Terrace [ប្រទេសចិន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Meili WEN
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Terrace
technologies_1367 - ប្រទេសចិន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - ប្រទេសចិន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
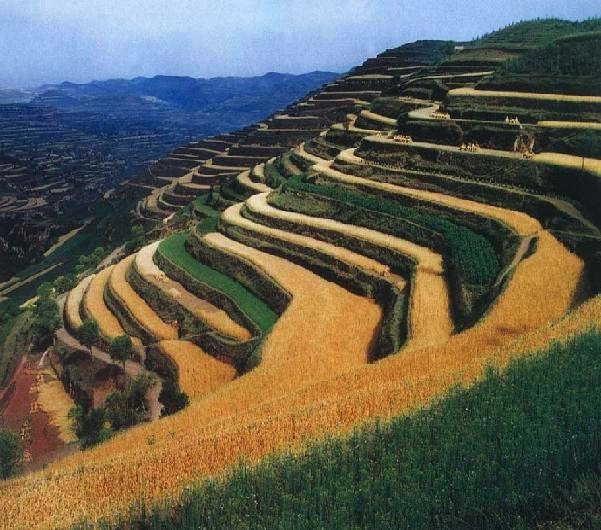
A terrace is a kind of measure to change the slope, which has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
A terrace has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top. It can reduce slope angle and length, retain runoff, increase infiltration and reduce the soil loss. Crops can grow well because water increases in soils. Meanwhile, ground cover is improved. Terrace can be constructed by manual labor or machine. Firstly, determining the width of the field according to the slope angle and soil texture. Secondly, putting the topsoil aside. Thirdly, leveling up the slope and constructing banks. At last, putting the topsoil to the top of the flat surface.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
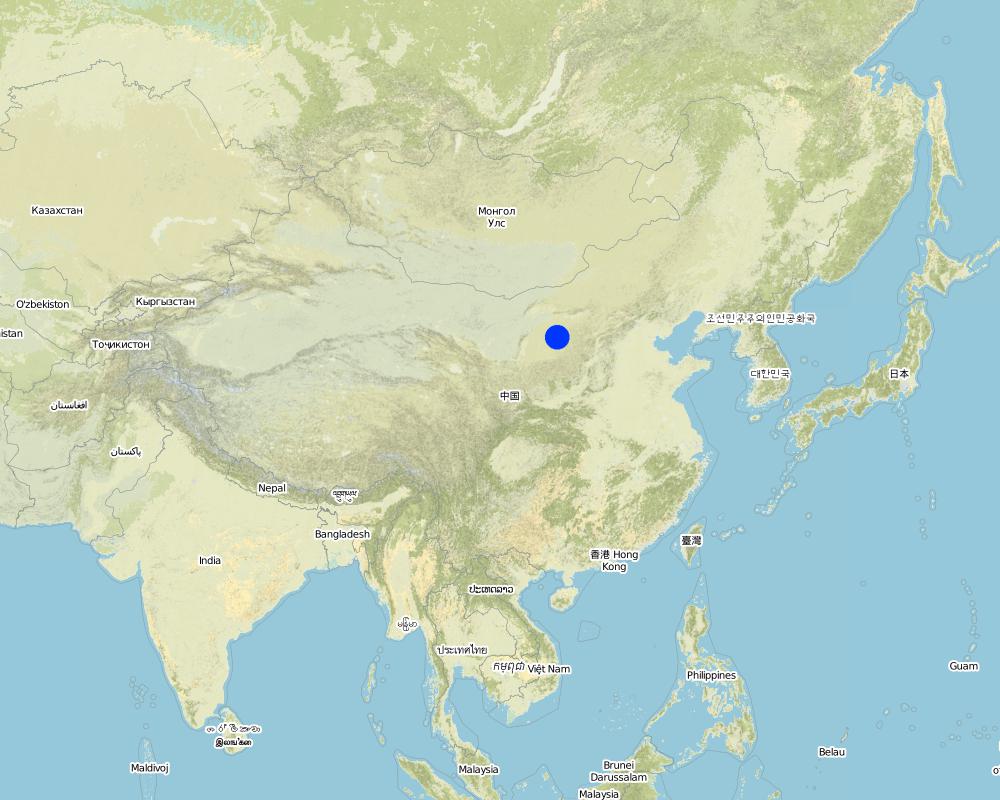
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសចិន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Shaanxi, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Henan, Gansu
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
26666,7
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- > 10,000 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 26666.7 km2.
Terrace is one of the most outstanding achievements in SWC in China. It can prevent soil and water loss so that slope land can be sustainable development. There are about 26.7 million ha of terrace in China, of which more than 13.3
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Summary from farmers' long term experience in SWC, later being innovated.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - គ្រាប់ហោឡាំងតាវ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: May-Sep
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water lose seriously, soil degrades, soil fertility decreases and crop yield declines.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): crop yield declines, weak ability of resisting drought
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S1: ការធ្វើដីថ្នាក់ៗតាមជម្រាលភ្នំ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
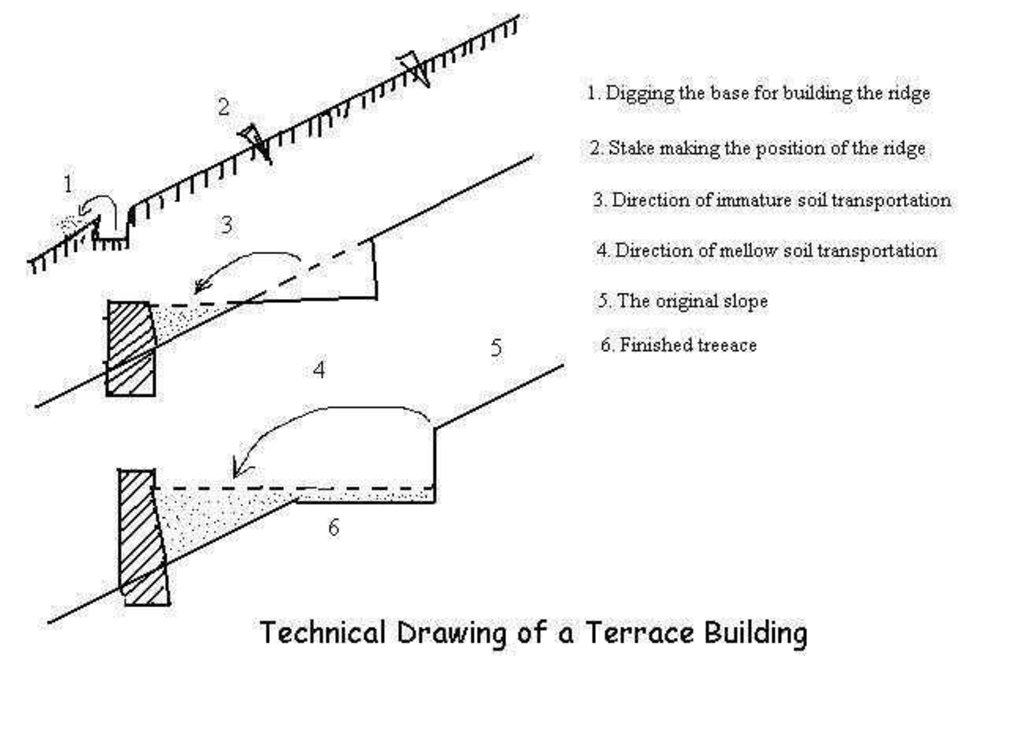
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Drawings of a terrace building in the Loess Plateau
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, Gansu, Inner Mongolia
Date: 2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Construction material (earth): Construct ridge of terrace
Construction material (stone): Construct ridge of terrace
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 80%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:6
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
BAI Zhanguo, Beijing China
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
3.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | survey | After harvesting crop |
| 2. | constructing terrace: determine the excavation line which should make the excavation and the filling equal and the least workload | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 3. | constructing terrace: pilling mellow soil up to the middle of a bench | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 4. | constructing terrace: moving the immature soil of lower part to fill the upper part or moving the soil from inside to fill up outside | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 5. | constructing terrace: building the ridge | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 6. | constructing terrace: spreading the mellow soil on the surface | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | periodically inspecting | After a storm/About 1 year |
| 2. | repairing where terrace is collapsed | Whenever finding it is destroyed/timely |
| 3. | level up the field | after harvesting crops/timely |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Terrace section, building by bulldozer.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The factors are topography, soil texture, means of construction. The section of terrace is the most important factor.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
449,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Slopes on average also rolling
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មាន
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Relative level of wealth: all selected
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, average, poor, very poor
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: estimate
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ភូមិ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
4
ដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
180
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
58
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If they have enough money, they would like to do, because they have known the benefits from terraces.
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
(inner resources) Suide Water and Soil Conservation examination station of Yellow River Water Resources Committee.. 1981.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
orpus of Test Research of Water and Soil Conservation (the second volume), p130~185.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
(inner resources) Water and Soil Conservation Department of Yellow River Water Resources Committee of Ministry of Water Resources and Electric Power.. 1987.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Corpus of economic benefits of water and soil measures, p77~102 ,510~514
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Dongyinglin,Changpiguang ,Wangzhihua. Discussion on the several questions on increasing production of the terrace with two banks.. 1990.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.1, p36~37
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Jiangdingsheng. Discussion on section design of the terrace on the Loess Plateau.. 1987.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ACTA CONSERVATIONIS SOLI ET AQUAE SINICA, Vol.1, No.2,p28~35.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Liangqichun, Changfushuang , Liming. A study on drawing up budgetary estimate quota of terraced field.. 2001.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, Vol.21,No.5, p41~44.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Liumingquan, Zhangaiqin, Liyouhua. Pattern engineering of reconstruction the slope cropland.. 1992.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p18~21.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Lixuelian,Qiaojiping. Synthetic technology of fertilizing and improving production on the new terrace.. 1998.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p13~14.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Ministry of Water Resources of China. Terraces in China.. 1989.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
The press of Jilin science & technology.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Wangxilong,Caiqiangguo,Wangzhongke. The consolidating function and economic benefit analysis of the terrace hedgerows in the hilly loess region of northwest Hebei Province.. 2000.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Journal of Natural Resources,Vol.15, No.1, p74~79.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Xuyuanxu.The surveying report of the terrace benefits in yanbian autonomous prefecture. 1995.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Water and Soil Conservation,No.4, p50~52.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Zhujianqiang,Lijing. Experimental study on soil compact characteristics and its shearing strength in changing slope field into terrace on south shaanxi province.. 2000.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ransaction of the CSAE,Vol.16, No.2, p36~40.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល