Intercropping of grain legumes with cereals [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Basile Brunner
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Maria Eliza Turek, Tatenda Lemann, Joana Eichenberger
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Joana Eichenberger
Mischkultur von Körnerleguminosen und Getreide
technologies_6235 - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Quillet Lucien
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Klaiss Matthias
Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Intercropping of grain legumes with cereals is a sustainable agricultural practice in Swiss farming. This involves growing grain legumes (such as peas or beans) alongside cereal crops (like barley or wheat) in the same field, reducing crop failure or yield risk, stabilising the grain legumes, promoting biodiversity and enhancing overall crop yield.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Intercropping of grain legumes with cereals is practised in the Broye catchment area, which covers the cantons of Vaud and Fribourg in Switzerland. The area is characterised by mixed dairy and arable production in the hills and predominantly arable production in the lowlands. The area has an average annual rainfall of 865 mm, an average temperature of 9.6°C and significant agricultural activity relies on irrigation from local rivers.
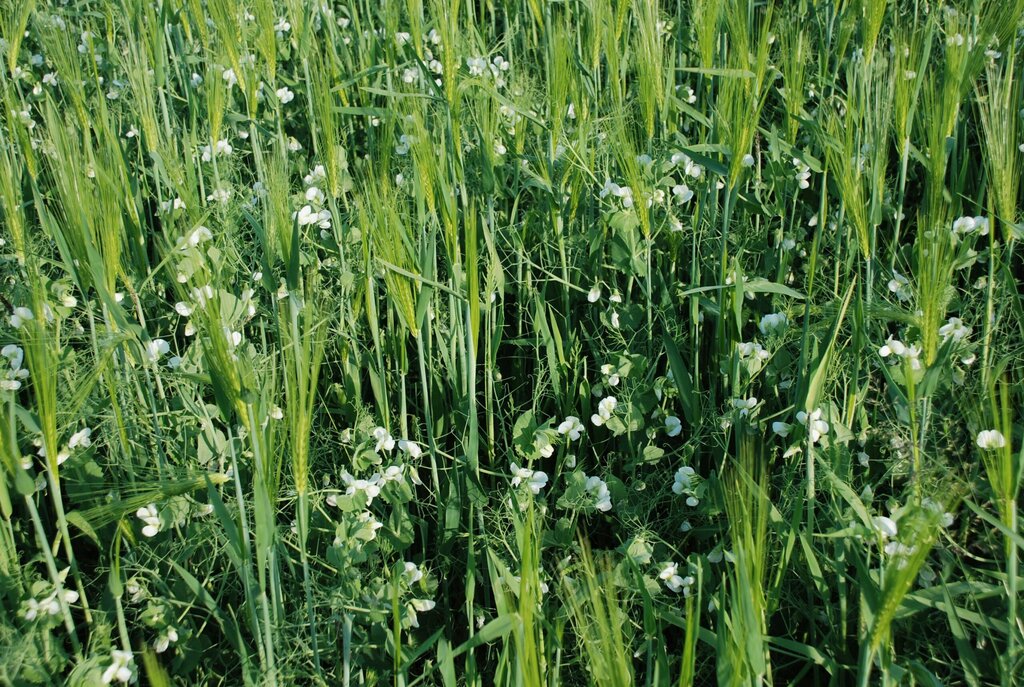
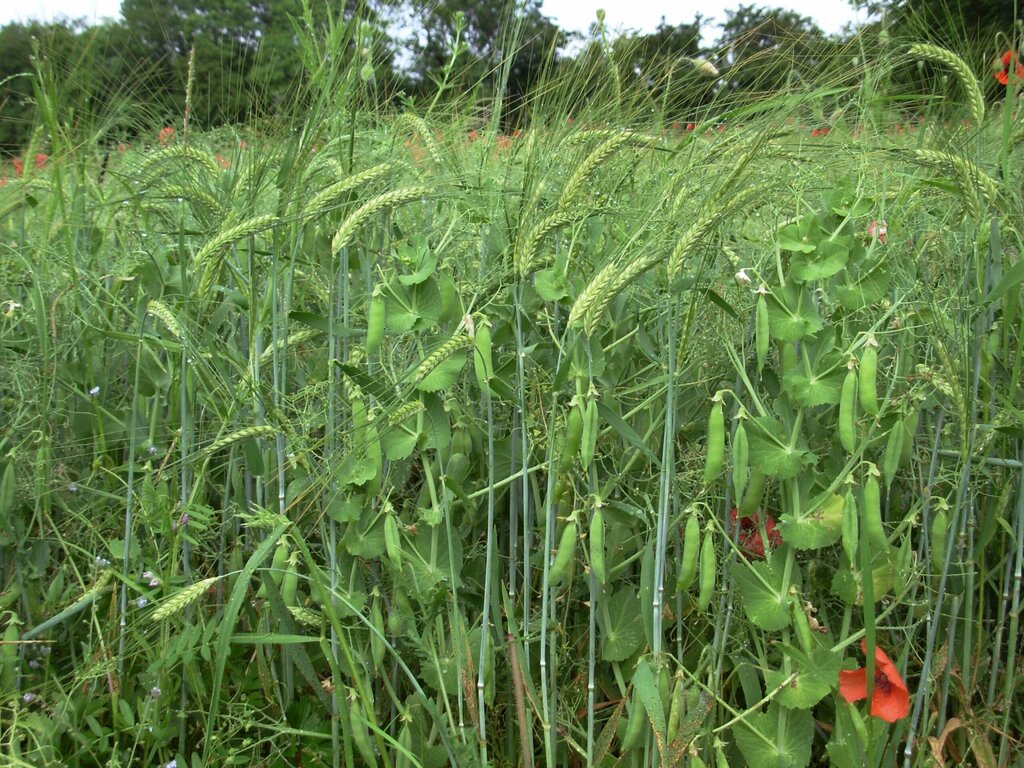
Intercropping is the simultaneous cultivation of two or more crops in the same field. In this case, grain legumes (such as peas, lupins or faba beans) are grown alongside cereals (such as barley, oats or wheat). The crops are sown together in a pre-prepared mixture, usually at a ratio of 65% legumes to 35% cereals by weight, compared to the standard weight sown in monoculture (100%). The seeds are fully mixed and sown in the same row. Crops are grown over the winter and harvested simultaneously in the spring, which requires compatible combinations whose breeding is continuously optimised for simultaneous ripening. The standard practice in Switzerland is to use a cereal plus a legume.
The main purpose of intercropping grain legumes with cereals is to increase ecological resilience and improve soil fertility. Including legumes in rotations significantly improves soil nitrogen levels, reducing the need for synthetic fertilisers. Intercropping also increases water infiltration, reduces runoff and increases biodiversity. The increase in biodiversity is small in terms of the overall biodiversity of agricultural land (e.g. soil micro-organisms, pollinators). The number of crops grown remains relatively constant. The practice aims to produce higher yields on a given piece of land by using resources that would otherwise not be used by a single crop. The overall yield is higher, although land equivalent ratios (LER) were not measured in this study. However, a cited paper (Chapagain & Riseman, 2014) shows that intercropping barley with peas can increase land productivity by 12-32% compared to monoculture plots, with a 2:1 arrangement producing the highest total land outputs and LER values.
Establishing and maintaining intercropping requires several key activities and inputs: (1) Use of tractors and seed drills for planting and harvesting intercrops. (2) Regular weeding, especially in fields with crops such as soy. (3) Episodic irrigation with water from local irrigation syndicates. (4) Minimal use of fertiliser and homemade manure to maintain soil health.
Intercropping has many benefits: (1) Increases biodiversity, improves soil fertility and increases water infiltration. (2) Reduces the need for synthetic fertilisers, making it economically viable for farmers. (3) Improves drought resistance and reduces the risk of crop failure. (4) Contributes to better water management and resilience to climate change. (5) Surface erosion is reduced by the greater cover of mixed crops (leaf area index).
Farmers appreciate the effectiveness of intercropping in achieving yields similar to monocultures, while adding the benefits of cereals. They also value the reduced need for synthetic fertilisers and improved soil health. However, challenges include seed selection and segregation, particularly for crops such as wheat and faba beans, and weed management in certain fields.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Missy / Vaud / Switzerland
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Only one farmer was interviewed who practices mixed cropping on 4 ha.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - ផ្សេងៗ
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - គ្រាប់ហោឡាំងតាវ
- Lupine (legume)
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំដែលដាំចន្លោះគ្នានោះ:
Pea - barley, and lupine - oat
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
field rotation is as follows: cereals, legumes or maize, cereals, legumes or maize ... And every six years, two successive legumes/maize
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
All the plots on the farm are connected to a stream. The farmer tries to irrigate as little as possible, as it's time consuming and expensive. As there was enough rain this year, there was no need to irrigate the fields.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការបង្កាត់ពូជរុក្ខជាតិ/ សត្វ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A5: ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រាប់ពូជ បង្កើនប្រភេទពូជ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
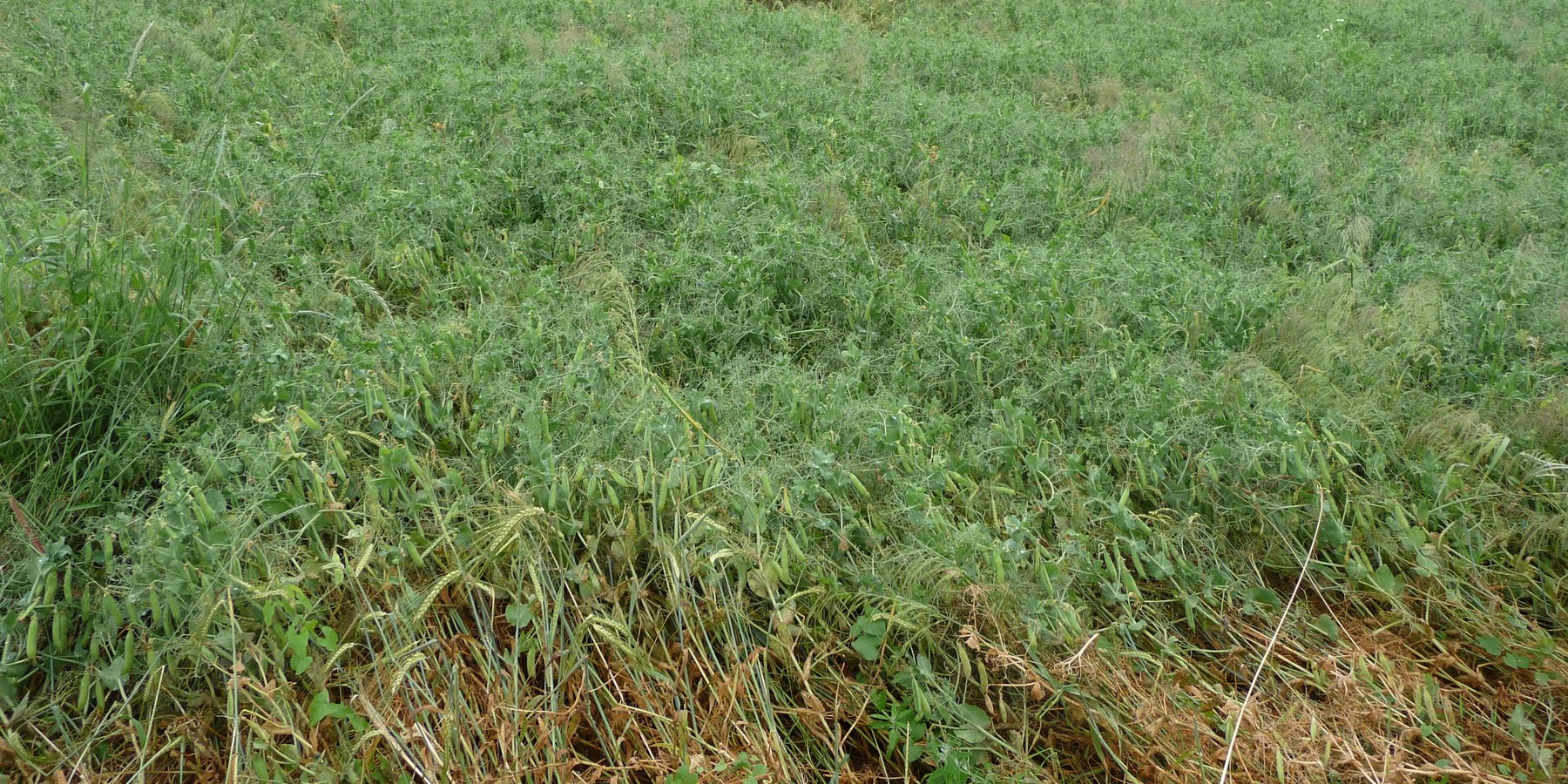
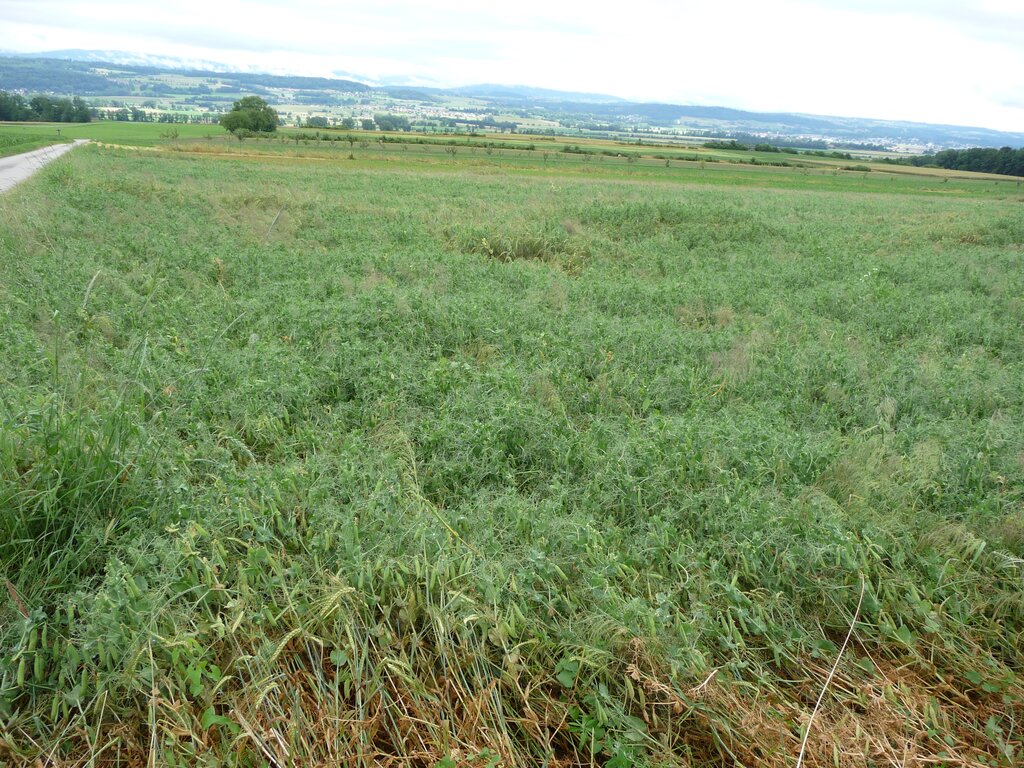
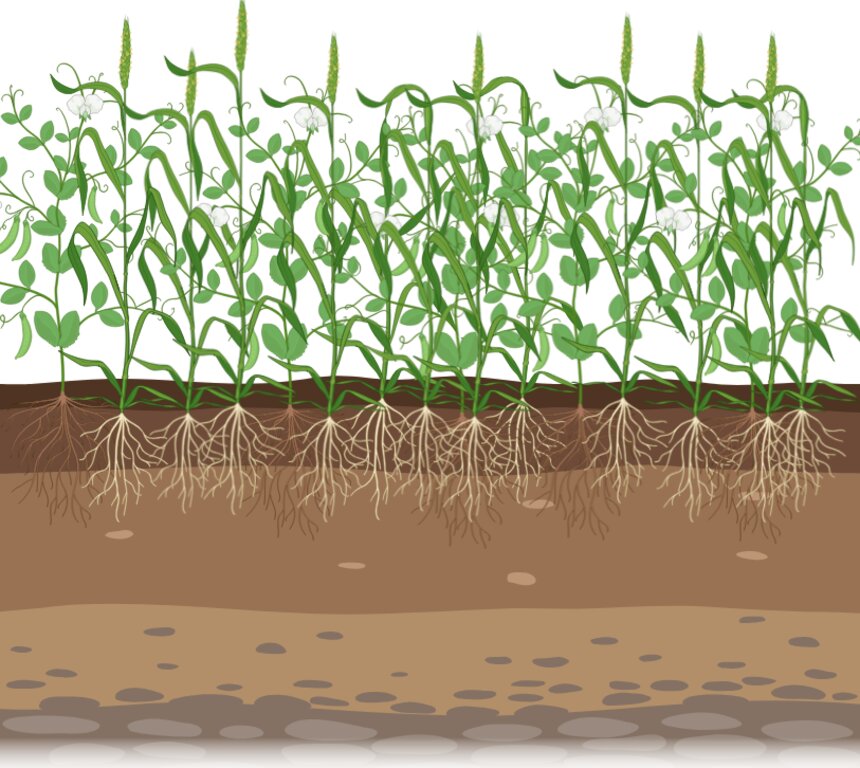
The illustration shows a field where peas and barley are grown together in a mixed cropping system. The plants with rounded leaves and tendrils are peas, while the taller plants with linear leaves are barley. The interviewed farmer typically grows these crops on an area of two to three hectares. The mixed crops are at an advanced stage of growth, several weeks before harvest, with both pea and barley producing seed. The rooting depth of the pea plants can reach up to 110 centimetres, while the barley plants can extend their roots up to 150 centimetres under optimal conditions.
These plants grow on brown soil composed of three main horizons. Horizon A is usually brownish in colour and extends to a depth of over 20 cm. It is rich in organic matter and mineral particles, making it biologically active with many soil organisms and plant roots. The B horizon is lighter in colour and typically extends from about 20 cm to 150 cm deep. It contains minerals leached from the A horizon and shows signs of weathering, with a more defined structure due to the accumulation of minerals and organic matter from the upper layers. The C horizon, or parent material, lies below the B horizon and extends beyond 150 cm. It consists of partially disintegrated and weathered parent material, is typically lighter in colour than the B horizon and has minimal biological activity compared to the upper layers.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Basile Brunner (UniBE)
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
15/08/2024
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
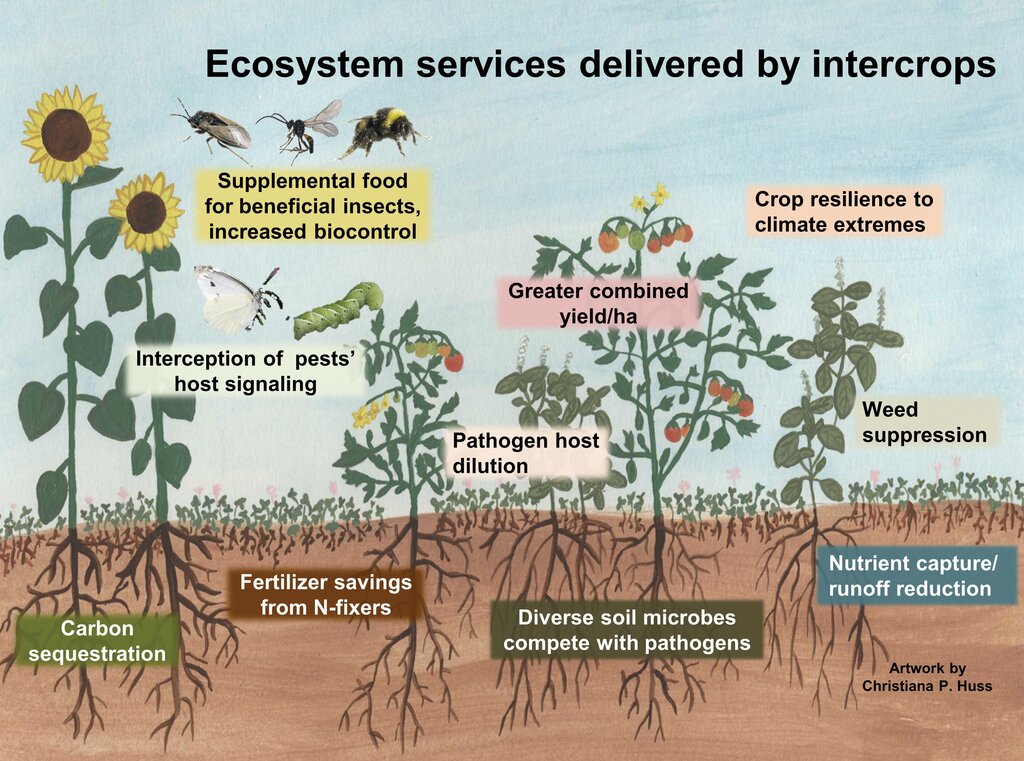
llustration of benefits of intercropping for crop resilience and crop yields, management of soils, weeds, pests, and pathogens, along with environmental benefits of carbon sequestration and reduction of fossil fuel inputs.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Christiana Huss
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
22/04/2022
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
CHF
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1,13
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
240 CHF
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mixing seeds: For single tank seeders, mix seeds at a ratio of 80% peas and 40% barley. For multi-tank seeders, apply seeds of mixture partners separately. | Before sowing, typically in late summer. |
| 2. | Sowing: Use a row spacing of 12 cm, and place seeds at a depth of 3 to 4 cm. | late october |
| 3. | Assess the mix’s condition after winter. | Spring, depending on winter severity. |
| 4. | Weed Control: Generally not needed due to the competitive nature of the mixed crop. If high weed pressure: Consider harrowing once (2-3 hours per hectare for weeding). | Spring, depending on winter severity. |
| 5. | Harvesting: Adjust harvester sieves for peas. Open threshing concave and hulling bars wide. Maintain low drum rotation. Monitor for grain loss regularly. Adjust Vario-table to an aggressive cutting angle. | Summer. |
មតិយោបល់:
Maintenance activities for a mixed intercropping culture of winter peas/barley.
Cultivate the mixed crop only every seventh year in crop rotation. Avoid growing lupins, vetches, lucerne, or pure stands of red clover in between. No nitrogen fertilisation. Irrigation only in very dry years.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Ploughing | person-days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Sowing the Mixture | person-days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Weeding | person-hours | 3,0 | 23,0 | 69,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | seeder | piece | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | tractor | piece | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | harvester | piece | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | plough | piece | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seed mixture protein peas / barley mixture (autumn sowing) organic | kg/ha | 200,0 | 6,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 71669,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 63423,89 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Normal machinery (tractor, seeder, harvester) can be used. In many cases it is already available on the farm.
Weed control is usually not needed. If there is high weed pressure, harrow or hoe it once.
No nitrogen fertilising for the crop. Irrigation would only be needed in an extremely dry year.
In order to avoid legume fatigue in the soil, only cultivate the mixed crop every seventh year. Also do not grow lupins, vetches, Lucerne or pure stands of red clover in between.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
No exceptional investments are needed as existing machines are used.
The cost of seeds and the seed sorting costs by the mills.
Time and labour required for weeding, which can vary based on crop type.
The demand and price for the crops grown. E.g. soy having higher demand and price compared to peas.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
865,00
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Payerne
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ភាពទៀងទាត់:
ម្តងម្កាល
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
ទេ
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher land use ratio (more biomass per hectare).
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Cereals in the mixture prevent weeds from spreading within the legumes. But cereals (e.g. barley) of a lower quality than if they were grown in a monoculture.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
If legumes are not growing well, fertiliser can be added and cereals can be harvested.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The same products are harvested as in a monoculture, but at the same time.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Less intervention (e.g. weeding, fertilisation) required.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Water demand remains approximately the same as in monoculture.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced expenditure on organic crop protection & weeding thanks to cereals' positive effect on weed control (compared to legume monoculture).
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As mixed cropping can be used within the crop rotation, it only leads to a slight increase in the farmer's income.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The same crops are cultivated as in monoculture.
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Less intervention (e.g. weeding) required as cereals protect legumes from weeds and legumes provide nitrogen to cereals.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Good soil cover due to mixed cultivation slightly reduces evaporation.
ដី
គម្របដី
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Legumes fix nitrogen in the soil.
ភាពប្រៃ
ជាតិអាស៊ីត
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Slightly higher due to mixed species.
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
slightly higher because of species mixture
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Slightly higher due to mixed species.
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Slightly less due to weed suppression in cereals.
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Legumes provide flowers for pollinators.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | និទាឃរដូវ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវស្លឹកឈើជ្រុះ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវរងា | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | និទាឃរដូវ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវស្លឹកឈើជ្រុះ | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវរងា | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះរន្ទះតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះទឹកកកតាមតំបន់ | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រលកកម្តៅ | មធ្យម |
| រលកត្រជាក់ | ល្អ |
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | ល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
In a very dry summer with limited irrigation, competition for water availability between the two species in the mix can lead to poor crop quality at harvest.
In the event of a very cold winter and poor legume growth, the technology has the advantage of allowing the farmer to apply fertiliser and still harvest cereals at the end of the season, reducing the risk of crop failure.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 11-50%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Decrease for market reasons (barley has low market price) & more adapted varieties (pea varieties that are more resistant to wind damage).
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Mixed cropping works very well, providing both legume and cereal yields. |
| Certain crops, like oats, help suppress weeds, reducing the need for additional weeding. Thus saving costs (PPPs & labour) and reducing workload (hours of weeding). |
| Legumes contribute to nitrogen fixation, improving soil fertility for subsequent crops. |
| Mixed cropping reduces the risk of total crop failure, as one crop can compensate if the other underperforms. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| If one crop fails, the other can still provide a harvest, ensuring some yield. |
| Mixed cropping can produce more biomass on the same land compared to monocultures. |
| It enhances soil diversity, supports pollinators, and contributes to nitrogen enrichment. |
| Good market price for protein peas. Additionally, the farmer receives a subsidy for grain legumes (including protein peas), if the harvest contains at least 30% grain legume seeds. In addition, the cantons of Jura and Vaud pay cantonal contributions to farmers who cultivate mixed crops. The farmers can also get extra payments by the organic farmer organisation Bio Suisse if certain grain legume species of high demand are cultivated (see Agridea Deckungsbeitrag catalogue for more information). |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Legumes are not growing well due to a cold winter. | Adding fertilizer can help growing the cereal and enables the farmer to still harvest something. |
| Water competition in a dry summer results in a bad crop quality. | Ensure efficient irrigation to reduce competition for water between mixed crops. |
| Barley has a very low market value. | Choose crop varieties that are better adapted to market demands. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| During drought stress, competition for water between the two crops can occur, leading to potential yield losses or low quality yield. | Use drought-tolerant varieties or species with deep roots for mixed cropping. This can help reduce competition for water and improve resilience during dry periods. |
| Limited market demand for certain crops like barley. | Focus on crops with higher market demand. |
| Need for minimal fertilization in mixed cropping can reduce yield quality of cereals like barley. | Implement targeted fertilization strategies to balance the needs of both crops. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
1 field visit to Missy, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1 interview with farmer Lucien Quillet
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
1 interview with researcher Matthias Klaiss (FiBL)
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Various written sources were used, with FiBL fact sheets being particularly informative for this context.
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
08/07/2024
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Huss, C. P., Holmes, K. D., & Blubaugh, C. K. (2022). Benefits and risks of intercropping for crop resilience and pest management. Journal of Economic Entomology, 115(5), 1350–1362. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toac045
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Klaiss, M. (2021). Intercropping of grain pea with cereals (Legumes Translated Practice Note 17, S. 1–4). Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL. https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/42384/
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Alföldi, T., Haug, B., Messmer, M., Goldringer, I., Forst, E., Mary-Huard, T., Enjalbert, J., & Hohmann, P. (2020). Mischkulturen Erbsen/Gerste - Braucht es eine eigene Züchtung? EU-Projekt ReMIX (Video). Forschungsinstitut für biologischen Landbau FiBL, CH-Frick. Retrieved 31 July, 2024, from https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/37276/
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Haug, B., Messmer, M., Enjalbert, J., Goldringer, I., Flutre, T., Mary-Huard, T., & Hoh-mann, P. (2023). New insights towards breeding for mixed cropping of spring pea and bar-ley to increase yield and yield stability. Field Crops Research, 297, 108923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2023.108923
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Hiltbrunner J., Wüst S., Blatter A., Vonzun S., Klaiss M., Messmer M. (2023). Optimierung des Mischkultursystems Erbse-Gerste zur Sicherung der lokalen Eiweissversorgung. Feld-rundgänge & Präsentation Projekt PROMISE 2023. Agroscope. Stiegenhof, Arenenberg, Utzenstorf & Sargans. https://ira.agroscope.ch/de-CH/publication/53643
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Vonzun S., Blatter A., Wüst S., Hiltbrunner J., Schneider M., Messmer M. (2023). Investi-gating mixed cropping systems with pea and lentils for climate-smart and demand oriented agriculture. Fourth International Legume Society Conference 2023. 19 September, Granada. https://ira.agroscope.ch/de-CH/publication/55455
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL. (2017). Erfolgreicher Anbau von Körnerleguminosen in Mischkultur mit Getreide.
វេបសាយ:
https://www.fibl.org/en/shop-en/1670-koernerleguminosen-mischkulturen
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
FiBLFilm. (2020, May 6). Increasing domestic protein supply with intercropping - Diverimpacts success story from Switzerland [Video file].
វេបសាយ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BadrJW-b_2g
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
FiBLFilm. (2015, September 29). Anbau von Mischkulturen (Colture consociate) - Körnerleguminosen Getreide [Video file].
វេបសាយ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gAYNXCw2CiE
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL. (2024). FiBL projects Grain legumes intercropped with cereals and other partners.
វេបសាយ:
https://www.fibl.org/de/themen/huelsenfruechte/huelsenfruechte-projekte
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL. (2024). Deckungsbeiträge. Praxispublikationen.
វេបសាយ:
https://www.fibl.org/de/shop/1104-deckungsbeitraege
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល