Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Joren Verbist
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6669 - ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Agricultural Economist:
Frija Aymen
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Forage Specialist:
Zaiem Anis
Office de l'élevage et des pâturages (OEP)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Agricultural and Resource Economist:
Boubaker Dhehibi
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Senior Livestock Scientist:
Rekik Mourad
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Director of ITGC research station in Setif, Algeria:
Louahdi Nasreddine
Institut Technique des Grandes Cultures (ITGC)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - ប្រទេសលីបង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
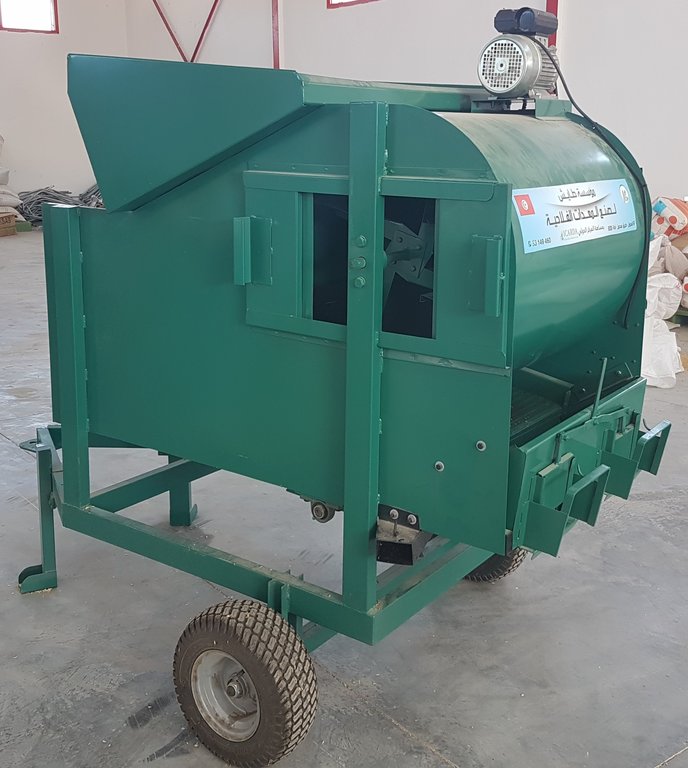
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
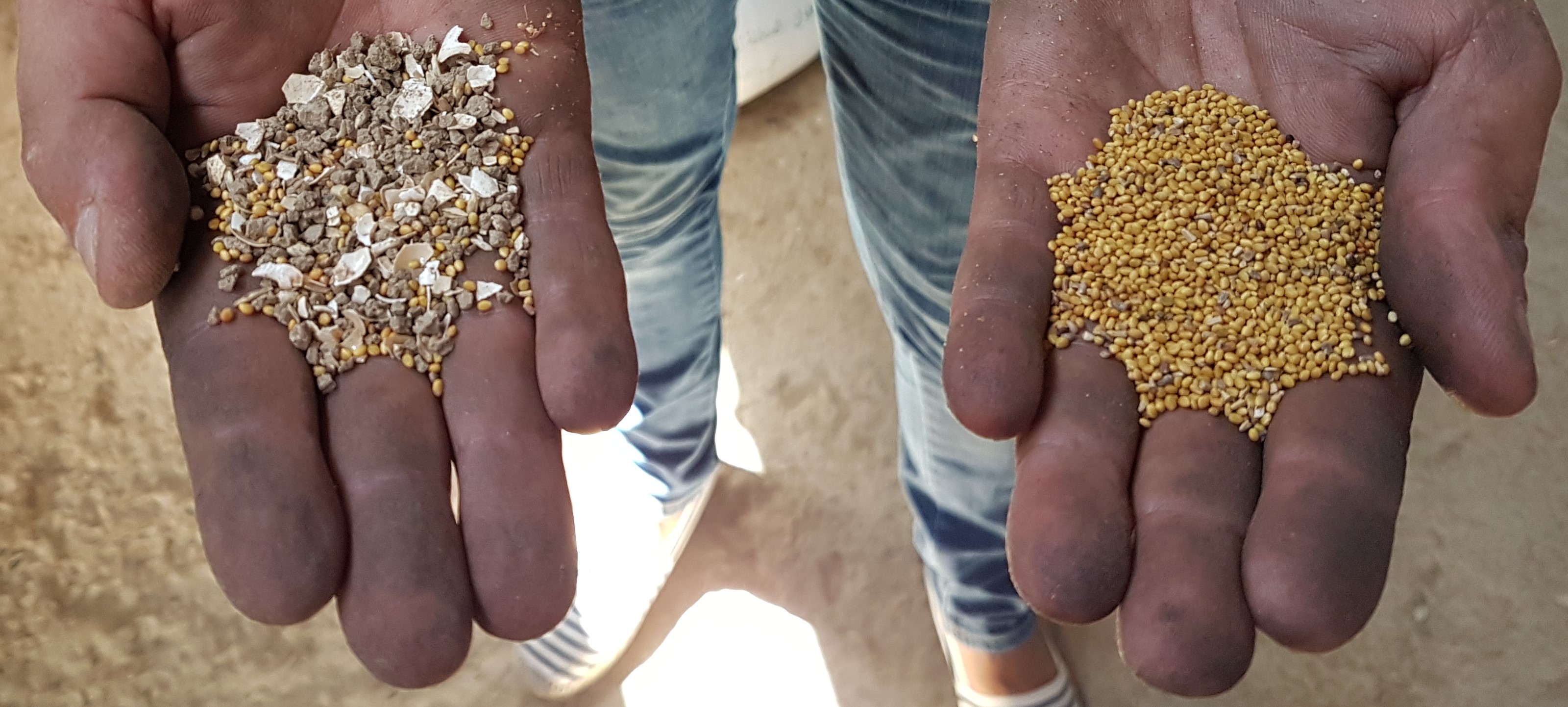
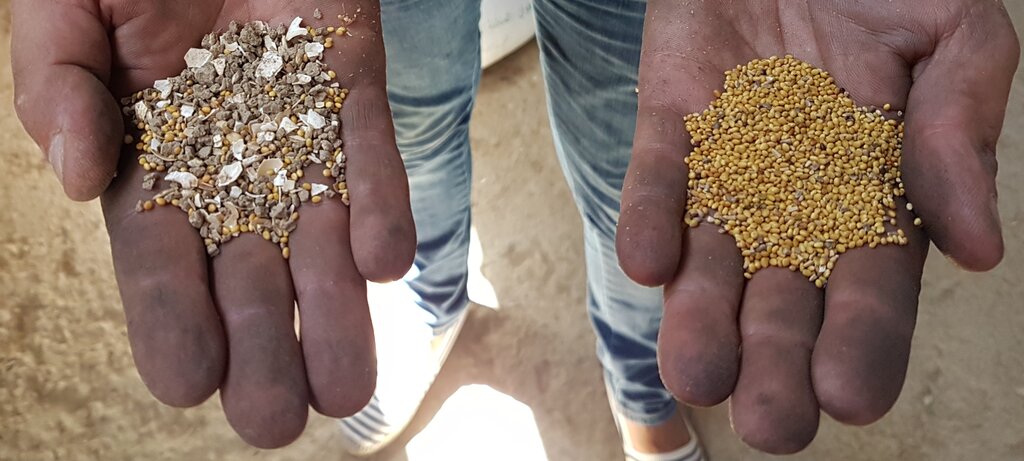
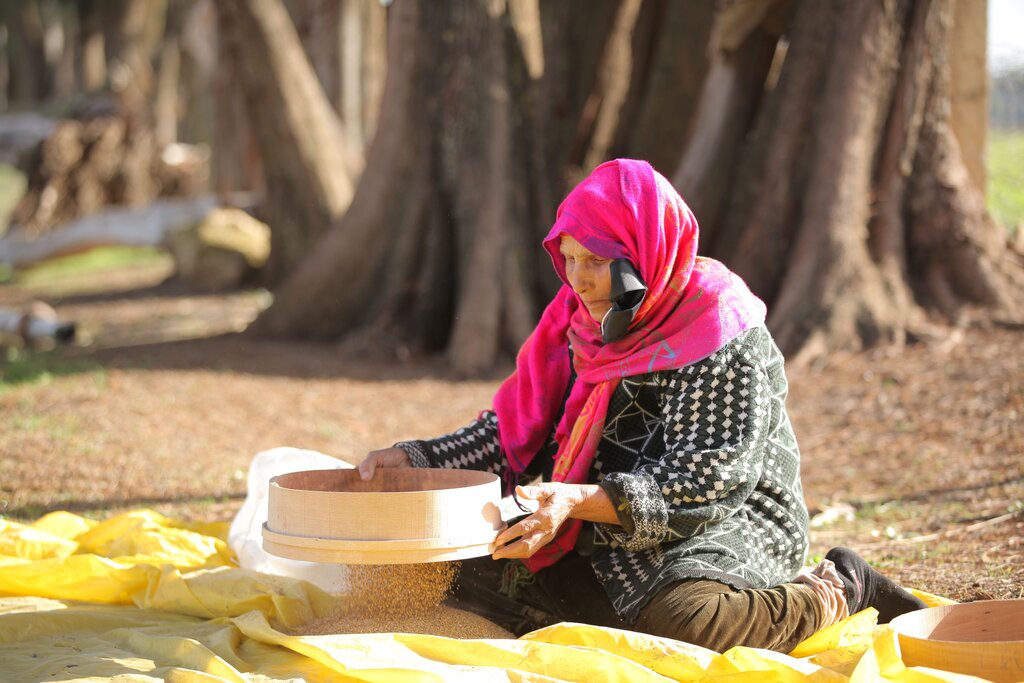
In Tunisia and Algeria, the agricultural system is characterized by low levels of mechanization, particularly among small and medium-sized farmers who cannot afford expensive imported machines. As a result, a substantial amount of manual labour is required to carry out various agricultural operations, such as seed cleaning, which is traditionally done by women and children. While seed production is often done by large suppliers, this does not always satisfy the demand. Therefore, many smallholder farmers in Tunisia prefer to use their own seeds, despite the time-consuming manual cleaning process and the risk of lower quality.
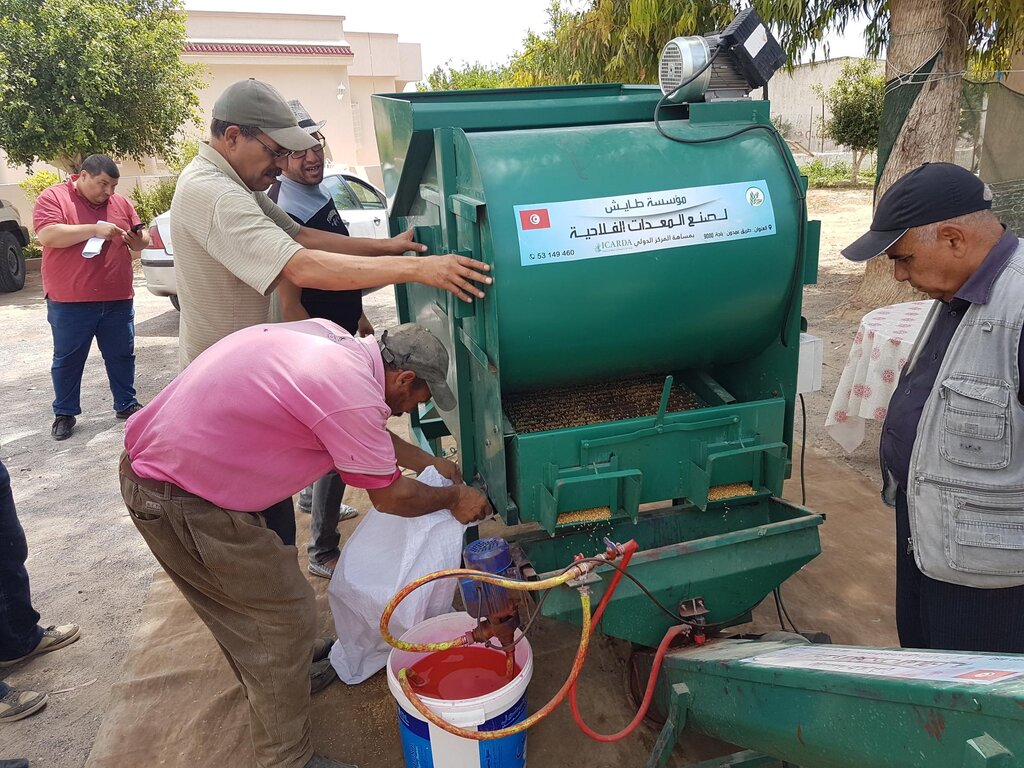
To address these issues, the International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) collaborated with national partners to develop a mobile seed cleaning machine for small-scale farmers. The prototype, designed and tested with input from a local manufacturer, is suitable for the primary field crops (such as wheat, barley, vetch, and faba beans) in Tunisia. The machine sort out damaged or small seeds and rock or pebbles, while treating the remaining seeds undoing them from any contamination or weeds, to ensuring quality and higher shelf-life.
The mobile seed cleaning machine, with a capacity of approximately 800 kilograms per hour depending on the seed type, was distributed to four farmer cooperatives, serving a total of 1,000 small-scale farmers. In order to promote ownership, the farmers contributed to a portion of the costs and received training on how to operate the machine effectively.
When using the mobile seed cleaning machine, farmers have the option to choose between two methods: solely cleaning the seeds or cleaning and treating them. The cost for cleaning alone is around 2 Tunisian Dinar per 100 kilograms, while the cost for both cleaning and treating, which includes the application of a fungicide, is 8 Tunisian Dinar per 100 kilograms. Life time is estimated between 5 and 10 years and worn out parts can easily be replaced.
The introduction of the mobile seed cleaning machine has several advantages, including a decrease in workload for women and children, improved production and quality of crops, higher productivity of the land, reduced dependence on imported seeds and machinery, and the promotion of local value chains and social cohesion through cooperative ownership and utilization of the machines.
However, there are still some challenges to overcome. For example, the initial prototype required heavy bags of seeds to be lifted to a height of two meters, leading to additional labour requirements and reduced efficiency. This challenge was addressed by equipping the machine with a conveyor screw, which can double its capacity at an additional cost. Additionally, the cost of purchasing the machine can be a significant investment for farmers, but this can be overcome through collective buying and organizing themselves in cooperatives.
In conclusion, the mobile seed cleaning machine represents an innovative solution that improves the (local) value chain and livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by reducing workload and costs, particularly for women and children. This technology has the potential to be scaled up and benefit other regions and cooperatives.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2019
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
see 2.2
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- កាត់ និងជញ្ជូន/ គ្មានវាលស្មៅសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
តើជាការអនុវត្តការគ្រប់គ្រងដែលរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Crops like barley, vetch and faba beans, are cultivated to feed livestock. The manure from livestock is used to fertilize the lands.
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- សាច់
- ទឹកដោះគោ
ប្រភេទពូជ:
សត្វចៀម
ប្រភេទពូជ:
សត្វពពែ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- បច្ចេកទេសប្រើប្រាស់ថាមពលមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព
- វិធានការក្រោយការប្រមូលផល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A5: ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រាប់ពូជ បង្កើនប្រភេទពូជ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S10: វិធានការសន្សំថាមពល

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ដែលមិនអាចអនុវត្តបាន
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
The seed cleaning machine has the following dimensions:
-Length = 180cm
-Width = 80cm
-Height = 175cm.
Equipped with a high-quality sieve measuring 140cm in length and 65cm in width, the seed cleaning machine ensures that even the smallest impurities are removed from the seeds. With a hopper capacity of 200kg, the machine can accommodate large batches of seeds, allowing for uninterrupted cleaning.
The machine has a cleaning capacity of around 600 till 1000kg/h.
Its lifetime is estimated to be between 5 and 10 years. Worn-out parts are easily replaceable and locally available.
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
100 kilogram cleaned and treated seed
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Tunisian Dinar
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
25
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Seed cleaning machine with conveyor screw | 1,0 | 12500,0 | 12500,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 12500,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 4166,67 | |||||
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Operating | person-hour | 0,1 | 10,0 | 1,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Electricity | kWh | 3,0 | 0,066 | 0,2 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Uncleaned seed | kilogram | 100,0 | |||
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Fungicide (for treating) | litre | 0,2 | 30,0 | 6,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 7,2 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 2,4 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Farmers can choose to only clean or to also treat. Treating consists of applying fungicide as well. Farmers usually pay 2 TD/100kg for only cleaning and 8 TD/100kg for cleaning and treating.
Cleaning (and treating) 100 kilograms of seeds results in 70 kilogram of good useful seeds.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The costs of purchasing the machine is substantial. However, this should be shared among farmers within the cooperation.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
This innovation can be implemented in many different environments.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
This innovation also affects the children of the land users because the children are often the ones who do the seed cleaning
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Is improved due to better yields and no/less costs on purchased seeds
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Cleaned seeds could be sold
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mechanically cleaning substituted the manual cleaning (often done by women and children)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
Dependency on seed distributors
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | ល្អណាស់ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Substantially reduced in workload. |
| Decreased costs, and decreased dependency on the seed market |
| Improved seed quality |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Improved gender equality because women and children mostly did the seed cleaning. |
| The unit is mobile hence many farmers can use it. |
| The seed cleaner unit and produced seeds improve the value chain on a local level |
| The seed cleaner unit is used within a farmer organization, hence it improves the cohesion within this organization. |
| Using cleaned seeds increased the productivity of the land. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Entering uncleaned seeds (bags usually weigh between 30 and 50 kilograms) into the machine, which is a lift around 2 meters, is too difficult for one person so additional labour is required. | The newer machines have a conveyor screw, to transport seeds from the ground to the entry. It is estimated that this will double the capacity. |
| Investment is required | Organizing in cooperations so costs can shared |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
2023
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Rudiger, U., Zaiem, A., Idoudi, Z., Frija, A., Rekik, M. and Taher, A. 2021. Mobile seed cleaning and treatment unit improves forage seed quality and quantity and presents a successful business model for farmer cooperatives. Business Model Brief. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/10568/116748
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Aymen, F., Idoudi, Z., Rudiger, U. and Rekik, M. 2020. Collaboration between ICARDA projects and linkages to IFAD investment portfolio for enhancing seeds quality and forage production through entrepreneurship and farmers associations. Some examples from ICARDA activities in Tunisia. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://repo.mel.cgiar.org/handle/20.500.11766/11134
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Rudiger, U. 2020. Report on small mobile seed treatment units for cooperatives in Tunisia
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12323
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Udo Rudiger. (15/12/2020). Workshop with beneficiaries.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12556
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Frija, A., et al. 2022. Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security – ProSol: Towards the Effective Scaling of Soil and Water Conservation Technologies under Different Agroecosystems in North and Central West Tunisia – SWC@Scale/ProSol: Technical Progress Report/ January – August 2022. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67835
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Idoudi, Z. 2020. Encouraging Entrepreneurship with Mobile Grinders and Seed Cleaning Machines
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://www.icarda.org/media/blog/encouraging-entrepreneurship-mobile-grinders-and-seed-cleaning-machines
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Idoudi, Z., Najjar, D., Rekik, M., Frija, A. 2022. Integrating Gender in the Use of Conservation Agriculture for Crop and Livestock System (CLCA). Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67126
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Rekik, M., Frija, A., Idoudi, Z. 2022. Overview of CLCA Main Achievements in NA and LAC Countries. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68177
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Rudiger, U., Zaiem, A., Idoudi, Z., Frija, A., Rekik, M. and Taher, A. 2021. Mobile seed cleaning and treatment unit improves forage seed quality and quantity and presents a successful business model for farmer cooperatives. Business Model Brief. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://hdl.handle.net/10568/116748
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល