Protected Agriculture for High Value Crops [ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nima Dolma Tamang
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Haka Drukpa
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6846 - ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Narayan Abi
Abimanyum Farm
ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Enhancing Agricultural Production Through Fallow Land Reversion [ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់]
The approach is to enhance production of local vegetables and fruits through fallow land restoration - under a group established for the purpose.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nima Dolma Tamang
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Protected agriculture (controlled environment agriculture) is the use of technology to modify the growing environment for crops to extend the growing period and increase yields. It can include greenhouses, shade nets or polytunnels. This technology is moderately expensive therefore it is used only for the cultivation of high-value crops and raising seedlings in winter.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
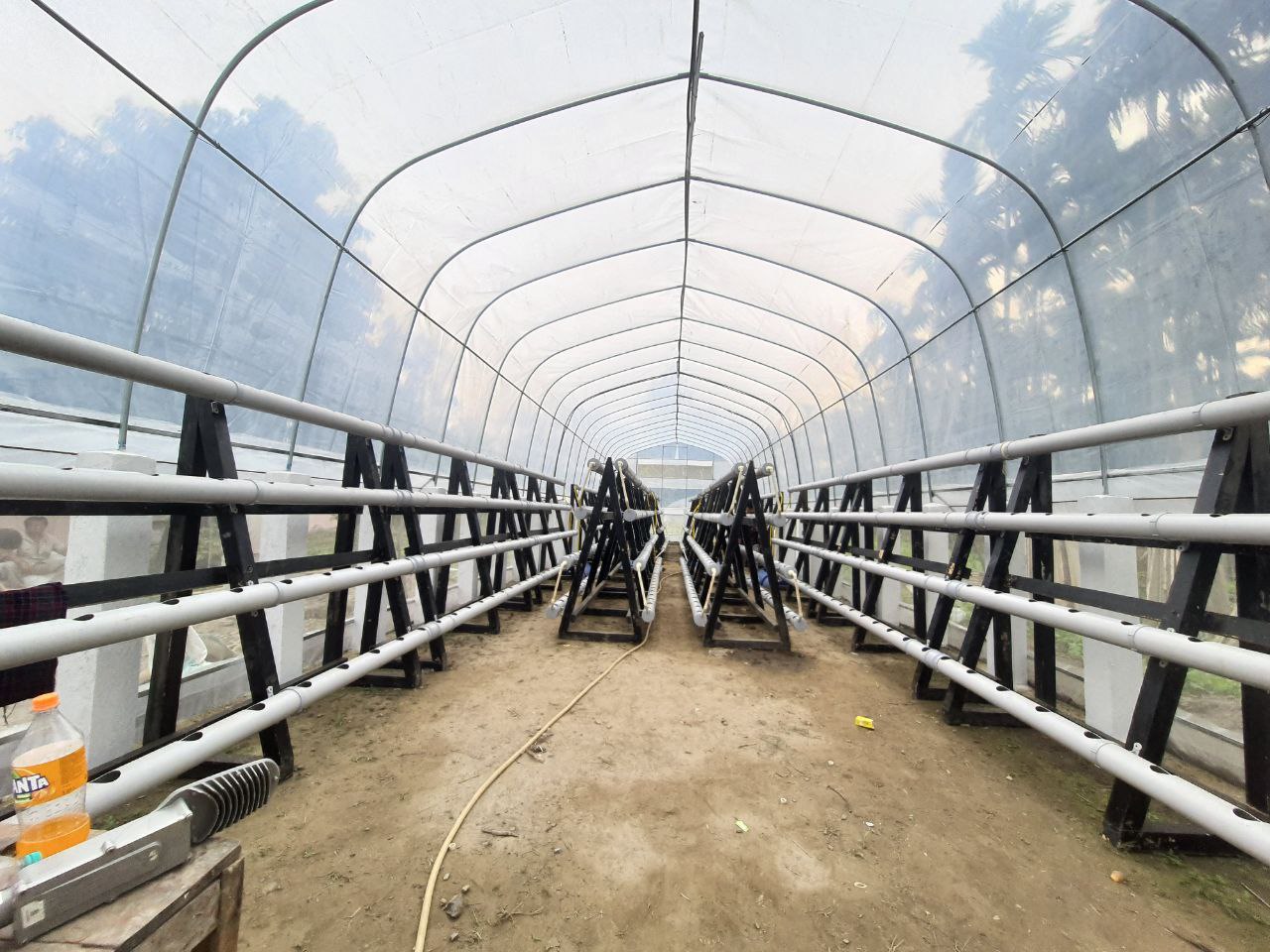
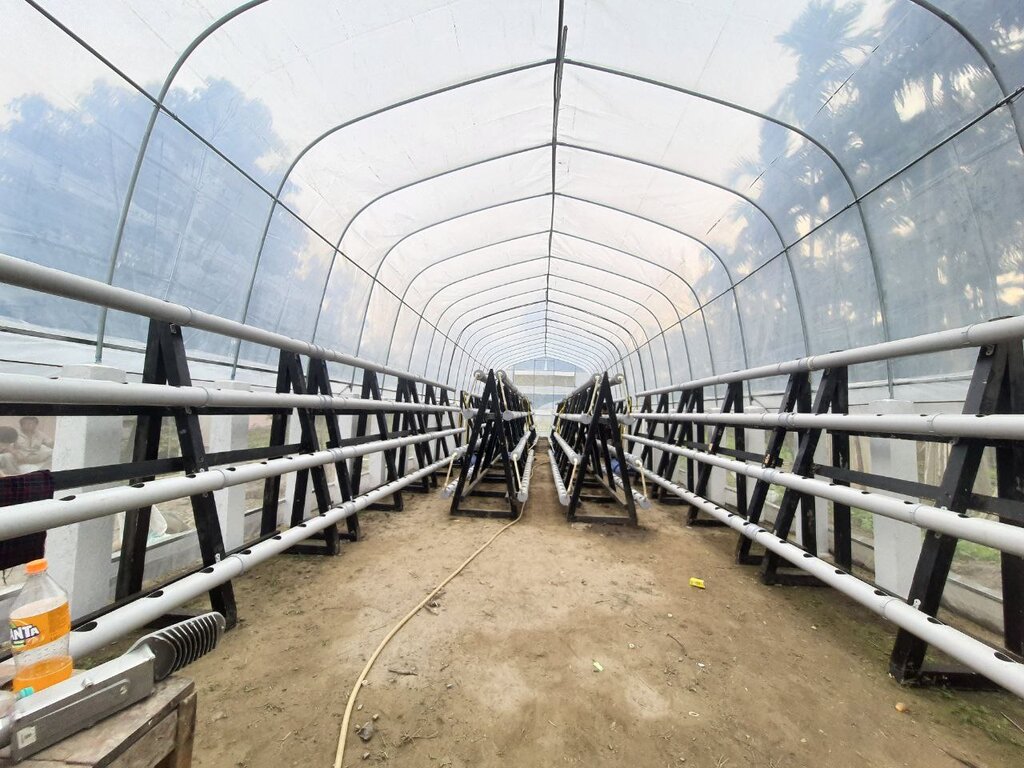
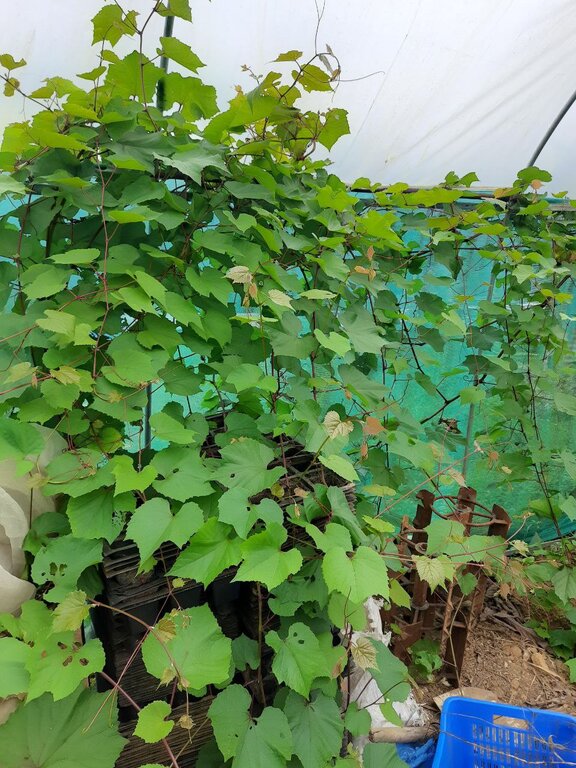
Protected agriculture, also known as controlled environment agriculture, refers to the practice of growing crops within an enclosed structure that provides controlled environmental conditions. There are various structures that can be employed, such as greenhouses, shade nets, polytunnels and glasshouses. This documentation focuses on greenhouses. These are commonly used for cultivating high-value crops that yield a higher economic return per unit area compared to traditional field crops. Technical specification for a 20 m x 5 m greenhouse set consists of a galvanized tubular frame, two doors, UV stabilized 120 GSM cross-laminated clear plastic sheet, channels and a nylon belt for holding the plastic sheet. Construction activities include clearing, levelling the ground and ensuring drainage. Installation of water lines, electrical connections, heating systems and ventilation systems is required.
Greenhouses are typically designed with a framework made of materials like metal, wood, or PVC. The structure must be sturdy enough to support covering materials and withstand environmental loads such as wind and snow. Coverings are transparent or translucent materials that allow sunlight to enter the structure. Common options include glass, polycarbonate panels, or plastic film. The choice of covering material depends on factors such as light transmission, insulation properties, durability, and cost. Greenhouses require adequate ventilation to control temperature, humidity, and air circulation. Vents, louvres, or roll-up side walls can be used to regulate airflow and prevent heat buildup. Exhaust fans or natural ventilation methods help remove excess heat, humidity, and carbon dioxide from the structure. Efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation, and micro-sprinklers, are used to deliver water directly to plants' root zones. Raised beds of 1.2 m width and 30 cm height and planting distance of 60 cm are applied for (for example) watermelon.
Greenhouses allow for the cultivation of plants throughout the year, regardless of the external weather. By maintaining a stable and favourable climate inside, growers can start plants earlier in the spring, extend the growing season into the fall, or even grow plants year-round in certain regions. It shields plants from adverse weather conditions such as frost, heavy rain, wind, or hail, which can damage or destroy crops. Greenhouses provide a physical barrier that safeguards plants from external threats, minimizing the risk of disease, pests, and other environmental stresses.
Greenhouses provide a range of benefits and impacts, including increased food production by extending the growing season and improving food security. They produce higher crop yields by providing optimal growing conditions and conserving water through efficient irrigation systems. Greenhouses also contributes to reduced pesticide use, energy efficiency, local and seasonal produce, employment opportunities, research and innovation, and serves as an attractive space for recreation and education. Overall, greenhouses offer sustainable and efficient solutions for agriculture while enhancing environmental stewardship and community well-being.
Protected agriculture through the use of greenhouses offers land users the ability to control environmental factors, leading to optimal conditions for plant growth and higher crop yields compared to open-field cultivation. It protects from adverse weather conditions, reducing crop losses due to frost, rain, or wind. Additionally, the controlled environment minimizes the risk of pests and diseases, resulting in fewer losses and reduced reliance on pesticides. Overall, greenhouses enhance productivity, profitability, and sustainability for land users. On the other hand, setting up a greenhouse requires a significant initial investment, including the construction or purchase of the structure, equipment, and environmental control systems. Operating a greenhouse involves ongoing costs for utilities, maintenance, and replacement of equipment, which can impact profitability. The cost can be reduced by establishing a low cost greenhouse with locally available materials such as bamboo.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
https://www.youtu.be/i8izu3PmQRE
This link provides poly house construction basics video prepared by ARDC Bajo officials and JICA experts of Integrated Horticulture Promotion Project
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/11/2020
ទីតាំង:
Agriculture Research and Development Sub Centre Tsirang
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
JICA Experts and ARDC Bajo Officials
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Dagana Dzongkhag
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Tsendagang Gewog
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
It is leased land and does not fall under a permanently protected area.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2020
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
- Through other farmers
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
- កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- To improve livelihood
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- បន្លែ - ត្រសក់ផ្អែម ល្ពៅ ពពួកបន្លែទ្រើង
- បន្លែ - ផ្សេងៗ
- Chilli
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ) - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ចេក/plantain/abaca
- ដំណាំយកផ្កា - មានរយៈពេលវែង
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ដើមឈើយកគ្រាប់ (brazil nuts, pistachio, walnuts, almonds, etc.)
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំដែលដាំចន្លោះគ្នានោះ:
Watermelon and zucchini are intercropped
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Watermelon is followed by chilli or beans cultivation on the same land
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
- Natural forest
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃស្រោង
មតិយោបល់:
The land is a cleared settlement from indigenous subtropical forest. Land use changed from subtropical forest to the agroforestry system where few native trees were retained with fruit trees and crops cultivated.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
មតិយោបល់:
Protected agriculture - especially greenhouses - depends on full irrigation with a drip irrigation system.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ប្រព័ន្ធដំណាំបង្វិល (ការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំ ការទុកដីចោលដើម្បីបង្កើនជីជាតិ កសិកម្មពនេចរ)
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវការបង្កាត់ពូជរុក្ខជាតិ/ សត្វ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S1: ការធ្វើដីថ្នាក់ៗតាមជម្រាលភ្នំ
- S11: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
មតិយោបល់:
For the introduction of the technology, excavated or cut-and-fill bench terraces were built to install greenhouses.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bp: ការកើនឡើងនូវសត្វល្អិត ឬជំងឺ បាត់បង់នូវសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
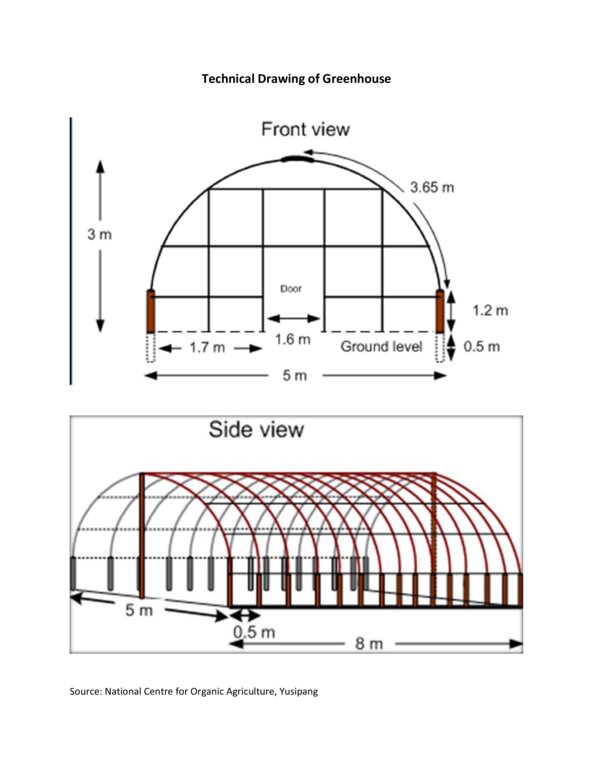
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
The technical drawing provided is for the low-cost greenhouse (Made up of bamboo). Generally, the length of a commercial greenhouse is 10 or 20 m and the width of 5 m. The greenhouse can be modified based on the crop to be cultivated. Additional facilities such as drip irrigation set, blower, fan, cooling pad and exhaust fan, temperature sensors are added modify the environment.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
National Centre for Organic Agriculture, Yusipang
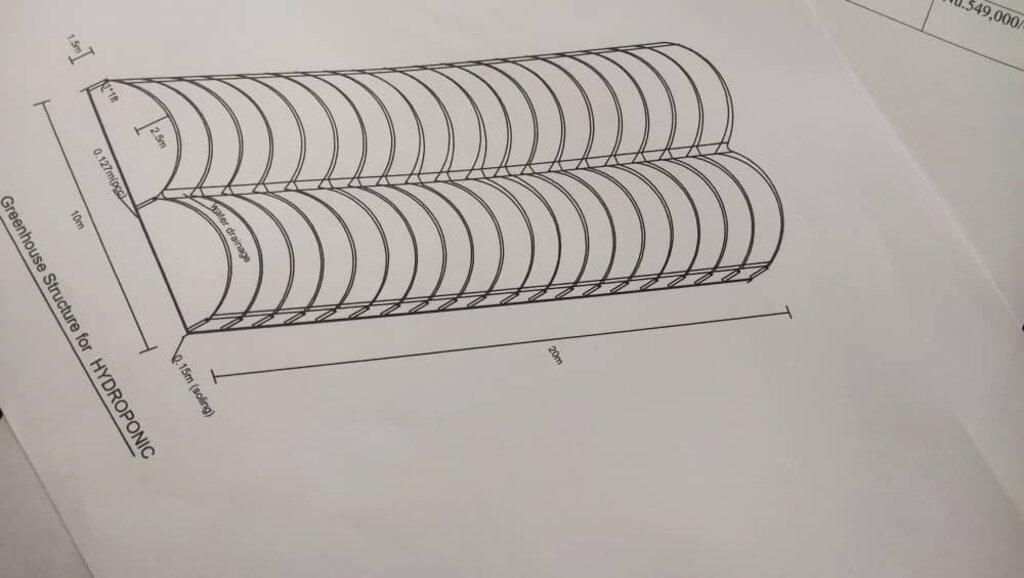
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical details for setting up 5m by 20m double poly house protected structure
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ARDC Bajo
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/07/2020
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
3.75 acres
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Ngultrum (Nu.)
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
79,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
500
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of vegetations | Winter |
| 2. | Agriculture land development | Winter |
| 3. | Field preparation | Winter |
| 4. | Installation of greenhouse and other structure | Winter |
| 5. | Sowing and plantation of crops and fruits (especially late winter crops) | Winter |
មតិយោបល់:
The installation of a greenhouse can be done in any season. However, the most preferred time for the installation is in winter when the crops standing in the field are minimal and the land users are not involved in other farming activities such as paddy cultivation.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Farm establishment | Number | 30,0 | 500,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Installation of structure and plantation | Number | 15,0 | 500,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Excavator (farm establishment) | Number of days | 12,0 | 24000,0 | 288000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Power tiller | Per hour | 16,0 | 250,0 | 4000,0 | 50,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Dragon fruit | Per sapling | 300,0 | 50,0 | 15000,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Watermelon seed | Per packet | 1,0 | 2700,0 | 2700,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Greenhouse | Number | 6,0 | 80000,0 | 480000,0 | 20,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Dragon fruit staking | Number | 39,0 | 700,0 | 27300,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 839500,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 10626,58 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Royal Government of Bhutan (RGoB)
មតិយោបល់:
For a greenhouse it costs Nu. 80000. Therefore, the total cost of six green houses that are available at the farm is Nu. 480000 (USD 5790). For the greenhouse, 80% is borne by the RGoB. However, for the overall establishment major costs were borne by the land user and a minimal cost was part of the subsidy/fund support from RGoB as shown in the table above. The land user has 4.9 acre of which 3.75 acre is cultivated and 0.11 acre is under protected agriculture.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
មតិយោបល់:
The land user haven't carry out any maintenance due to the recent establishment of the farm. However, there is likely to have a maintenance cost of Nu. 5000 (USD 289) for the greenhouses and overall recurrent cost of Nu. 41975 (USD 506) per annum.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
No maintenance has been carried out
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Infrastructure and machinery.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
The area falls under a humid subtropical and warm subtropical zone among the six agro-ecological zones of Bhutan.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Moisture content 3.31%, organic matter 5.03%, organic carbon 2.92%, pH 5.67, electrical conductivity 337.67 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.15%, phosphorus 0.09 ppm, potassium 123.07 mg/100ml, texture sand clay loam.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
The soil data shared under the section 5.2 is for the growing media used inside the greenhouse. Land user adds organic manure to the existing topsoil which is used as a growing media.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
There is a water shortage during the winter season.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
The species and habitat diversity in the questions above are referred to the farm and not inside the greenhouse.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
The land user has 4.9 acres of which 3.75 acres are cultivated. The average land holding in Bhutan is 3.4 acres, therefore the land users owning/farming more than 3.4 acres are categorized as large-scale.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Land leasing is a traditional legal system where the land user has a contract with the owner for 20 years. After the completion of the contract term, the land and the infrastructures are to be handed to the land owner.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Compared to open fields, protected agriculture has shown an increase in production. This could be due to the extended growing period, reduced disease incidence and ease of performing cultural activities.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The crop quality is improved in the protected agriculture as the optimum environmental conditions are provided.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The risk of production failure is reduced as the crop is not exposed to abiotic stress.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
20%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Land management in the protected cultivation is easier compared to open field.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Initial investment for the establishment of the protected structure is high. However, the expenses on agricultural inputs were reduced after establishment. Further, the initial negative expenses are compensated by the return from selling the farm produce.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
70%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
There is a significant increase in the farm income after the establishment of the protected structure as the quantity and the quality of the high-value crops increased fetching higher prices. This has led to an increase in farm income.
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The workload has reduced after the establishment of the greenhouse. For example, the greenhouse is equipped with a drip irrigation system in which the land users can regulate the irrigation frequency and need not water the plants manually.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
80%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The increase in agricultural production has made the land user self-sufficient in certain fruits and vegetables. The technology has also contributed to the food security of the farm household as the income generated from the farm can be used to purchase nutritious foods that are not available on the farm.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Unlike flooding irrigation in open fields which requires a large amount of water, a protected structure optimizes water usage. It is achieved by drip irrigation and manual irrigation leading to minimum water wastage. This increases water availability on other parts of the farm or for the community.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | ល្អណាស់ |
| ការមានបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិត/ដង្កូវ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Improved market access. Protected structures enable off-season cultivation of certain high-value crops such as chilli and beans leading to higher market access and increased income. |
| Reduced pest and disease incidence. This could be due to optimum growing conditions provided to the plant and ease of pest and disease management. For example, the land user can remove a part of the plant that is infested or remove the crop that is infested in the particular greenhouse and still obtain the yield from other greenhouses. This is not possible in the open field condition. |
| Improved quality of the crops. The environmental conditions inside the greenhouse can be maintained at the optimum level required by plants leading to better quality produce. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Reduced workload. After the establishment of the protected structure, there is less workforce required for the cultivation. |
| Increased production. The land users can extend the growing period in the enclosed structure which leads to increased cropping season per year maximizing agricultural production. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The establishment of the technology has high initial investment. | Getting loans from financial institutions and sourcing fund from the government. |
| The farm is challenged with labour shortage. | Increasing the daily wage of labour and providing necessary facilities such as clean drinking water, washing and toilet facilities and providing incentives to retain them. |
| Difficult to manage the farm. | Improving record keeping, developing farm calendar and scheduling activities. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
One
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
One
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
12/07/2023
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
ARDC Wengkhar. (2017). Activity completion report for CARELP support to ARDC-Wengkhar.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.carlep.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Activity-Completion-Report-2016_17_CARLEP-Support-to-ARDC-wengkhar_FINAL.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwi3wZSPj_CAAxUB3TgGHTh_A0cQFnoECBEQAQ&usg=AOvVaw3lsXjKzuaScR91V1MntyJZ
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Polyhouse Construction Basics in Bhutan (Dzongkha language)
វេបសាយ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=i8izu3PmQRE
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Enhancing Agricultural Production Through Fallow Land Reversion [ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់]
The approach is to enhance production of local vegetables and fruits through fallow land restoration - under a group established for the purpose.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nima Dolma Tamang
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល