Reconstitution of Soils [ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Chiara Cassinari
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ricostituzione
technologies_7346 - ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Manfredi Paolo
mcm Ecosistemi
ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី
co-compiler:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
NEW LIFE Project (NEW LIFE)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
m.c.m Ecosistemi (m.c.m Ecosistemi)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
Reconstitution is a technology that counters land degradation and according to the theory of "Circular Economy" it's a sustainable land management technology
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Chiara Cassinari
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Reconstitution of soils is a pedotechnique based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials to achieve benefits in areas with barren, degraded, desertified and/ or sealed soils.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
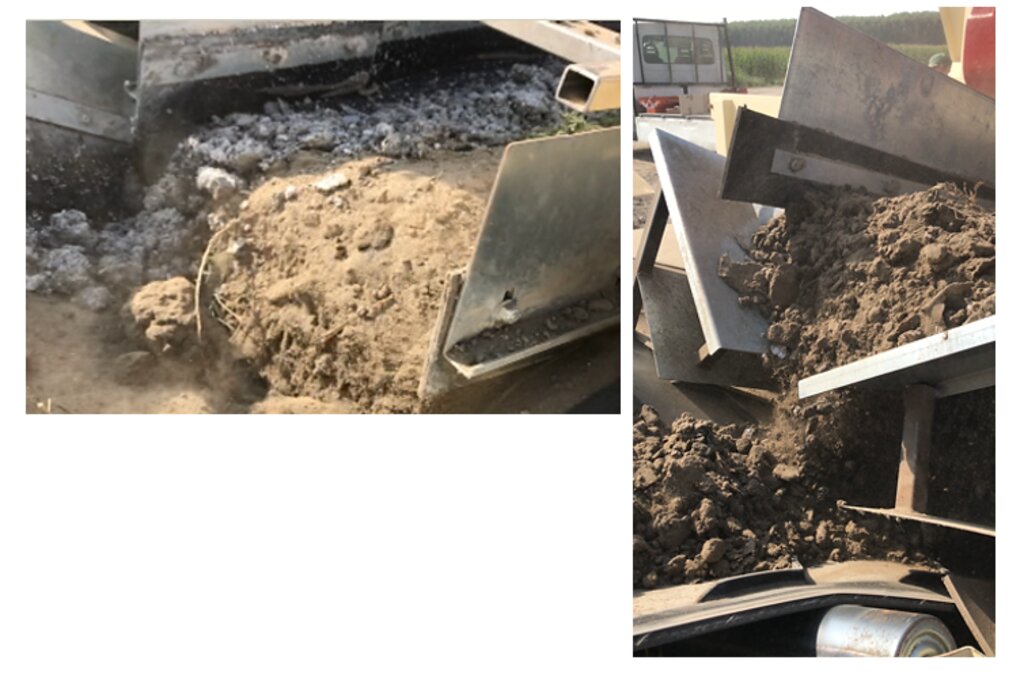
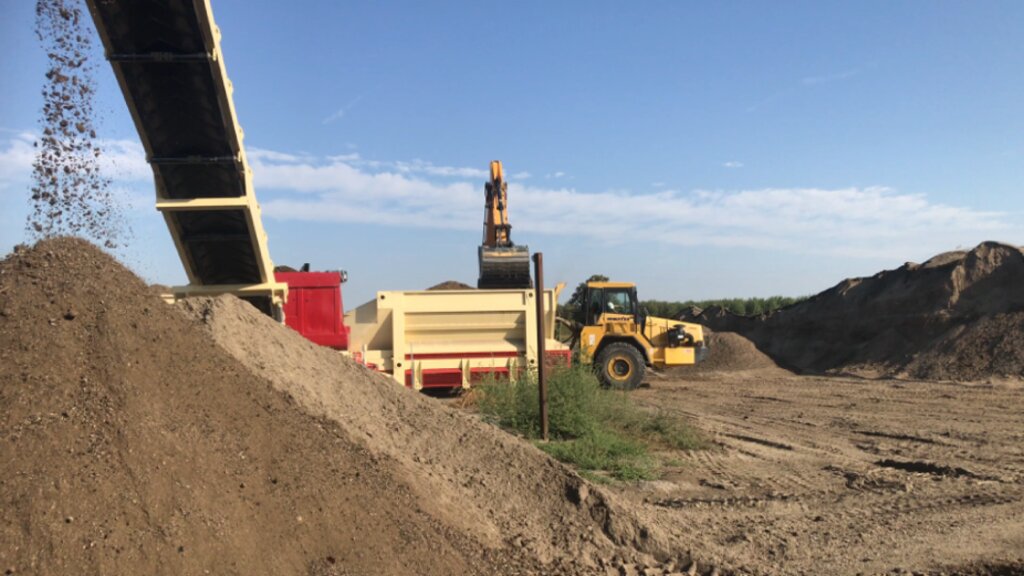
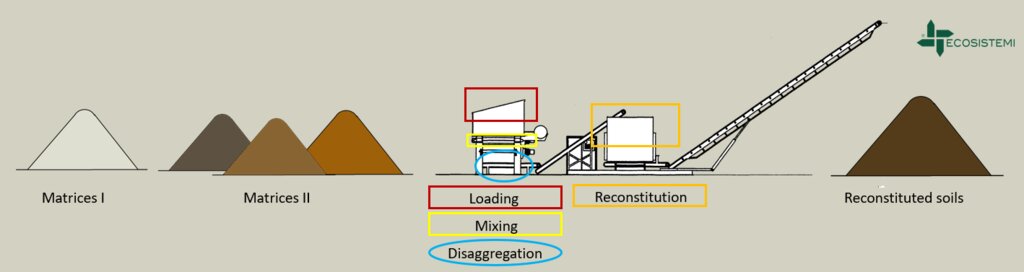
Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
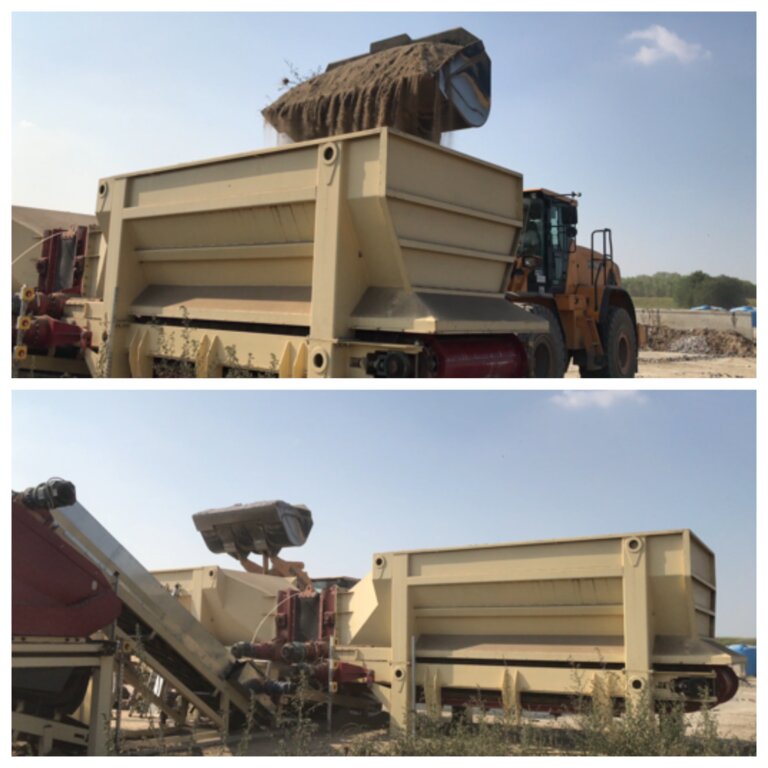
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
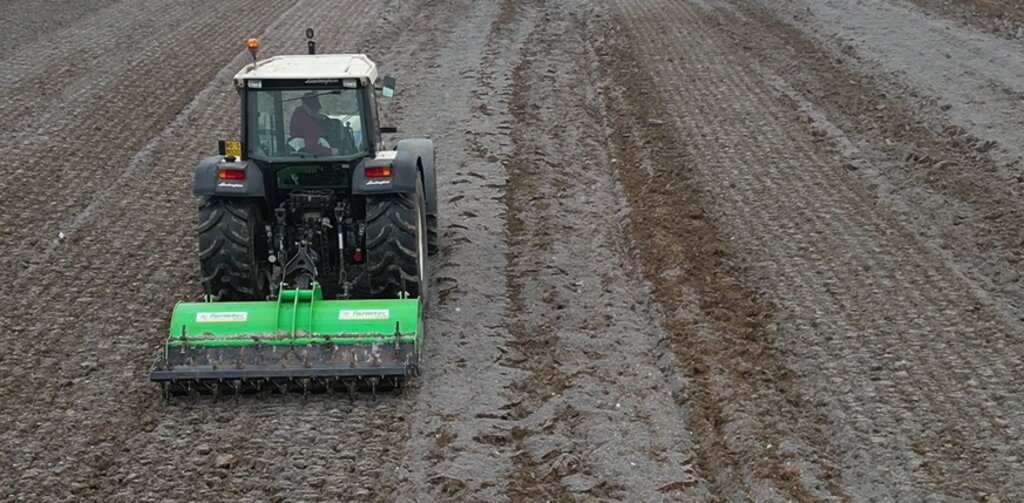
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
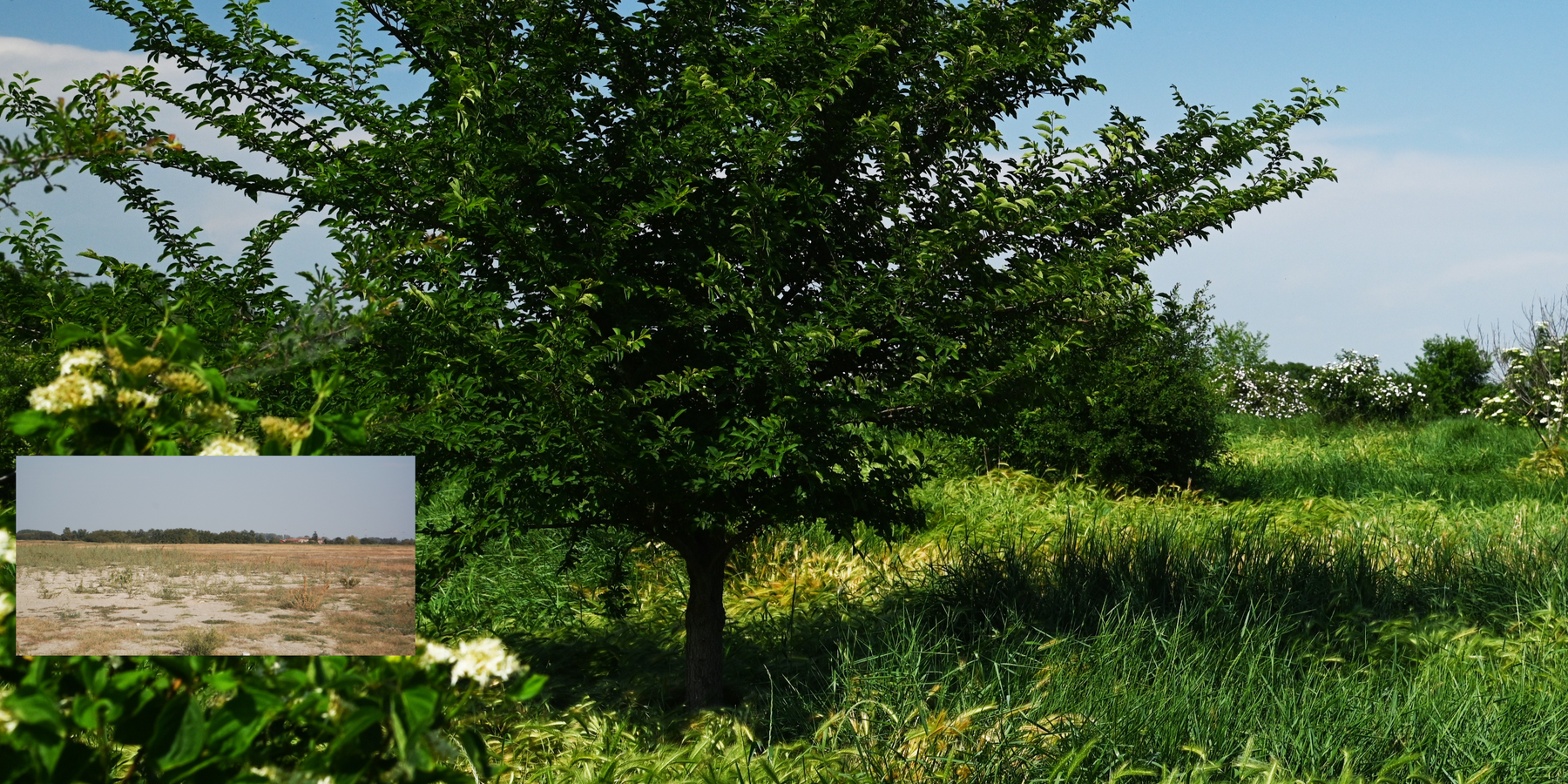
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF3nl4S5X8M
Reconstitution plant
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
18/12/2024
ទីតាំង:
Piacenza, Loc. Mortizza
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Paolo Manfredi
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kjy95Kz-e70
Construction site: collection of degraded soil to be reconstituted
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
18/12/2018
ទីតាំង:
Piacenza, Gossolengo
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Paolo Manfredi
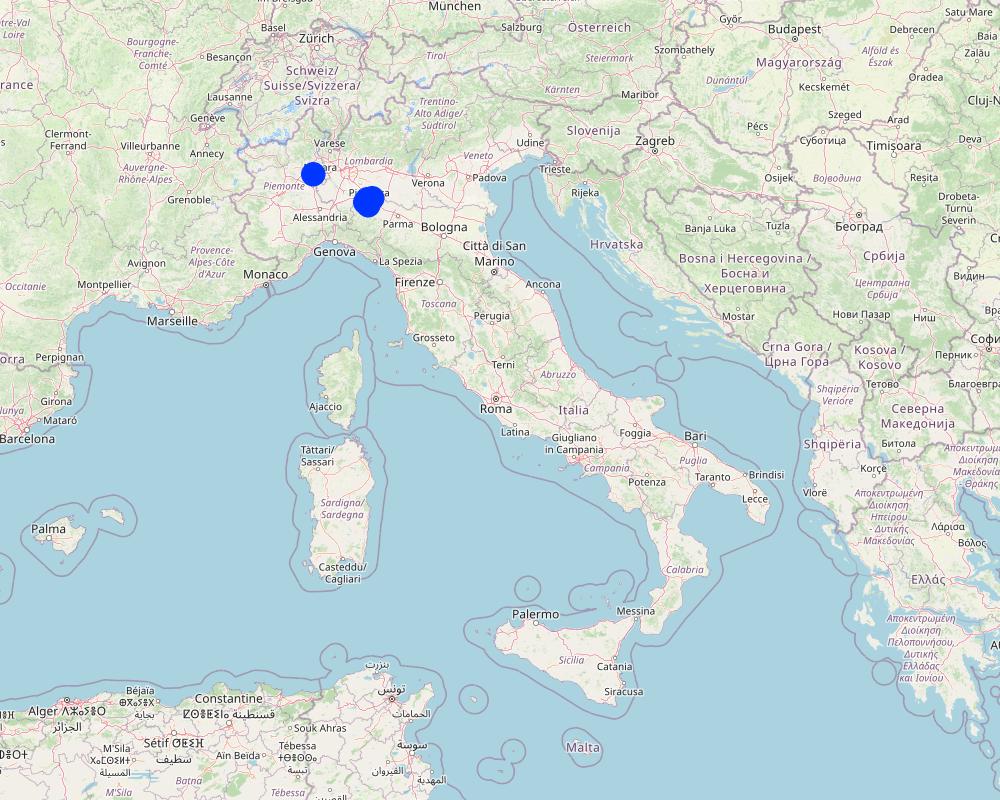
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 1-10 គម2
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Regional, National and International projects
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- tomato, fodder crops
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
maize - wheat - tomato

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ប្រភេទព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ:
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៃព្រៃស្ងួតធម្មជាតិតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ពូជបញ្ចូលគ្នា
ប្រភេទដើមឈើដែលដាំនៅកន្លែងដែលមិនធ្លាប់មានឈើពីមុន :
- ព្រៃស្ងួតដាំតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច
ប្រភេទឈើ:
- Acacia species
- Populus species
- Salix species
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃល្បោះចម្រុះ/ ព្រៃស្រោង
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ការអភិរក្ស/ការការពារធម្មជាតិ
- ការកំសាន្ត/ទេសចរណ៍
- ការពារពីគ្រោះធម្មជាតិ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
ឧស្សាហកម្មទាញយករ៉ែ

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
degraded, desertified and sealed soils
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់/ ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកកង្វក់
- ecosystem rehabilitation
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A4: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងក្នុង

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S11: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងសំណល់ (កែឆ្នៃទ្បើងវិញ ប្រើប្រាស់ឡើងវិញ ឬបន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់)
- M7: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការផ្សេងៗ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
addition of organic matter, new soil aggregates, increase water holding capacity
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
- Ca: អាស៊ីតកម្ម
- Cs: សារធាតុប្រៃ/អាល់កាឡាំង

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pi: ការគ្របផ្ទៃដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Reconstituted technology: phases of work:
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected and dosed
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity
3) Disaggregation through rotating movements at variable power
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Paolo Manfredi
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
12/04/2023
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
10 hectares
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
EUR
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,89
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
123.00, gross income
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | characterization of the intervention site | no timing |
| 2. | morphological planning | no timing |
| 3. | environmental planning | no timing |
| 4. | pedo-agronomic planning | no timing |
| 5. | moving-plant placement only if the area to be restored is distant from the area where the permanent plant is located | no timing |
| 6. | degraded soil removal and collect | after harvest of crops, if there are |
| 7. | reconstitution | no timing |
| 8. | replacement of reconstituted soil | no timing |
| 9. | final soil placement | no timing |
| 10. | site-specific planting to make soil ready for use | dependence of plants species |
| 11. | land use | no timing |
មតិយោបល់:
The reconstitution plants are 2: one is fixed that is located in an area, the other is a moving-plant: that is it can be located near the area to be restored.
According to the distance between the intervention site and the fixed plant it can be more useful using the moving-plant
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 3 Workers | person/day | 232,0 | 123,0 | 28536,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Earth moving vehicles | number | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000,0 | 15,0 | 1125000,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Reconstitution | m3 | 100000,0 | 2,5 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1473536,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1655658,43 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Costs related to the matrices to be used and transport (1125000.00 EUR) are covered by company producing waste used. The costs to dispose of matrices II are much higher than taking them to the reconstitution plant.
មតិយោបល់:
degraded land value 0 EUR
restored area value 390000 EUR
restoration using allocation of natural soil (8 EUR/m3, cost of natural soil in Piacenza) added to transport costs = 2100000.00 EUR
restoration using reconstituted soil technology = 28536 + 30000 + 40000 + 250000.00 EUR because 1125000.00 EUR are covered by company producing waste and so not spent for restoration.
Cost related to construction area and mobile plant are the costs for the set up of the area where to put the mobile plant and for it' transport to the intervention site.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ordinary plant maintenance | every 6 months or when needed |
| 2. | Reconstituted soil analysis | every 6 months |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 1 Worker | person/day | 20,0 | 123,0 | 2460,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100,0 | 115,0 | 11500,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 13960,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 15685,39 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The most important factor affecting costs could be the transport of degraded soil or matrices I to be used to the restoration site in the case of soil sealed
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
891,02
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
May: average monthly regionally anomaly +230% (heavy rains); October: heavy rains
February 2023 is the month with less rain 27.6 mm; in May is the rainiest 250.7 mm
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Bulletin ARPAE 2023
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
mean annual temperature 14.4 °C Bulletin ARPAE 2023
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Following the soil characterization (data are mean of 30 soil samples) of the last area of intervention with reconstitution; the data describes soil condition before reconstitution.
The soil texture is silty-loam
The aggregate stability index describes soils with poor stability
pH (1:2.5 in H2O) 6.98 ± 0.37
EC (saturated paste) 0.93 ± 0.41 dS m-1
tot CaCO3 10.33 ± 4.36 g kg-1 SS
active CaCO3 3.08 ± 1.24 g kg-1 SS
tot C 10.62 ± 3.68 g kg-1 SS
organic C 10.26 ± 3.44 g kg-1 SS
tot N 1.47 ± 0.43 g kg-1 SS
HA + FA 2.54 ± 1.26 g kg-1 SS
Olsen P 87.83 ± 44.19 mg kg-1 SS
available Fe 74.68 ± 32.97 mg kg-1 SS
available Mn 27.92 ± 15.78 mg kg-1 SS
available Zn 2.30 ± 1.72 mg kg-1 SS
available Cu 4.32 ± 1.34 mg kg-1 SS
soluble B 0.71 ± 0.25 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable K 21.61 ± 34.72 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable Mg 92.68 ± 28.13 mg kg-1 SS
CEC 26.22 ± 4.42 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Mg2+ 2.39 ± 0.50 cmol(+) kg-1
exch K+ 0.42 ± 0.33 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Na+ 0.48 ± 0.22 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Ca2+ 11.82 ± 4.75 cmol(+) kg-1
Chemical fertility is low, intrinsec fertility is poor, global fertility lower-intermidiate
In the link other data about soil analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Hb0PcmSYGY&list=PLXcG4R_rAdFaqGnKCa0qaL6FcrafvU0VE
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកក្រោមដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
60%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
គុណភាពដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
70%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
95%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
65%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
these increment are estimation
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
0
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
60%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
60%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
60%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
15%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
ដី
សំណើមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
គម្របដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
50%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
ដីប្រេះ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
50%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
0%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
ដីហាប់
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
50%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
60%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
80%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
80%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
80%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
0%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
40
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
20%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
50%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
50%
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
10%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ស្ថានភាពខ្យល់ខ្លាំង | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
The recycle of suitable waste materials used defrays the reconstitution technology in short and long term
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ផ្សេងៗ (សូមបញ្ជាក់):
the Technology is partly modified to face every restoration project
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
design, matrices to be used
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Strengths: to change soil class in Land Capability Classification, to improve soil workability, to create new soil aggregates (the organic matter is covered by fine soil mineral fractions) |
| Advantages: to increase soil fertility, to implement Circular Economy |
| Opportunities: to create a non-renewable resource (soil) and/or to restore it, to implement Circular Economy |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Strengths: to produce the suitable soil for the environment where it will be placed |
| Advantages: to reduce the use of fertilizers |
| Opportunities: to restore soil using suitable waste, Circular Economy |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: demand exceed supply, concerning current number of workers employed in the reconstituted plant | formation of new workers |
| Risks: crisis of industries producing suitable waste | non-stop search for suitable waste to use |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: contamined soils | studies about possibility of using reconstitution to clean soils |
|
Risks: the pedotechniques include all the anthropic activities that determine a growing influence of man on pedogenesis and pedolandscapes; they have to satisfy man needs while avoiding any undesirable environmental consequences (Dazzi et al., 2010). This is the main core of reconstitution of soils, but sometimes, the use of waste material, even if, environmental suitable, isn't understood because of waste are considered materials only for disposal. |
Dissemination concerning the laboratory analysis before the waste use, studies and research projects with University to test environmental suitability of reconstituted soils |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
2 visits/survey a year
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
each land user where technology was adopted
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
15/03/2023
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
The reconstitution pedotechnique: Applications, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102246
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
The reconstitution: environmental restoration assessment by means of LCC and FCC, 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/8500
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Trees and shrubs monitoring using an ecological approach: the conclusion of the restoration project of Borgotrebbia landfill (Northern Italy), Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Meloni F., Stragliati L., Trevisan M., Giupponi L., 10.31031/EAES.2019.06.000635
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
A new technology to restore soil fertility: Reconstitution, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Francaviglia R., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201933
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Growth and yield response of tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) to soil reconstitution technology, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Gatti M., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201916
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Test on the effects of reconstituted soil on emergency speed and root growth in maize, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Salvi R., Battaglia R., Marocco A., Trevisan M., 10.1515/contagri-2018-0035
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Osservazione di Lycogala terrestre Fr. e Stemonitis axifera (Bull.) T. Macr. su suoli ricostituiti sabbiosi, Manfredi P., Salvi R., Bersan M., Cassinari C., Marocco A., Trevisan M.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Relationship between hydraulic properties and plant coverage of the closed-landfill soils in Piacenza (Po Valley, Italy), Cassinari C., Manfredi P., Giupponi L., Trevisan M., Piccini C., 10.5194/se-6-929-2015
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Soil temperature fluctuations in a degraded and in a reconstituted soil, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., ISBN 20385625
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Confronto tra dati produttivi di mais coltivato su terre ricostituite e terre naturali, Manfredi P., Tassi D., Cassinari C.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Scientific Journal
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Ecosistemi web site
វេបសាយ:
https://www.mcmecosistemi.com/
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Paolo Manfredi ResearchGate
វេបសាយ:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Manfredi-2
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Chiara Cassinari ResearchGate
វេបសាយ:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chiara-Cassinari
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
All the publications with DOI mentioned above
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Ecosistemi YouTube channel
វេបសាយ:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCOloFv-BLgvIVt9kBZuZyZg
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
Very useful questionnaire
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [ប្រទេសអ៊ីតាលី]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Chiara Cassinari
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល