Alliance Farming [ប្រទេសកាមេរូន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Blasius Azuhnwi
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Brigitte Zimmermann, Donia Mühlematter
Alliance Farming
technologies_3342 - ប្រទេសកាមេរូន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Jiedoh Duni
237 677828136
jeidohduni@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda
ប្រទេសកាមេរូន
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Sali Usmanu Mallam
237 674433655
saliusmanu@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda CAMEROON
ប្រទេសកាមេរូន
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Hammadu Bawuro Abubakar
675005574
abubawuro@gmail.com
MBOSCUDA
P.O. Box 221 Bamenda CAMEROON
ប្រទេសកាមេរូន
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
In Search of Common Groundឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Mbororo Social and Cultural Development Association (MBOSCUDA) - ប្រទេសកាមេរូន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
03/12/2018
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Alliance farming refers to collaboration between crop farmers and pastoralists, who agree to use the same land and related resources (crop residues as fodder for pastoralists; dung as fertilizer for crop farmers) for their mutual benefit.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
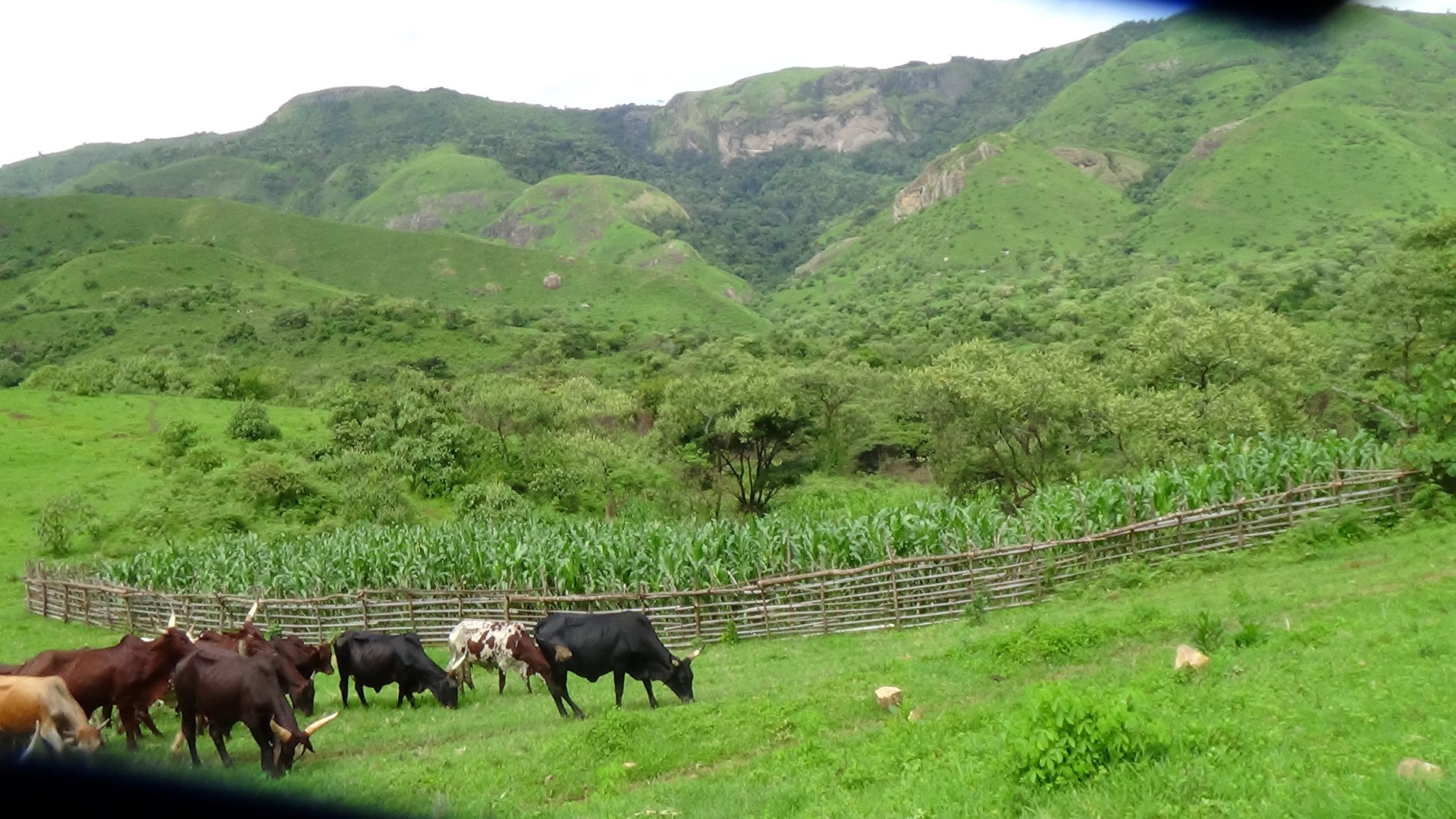
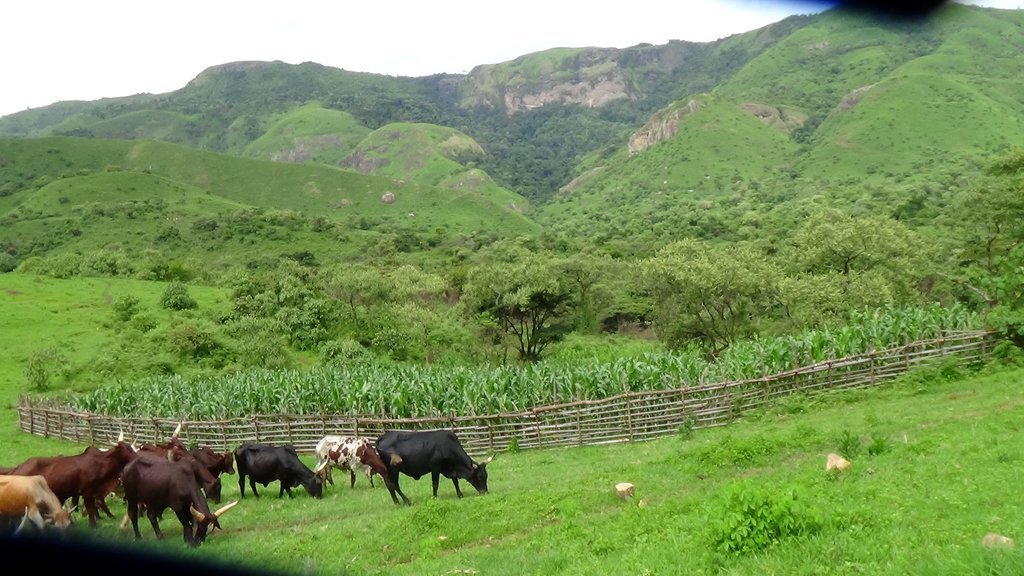
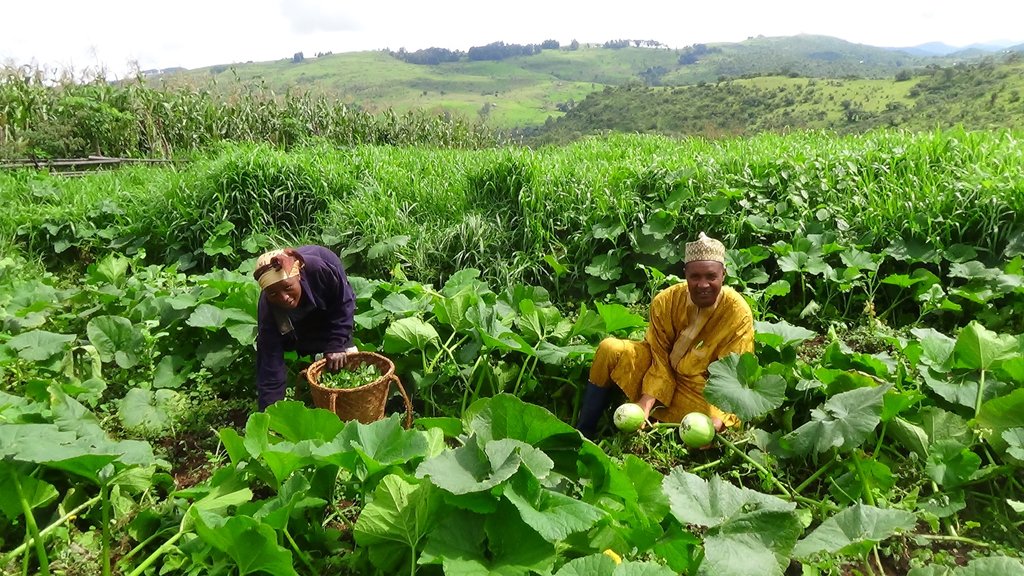
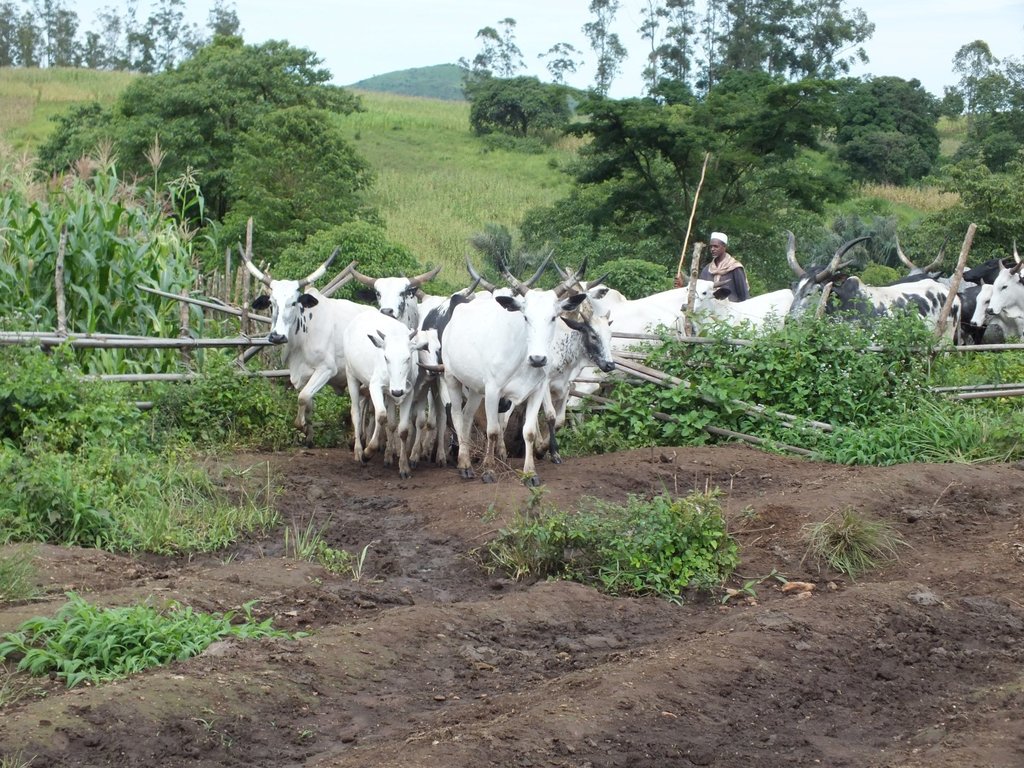
Alliance farming is partnership between pastoralists and subsistence farmers to share resources. They agree to use the same land and related resources sequentially: growing crops during the rains, and grazing cattle in the dry season. It is a further development of the conflict mediation process under which cattle are allowed to graze on cropland after harvest. The cattle consume crop residues and weeds (including some grass) on the farm and they produce dung and urine in turn, which increases nitrogen content and organic matter in the soil. This enhances its fertility and makes it more productive for the next round of crop cultivation. The crops grown are mainly annuals including maize, beans, soybeans and groundnuts. The livestock are mainly zebu cattle for beef (Bos indicus). There exists several variants (or components) of this arrangement: 1) The farmer constructs a night paddock (a corral) in farmland and invites pastoralists to kraal their animals in the paddock overnight; 2) The farmer arranges with the pastoralist to farm on areas where animals have been held overnight, in grazing land – and constructs a fence to protect the crops; 3) In communities where transhumance is common, the farmer allows a pastoralist to graze his cattle on crop residues remaining after harvest; 4) Pastoralists allow farmers to collect dung and apply it in their farms. Contracts for the most part are verbal and non-written, and each party counts on the good conscience and honesty of the other.
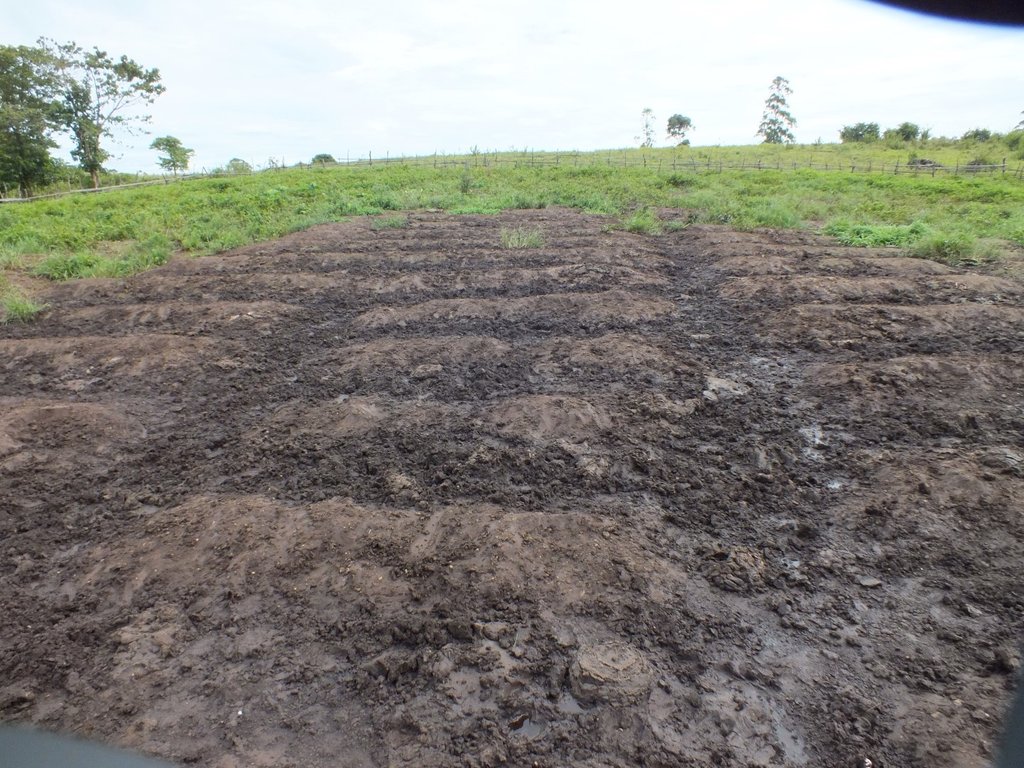
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
4 different photos showing pastoralists and farmers who are benefiting from this technology have been provided.
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
There are two videos of this technology available but each is about 125 MB and just too heavy to be uploaded on to this site.
ទីតាំង:
n.a
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
n.a
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកាមេរូន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
North West Region
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
This approach has been piloted in 23 communities in the North West Region.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2011
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Some aspects of this technology were already in practise in the region over the decades but due the facilitation of Mbororo Social and Cultural Development Association (MBOSCUDA) this technology is being adopted now by many locals
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពនេចរ
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ប្រភេទសត្វ និងផលិតផលចម្បងៗ:
Zebu cattle under extensive production which produce dung and urine.

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ដីដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ផលិតផល/សេវាកម្មចម្បង:
Annuals such as maize, beans, soybeans and groundnuts, while livestock kept under extensive system of production produce dung and urine to enrich the soil.
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Land use is changing due to the use of this technology but this change is principally driven by the increasing demographics. Through the use of this technology, much more rangelands is being cultivated for crop production
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
This is a very low-input land use.
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Usually one growing season.
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Presently common in pilot villages/communities.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ
- V4: ការជំនួស ឬការយកចេញនៃប្រភេទរុក្ខជាតិក្រៅស្រុក/ ការរាតត្បាត

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
- M4: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរចម្បងៗក្នុងការកំណត់ ពេលអនុវត្តសកម្មភាព
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
មតិយោបល់:
Some degraded land is being rehabilitated as pastoralists do invite farmers to come farm in the rangelands which have been invaded by braken fern. By tilling of the soil and removing the rhizomes in them, the spread of the invasive species is being put to check.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
MBOSCUDA North West Region Cameroon
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
13/01/2018
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
• Alliance farming is an advanced outcome of the conflict mediation process whereby cattle are allowed to graze on crop lands after harvest.
• Livestock consume crop residues and weeds (including grass).
• When the land is used to paddock cattle, their manure and urine fertilize the soil making it more productive when the crop farmers return to cultivate.
• Crops are planted on the plot of land once the cattle are taken away.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
0.5 hectares
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
FCFA
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1500 FCFA
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmer harvests annual crop e.g. maize, beans | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | At the end of growing season which is usually in October |
| 2. | Farmer invites pastoralist to bring herd to graze off crop residues | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | After harvest of crops in Octorber |
| 3. | Cattle graze on crop residues and weeds on farm | ផ្សេងៗ | During grazing in the dry season from mid-November onwards |
| 4. | Dung and faeces passed out by animal increases N content of soil | ផ្សេងៗ | During grazing, mostly in the dry season mid-November to mid-March. |
| 5. | Pastoralist takes animals away from farm | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | At the beginning of the rains in mid-March. |
| 6. | Farmer then returns to till soil and plant annual crops in the field | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | At the beginning of the growing season by mid-March. |
មតិយោបល់:
This is actually a low input technology.
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Land users bore all of the costs
មតិយោបល់:
A low input technology.
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | n.a. |
មតិយោបល់:
There are no maintenance costs.
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
n.a.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The only costs pertain to herding the animal to farmer's farm which is done by pastoralist or his a herder he has paid
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
It is a uni-modal in nature with rains coming in by mid March and going by mid October.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Institute of Agricultural Research for Development
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Sub-humid climate with mainly sudan savana characterized by undulating hills and short grass species interspersed with shrubs.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
The land users are predominantly resource poor livestock and crop farmers.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved soil fertility from dung and urine leads to increase crop production.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved crop quality as little or no pesticides are used.
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increase fodder production from crop residues such as maize stover, legume haulms and sweet potato vines.
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farmers do not use chemicals on the crops so quality of resulting crop residues is also good.
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The greater access that the livestock have to crop residues has led to increased animal production.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The risk of production failure has decreased since farmers have increased the effective sizes of their farm holdings.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Production area has also increased as farmers have increase land area under cultivation mostly when they are invited to come farm in rangelands in order to till the soil and break the cycle of spread of invasive species
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Better land management now with the same land put to multiple uses and more productive than previously i.e. when the two land uses were separated.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farm income has increased from improved production and productivity of crops and animals.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Income sources have been diversified. With increased income from farms, farmers most especially are going for other off- farm enterprises such as petty trading.
ភាពខុសគ្នាផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Economic disparities are being bridged because of the increased income from either livestock production or crop farming.
បន្ទុកការងារ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Workload is also being eased as farmers and pastoralists are witnessing improved crop and livestock productivity. Farmers, especially, do not have to bring much more new land under cultivation.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Food self-sufficiency of alliance farming practising families has improved from the increase in production.
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
From the improved income as a result of increased production and productivity, alliance practitioners have more disposal income to take care of medical bills.
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Land use rights especially of pastoralists has improved since farmers now acknowledge that pastoralists do own land. Pastoralists, due to their late arrival in the region, are looked upon as 'strangers' by their farming neighbours. However this perception is changing because of the positive engagement between the these two main land users.
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase cross-cultural dialogue within the community: pastoralists are predominantly Moslems while crop farmers are mainly Christians.
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Community institutions like the Dialogue Platforms have been strengthened, as they have grown in recognition among community members as a low- stake solution to resource use conflicts.
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Agro-Pastoral Commissions, which are the statutory bodies adjudicating conflicts between farmers and pastoralists, have come to see effectiveness of the Dialogue Platforms and are incorporating the Alternative Conflict Management practices in their modus operandi.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-2
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
There has been a great decrease in the number, frequency and intensity of the conflicts as the two sets of land users have seen good reason to collaborate instead of antagonize each other.
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The self-esteem of the Mbororos who make up the majority of pastoralists community has been improved through this positive engagement with farmers.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Nutrient cycling has improved as dung and urine are returned to improve soil fertility and help subsequent crops.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Soil organic matter has also being improved from the increase crop residues which animals do not eat all.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase soil fertility has meant increase crop cover
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase crop yields also mean increase crop biomass
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Plant diversity has been somewhat increased due to fertile soils make it possible for different plant species to grow
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
-1
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
1
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The spread of alien species such as bracken fern on rangelands is being controlled since farmers are being invited by pastoralists to come and cultivate crops on rangelands. The tilling of the soil is a good mechanical method of controlling the spread of these invasive species.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមការវាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់:
n.a.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះទឹកកកតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រលកកម្តៅ | មិនល្អ |
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
| ភ្លើងឆេះ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការមានបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិត/ដង្កូវ | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
Growth of the crops most especially will be affected by climate change events such as droughts or too much rainfall. The crops are C4 crops and so will get very little benefits predicted rise in temperatures associated with climate change.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
More than 800 alliance farming pairs have been facilitated by this process.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
Farmers have not received any incentives from project in order to adopt this.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Technology leads to increased crop yields because of the improved soil fertility. |
| Technology leads to improved crop quality because of the use of organic manure and less chemicals fertilizers. The use of chemical fertilizers can lead to leaching of inorganic nutrients into ground water, and also eutrophication of water bodies. |
| It has led to stronger social relationships between farmers and pastoralists. |
| Invasive species such as Pteridium aquilinium (bracken fern) that has invaded rangelands is being controlled. Tilling of the farms is a mechanical method of stopping its growth and spread. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| More productive use of land than when two land uses were separate. |
| More environmentally friendly since organic manure is being used. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The ratio of pastoralists to farmers is really low (about 1:6) meaning that there are not many pastoralists to form Alliance Farming pairs with willing farmers. | Increasing herd sizes to ensure more production of manure could alleviate this problem. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Agreements are verbal. | Formalizing the contracts. |
| Some variants of the technology, for example that in which pastoralists allow farmers to collect dung to go to farm in another area may lead to nutrient export. The dung does not contribute to improve the fertility of the soil where it was collected but does so at a different site where farming will take place. There is no net loss of nutrients out of the whole system though. | Transportation of dung to different sites should be discouraged. Farming should take place as much as possible on the farm that supplied crop residues to feed the animals. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
4 field visits were done.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
About 30 people were contacted during focus group discussions and key informant interviews.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
4 SLM specialists were contacted.
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Secondary data sources were consulted.
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
MBOSCUDA Searchlight Magazine Vols 1, 2,3. 2014, 2015, 2016
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Free copies
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Blasius Azuhnwi and Fiona Flintan (2017)- Making Rangelands Secure, Issue Paper 8, Rangelands Series
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
From ILC Rome for free
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
n.a.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល