Reduced livestock numbers [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Christian Wirz
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1343 - ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Sahdullo
Karsang 1
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - ប្រទេសកៀហ្ស៊ីស៊ីស្ថាន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
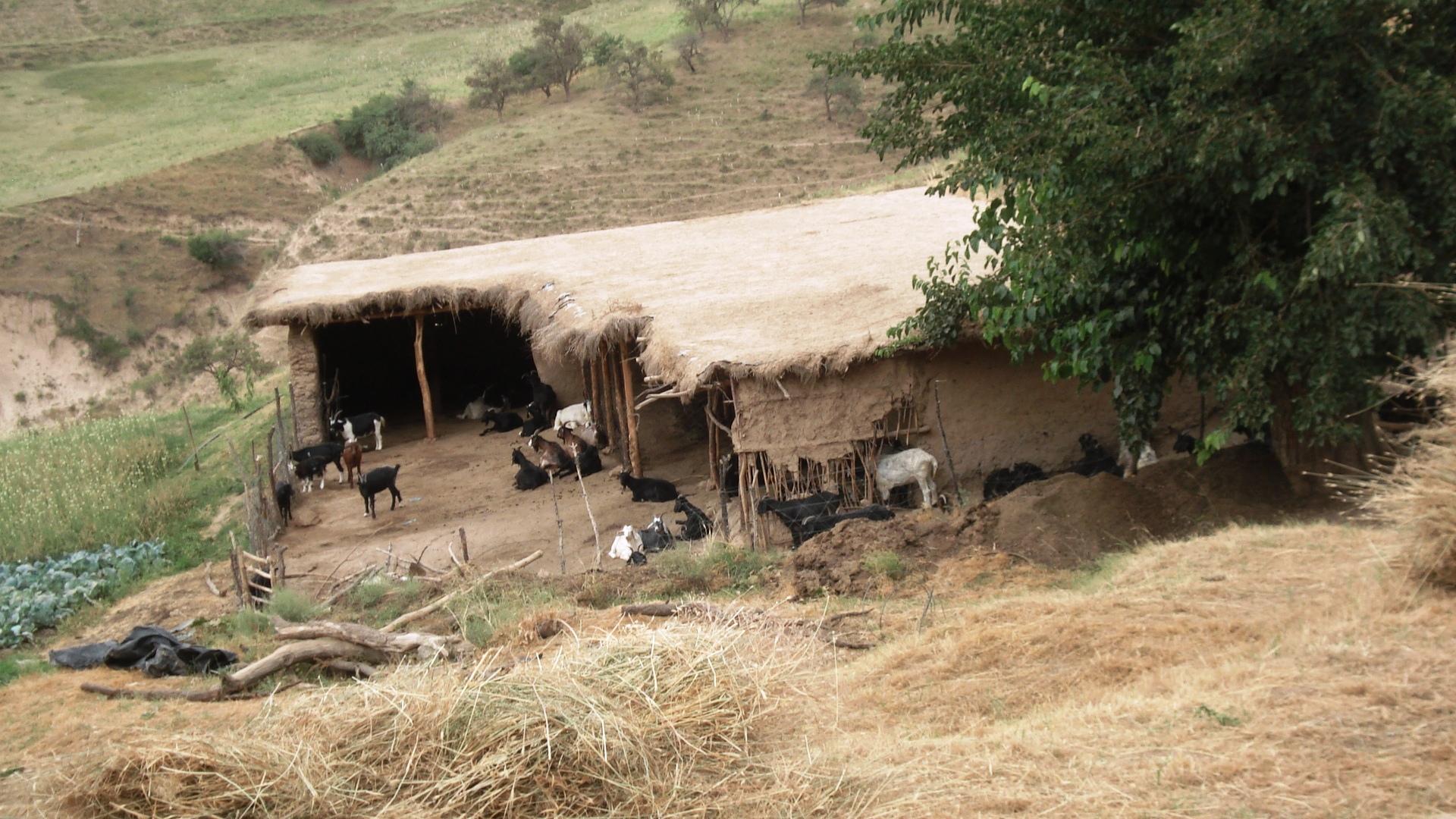
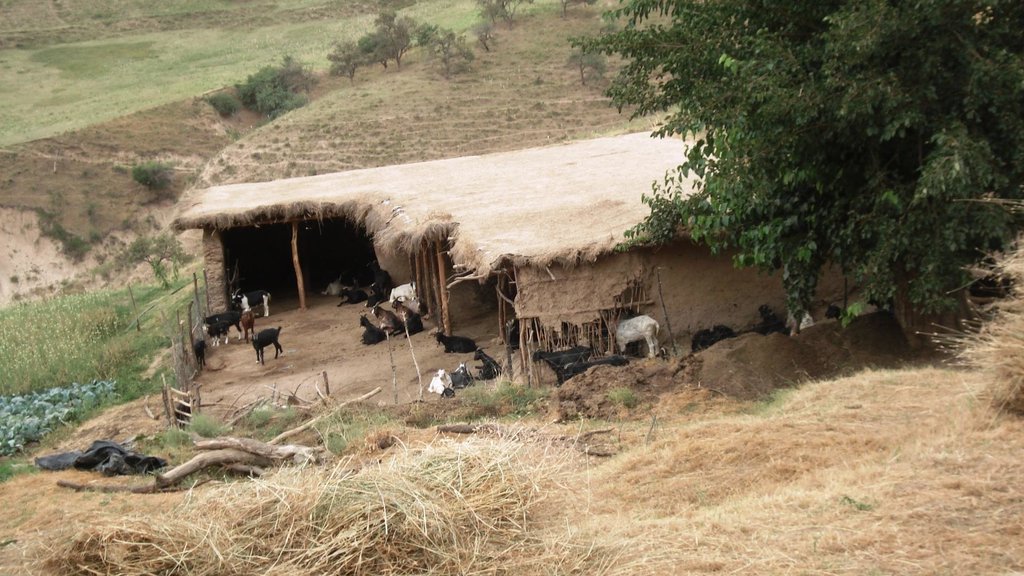
The grasslands are used as pastures by a reduced number of livestock belonging to an individual land user.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
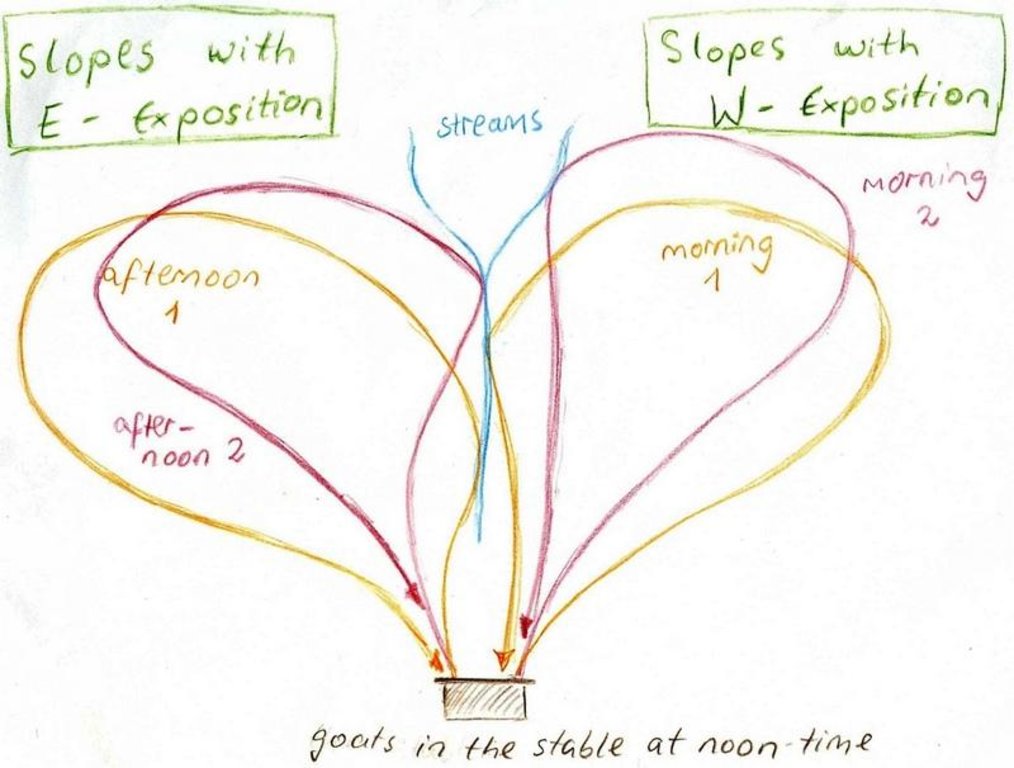
The around 50 goats are brought to the pastures early in the morning and will be brought back to their stable from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. After this, they will be accompanied to the pastures again. In the morning the west-exposed and in the afternoon the east-exposed pastures are visited. The same rotational scheme is applied over the whole year, which means that the same pastures are visited daily. The pastures are exclusively used by the land user fror more than the half of the year (from autumn to spring). In summer the pastures are also used by the village herd of the nearby village (Karsang). Herding is mostly the task of the land user's sons but sometimes he will accompany the animals by himself. Cows are let out on the pastures in the morning and come back in the evening by themselves.
Purpose of the Technology: The reason for west-facing grazing in the morning and east-facing in the evening is that grass is moist at these times of day. This is also why at noontime animals are not on the pastures. The animals are led slowly by the herder as to not tire them, to make them fatter and to avoid damages on vegetation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: No special pasture maintenance activities are undertaken.
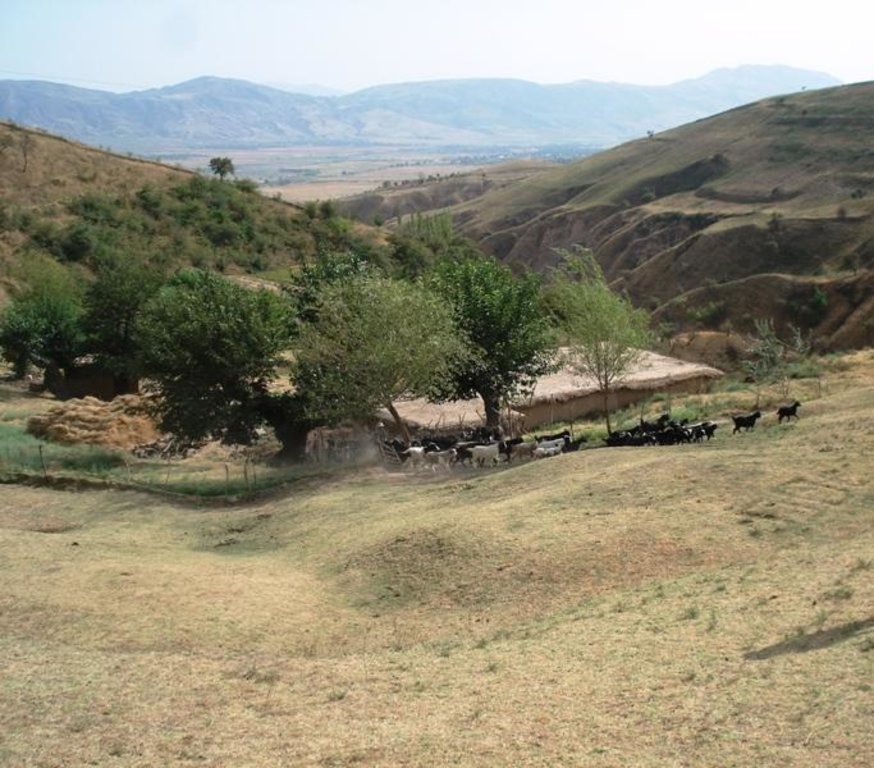
Natural / human environment: The area is around one hour away from the village which actually controls the pastures (communal pastures). In addition snow lies longer in spring than further down. This means that the village herd only comes here from late spring to late summer, which decreases the pressure on the pastures. Together with the situation in a small depression that protects from high radiation in summer this contributes to the generally better pasture quality (greener, more grasses) compared with the village pastures in proximity to the villages. An important factor contributing to the generally good conservation state are the reduced livestock numbers. They are only reduced because the land user is close to these more distant pastures and the village is quite far away.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Region of Republican Subordination
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Faizabad
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 0.1-1 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.5 km2.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The land user has rented land for the establishment of a self-sufficient agropastoral system after independence (early 1990ies). A part of the area was used as cropland when there was still a village (in the middle of the 20th century) whereas other parts of the land were also used as pastures.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពពែ
- cows
ប្រភេទពូជ:
សត្វពពែ
ចំនួន:
50
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Especially in the places where animals pass regularly and where they stay for longer times physical degradation of soils (compaction, crusting) together with the degradation of vegetation (cover and biomass) are major problems. In addition, low fertility is also a problem for vegetation growth.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water erosion problems associated with wood chopping. And trees wood be very important for climate regulation.
Ranching: Goats, cows
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pi: ការគ្របផ្ទៃដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Big herds passing daily), other human induced causes (specify) (Inappropriate soils used for grazing), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional (Incapacity of government to implement soil conservation.)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Daily rotation on pastures of the village Karsang.
Location: Above Naobad. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user developed his own rotational scheme.)
Technical knowledge required for herders (sons and grandsons of land user): low (They just need to apply the scheme.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Reduced livestock numbers
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Somoni
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
3.42
4.4 Establishment activities
Activity Type of measure Timing
1. Buying livestock Management Reduced livestock numbers
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Specify input Unit Quantity Costs per Unit Total costs per input % of costs borne by land users
Other Buying livestock Goats 50.0 87.7 4385.0 100.0
Total costs for establishment of the Technology 4385.0
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
Activity Type of measure Timing/ frequency
1. Herding Management Daily
2. Giving salt to livestock Management Twice per week
3. Fodder for livestock Management In winter
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Specify input Unit Quantity Costs per Unit Total costs per input % of costs borne by land users
Labour Herding daily days 365.0
Other Salt for animals for one year 1.0 12.0 12.0
Other Fooder for livestock winter 1.0
Total costs for maintenance of the Technology 12.0
Comments:
The only effective costs mentioned by the land user is salt for animals. Other inputs - be it labour or winter forage - does not have to be paid, respectively bought.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour input is decisive: As long as work is done by family members costs are restricted on alimentation. If external labour is hired, wages have to be added.
5. Natural and human environment
6. Impacts and concluding statements
Links and modules
Expand all
Links
Modules
Primary recommended database
UNCCD
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Somoni
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3,42
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying livestock | Reduced livestock numbers |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ផ្សេងៗ | Buying livestock | Goats | 50,0 | 87,7 | 4385,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 4385,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1282,16 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herding | Daily |
| 2. | Giving salt to livestock | Twice per week |
| 3. | Fodder for livestock | In winter |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Herding daily | days | 365,0 | |||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Salt for animals | for one year | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Fooder for livestock | winter | 1,0 | |||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 12,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 3,51 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The only effective costs mentioned by the land user is salt for animals. Other inputs - be it labour or winter forage - does not have to be paid, respectively bought.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Labour input is decisive: As long as work is done by family members costs are restricted on alimentation. If external labour is hired, wages have to be added.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility: Mainly medium, but also low
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: Mostly no groundwater, since very hilly.
Water quality (untreated): Good source water, since no diarrhae after drinking it.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Many medical plants
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are implied in housework, whereas men are working as herders, because of traditions.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: The land user only depends on the rented land, cultivated together with his two sons and their families.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
The household has much more grazing land than average village households.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់:
Pastures are in theory used by village communities, but enforcement of rotational grazing in remote ares is difficult. These pastures are therefore something between communal and open access pastures. The water is used by the land user without any restrictions.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
His animals yield higher prices on the market than average livestock.
ភាពខុសគ្នាផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The productive success of the land user lets him appear richer than the rest of the village.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Having a big herd on a big pasture area is a guarantee for better self-sufficiency.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially in the establishment phase there was jealousy about the success, especially in fruit-production.
Livelihood and human well-being
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially biomass is reduced by daily grazing.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially the proportion of grasses is higher compared with other village pastures
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
On the long term benefits of animal husbandry might be slightly reduced due to damages on vegetation (and soils) by the own and by the animals of the village herd.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The only land user with this form of management known is the one interviewsd
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: This form of management combines an exceptional personal spirit of innovation and financial means to lease land as to establish a self-sufficient system in the hills. It is also necessary to have a truck and / or car to transport goods to the market and to stay in touch with the rest of the family in the village, since it is too small to offer space to all the household members.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Self-sufficiency is the main success for him. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It requires high labour inputs and motivation, which for the land user are necessary to have success in the post-USSR setting. |
| The animals yield a higher price because they are fatter than the other animals. |
| The geographic location is clearly an advantage, because the land user is far away from the negative impact of village herds. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
At the same time quite positive for soil and water conservation and productive in terms of meat and sold livestock. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land user could rent (parts of the) pastures the interest of planting trees as a measure of rehabilitation would increase. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Trees cannot recover because of constant grazing. | Only if the land user is sure that investments will profit him, that is if land tenure is clarified, will he invest into active conservation measures. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Especially at the crossing-points of the land user's herd with the village herd degradation phenomena (trampling paths) are visible. | By an agreement between the village (land commitee) and the land user the land use could be reglemented clearer. |
| This form of land use is difficult to maintain for young people who want to participate in social life. And it is not sustainable because it does not permit allvillagers to practice such forms of herding that require much land. | The land user should be able to rent a part of the pastures (smaller than the actually grazed 50 ha) where he would be need to conserve soils and vegetation (for instance. by tree-planting or more sophisticated rotation. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល