Tree Plantation Pits in Arid Zones [ប្រទេសអារ៉ាប៊ីសាអូឌីត]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Eric Lacroix
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Plantation pits
technologies_7380 - ប្រទេសអារ៉ាប៊ីសាអូឌីត
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Al Eissa Abdullah
NCVC
ប្រទេសអារ៉ាប៊ីសាអូឌីត
co-compiler:
co-compiler:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Boudi Dr. Nabeel
FAO
ប្រទេសអារ៉ាប៊ីសាអូឌីត
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Sustainable Rural Agricultural Development Programme (UTF/SAU/051/SAU) (SRAD Saudi Arabia)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
FAO Saudi Arabia (FAO KSA)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
This method allows sustainable plantations with a satisfactory level of success in hyper-arid zones (under 100 mm rainfall per year).
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Tree plantation pits are water harvesting structures which capture rainfall runoff for trees and shrubs. They receive supplementary water until seedlings are well established. Species planted are indigenous, and provide both shade and honey.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Plantation pits are water harvesting structures that capture rainfall runoff for planting trees and shrubs. They are given supplementary water until vegetation is established. The pits are dug within national parks managed by the National Centre for Vegetation Cover Development and Combating Desertification (NCVC), which is the leader in this technology.
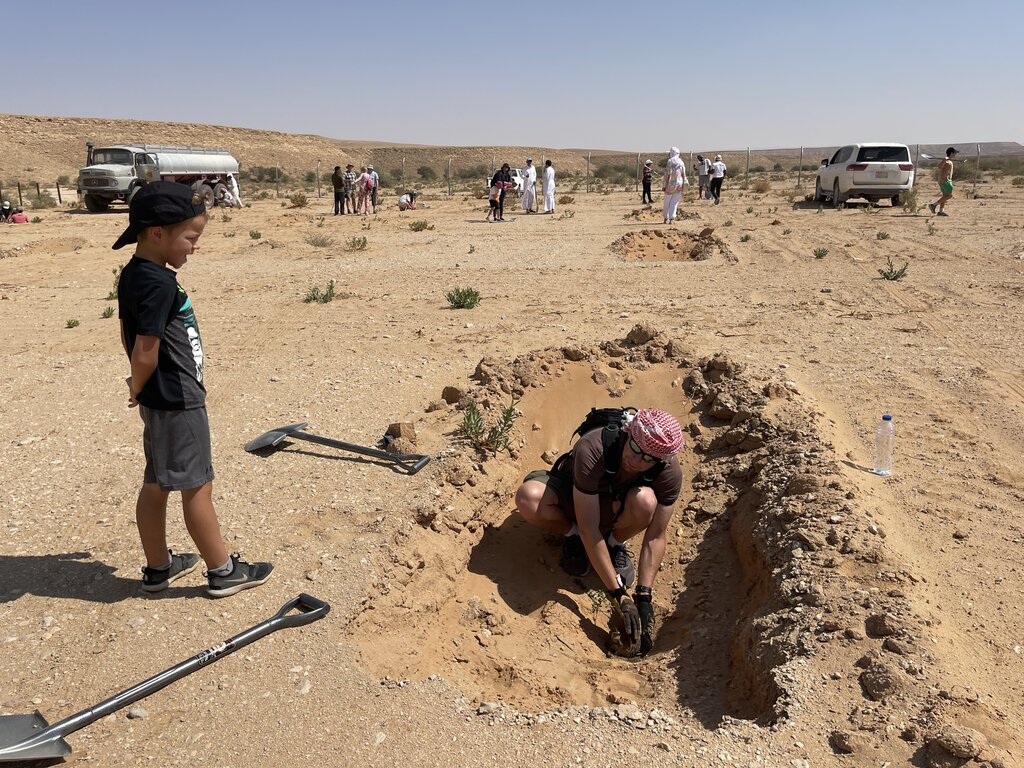
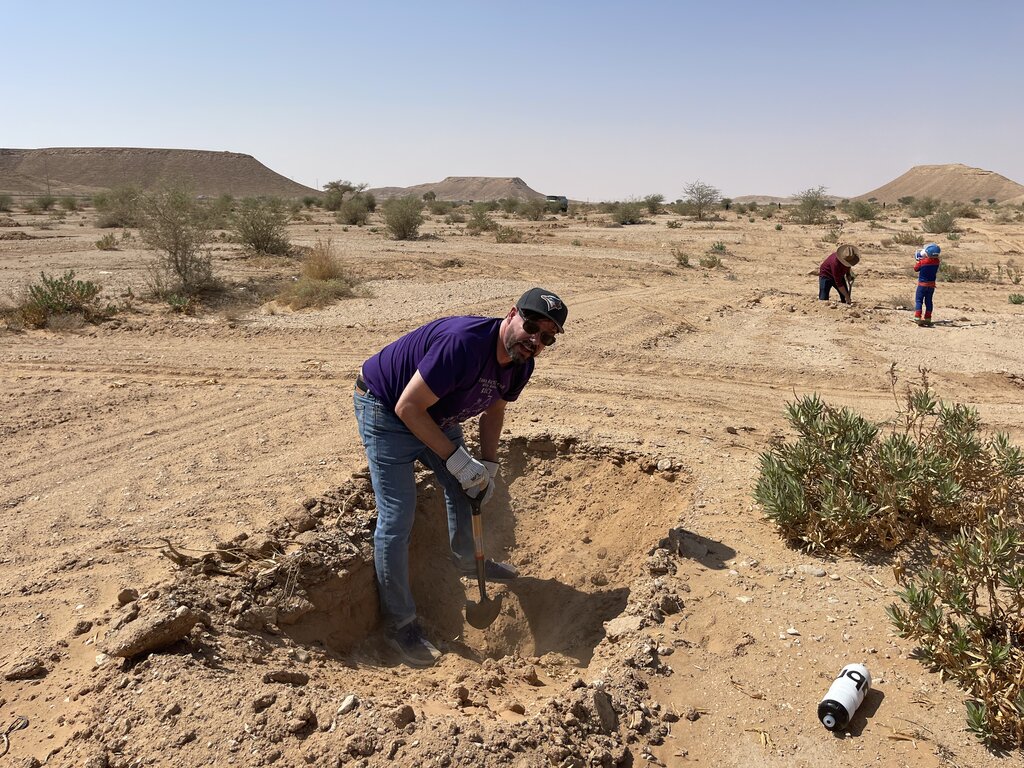
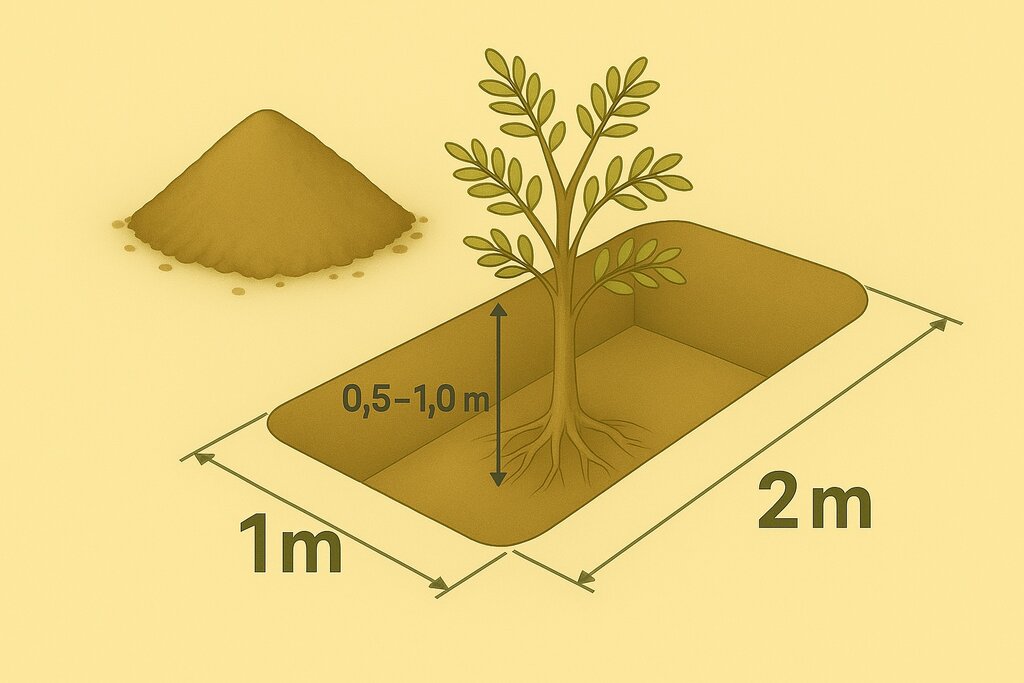
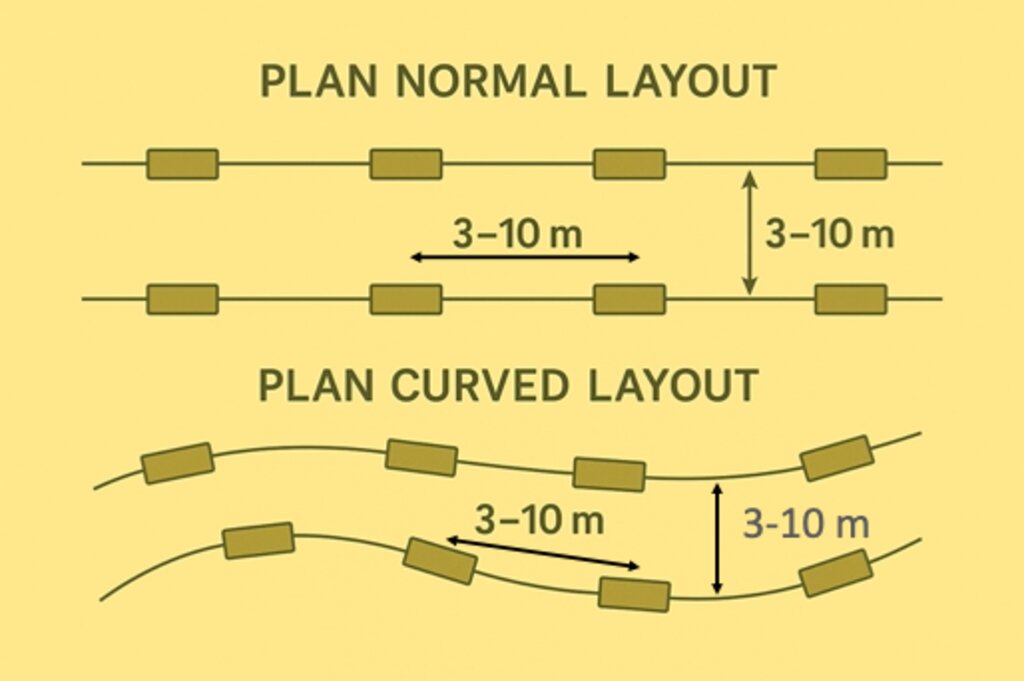
Pits may be located within wadis and sheyhib (small wadis), ranging in plots from ten to several hundred metres in length, and on high plateaux. The pits are often dug close to terraces and cross-wadi walls where runoff water is captured in the soil. Each plantation pit is rectangular, measuring (approx) 2m long, 1m wide, and up to 1m deep (depending on the depth of the soil). Spacing is from 3 to 10 metres between pits. The pits are excavated with mechanical diggers.
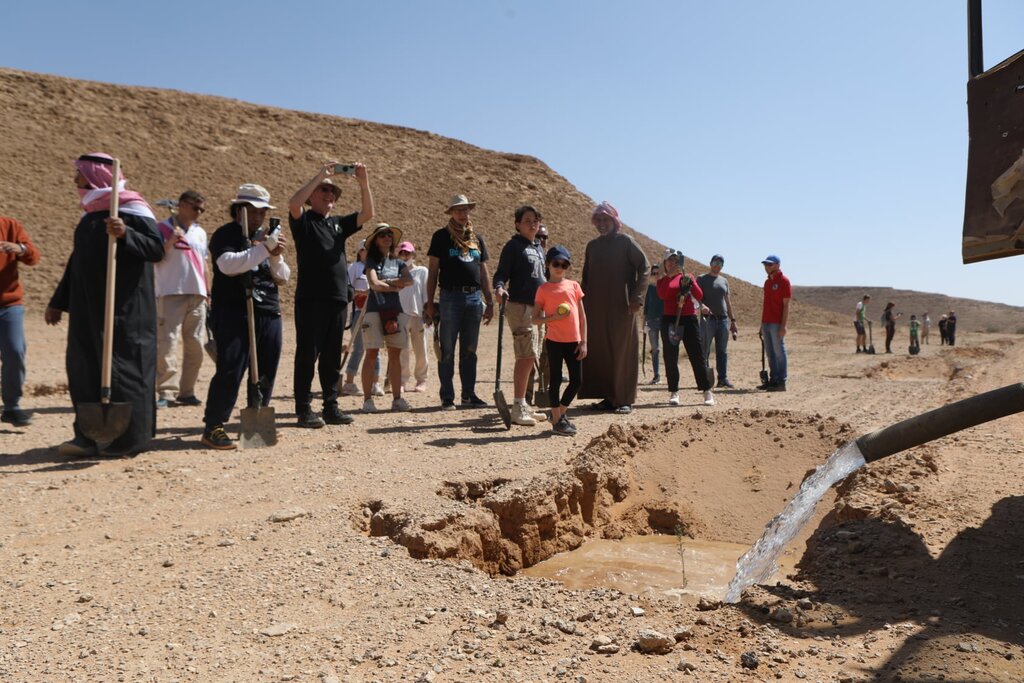
Pits are dug a year before planting, and they collect both runoff and the rich organic and mineral matter carried in the runoff. After one year, many annual and even perennial plants colonise the bottom of the pits. The trees and shrubs that are planted the most are Vachellia (Acacia) spp., Ziziphus spp. and Haxloylon spp. One (or two) seedlings are planted in the middle of each pit, without disturbing the existing vegetation as far as possible. These species attract bees, and beekeeping has been promoted alongside tree planting. Ziziphus honey is particularly high in value and Vachellia (acacia) honey is also good.
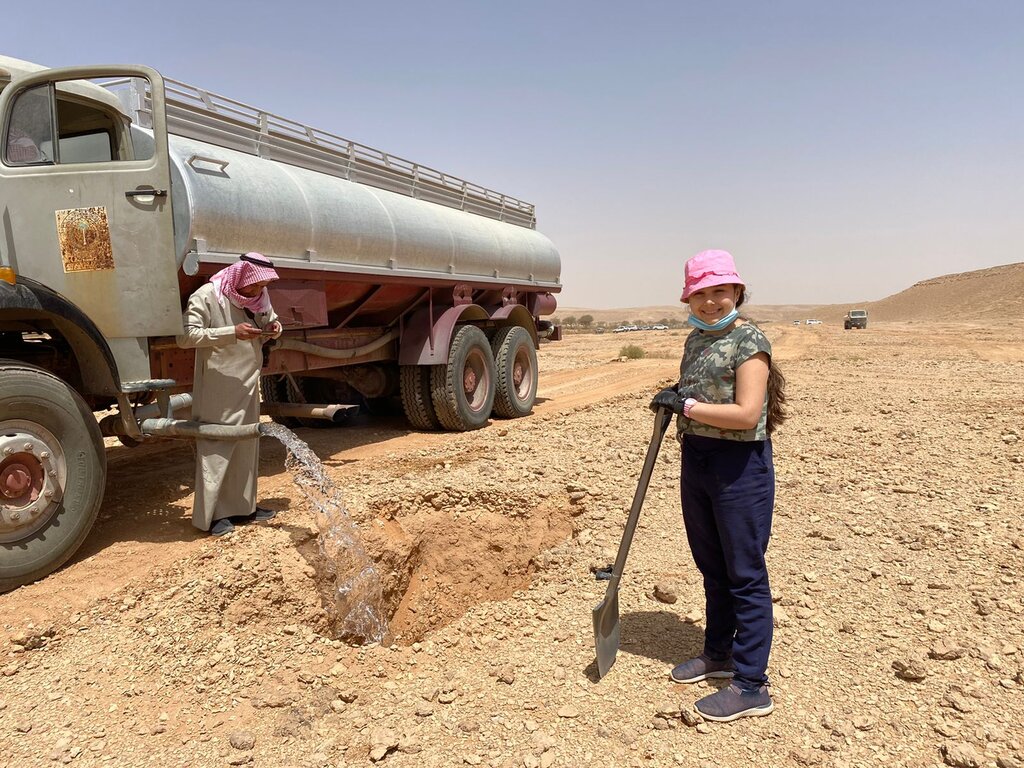
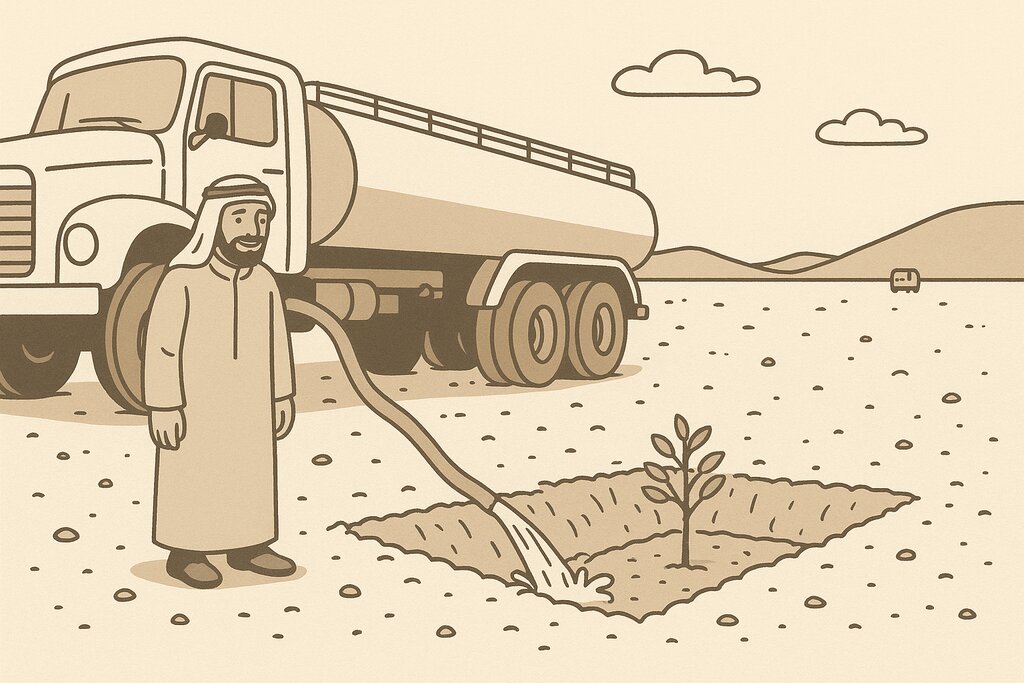
This water and nutrient harvesting technique is effective even in hyper-arid conditions, where rainfall may be less than 100 mm yearly. However, some supplemental irrigation is needed, and each pit is watered - every 4 months over 3 years - with a volume of water ranging from 20 to 100 litres each time per pit, depending on availability. Water is found in wadi beds and brought to the site in a bowser mounted on a lorry. Watering helps the plants to survive, and as it penetrates, it draws the roots down until they reach the water table. This is when watering can be stopped.
Although the costs are high, the results are generally very satisfactory regarding the survival rate. The local impact is significant when there are large blocks of pits and/ or greater numbers of pits per hectare (where this is possible). Over the last five years, a million pits have been dug.
Abdulla Al Eissa, the park manager, formulated the technical design of the pits, and FAO through the project "Strengthening MoEWA's Capacity to implement its Sustainable Rural Agricultural Development (SRAD) Programme (2019-2025) UTF/SAU/051/SAU" has been responsible for technical advice on locating pits, spacing and layout timing of operations, fertilization and planting operations. The activities are part-funded by the NCVC, while local donors and volunteers contribute the remainder.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
https://vimeo.com/1026092452?share=copy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
04/11/2024
ទីតាំង:
Thadiq national park
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Abdullah Al Eissa
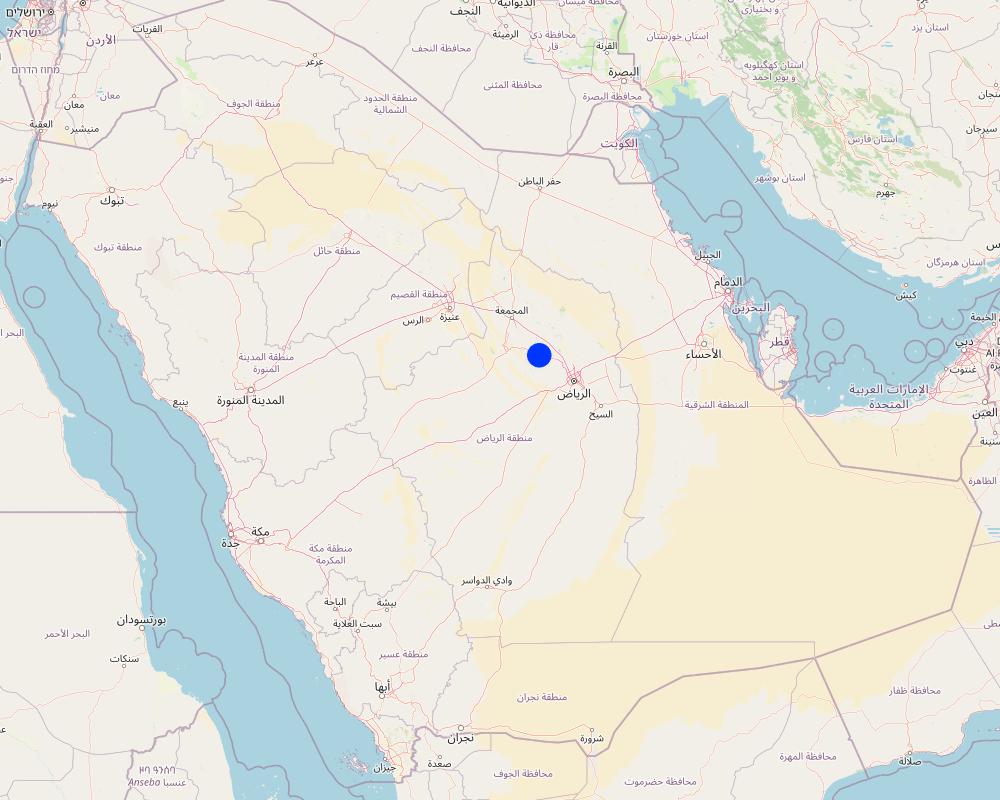
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអារ៉ាប៊ីសាអូឌីត
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Riyadh Region (Province)
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Thadiq National Park
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
148,0
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 100-1,000 គម2
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Dispersed within Thadiq National Park
មតិយោបល់:
This is a protected area (category V), IUCN, not yet registered in WDPA, 145 SQKM. This protected area is within the North Riyadh Geopark UNESCO (3000 SQKM). In the future, the National Park may extend and become a IUCN Protected area Category II.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2019
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Pits are established under a project which sets out to develop vegetation to protect the environment in the National Parks and to support tourism in the region, partly financed by the NCVC (paying for workmen's salaries, etc. ) and local donors (trucks, machines) and volunteers planting.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- ប្រើប្រាស់អនុផលព្រៃឈើ
ប្រភេទព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ:
- សារពើរុក្ខជាតិនៃព្រៃស្ងួតធម្មជាតិតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ពូជបញ្ចូលគ្នា
ប្រភេទដើមឈើដែលដាំនៅកន្លែងដែលមិនធ្លាប់មានឈើពីមុន :
- ព្រៃស្ងួតដាំតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច
- ព្រៃស្ងួតដាំតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច - ឈើស្លឹកធំ
ប្រភេទឈើ:
- Acacia species
- Acacia tortilis
- Ziziphus mauritiana
- Balanites aegyptiaca
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃល្បោះ
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ការអភិរក្ស/ការការពារធម្មជាតិ
- ការកំសាន្ត/ទេសចរណ៍
- ការពារពីគ្រោះធម្មជាតិ
មតិយោបល់:
The Royal Botanical Garden Kew's Plants of the World website now uses the name Vachellia for the genus formerly known as Acacia.
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
Supplementary water sourced from wadi beds (3 deep wells with electrical pumps).
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងព្រៃធម្មជាតិ និងព្រៃពាក់កណ្តាលធម្មជាតិ
- ការស្តុកទុកទឹក
- ការចិញ្ចឹមឃ្មុំ, វារីវប្បកម្ម, ការចិញ្ចឹមបសុបក្សី, ទន្សាយ, ដង្កូវនាង ។ល។
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S4: កម្រិតភ្លឺ រណ្តៅ
- S7: ការប្រមូលទឹកស្តុកទុក/ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក/ សម្ភារៈស្រោចស្រព
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pu: បាត់បង់នូវផលិតភាពជីវៈដោយសារសកម្មភាពផ្សេងៗ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
- Hp: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Each pit is 2 m long, 1m wide, up to 1m deep, spacing from 3 to 10 meters between structures in curved lines, or 3 meters apart in clusters. Watering with 20 to 100 litres depending on the availability and price of water and cost of transportation and watering. 100 pits minimum per hectare (maximum 1100, which is rare in this environment). One to three seedlings (tree, shrub, plant) per pit.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Éric Lacroix,
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
04/11/2024
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Watering system: truck with bowser (tank) and hose
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ChatGPT based on an image and explanations.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
04/05/2025
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Between lines and between pits: 3-10 meters. In lines or in curves or at random.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ChatGPT based on an image and instructions.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
06/05/2025
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
hectare with 100 pits
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
33-50 dollars
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identify the site | Dry season: Year 1 |
| 2. | Layout and mark the pits with stakes | Dry season: Year 1 |
| 3. | Dig the pits | Dry season: Year 1 |
| 4. | Produce the seedlings in a nursery | Dry season: Year 1 |
| 5. | Plant the seedlings | Rainy season: Year 2 |
| 6. | Water the seedlings (and replace dead ones) | Dry season: Years 2-4 |
| 7. | Check the pits during the first rain. | Rainy season: Years 2-4 |
| 8. | Check the pits after flooding | After flooding: Years 2-4 |
មតិយោបល់:
Based on a 4 year period - with trees seedlings planted 1 year after the pits are dug.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Workers for planting | Worker/day | 5,0 | 50,0 | 250,0 | 90,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Workers for watering | Worker/day | 18,0 | 33,0 | 594,0 | 90,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Excavator for digging pits (2 x 2 x 1 m) 100 pits /ha | Hour | 25,0 | 93,0 | 2325,0 | 90,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Truck with bowser/ tank for watering (100 litres /pit / 9 times over 3 years) | Truck/ 5000 litres | 18,0 | 47,0 | 846,0 | 90,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Tree Seedlings 200 /ha | Seedling | 200,0 | 4,0 | 800,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 4815,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 4815,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
The costs are paid through the National Park: 90% from private donations/ volunteer work and 10% by the National Center for Vegetation Cover NCVC. Seedlings supplied by NCVC.
មតិយោបល់:
The costs are spread over 4 years, by hectare, for 100 pits, including digging, planting - and watering for 3 years.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking the pits after the first rain | Once, after the first rain. |
| 2. | Checking the pits after floodings | After flooding. |
| 3. | Replacing seedlings when needed (with extra watering if necessary). | During the wet season |
មតិយោបល់:
Depending on the climate
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Workers for maintenance including repairs, weeding and planting replacement seedlings | Worker/day | 10,0 | 50,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Tree seedlings | seedling | 30,0 | 4,0 | 120,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 620,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 620,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Local donors 100 % of workers costs and NCVC 100 % of the seedlings.
មតិយោបល់:
Depending on the type of soil, drought and flooding. Figures are an average per year for first few years. Extra watering may be necessary at an extra cost for the truck/ bowser (not costed here).
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Type of soil, drought and flooding.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
70,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
The distribution and seasonality of rainfall in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, are characterized by low annual totals, high variability, and a distinct seasonal pattern associated with its arid desert climate.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Internet, available climate data
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- ស្ងួត
Arid or hyper-arid, to be exact. Riyadh region, in general, experiences a hot desert climate. Summers are extremely hot, with temperatures often exceeding 45°C (113°F), while winters are mild, with daytime temperatures averaging around 20°C (68°F). Rainfall is scarce and irregular, mostly occurring between November and April, with an annual average of less than 100 mm.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
This technology is specific to the Thuwayq wadis and plateaus
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Rocky limestone soils, sometimes sandy.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកមិនអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកក្រោមដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ភាពទៀងទាត់:
ម្តងម្កាល
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
One to three floodings a year.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Arid ecosystems, low but relatively rich for the region.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ផ្សេងៗ (សូមបញ្ជាក់):
Various
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កុមារ
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
The land manager is the Government, National Centre for Vegetation Cover Development and Combating Desertification, which facilitates tourism/ picnicking in the park and protection of the environment (for all genders and ages of tourists). Land users can be considered to be local people who volunteer their labour and use the area for recreation.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
មតិយោបល់:
Sizes of National Parks where such interventions are/ will be found
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- under park management
- under park management
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
National Park, government property
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
Tourism:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
មតិយោបល់:
Tourism is with guides and tour operators - facilities are being improved
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
គុណភាពព្រៃឈើ/ដីព្រៃ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Can double the vegetation cover in 10 years
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Development of picnic and recreational areas once trees have grown
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Recharges the water table
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ការកើនឡើងដី
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
អាកាសធាតុ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Expert estimates/expectations
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Expert estimates/ expectations
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ដោយទឹកភ្លៀង | ល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
The impact will depend on the density of pits per hectare. Experimentation with different spacing as low as 3 metres apart could/ should be tested and evaluated for costs and results.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
It depends on the case, but the success in terms of vegetation establishment and thus related benefits is generally very high.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
The technology is no longer experimental. It is routine in Thadiq National Park up which is creating up to 300,000 new pits per year.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
Joint ventures between NCVC, local donors and volunteers.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Radical change to the ecosystem and landscape to improve it environmentally. |
| Attractive to tourists after 5 years. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Adapting to climate change (rising temperatures, increased flash flooding). |
| Necessary if we want to turn desert into forests and steppes. |
| One of the best ways to revegetate the desert. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High costs. | Use climate change budgets or convince donors and the Government and Vegetation Centre to finance it. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High costs. | Use climate change budgets or convince donors and the Government and Vegetation Centre to finance it. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Many times during 3 years
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
In depth interviews with the National Park manager
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
In the FAO office, climate change and forest experts.
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
06/05/2023
មតិយោបល់:
2021-2024 many times
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
FAO 2024. State of land degradation, desertification and sand encroachment in Saudi Arabia.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
FAO Project internal report, Saudi Arabia, 051. Fao-sa@fao.org
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
FAO 2022. Forest Sector Review of The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
FAO Project internal report, Saudi Arabia, 051. Fao-sa@fao.org
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
FAO, 2022. National Park Sector Review of The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
FAO Project internal report, Saudi Arabia, 051. Fao-sa@fao.org
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
FAO, 2022. Rangeland Sector Review of The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
FAO Project internal report, Saudi Arabia, 051. Fao-sa@fao.org
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
National Center for Vegetation Cover NCVC
វេបសាយ:
https://ncvc.gov.sa/
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
Add the FAO Project UTF/SAU/051/SAU, Strengthening the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture’s Capacity to Implement the Sustainable Rural Agricultural Development Programme
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល