Sustainable traditional native bee (Melipona favosa) keeping [ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Beatriz Ramirez
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Luisa F. Vega
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Hanspeter Liniger
Cría de abeja mancita
technologies_5797 - ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Abril Héctor
Finca La Reforma
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Abril Héctor Frugo
Finca La Corocora
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Abril Damaris
Finca La Esmeralda
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Abril Boncieth
Finca Arbolitos
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Abril Héctor Daniel
Finca La Berraquera
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Onsite and Offsite Benefits of SLMឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Centro de Estudios Ambientales de la Orinoquia- Asociación de Becarios de Casanare (ABC) - ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Native stingless bee keeping (Melipona favosa) protects bees and plants found in forest and savannah ecosystems to produce honey. In contrast to current destructive wild bee honey harvesting, members of the Abril family keep the traditional practice of capturing/rescuing wild nests, and adapt them so that honey can be extracted from the same nest for many years (up to 30 y) without killing the bees.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
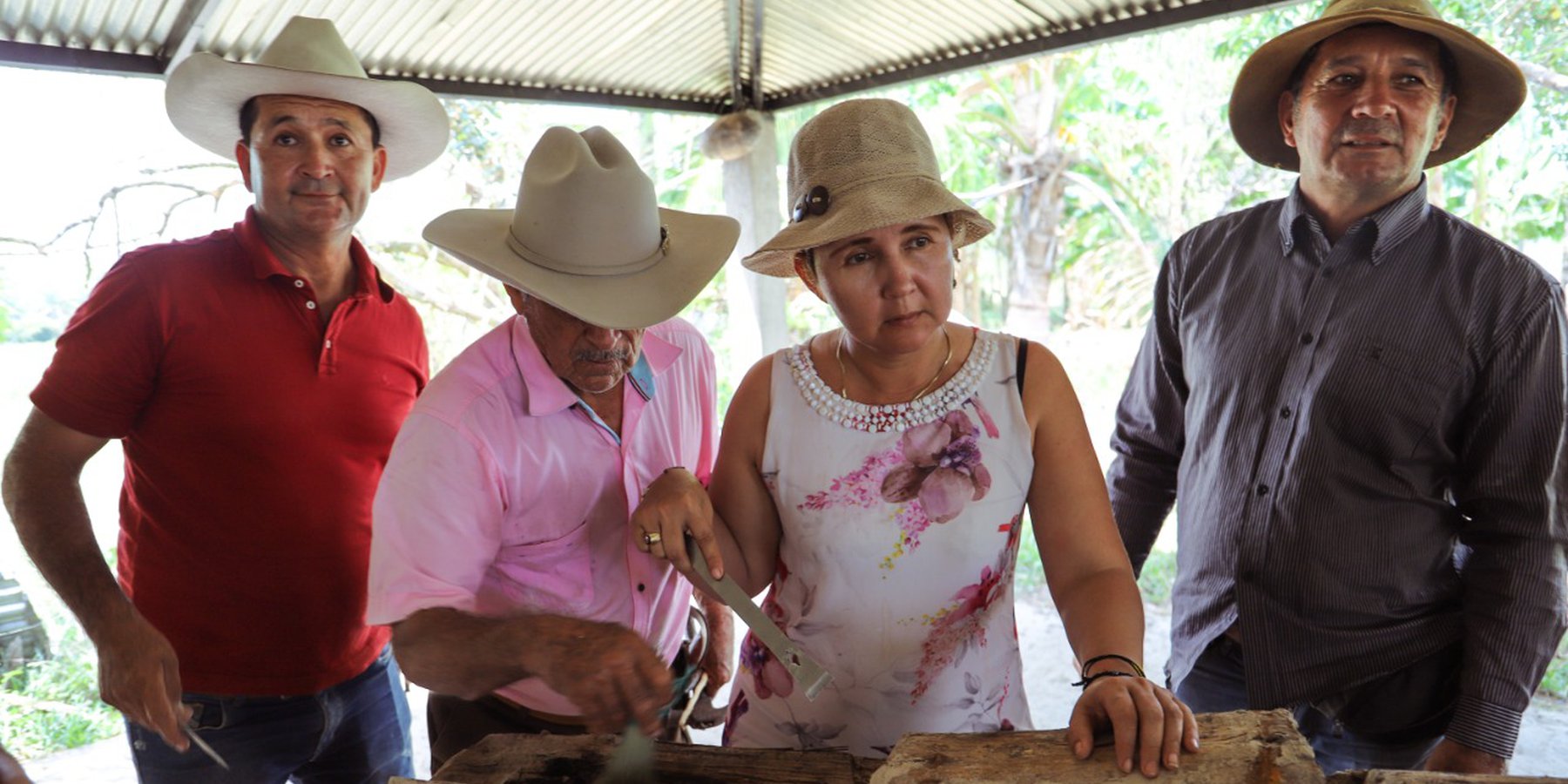
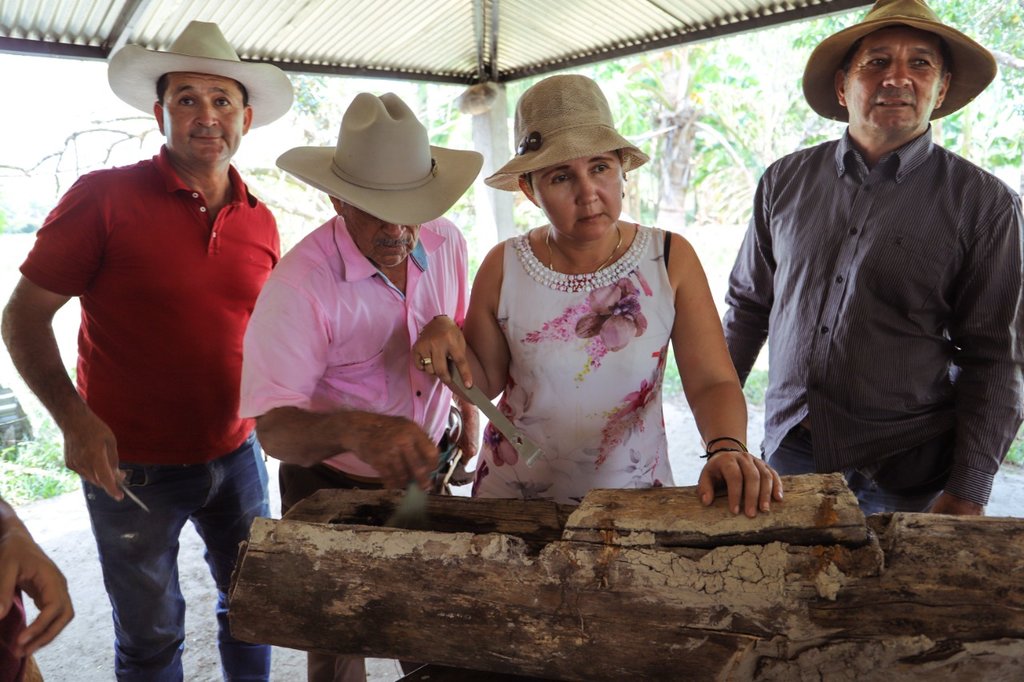
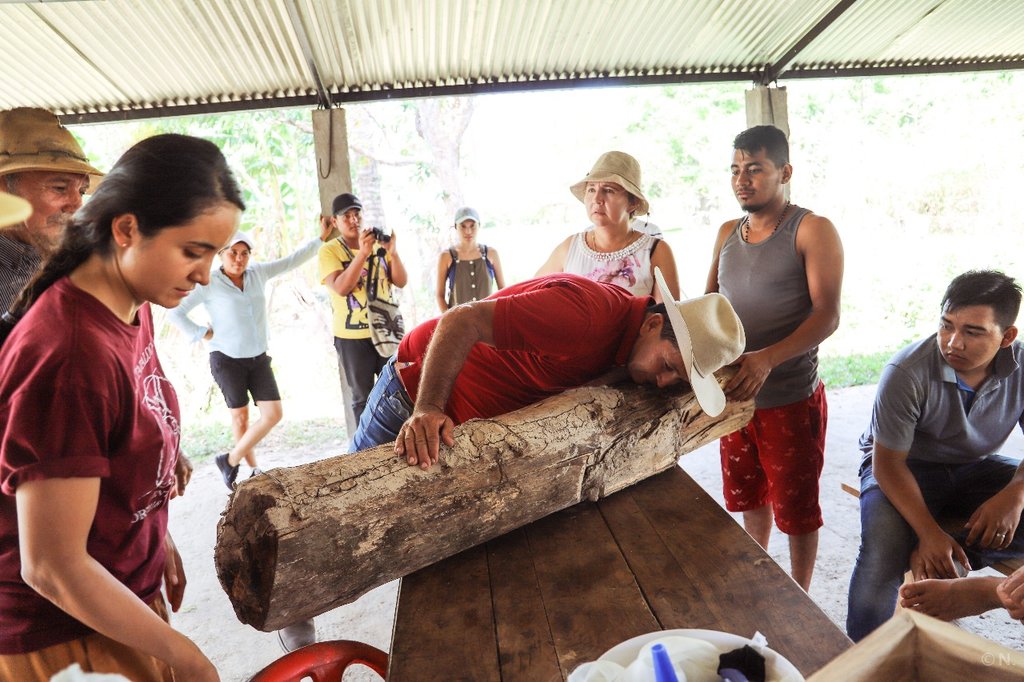
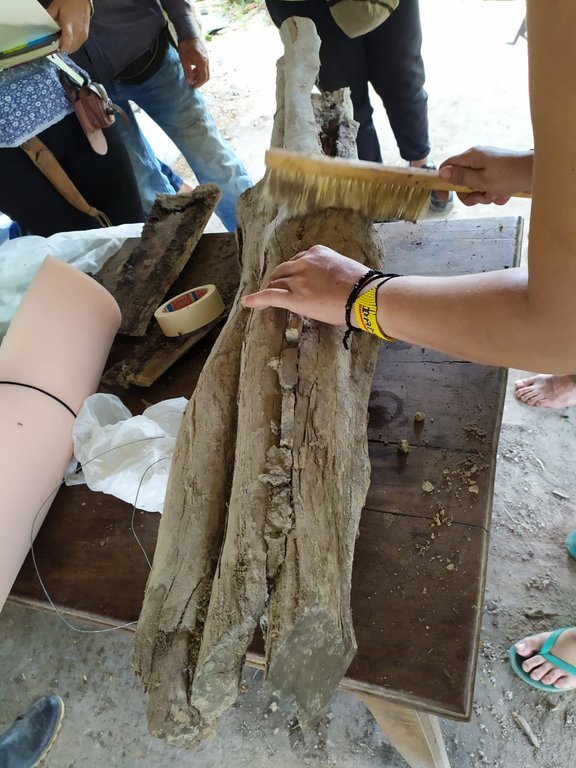
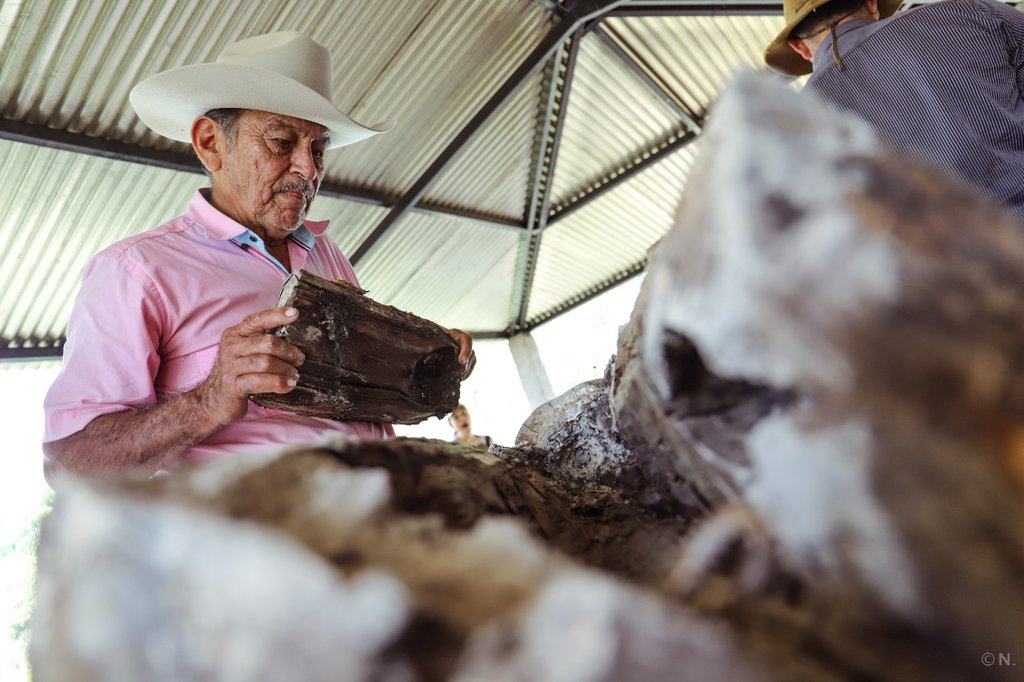
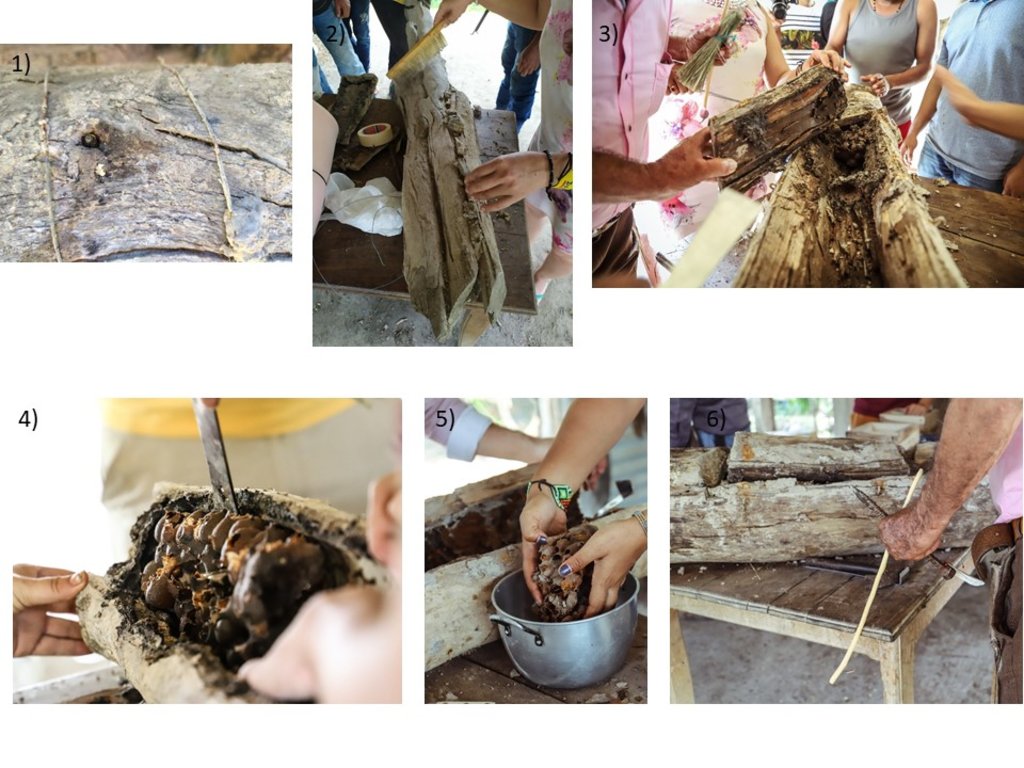
Native bee honey production in the floodable savannahs of the eastern Colombian Llanos (Orinoco River Basin), relies on stingless bees of the species Melipona favosa. These bees nest inside tree trunks. The main characteristics of the native bee keeping, as currently performed by three generations of the Abril Family, is that it is sustainable, promotes de conservation of native ecosystems, and as far as we know, constitutes the only sustainable and profitable direct use of local biodiversity in the floodable savannahs of the eastern Llanos in Colombia. Its sustainability is due to the adaptations and management of the nests, so that honey can be extracted without damaging the bees. On one hand, they know how to retrieve wild nests, either by rescuing them from rotten trees or the ground, or by cutting the branch with the nest, and then keeping its natural position at all times. Once at their houses, they will study the outside of the nest and listen to the bees inside the nest, with this information they will cut out a part of the tree trunk to create a window. Once opened, they verify the location of the honey and pollen pots and the broods. Then, they will reattach the cut part on to the trunk by using metal wire and sealing the edges with mud. The nest will be hanged with wire in the position it was originally found. Once on site they will check every day for the presence of the sentinel bee and bee activity. Furthermore, they only extract honey during the end of the dry season when bees have enough food reserves. For the extraction, they will reopen the previously cut window, and extract the honey and pollen pots, making sure enough are left behind so that bees can have access to food as well. The mean honey production from each nest is around the 750 ml- 1000 ml. Honey is kept for their own use and sold to some people for a fairly high price (30 dollars per 750 ml). The honey is mainly consumed as a medicinal product, and its low quantity makes it highly sought after. If someone requests it for sight issues, Héctor will extract the honey with a syringe so that it is as clear as possible.
The native bee keeping contributes to protect native bees, as the management of nests can keep them functional for up to 30 years. The Abril family members are well aware of the dependency between honey production and presence of native plants from where bees forage for nectar and pollen. Therefore, they avoid forest clearing and selectively keep shrubs in the grasslands to guarantee food supply for their bees. Also, they plant fruit trees such as guayaba (Psidium guajava) and arazá (Eugenia stipitata), that benefit the bees, which at the same time benefit pollination. Fruit production is mainly used for home use and very seldom they are sold. They also witness the negative impacts that agrochemical airborne dispersion from rice production in the neighbouring farms, have on wild bee populations. So far, their main concern is that they do not know how to multiply the nests.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
They are harvesting the honey from the pots throught the window, without affecting the brooding area. https://youtu.be/ZS_TbwV3fnw
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/01/2020
ទីតាំង:
Finca La Reforma, Vereda Los chochos, Municipality: Trinidad, Department: Casanare, Colombia
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Mildred Sossa
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Casanare
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Municipality: Trinidad, Vereda: Los Chochos
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
All farms are neighbors and they all belong to the Abril family members (Father, two sons and a daughter)
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Héctor Abril, has been working with this traditional systems since more than 50 years ago. The traditional system consists in creating a window implied o extract honey without damaging the nest. This knowledge has been passed on to his sons and daughter.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមមិនយកទឹកដោះតែសម្រាប់យកសាច់
តើជាការអនុវត្តការគ្រប់គ្រងដែលរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- សាច់
ប្រភេទពូជ:
សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមមិនយកទឹកដោះតែសម្រាប់យកសាច់
ចំនួន:
150
ប្រភេទពូជ:
beekeeping, apiculture
ចំនួន:
80

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- កាប់តែមួយចំនួន
- ប្រើប្រាស់អនុផលព្រៃឈើ
ប្រភេទព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ:
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៅព្រៃល្បោះសើមធម្មជាតិតំបន់ត្រូពិច
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៃព្រៃគុម្ពោតធម្មជាតិតំបន់ត្រូពិច
- Natural strips of gallery forest along savannah's rivers
មតិយោបល់:
The main economic activity of this group of farms is extensive cattle ranching on natural floodable savannhas (242 ha), but they all have bee keeping in their houses. The number 80 refers to the nest quantity. They preserve gallery forests (108 ha) and allow for fallows (28 ha) to develope near the houses for supplying nectar and pollen to the bees.
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- ប្រើប្រាស់អនុផលព្រៃឈើ
ប្រភេទព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ:
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៅព្រៃល្បោះសើមធម្មជាតិតំបន់ត្រូពិច
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៃព្រៃគុម្ពោតធម្មជាតិតំបន់ត្រូពិច
មតិយោបល់:
The fact that their traditional practice allow for them to keep the bee nests in their houses for up to 30 years, means that they had to protect surrounding forests and allow for shrubland recovery nearby the house. Otherwise, they would just either collect honey directly in the field in a single destructive event or bring a couple of nests per year home and then extract honey in a destructive way.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
The farms have some windmills for water extraction for the cattle ranching, but these are not used for the natural ecosystems that sustain the bees during the dry season.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការចិញ្ចឹមឃ្មុំ, វារីវប្បកម្ម, ការចិញ្ចឹមបសុបក្សី, ទន្សាយ, ដង្កូវនាង ។ល។
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
មតិយោបល់:
Bee keeping implies supplying the bees nectar and polen demands, thus, for sustaining their bees the Abril family is particularly keen on protecting their gallery forests and allow shrub regeneration. In addition, they are cultivating fruit trees (guayaba- Psidium guajava; arazá- Eugenia stipitata) near the houses, impplying a change in land cover from grazing land to fruit crops.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
មតិយោបល់:
Forest conservation and shrub recovery and fruit crops aid in the reduction of erosion by water during the wet season, and erosion by wind during the dry season. Forest conservation and shrub recovery and fruit crops reduce areas exposed to cattle trampling. Forest conservation, shrub recovery and fruit crops are likely important to protect soil fauna, to enhance the survival of bees and many other animal and plant species. A high density of pollinators is also important for natural vegetation and fruitting crop
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
On the one hand, they actively preserve the riparian forests because of their awareness of the relation between bee survival and honey production with forest cover. This reduces land degradation. On the other hand, surrounding their houses where they keep the bees they have planted trees and allowed for fallow areas to offer pollen and nectar to their bees, restoring land that has been previously used for cattle ranching
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
This is too complex to draw, so we presented the sequence of extracting honey in a nest that has been modified so that the nest can live up to 30 years.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Natalia Roa y Beatriz Ramírez
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/01/2020
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
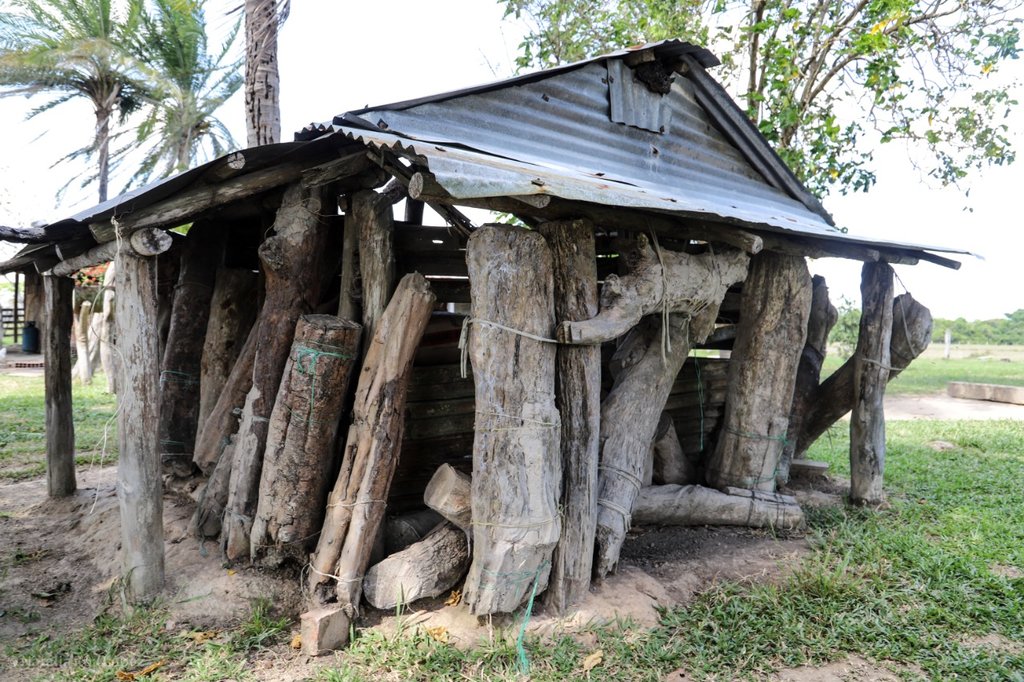
This is the housing for the nests. These nests have been collected or rescued from field. The youngest has 3 years the oldest has around 30 years. It is very important to keep the nests in the position they were originally found. The housing is to prevent direct sunshine and rainfall exposition.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Natalia Roa
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/01/2020
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
bee nest
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
$ 15
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wild nest recue or extraction and transport to the house | Depends on the finding, but it is preferred in the dry season where more floral resources are available |
| 2. | Opening of a window in the nest | A couple of days after being collected/recued |
| 3. | Locating the nest under housing | Just after the window opening |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Two people for wild nest recue or extraction and transport to the house | day | 2,0 | 15,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Opening of a window in the nest | day | 0,5 | 15,0 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Housing construction (two people) | day | 2,0 | 15,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 100,0 | |||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Saw | unit | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Chissel | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | hammer | unit | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Metal wire | kilo | 0,5 | 11,0 | 5,5 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Ax | unit | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | boles minimum 15 cm diamater and 2 m of height | boles | 4,0 | 8,0 | 32,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | wood support 4 m long | unit | 4,0 | 6,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Roof laminas (3 m) | laminas | 3,0 | 18,0 | 54,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Nails | box | 2,0 | 9,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 259,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 259,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The construction of a bee nest house can hold up to 30 bee nests.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking the bee nests | daily |
| 2. | Harvesting honey | yearly |
| 3. | Seedling collection | monthly |
| 4. | tree nursery care | daily |
| 5. | planting trees | monthly |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Daily check per bee nest | day | 0,005 | 15,0 | 0,07 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | honey harvest per bee nest (2 people) | day | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Seedling collection | month | 2,0 | 15,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Planting of fruitting trees | month | 2,0 | 15,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Chissel | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Broom | unit | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hammer | unit | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Syringe | unit | 1,0 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Empty glass bottles (750 ml) | unit | 70,0 | 0,4 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Table | unit | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | shovel | unit | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Bags x 50 units | bag | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Soil | sack | 4,0 | 6,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 203,27 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 203,27 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The way they manage the bee productive system is fairly cheap and most materials are already accessible within the farms.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
1938,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
highly monomodal seasonal rainfall with 4 months without rainfall (< 60 mm/ month), and 8 months with rainfall (>100 mm/ month) with June as the month with highest rainfall (> 300 mm)
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Estación pluviométrica de Trinidad (IDEAM)
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
The highly seasonal rainfall, implies four months of extreme drought and at least 6 months of flooded areas. Both severely limit crop growth.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
This is a low elevation flat area. Overall the floodable savannahs are concave but microtopography has primarily concave areas (bajos) with a lower extent of convex areas (bancos).
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
In the seasonally floodable savannhas there are three main soil types: 1) Clayey sediments, 2) fine and coarse alluvial sediments, and 3) lime and sand eolic deposits. Soil description is based on the 1:100.000 scale Casanare soil study, by the National Geographical Institute Agustín Codazzi.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ភាពទៀងទាត់:
ញឹកញាប់
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Drinking water is usually provided by ground water year round. During the wet season there is a generalized flood, and during the dry season there is severe drought. Thus, the water table level goes from surface to deeper than 9 m.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ខ្ពស់
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Habitats include: Gallery/riparian forest, isolated tree islands (matas de monte), seasonally flooded savannhas, wetlands.
Reported biodiversity for the seasonally floodable savannahs is: 183 spp of mammals, 507 spp of birds, 108 spp of anphibians, 119 spp of reptiles, 567 spp of fish, 1479 spp of plants (Mora-Fernández et al., 2015).
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
All the land user's reported here are family members.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
For the area 30 ha farms are very small, whereas 200 ha is small-medium. This is considering that farms in this region of colombia have on average 700 ha.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
They are in the process of gaining rights, given the farms have been theirs for more than 50 years.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
មតិយោបល់:
These farms are in fairly remote area with poor access roads, there is a rural school but for the other services people have to travel for at least 2 hours by car to the closest urban center.
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
អនុផលព្រៃឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Honey harvesting from collected bee nests
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Honey harvesting contributes with about 10% of farm income
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Honey harvesting is an additional income source from cattle ranching
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Part of the honey and most of the fruits harvested are consumed by the land user theirself.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The preservation of bee nests increases pollinator presence, whilst the conservation of gallery forests preserves habitats for wild bee populations.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
allowing for fallows to regenerate for providing bees with resources (nectar, pollen, resins and seeds) increase habitat diversity.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Measurements are qualitative estimates
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Riparian forest conservation contributed to water regulation
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Measurements are qualitative estimates
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Honey harvesting is only possible once per year so for the short term it takes some time before retrieving income. However, once the nests are re-established at home the maintenance is fairly easy. The rareness and uniqueness of the product sells well in the local market. The external markets are not aware of such a product.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
5
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
Talking with other local people we found that the traditional practice is very rare, mainly because it used to be the only source for sweeteners, but with the arrival of sugar cane and sugar, people stopped the practice, and for new generations the tradicional way is almost forgotten. This is highly menacing because when people find a wild nest they only destructively extract the honey affecting wild bee populations.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The medicinal properties attributed to the product make it highly sought after. |
| Having the nests at home, and passing on the traditional practice to new generations is very important, because they find very interesting to know about bee behaviour and pollination function for fruitting trees. |
| Costs are fairly low, and despite production is synchronized the demand of the product is higher that the production, so it is a welcome income to the family household assets. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Their practice is non destructive and bee population is enhanced in the houses, it is very likely that bees will find new wild nesting sites. In this regard bee nests at houses are a source of individuals for wild populations, given that there are trees and forests nearby. |
| This practice and their knwoledge on bee behaviour and biology motivates people to conserve forests and trees and allow for fallows surrounding their houses. |
| Negative effects on their bee populations derived from land use change int heir surroundings and application of agrochemicals by neighboring rice crops serve as an indicator for them to know if those practices are deteriorating their environment. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Despite the long term survival of captured wil bee nests, they still rely on collecting wild nests. Which in time they feel are more scarcee | For them it is crucial to learn how to split their "domesticated" nests so they can increase production without depending on wild nests. |
| The expansion of rice crops in the area is a major threat | Public policy and law inforcement in aerial agrochemical application is urgent. Also, the transition from usual rice crop management to a more enrionmental management is required. |
| New generations are less likely to adopt traditional practices, endengering the persistence of this knowledge in time | The recognition of this traditional productive system is fundamental. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| A one time per year harvesting of the product could potentially be increased to expand this sustainable practice | Restoration of key dietary elements surrounding their houses and an increase in connectivity with remaingin forest patches could potentially increase honey production |
| We agree that the loss of this practice is inminent if it is not protected as a cultural heritage | Knwoledge transfer to new generations and the recovery of this productive system, once "domesticated" bee nest can be divided or multiplied. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
4
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
4
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
30/01/2020
មតិយោបល់:
Land-users were very pleased with the recognition of the their prodcutive systems and were very happy to contribute us to understand how it works.
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Diversidad de abejas sin aguijón (Hymenoptera: Meliponini) utilizadas en meliponicultura en Colombia. Nates-Parra, G. and Rosso-Londoño, J.M. (2013).
វេបសាយ:
https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/3190/319029232001.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Policy Brief: Land Use Change Impacts in the Cusiana Watershed of the River Basin, Orinoco River Basin, Colombia Author: Liniger HP, Vega LF, Ramírez BH, Eichenberger J, Year: 2020
វេបសាយ:
https://www.wocat.net/en/projects-and-countries/projects/onsite-and-offsite-benefits-sustainable-land-management/colombia
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Video: Land Use Change Impacts in the Cusiana Watershed of the River Basin, Orinoco River Basin, Colombia
វេបសាយ:
https://vimeo.com/429999595
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
It is a bit too long but feasible to fill in.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល