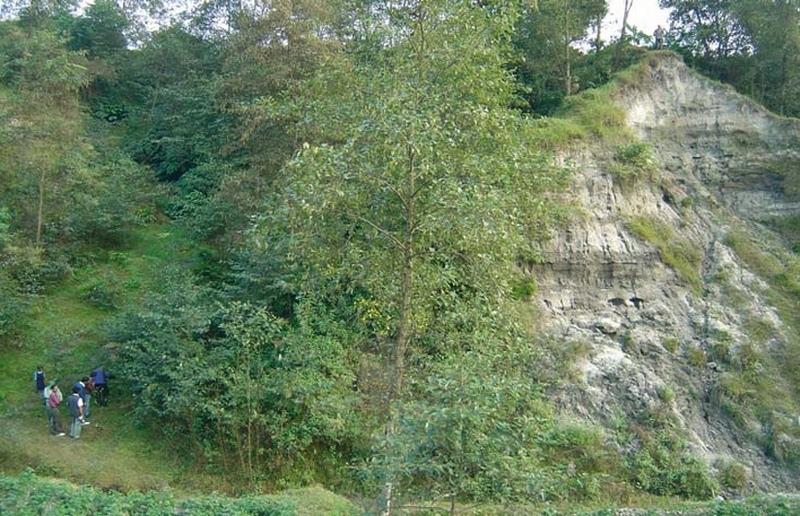
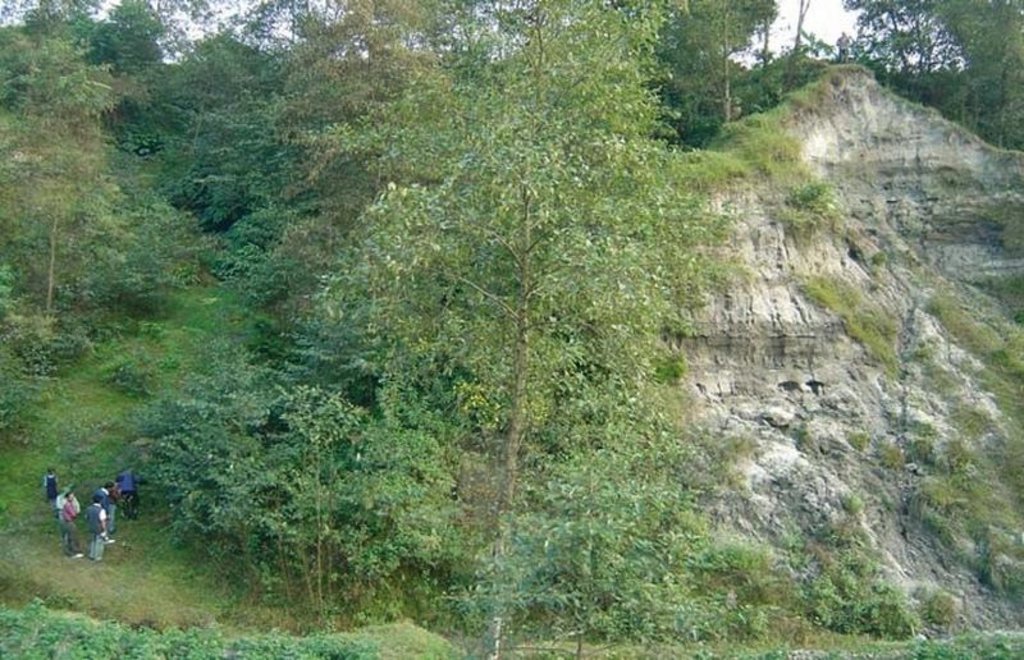
Integration of vegetative and structural measures for landslip, stream bank and gully stabilisation on hillsides.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
A combination of measures, implemented by a group of neighbouring families, is used to address landslips, gully formation and stream bank erosion problems in the middle hills of Nepal. All these processes affect the stability of adjacent agricultural land and cause problems downstream. Small-scale farming is dominant in the area surrounding the treated land - which theoretically belongs to the government but is used by these families.
This pilot technological package is proving suitable in Nepal for steep/very steep slopes under subhumid climates within an altitudinal range of 1,000-1,500 m a.s.l. This type of intervention, combined with the active involvement of stakeholders (who contribute three quarters of the cost), was recently introduced to Nepal under a watershed management programme, co-funded by the European Commission (see related approach ‘Integrated watershed management’).
Initially, ditches with bunds on the lower side are constructed along the contour. Within the gullies and along the stream banks, cement bags (filled with cement, brick chips, sand and/or earth) are placed to avoid deepening of the channel. Wattle fences, made from woven bamboo are also used as checks in the gullies. These structures are complemented by vegetative measures: Nepalese alder (Alnus nepalensis), bamboo (Dendrocalamus sp.), cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum), and broom grass (Thyosonaelana maxima) are planted. These species establish quickly in degraded sites and also control erosion, stabilise land and serve as cash crops, and for fodder, fuelwood and timber. Alder (locally called utis) is a nitrogen-fixing multipurpose tree which helps restore soil fertility.
Farmers can get economic benefits within a few years from these plants. Another advantage of this package is that the vegetative resources needed are locally available and cheap. Furthermore farmers already know how to propagate them. Maintenance costs are negligible. Once established, the stabilised and revegetated sites provide improved environments for birds and insects – thus favouring biodiversity - and they help protect natural springs. In this case study, the economic returns from the cash crops mainly go to one family. Another few families also utilise this site, extracting common products (fodder, litter, timber) for domestic use. Additionally, the location is regularly used as an unofficial demonstration site, being visited by various people (farmers, SWC specialists) interested in the technology. This represents an indirect benefit to a larger number of people and strengthens institutions at household and community levels.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kathmandu
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kathmandu/Bagmati watershed
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ដីព្រៃឈើ និងដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ផលិតផល/សេវាកម្មចម្បង:
major cash crop: Nepalese Alder (Alnus nepalensis), Bamboo (Dendroc) and broom grass (Thysanolaena maxima)

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Wasteland (degraded shrubland before SWC)
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
degraded , no annual crops, occasionally grazed
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - concentrated runoff from upstream agricultural areas
- landslides, gullies and stream bank erosion
- gullies back-cutting into fertile agricultural land and threatening irrigation canals and homesteads
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Landslide and gully erosion due to poor vegetative cover (steepness and lack of effective drainage/ diversion system).
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ma: Agro-silvopastoralism
Constraints of wastelands (degraded shrubland) (before SWC) (degraded , no annual crops, occasionally grazed)
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Nov
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃបញ្ហាលើប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- 0.1-1 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.14 km2.
The Approach covered a bigger area. This is just one example.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wm: ការបាក់ដី
- Wr: សំណឹកដីច្រាំងទន្លេ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Land slip and stream bank
protection: an overview of the
multiple and integrated vegetative
and structural measures: cut-off drain
1. landslip area
2. banana trees
3. alder trees
4. bamboo wattle fences
5. cardamom
6. planting bamboo
7. cement bag check dams
8. broom grass
9. cutting bamboo
10. stream bank
11. agricultural fi elds in a fl at area
Insert 1: Bamboo wattle fence
combined with retention ditch and
grassed bund to stabilise steep slopes and gullies.
Insert 2: Old cement bags fi lled to
form checks in gullies
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of infiltration, introduction of cash crop
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2 m
Trees/ shrubs species: Alnus nepalenses
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Dendrocalamus sp.
Perennial crops species: Large cardamom
Grass species: Broom grass
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Spacing between structures (m): 10 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25 m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1 m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10 m
Terrace: forward sloping
Spacing between structures (m): 10 m
Structural measure: sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-4 m
Spacing between structures (m): 0.3 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3-4 m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8 m
Structural measure: cement bags
Structural measure: wattle fences
Construction material (concrete): Sand/cement .
Construction material (other): Bamboo culm cutting (1.5 m long)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 100%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 15%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1.4 ha
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារអាមេរិក
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1.35
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparing site for implementation of vegetative measures | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | June |
| 2. | Planting of alder (Alnus nepalensis,), cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum), | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | July - August |
| 3. | Watering of new plants using buckets | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Mar- May (1st year) |
| 4. | Application of farmyard manure at time of planting | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Time of planting and every December |
| 5. | Weeding | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | January |
| 6. | Earthing up new plants with soil | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | January |
| 7. | Construction of contour bunds and ditches | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | January–April |
| 8. | Stabilisation of slopes using bamboo wattle fences, and gullies using the check dams | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | |
| 9. | Gully stabilisation as walls of cement bags are placed across the gullies and along stream banks | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | June |
| 10. | Preparing the site for planting | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | June |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Stabilisation of gully and vegetative measures | Persons/day | 1567,0 | 1,35 | 2115,45 | 75,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 55,0 | 55,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Empty cement bags | pieces | 600,0 | 0,0166666 | 10,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Bamboo cuttings | pieces | 600,0 | 0,9416666 | 565,0 | 50,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Cement bags filled | pieces | 30,0 | 4,166666 | 125,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Alder saplings | pieces | 2500,0 | 0,016 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Seedlings cardamon | pieces | 400,0 | 0,0125 | 5,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2925,45 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
By different stakeholders
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Apply farmyard manure | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | January /1 |
| 2. | Weed | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | January /1 |
| 3. | Prepare land for further planting of large cardamom and broom grass | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | March-April /1 |
| 4. | Thin cardamom, bamboo, alder, broom grass with a knife: | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | May,June /1 |
| 5. | Replant cardamom, broom grass, bamboo that did not establish | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | June,July /1 |
| 6. | Earth up | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | Aug-Sep and January /1 |
| 7. | Prune alders | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | December.,January /1 |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Maintaining plants | Persons/day | 41,0 | 1,35 | 55,35 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 70,35 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: Activities are carried out manually using local and traditional tools:
The costs (per ha) are calculated for the entire SWC site (consisting of 1.4 ha) including all establishment and maintenance inputs. Labour costs: information based on oral information by farmer. Estimate was approx. 3 people per working day over 2 years.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
labour is the major input.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Slopes on average: Also hilly
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is low (sandy) - medium (loam)
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
2% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
85% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land.
3% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
3% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm activities: occasionally teaching at farmer's school; selling non-timber forest products on the market; some people workin markets/shops/onconstruction, sites, and similar ..
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
including fuel wood
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
cash crop introduction
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
high during establishment, low during maintenance
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
input constraints
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
high during establishment, low during maintenance
input constraints for maintenance
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
due to cardamom’s medicinal properties
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
by way of community resource mobilisation (e.g. as a result of common establishment activities; visits to the site by outsiders)
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
especially in case of insecure land tenureship
Illegal extract of non-timber forest products
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
because of remoteness
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
80 m3/ha/y
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
35 m3/ha/y
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
200 t/ha/y
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10 t/ha/yr
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
soil erosion and sediment transport(locally)
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
soil erosion increase and increased sediment transport locally during establishment of structural measures (construction of wattle fences, terraces, cement bag walls in gullies)
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
stabilisation of upstream agricultural land
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The agricultural land which is located on the upper portion of the SWC area is stabilised
runoff/transported sediments
grazing pressure
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
grazing pressure will increase on another site because of the SWC site is closed for grazing
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- ច្រើនជាង 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
38 households in an area of 1.4 ha
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 50-90%
មតិយោបល់:
47% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
53% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: estimates by the authors, based on the past trends of adoption.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Family members have learnt the technology. it is easy to replicate. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provide training and schooling to farmers to spread this information to others (eg through village initiatives supported by government). |
|
Better environment, increased biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
|
Soil and water conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
|
Fresh products, health benefits from cardamom How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
|
Income generation from cash cropping of cardamom, bamboo, broom grass) How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
The technology requires resources which are largely locally available and of low costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Raise awareness that landslide threatened stream banks and steep slops can be protected using local resources. |
|
Technology addresses livelihood constraints How can they be sustained / enhanced? Raise awareness that the technology is profitable. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The technology is adopted more by better ressourced farmers | Government programmes should seek to involve poor farmers in land development with incentives for adopting recommennded technologies |
| Establishment costs are high | Subsidise the cost (extension service, projects), reduce establishment costs by designing alternative structural measures without use of cement. |
| Socio-economic conflicts can arise when the value of land is raised | Take equity issues into account when implementing such a programme, and spread the benefits. |
| Establishment is very labour intensive. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
IBIWMP (2003) Engineering Field Manual. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Programme,Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Howell, J. (ed) (1999) Roadside Bio-engineering Reference Manual. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Roads
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Integrated watershed management for landslip and stream bank … [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
Integrated watershed management as an example for landslip and stream bank stabilisation based on fostering a partnership between community institutions, line agencies, district authorities and consultants
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Dileep Kumar Karna
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល