Cactus Fruit Plantation in Arid Dry Lands [ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Joren Verbist
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5847 - ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
Research Team Leader of Rangeland Ecology and Forages:
Louhaichi Mounir
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី
Research Associate Coordinator of Forage Systems:
Hassan Sawsan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - ប្រទេសលីបង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
This technology is based on the natural advantages and the multi-purpose usage of spineless cactus pear (Opuntia fiscus-indica), to cultivate marginal lands in Jordan, generating environmental and socio-economic benefits.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
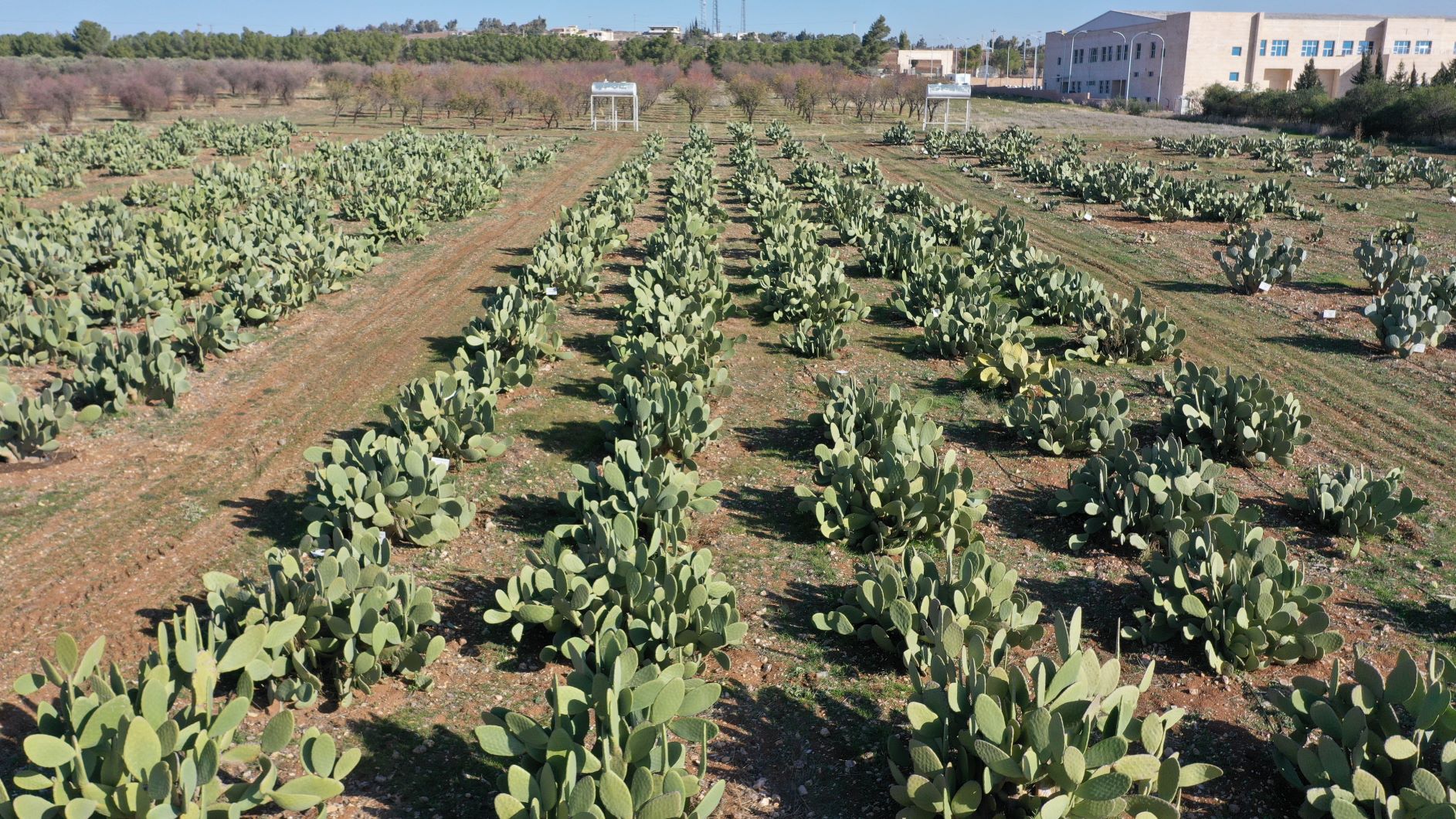
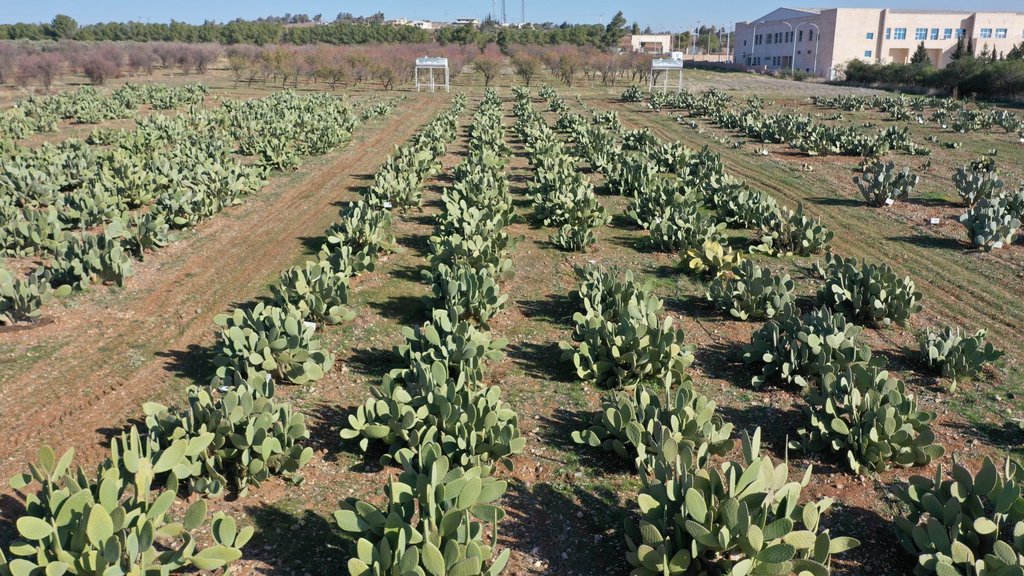
In the arid parts of Jordan with limited rainfall, little irrigation, high water evaporation, poor soil quality and unsustainable land management result in land degradation (erosion and salinization) and productivity loss. Therefore, the International Center Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) and National Agricultural Research Centre of Jordan (NARC) organized field days (started in 2014) to disseminate knowledge regarding the cultivation of the cactus pear, Opuntia ficus-indica, cactus crop. Cacti can cope with high temperatures and grow well in (semi)-arid areas with 250-600mm annual rainfall or where irrigation is available. Additionally, the plant is very resilient as it can withstand a long dry season due to its high water-content and water-use -efficiency, which are a result of its morphology (waxy cuticle, no actual leaves) and the Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). In CAM plant, stomata in the leaves remain shut during the day to reduce evapotranspiration, but open at night to collect and fix carbon dioxide (CO2). In general, cacti have multiple products that benefit local livelihoods, these are for example stable production of fodder for livestock and fruits for human consumption. Also, cactus can grow and produce requiring few inputs such as fertilizers, therefore marginal lands are well suited for cactus cultivation.
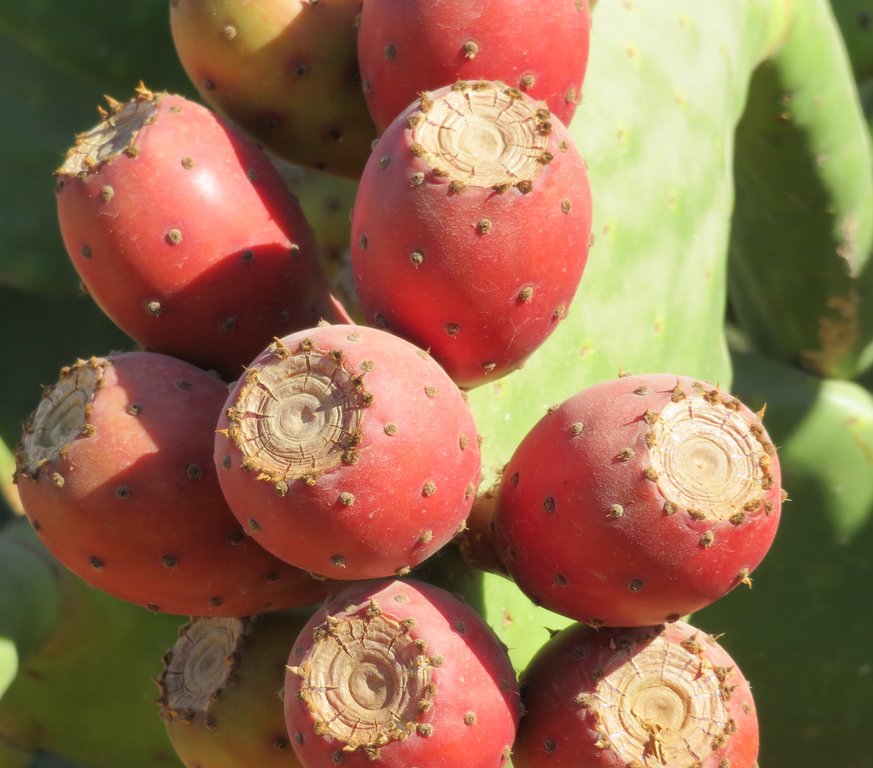
The market for cactus fruits is very promising in Jordan. Nowadays, there is high demand for cactus fruits as people grow fond of the fruits but also for medicinal uses. This documentation is focused on a farm covering roughly 10 hectares, where cactus was planted due to its socio-economic and environmental advantages i.e. the high prices for cactus fruits and the ability of cactus to grow in marginal lands with little input and cover the soil hence preventing soil erosion. However, the farm is not located ideally for cactus cultivation. Therefore, the farm is currently intensively managed in terms of fertilizer application and the irrigation. The previous land use was poor cultivation of barley to feed (grazing) sheep and goats. This led to little soil cover resulting in land degradation in the form of erosion. The farmer paid for the establishment of the cactus-plantation. The cacti are spaced by 4 meters between plants and 3 meters between rows. This spacing is specific for fruit production, in case of fodder production a higher crop density is recommended. The cacti are planted on the contours in pits (40 centimetres depth and diameter) to ensure rain-water collection and efficient fertilizer application as the farm is situated on a 15% slope. The cacti reduce erosion as the roots hold the soil together. Field preparation for the establishment of the cactus field includes: (1) soil scrapping; (2) deep soil ploughing; (3) surface soil ploughing; and (4) pit digging. No fertilizer was applied in the establishment stage. Recurrent activities and costs are weeding, applying fertilizer and organic manure, maintaining the pits and harvesting. 200 kilograms per hectare of inorganic fertilizer (NPK) is applied between March and May. A total of 4 tons per hectare of organic manure is applied in September-November. These activities are non-mechanized, and therefore labour intensive.
The farm receives less than 200mm of annual rainfall and a public dam for irrigation is available. Therefore, the farmer invests in three water tanks to store water brought from the dam using his own truck, and in a drip irrigation system for high irrigation efficiency. The farm is irrigated by 360 cubic meter per month, divided in three events. The costs per cubic meter is 0.95 Jordanian Dinar (JOD) (including transportation costs). Before the realization of the drip irrigation system, the cacti were watered by hand (19991-2015). During the initial three years, cacti produce no fruits making the short-term return on investment rather negative. Currently, the cactus-plantation produces 32.5 ton/ha, equivalent to 65 kg /plant. The average net income per hectare varies between 1650 JOD to 2750 JOD. This makes the farmer relatively medium- wealthy with respect to the area. Most costs are induced by labour as the farmer uses manual weeding, harvesting and fertilizer application.
Even though the cultivation of cacti for its fruits on marginal lands has many benefits like the reduction in erosion, stable production, high output/input efficiency and good prices. There are some weaknesses, for example the relative young market of cactus products in Jordan compared to Tunisia. The Tunisian market for cactus products has a longer history, a high demand for other cactus-products like oil and juice and a better infrastructure (e.g. processing units) exist. These create more consistent prices for farmers, so less price drops during harvesting periods. Another weak point is the fact that cacti are cultivated in mono-culture. This significantly increases the risk of new pests and potential damage of the cultivated crop.
To conclude, this documentation shows that even though the selected farm does not represent an ideal site for cactus pear cultivation, the implementation of cacti is socio-economically and environmentally appropriate to cultivate dry marginal lands as cacti uses water and nutrients highly efficient while reducing land degradation. Therefore, the out-scaling of cacti is very valuable and a practical option to fight land degradation and enhance smallholder’s income.
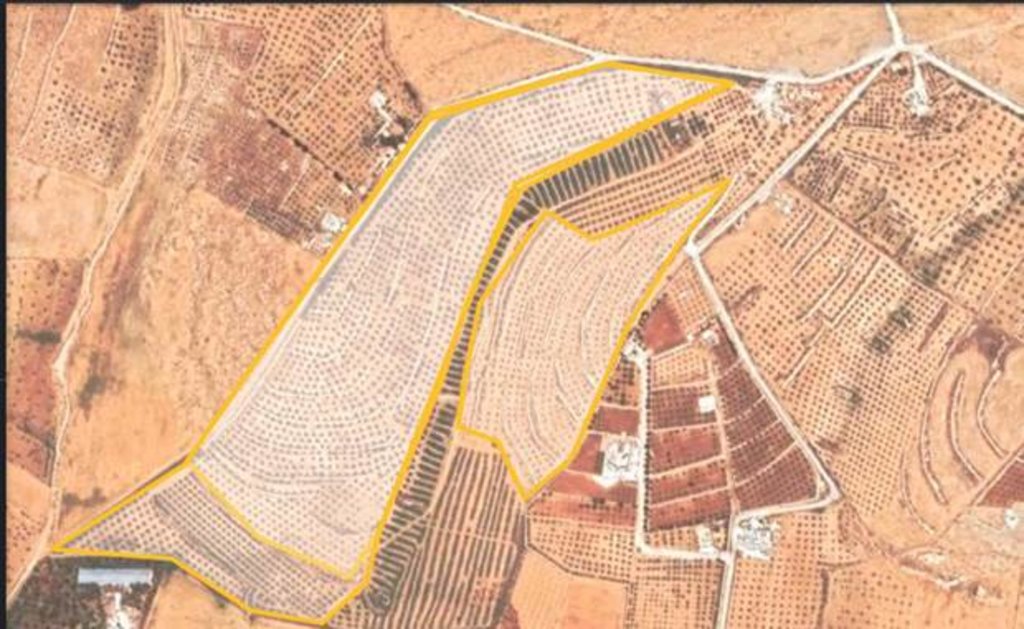
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
0,09
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2014
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- cactus, cactus-like (e.g. opuntia)
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
ទេ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- Agro-pastoralism ( រួមបញ្ចូលទាំងដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
ទេ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពពែ
- សត្វចៀម
តើជាការអនុវត្តការគ្រប់គ្រងដែលរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- សាច់
- ទឹកដោះគោ
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
មតិយោបល់:
360m^3 of water applied through drip irrigation. The annual precipitation is less than 200mm
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S7: ការប្រមូលទឹកស្តុកទុក/ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក/ សម្ភារៈស្រោចស្រព

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cs: សារធាតុប្រៃ/អាល់កាឡាំង

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
The rows are placed 3 meters apart (A), and are located on the contour for rainwater collection as the farm field has a slope of 15% (E). The interspace is 4 meters (D). The cacti are planted in pits that have a diameter of roughly 40 centimeters (C) and a depth of 40 centimeters (B).
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Meike Kleinlugtenbeld & Joren Verbist
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
20/12/2020
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
9.1 hectare
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
JOD
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,71
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
20
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil scrapping | Prior to planting |
| 2. | Deep soil ploughing | Prior to planting |
| 3. | Surface soil ploughing | Prior to planting |
| 4. | Pit digging | Prior to planting |
| 5. | Planting cacti | Last third of the dry season (August - October) |
| 6. | Establishment of drip irrigation | If feasible (This case 2015) |
មតិយោបល់:
Drip irrigation can be establishment when feasible (e.g. funds available). It would greatly enhance cactus-production but cacti can survive and produce without it.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Pit Digging & Planting | Person Hour | 47,0 | 100,0 | 4700,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 100,0 | |||||
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 100,0 | |||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Soil Scrapping (Jackhammer) | Machine-Hour | 35,0 | 200,0 | 7000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Deep Soil Ploughing (Tractor) | Machine-Hour | 9,0 | 250,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Surface Soil Ploughing | Machine-Hour | 9,0 | 250,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Cactus Pads | Pad | 5000,0 | 0,1 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Drip Irrigation (including labour for installation: 14 person days) | Whole System | 1,0 | 13700,0 | 13700,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Water Tanks (including labour for construction: 10 person days) | Tank | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 31900,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 44929,58 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The cacti are planted in pits. The digging of pits and planting of the cactus pads into the pits is done simultaneously, hence this is grouped in terms of labour. For soil preparation (scrapping and ploughing), the costs of labour are included in the machine costs as this was a hired service. The installation of the irrigation system and the construction of the tanks was each offered as a package and hence include the costs of labour.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | NPK Fertilizer (1x) | March - May |
| 2. | NPK Fertilizer (1x) | September - November |
| 3. | NPK Fertilizer (1x) | December - February |
| 4. | Organic Manure Application | September - November |
| 5. | Manual Weeding (2x) | March - May |
| 6. | Maintenance of planting pits | April |
| 7. | Harvesting | August - September |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | NPK Fertilizer Application | Person-Day | 9,0 | 20,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Organic Manure Application | Person-Day | 7,0 | 20,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Total Weeding | Person-Day | 200,0 | 15,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Harvesting / Fruit Grabbing | Person-Day | 280,0 | 20,0 | 5600,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Irrigation Management | Person Hour | 252,0 | 100,0 | ||
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | NPK Fertilizer | Ton | 2,0 | 1000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Organic Manure | Ton | 40,0 | 30,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Pit Maintenance | Per Pit | 4550,0 | 0,25 | 1137,5 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Water for Irrigation (360m3 per month) | Kubic Metre | 4320,0 | 0,95 | 4104,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 17361,5 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 24452,82 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Irrigation Management consists of filling the tanks and using the drip irrigation.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
On the farm most work (e.g. weeding) is done manually. Therefore, the cost of labour contributes significantly to the total cost.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
200,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
- ស្ងួត
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទាំងទឹកក្រោមដី និងលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ក្រុម
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Most government land is open access.
មតិយោបល់:
The water comes from a public dam.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពដំណាំ
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះទឹកកកតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះព្រិលតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រលកកម្តៅ | ល្អណាស់ |
| រលកត្រជាក់ | មិនល្អ |
| ស្ថានភាពខ្យល់ខ្លាំង | មិនល្អ |
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អណាស់ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
Hail storms and snow storms may occur, but very rarely. An example of an epidemic disease is black spot or rots.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
The Net Income per hectare varies between 1650 and 2750 JOD.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
200 ha
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
All farmers who planted cactus started after requiring knowledge about the good prices for cactus fruits and the natural advantages of the cacti. So, this specific technology (Irrigated Cactus plantation) is not necessarily adopted by many farmers. But the use of cacti as a resilient, efficient and profitable crops is however adopted among many other farmers.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
The market demands increase for cactus pears. This results in different crop-spacing because cactus for pear production requires wider spacing, while cactus for fodder production can be planted more dense. Hence, changing market demands for the different products of cactus require different agronomic practices.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The cacti are highly productive with minimum inputs. |
| It does not require much water, which is important as irrigation water availability is a bottleneck for the farmer as well as for most areas in Jordan. |
| The cacti are even productive in poor soil and by growing cacti on these soils, it also reduces erosion. |
| The reduced risk of drought deteriorated yields is important as climate change leads to more extreme weather event, such as droughts. This will only increase in the future. Therefore the cactus's ability to cope with climate change (resilience to climate fluctuations) is a great advantage and increasingly important. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Due to the suitability of cacti to be cultivated in marginal lands, the soil is partly covered permanently by vegetation in these areas which protects these degraded lands. Therefore, cacti cultivation could offer incentive to prevent land degradation. |
| The technology offers increased resilience of the environment and its involved livelihoods. This is because cacti are more resilient to climate change induced effects such as increased droughts and increasing (summer) temperatures, as result of their high-water content and efficiency. Therefore, this technology is better suited for the future. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The significant cost related to labour. | According to the farmer there were no alternatives. |
| Marketing can be considered a weakness as during harvest, the supply of cactus fruits was high and thus the selling-prices were low. | By investing in manufacturing/ processing the cacti and stably provide the market with other cactus-products, such as the Tunisian market. |
| The increased risk of new pests. | More awareness is required so the new pests can be identified, allowing proper and timely action. |
| The absence of agro-industrial processing units. Currently, the market demand is mostly related to the cactus fruits. However, cacti offer more such as seeds for oil extraction (such as the Tunisian cactus value chain) . | Investments to enhance cactus-value chain as is done in Tunisia. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The possible knowledge gap for farmers to switch from their conventional/traditional agricultural practices to a more innovative one could be a bottleneck for out-scaling the technology. | This bottleneck can be overcome, by developing social capital such as (e.g.) institutions or farmers networks to disseminate knowledge. A good example is the field days for farmers organized by NARC and ICARDA. |
| The risks of pests and diseases is a weakness of the cacti as these plants are vulnerable to this. Also, due to the density and mono-cropping of the cacti, the pest/ disease may spread easily and rapidly over the field. Eventually, risking the production of the cacti, thus possibly reducing the income of local farmers. | A solution may be found in changing the agricultural activities. An example of such a possible solution is the introduction of intercropping, this could increase bio-diversity and reduce the potential loss of income in case of a pest-outbreak. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
06/12/2020
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Fethi Ghouhis, Mounir Louhaichi, Ali Nefzaoui. (12/8/2019). Cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) utilization for rehabilitating rangelands in arid regions of Tunisia. Acta Horticulturae, 1247, pp. 95-102.
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10394
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Mounir Louhaichi, Sawsan Hassan, Giorgia Liguori. (30/12/2019). Manual: Cactus Pear Agronomic Practices.
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10558
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
HO de Waal, Mounir Louhaichi, Makiko Taguchi, Herman Fouché, Maryna de Wit. (25/1/2015). Development of a cactus pear agro-industry for the sub-Sahara Africa Region. Bloemfontein, South Africa: HO de Waal (Curator).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/7109
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Mounir Louhaichi, Sawsan Hassan. (7/10/2018). Managing rangelands: promoting sustainable shrub species: Opuntia ficus-indica (L. ) Mill: a sustainable fodder plant for the dry areas. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9048
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Mourad Rekik, Mounir Louhaichi. (9/3/2014). Cactusnet: Promoting the social and ecological benefits of cactus production: Enhancing sheep reproduction through cactus-based feed diets. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8523
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Hichem Ben Salem, Mounir Louhaichi. (30/11/2014). Cactusnet: Promoting the social and ecological benefits of cactus production: Promoting Cactus as an alternative and sustainable livestock feed. Beiurt, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/5454
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Ali Nefzaoui, Mounir Louhaichi, Hichem Ben Salem. (30/1/2014). Cactus as a Tool to Mitigate Drought and to Combat Desertification. Journal of Arid Land Studies, 24(1), pp. 121-124.
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/7319
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Mounir Louhaichi (Producer), Sawsan Hassan (Director). (17/1/2021). Best Agronomic Practices for establishing cactus Orchard. Jordan: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) (Executive Producer).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12374
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល