Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means [ប្រទេសណាមីប៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Johannes Laufs
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Asellah David
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Donia Mühlematter, Simone Verzandvoort, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano
Bush Thinning
technologies_2203 - ប្រទេសណាមីប៊ី
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 17 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 31 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2019 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 22 ខែ សីហា ឆ្នាំ 2017 (inactive)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 2 ខែ វិច្ឆិកា ឆ្នាំ 2021 (public)
- Bush Thinning and Biomass Processing by Manual or Mechanised Means: 21 ខែ កុម្ភៈ ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Gschwender Frank
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
GIZ Support to De-bushing Projectឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
The technology described is a means to rehabilitate degraded rangeland. Through targeted harvesting of bushes, the bush density is reduced, allowing for better growth of grass.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
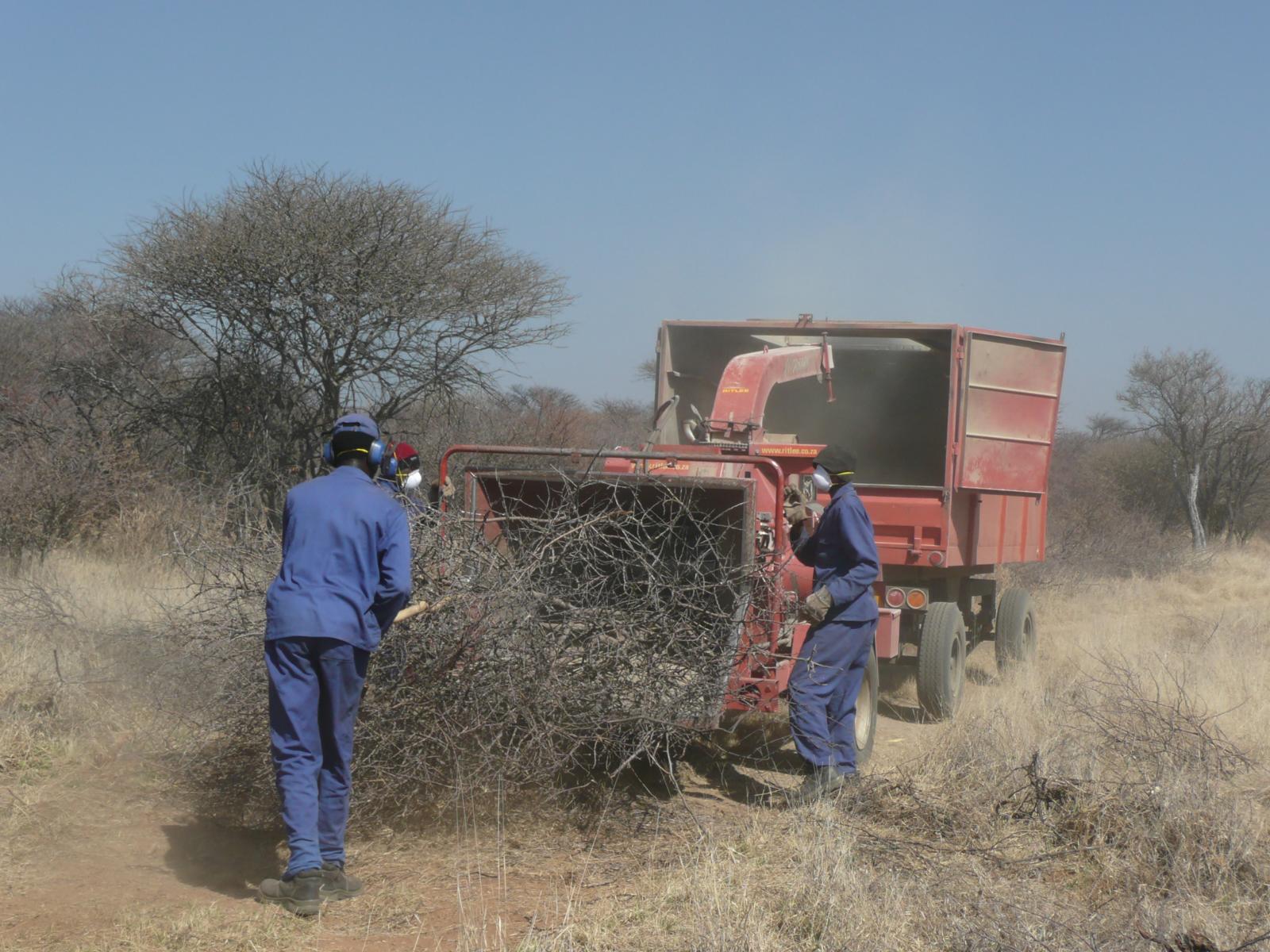
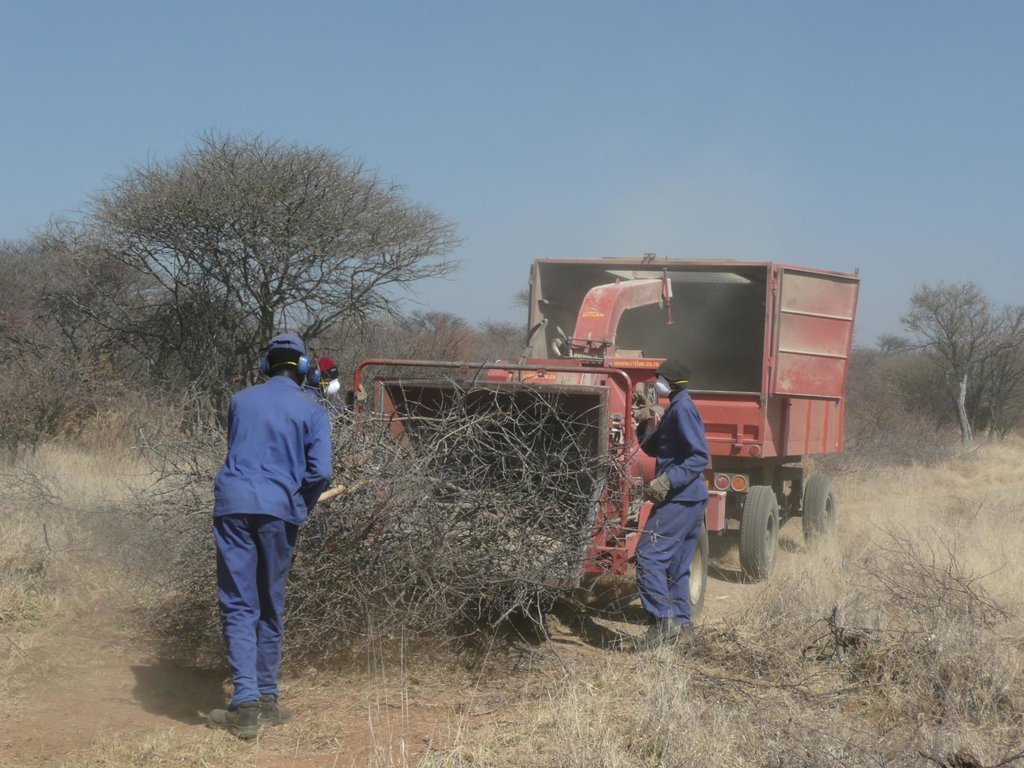
In Namibia, excess bush is harvested to reduce competition with other plants, especially grasses. Bush can be thinned manually (e.g. with axes), semi-mechanised (e.g. chainsaws) or fully mechanised (e.g. customised equipment). After cutting, the bush is left to dry and then processed into chips or other products.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Bush thinning is carried out in Namibia to restore degraded rangeland by stimulating the re-growth of grasses – which are suppressed by excess bush. About 30-45 million hectares are affected by bush encroachment, and this affects biodiversity, groundwater recharge and the carrying capacity of rangeland. There are many causes of bush encroachment, including overgrazing and reduced frequency of wildfires. Most bush encroachment involves indigenous, rather than invasive, species.
While natural transitions in the ecosystems may lead to reductions in bush encroachment, active rehabilitation measures are required for the short-term improvements. This is an absolute necessity for many farmers, who experience severe economic difficulties due to the reduced productivity of their rangeland.
Bush control comprises responsive measures (bush thinning), follow-up measures (aftercare) as well as preventative measures (good rangeland management). Since vast areas of Namibian rangeland are heavily encroached by bush, the focus is currently on bush thinning. This entails selective harvesting of bush. To determine the density of bush remaining after thinning, a formula based on tree equivalent (TE) and average annual rainfall is used. One TE is defined as a woody tree or bush of 1.5 metres in height.
As rule of thumb for attaining optimal bush density, about 30-35% of encroacher biomass should be removed. This is based on research carried out mainly in South Africa, measuring and comparing the re-growth after bush removal. Where too much bush was removed, this often resulted in even heavier encroachment.
Bush thinning follows strict environmental guidelines set by the Directorate of Forestry (DoF) through the Forestry Act and the Directorate of Environmental Affairs (DEA) through the Environmental Management Act. This governs the equipment used (to avoid soil disturbance) and the amount of bushes harvested (to achieve a healthy number of the desired bush species). The amount of bushes to be harvested is determined by an expert and depends on various factors.
While there is a lack of precise knowledge on the long-term effect of bush thinning, there is no doubt that control has an overall positive effect on the savannah ecosystem in Namibia. The need is widely recognised among land owners and acknowledged on the national political agenda.
To render bush thinning economically feasible, value chains have been developed. Through processing and utilisation of the woody biomass, income can be generated. Processed bush biomass can, for example in the form of chips, can be used for thermal and electrical energy applications (e.g. local biomass power plants or biomass boilers for industry). Currently two such energy installations exist in Namibia, one at a local brewery and one at a local cement factory. In addition, the national power utility NamPower currently considers the construction of a 20-40 MW biomass power plant.
Other existing value chains include the production of charcoal, firewood, poles, as well as bush -based animal feed. Further value chains under consideration include composite materials, such as wood-plastic, as well as biochar.
Scientific observations have shown, that bush thinning requires regular follow-up. These measures (“aftercare”) include the prevention of coppicing and re-growth. This can be achieved by applying aboricides selectively to the cut stems, stem fires or the introduction of browsers (e.g. goats). Research on the effectiveness and possible side effects of each of these methods is limited.
A major challenge is the limited suitability of available machines. The process leads to high wear and tear on the equipment (both harvesting and processing technology, (like chippers and pelletisers), often rendering operations unprofitable. Research into, and development of, more suitable machinery is necessary. Other requirements are improved skills training and continuous monitoring of the long-term effects on rangeland.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
All photos have either been taken by the GIZ Support to De-bushing Project or were provided to the project by third parties.
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=859GshR9hso&t=3s
Bush Encroachment in Namibia: Causes and Extent
An explanation of the root causes of bush encroachment and its impact on land in Namibia.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/11/2015
ទីតាំង:
Namibia
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bmlzPDiqlxo&t=45s
Biomass Value Addition: Bush Based Products
An overview of existing and potential value chains based on encroacher bush.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/11/2015
ទីតាំង:
Namibia
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MMSOfV2KBjA
Biomass Energy: From Bush to Electricity
Overview of the energetic applications of woody biomass from encroacher bush.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/11/2015
ទីតាំង:
Namibia
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសណាមីប៊ី
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
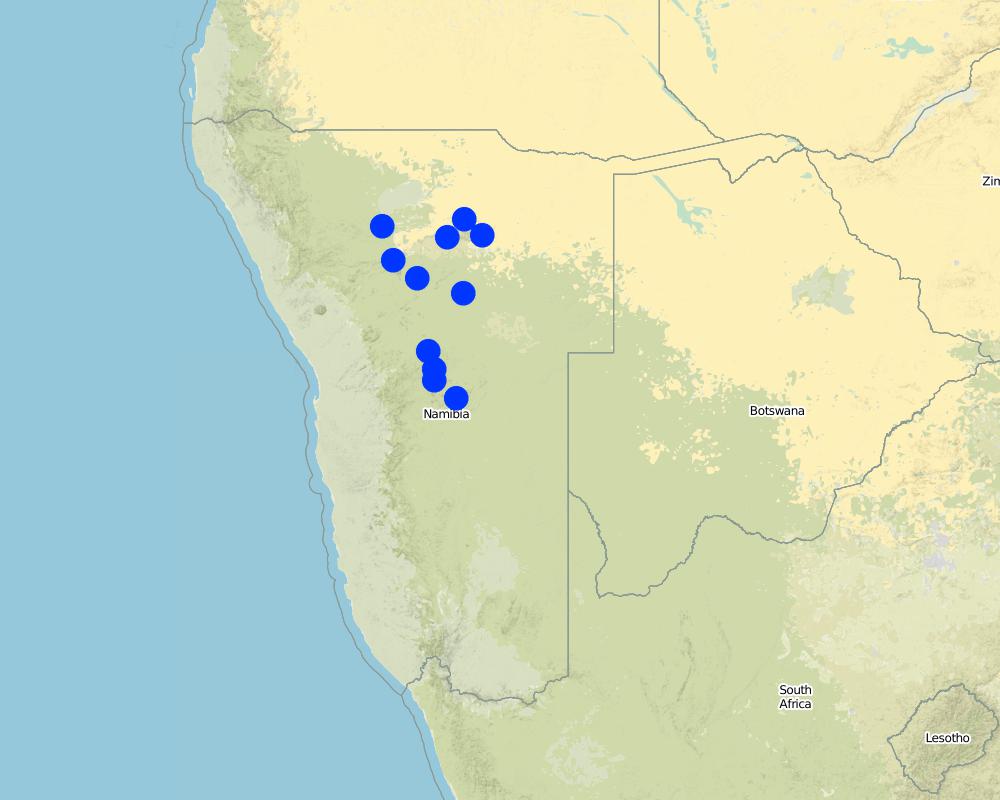
Bush control is applied across Namibia on many privately owned farms. Activities are most concentrated in the regions Khomas, Omaheke, Otjozondjupa and Oshikoto.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
1200,0
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 1,000-10,000 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Pointers on the map only indicate points (e.g. urban centres) around which activities are concentrated. It is not possible to depict each site where bush control is implemented due to the high number of individual activities and projects.
Currently bush thinning is implemented on a total of approximately 120.000 hectares (1.200 km2) of farmland per annum. These activities are not confied to certain areas, but spread across all of Namibia, typically concentrating in the most encroached areas (e.g. Otjozondjupa, Khomas, Oshikoto and Omaheke regions).
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2015
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Since the 1950s the phenomenon of bush encroachment has been recognised by farmers in Namibia and counter measures have been implemented over the decades. The technologies applied largely relied on the means and innovative capabilities of the respective land owner. Only as of 2014, through the introduciton of a national Support to De-bushing Project, are technologies systematically researched and tested in the field.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពពែ
- cattle
មតិយោបល់:
Main animal species and products: Cattle, goats, game
Namibia is characterised by large commercial cattle farms. Du to its aridity the land is largely unsuitable for crop farming, with exceptions in high-rainfall areas such as the Grootfontein, Tsumeb, Otavi triangle.
The Northern parts of Namibia are managed as communal land, where farmers have lease holds for their land. In these areas a combination of millet production and cattle herding is common.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: 284 000 in targeted area (105460km2) of bush thinning (Otjozondjupa region).
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
មតិយោបល់:
The implementation of bush thinning allows to maintain the land use (e.g. cattle ranching) and is typically applied to increase productivity in the long-term.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V4: ការជំនួស ឬការយកចេញនៃប្រភេទរុក្ខជាតិក្រៅស្រុក/ ការរាតត្បាត

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
- M5: គ្រប់គ្រង/ ការប្លាស់ប្តូរសមាសភាពពូជ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
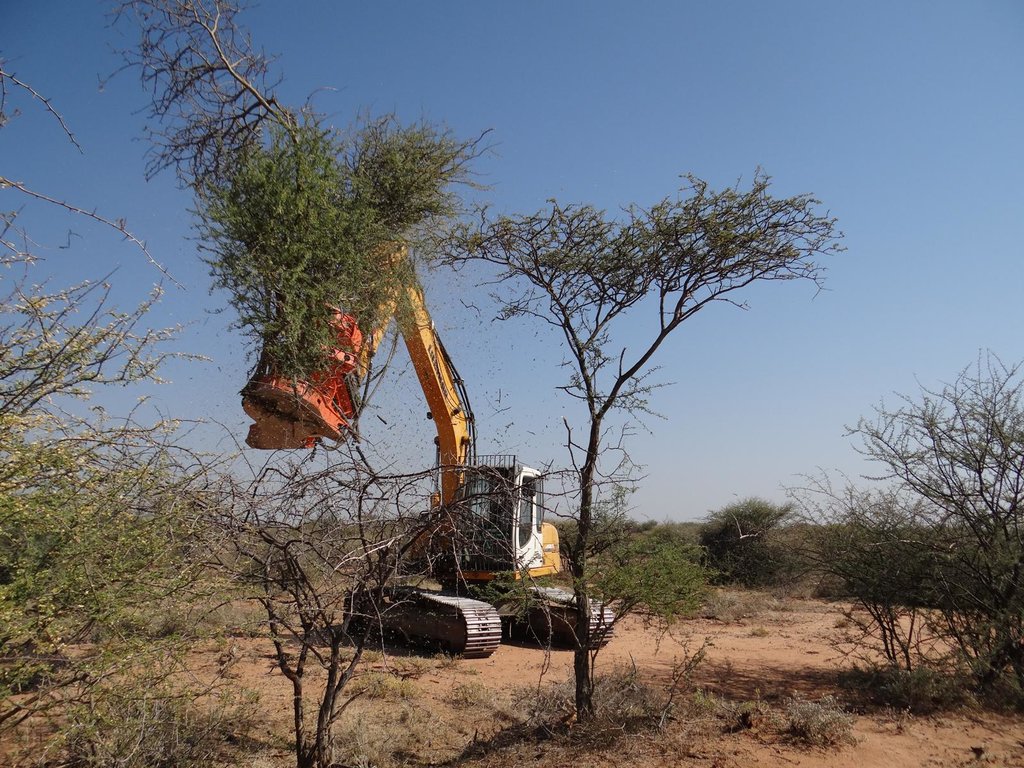
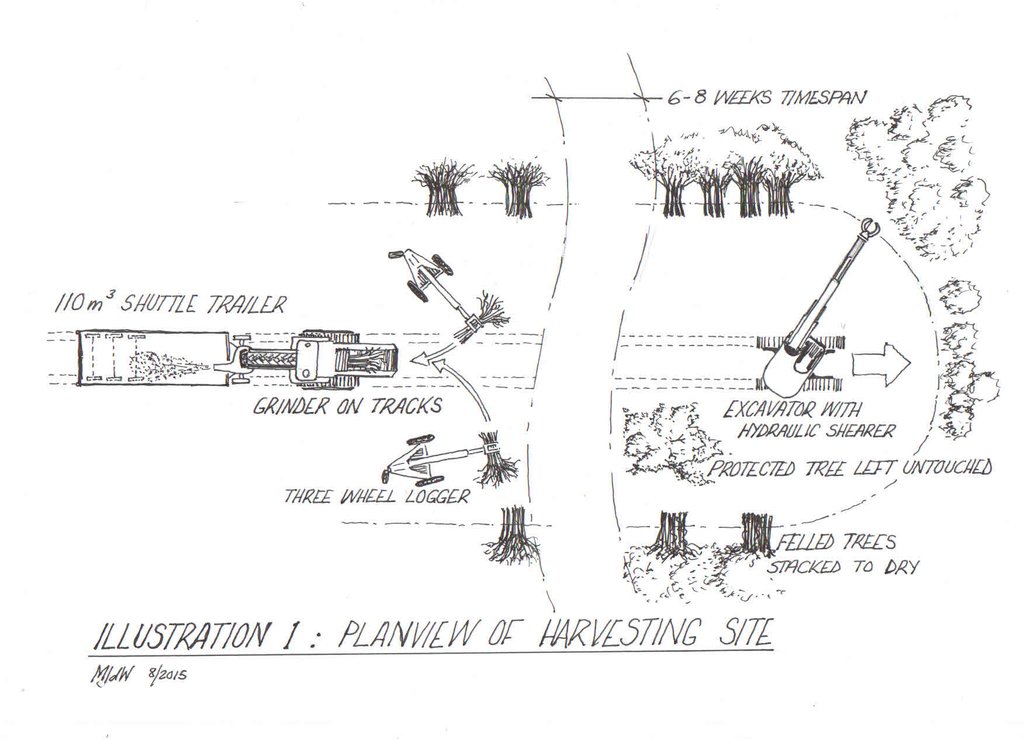
Drawing of a bush harvesting site layout. The drawing depicts fully mechanised bush harvesting and immediate processing into wood chips. This set-up is most suitable for large-scale bush thinning, e.g. for the purpose of supplying biomass in larger quantities. Such off-take includes the potential export of bush in processed form (pellets) or energetic utilisation (e.g. local biomass power plants or biomass boilers in the industry). Currently two such energy solutions exist in Namibia, one at a local brewery and one at a local cement factory.
Note that a range of bush harvesting methods exist, ranging from fully mechanised (as depicted) to manual bush harvesting (e.g. with axes). The site layout and principles are the same in all scenarios, but harvesting speed and costs differ.
The bush harvesting process:
Bushes are harvested selectively with and excavator, to which a hydraulic sheer cutter is attached. The biomass is stacked in rows and left for drying some six to eight weeks (depending on weather conditions). The biomass is then further processed with a chipper and collected with a trailer for further transport off the farm (e.g. to a biomass power plant or industrial off-taker). As a rule of thumb, one third of the standing biomass is removed, leaving two thirds standing. Harvesting starts with smaller plants and then moves to larger ones, cutting only plants with 15 centimetres of diameter or less (as per Namibian forestry regulations).
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
M.J. de Wet Pr. Eng., NRGen Advisors (Pty) LTD
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
18/09/2015
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1 hectare
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Namibia Dollar (NAD)
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,078
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
Namibia Dollar (NAD) 110
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bush harvesting/felling | Year around |
| 2. | Stacking (and drying) | Year around |
| 3. | Feeding the chipping operation | Year around |
| 4. | Transport | Year around |
មតិយោបល់:
The restorative measure includes bush harvesting/felling as well as aftercare measures. Additional activities include the processing (e.g. into chips) and transport of the woody material off the farm/land.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 1 x Mechanic | person days | 0,2 | 2000,0 | 400,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 4 x Operators | person days | 0,8 | 300,0 | 240,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 1 x Operation manager chipping | person days | 0,2 | 1000,0 | 200,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 1 x Chipping operator | person days | 2,0 | 150,0 | 300,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | 1 x 12t Excavator | pieces | 1,0 | 120,0 | 120,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | 2 x Hydraulic grab and shearing attachments | pieces | 2,0 | 60,0 | 120,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | 2 x Three wheel loggers | pieces | 2,0 | 180,0 | 360,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | 1 x Chipper | pieces | 1,0 | 840,0 | 840,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Management and administration overhead | lump sum | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | 12,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2780,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 35641,03 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Cost of bush harvesting can be calculated per hectare (e.g. land owner's perspective) or per tonne (in fuel supply agreements with off-takers). All given costs are approximations, as costs vary widely depending on the local framework conditions on a given piece of land. Typically the costs to harvest and process bush on one hectare range from 2,000 NAD to 4,000 NAD.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Aftercare | Annually |
មតិយោបល់:
When land is thinned it creates a vacuum in which weeds and woody plants (sometimes more aggressive colonisers than the original encroacher species) will quickly establish themselves. Regular aftercare needs to be applied in order to prevent the excessive re-growth of bush (and therewith new degradation of the land). Various methods are in use to manage the re-growth of bush following harvesting. These include selective application of arboricides, stem burning, and intensive browsing by goats or antelopes.
The more sustainable the bush harvesting itself has taken place, importantly not completely clearing larger areas of vegetation, the less likely is agressive re-growth of bush. In all bush thinning exercises it is important to leave larger bushes and trees untouched and to start by removing the smaller, less established bushes. In addition, not only individual larger bushes must be left standing, but also islands/patches of bushes, which fulfill important ecosystem services, e.g. habitat for animals.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
ប្រសិនបើមិនអាចបំបែកតម្លៃដើមក្នុងតារាងខាងក្រោមទេ សូមផ្តល់នូវតម្លៃប៉ាន់ស្មានសរុបក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសនោះ:
500,0
មតិយោបល់:
Commonly aftercare is applied in form of manual application of herbicides to the cut stems, in order to prevent re-growth of the bushes.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
(1) Investment in machinery (if not applied manually).
(2) Maintenance of machinery (high wear and tear due to hardness of wood and high mineral content).
(3) Remoteness of farms/land from buyers/markets.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
350,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Namibia is a semi-arid country and rainfall ranges roughly from 150-550 mm per year (rough approximation due to the vastness of the area described).
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Various
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
Typical commercial farm size is 5.000 ha. The size increases with decreasing rainfall (towards southern Namibia).
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Bush-based animal feed production has been successfully trialed and is implemented by various farmers across Namibia.
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Carrying capacity of bush controlled land increases if regular aftercare is implemented.
ការបង្កើតថាមពល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Bush-to-electricity value chain under development. Several industrial off-takers use woody biomass for boilers (heat), the national power utility currently develops a first biomass power plant.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Studies show a direct positive correlation between the extent of bush control and the availability of groundwater.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Bush based value addition, e.g. charcoal production, leads to additional income for land owners and farm workers.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Alien species are completely removed where possible (e.g. Prosopis).
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
Despite only limited research exists, long periods of drought that the country has recently faced, are credited to climate change. Drought intensifies the challenge for farmers, as already degraded rangeland has limited capacity to recover in the absence of rain. The technology of bush thinning itself has limited effect if no rain follows the removal of bushes.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Bush thinned land takes 3-5 years to fully recover its productive grass layer, thus direct economic benefits are only experienced with a delay.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
120'000 hectares are bush thinned per year in Namibia; figures on the increase
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 51-90%
មតិយោបល់:
Farmers largely implement bush control on their own initiative; increasingly value chains are being developed and dedicated service providers offer bush control.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Increasingly bush harvesting is carried out with mechanised means, aiming at large scale production for large biomass off-takers, both in the country and internationally.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Effective measure against bush encroachment |
| Costs can be balanced with additional income through the sale of the biomass/biomass based products |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Apart from the main purpose of rehabilitating rangeland, bush control has various side benefits, such as employment creation and industrialisation. |
| Bush control and biomass utilisation can contribute to energy security in the country. |
| The available range of technologies (from manual to fully mechanised) allows to develop viable concept for all types of land/land ownership scenarios. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High initial costs involved. | Development of dedicated financial products. |
| Possible negative consequences, such as more aggressive re-growth of species. | Increased knowledge dissemination, skills development and mentorship programmes. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Necessity of cross-sector collaboration, e.g. agriculture, forestry, environment, industry, energy and resulting complexity. | Introduction of effective steering body on national level. |
| Challenges to sustain operations in communal areas/on land that is not owned by individuals. | Development of concepts for community based projects and cooperation with relevant regional authorities and decision making bodies (e.g. Regional Councils, Conservancies). |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
De-bushing Advisory Service Demand Survey (2015), 361 respondents
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Various
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/08/2014
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Baseline Assessment for De-bushing Programme in Namibia (2014)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Demand Survey for the implementation of a De-bushing Advisory Service (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Value Added user-opportunities for encroacher bush (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Compendium of harvesting technologies for encroacher bush (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Assessment of biomass resource and potential yield in Namibia (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) on bush thinning and biomass utilisation (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Assesment of financial products and incentive schemes for bush harvesting and value addition (2015)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Environmental and forestry bush harvesting guidelines and generic Environmental Management Plan (2016)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Regional assessment of the economics of land degradation related to bush encroachment in Otjozondjupa, Namibia
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
GIZ Support to De-bushing Project, www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
De-bushing Advisory Service (DAS) Namibia, Resource Section
វេបសាយ:
www.dasnamibia.org/downloads
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Namibia Biomass Industry Group (N-BiG)
វេបសាយ:
www.n-big.org
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Videos
វេបសាយ:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCwCICCfwf0SdVBqg2ZcAcKA
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Namibia Charcoal Association (NCA)
វេបសាយ:
www.ncanamibia.com
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល