Non-inversion tillage in UK arable cropping; Loddington [ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Ceris A. Jones
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
minimum tillage (English), conservation tillage (English)
technologies_986 - ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust - ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
02/11/2004
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Participatory on-farm demonstration in UK arable cropping: Loddington [ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស]
Provision of expert knowledge in appropriating equipment and setting up small scale on farm trials in collaboration with the land manager
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Ceris A. Jones
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Surface cultivation of the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
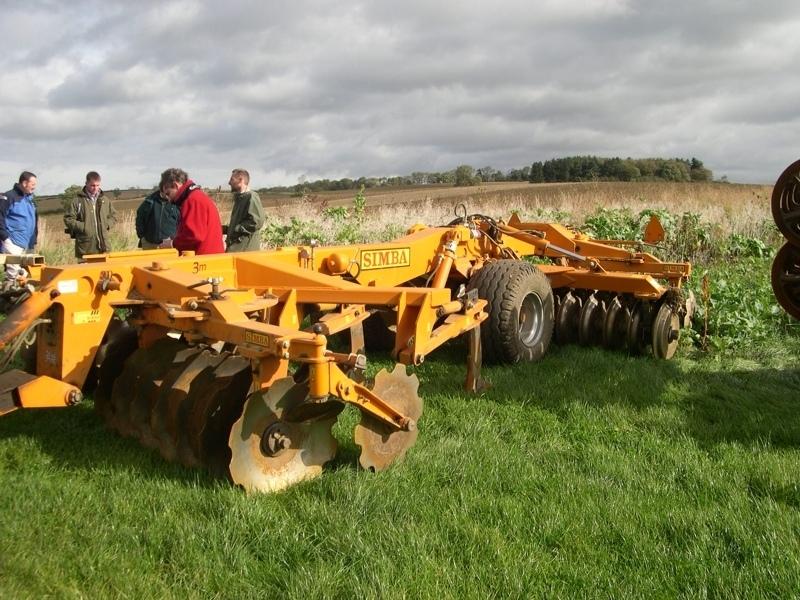
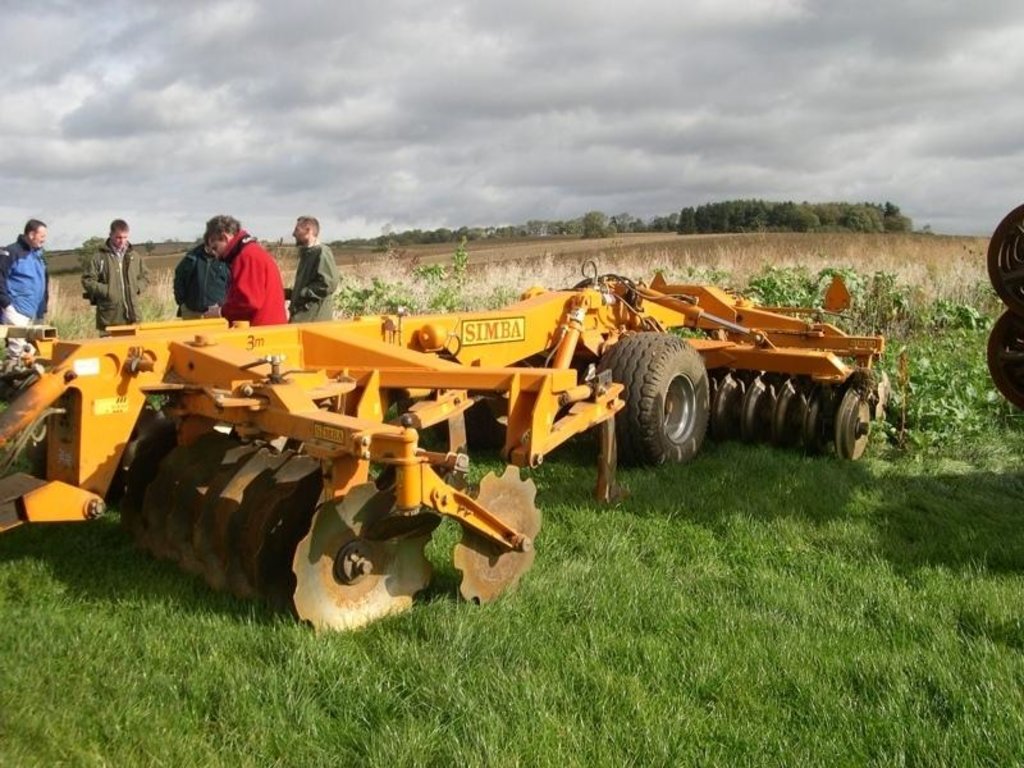
machinery with discs or tines replace the plough.
Purpose of the Technology: (i) improved crop establishment particularly by speeding up of operations (ii) improved soil structure.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: appropriate machinery, soil condition and following crop all determine establishment.
Maintenance: on an annual basis.
Natural / human environment: farmer working to protect environment and maintain rural employment
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Leicestershire
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Loddington
Map
×2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
From the USA where in te 1930's the 'dust-bowls' necessitated the development of soil conservation in intensive agriculture
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Major cash crop: Wheat
Other crops: Oilseed rape, beans
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water turbidity, compaction, erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Compaction
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: wheat - oilseed rape - wheat - beans. Typically these will be winter-sown (Sept) crops rather than spring sown (March)
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 330Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Aug
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.46 m2.
This represents 60% of the total arable area on the farm
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residue
Quantity/ density: 5 t/ha
Remarks: dispersed over soil surface
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: NPK
Quantity/ density: 0.14 t/ha
Remarks: broadcast
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: cereals/ broad-leaved crops
Remarks: alternate years
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: localised
Minimum tillage
Remarks: using discs and tines
Breaking compacted subsoil
Remarks: localised
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: localised
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
UK pounds (£)
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,56
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
155.00
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Year1: chop straw as low to the ground as possible | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | at harvest (usually August) / annual |
| 2. | Year1: incorporate straw to 10cm depth, though this is dependent on density of straw | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | September / per crop |
| 3. | Year1: additional cultivation | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | early October / per crop |
| 4. | Year1:drilling (4cm depth) | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | early October / once per crop |
| 5. | Year1: consolidation (more in Annex 3) | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | early October / once per crop |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 204,0 | 204,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine hours (year 2) | ha | 1,0 | 184,0 | 184,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine hours (year 3) | ha | 1,0 | 236,0 | 236,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 624,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: Simba Solo, Cambridge rollers, Vaderstad drill
Per hectare of land where technology applied. The costs represent the total crop establishment costs (machinery + labour) for this technology. Other costs eg seeds, fertiliser, are not included as these are identical to those incurred by other technologies (UNK1b) at this farm. These costs are related to the prevailing conditions - crop type, state of the soil, climate etc. Crop establishment costs by ploughing were: 224 (year1), 204 (year2), 263 (year3)
Additional info: - Year2: chop straw as low to the ground as possible: after harvest / annual - Year2:incorporate straw to 10cm depth, though this is dependent on density of straw: September / per crop - Year2: additional cultivation: March / per crop - Year2: drilling (2.5-4cm depth): March / once per crop - Year3:chop straw as low to the ground as possible: after harvest / annual - Year3: incorporate straw and relieve compaction of soil: October / per crop - Year3: additional cultivation: October / per crop - Year3: drill (2.5-4cm depth): October / once per crop - Year3: consolidation: October / once per crop
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Equipment costs, slope (higher horse power required for steeper slopes), presence of weeds (higher herbicide costs),
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
660,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Landforms: Hill slopes (some slopes < 8%)
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
50% of the land users are rich and own 60% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The time saved by practising non-inversion tillage (52 minutes/ha) allows the land manager to undertake contracted work on other farms
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
មតិយោបល់:
250 ha of cultivated arable land
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
- Trust
- Trust
- Trust
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In good (weather) conditions, yields from ploughed fields often better
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
timeliness of operations
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Speed of working allows larger acreage to be managed
Input constraints
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
herbicide resistance is increasing in a number of weed species therefore a better range of herbicide options required
Window of operation
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Can be more narrow than when ploughing
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Better infiltration of water
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Better germination in dry years
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Crop residue
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0.01
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
0
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Better soil structure
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
Maintenance of rural employment
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
enabled the farm to just about support the land manager and farm worker
Soil fertility
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher organic matter levels
Biodiversity enhancement
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher bird and invertebrate numbers
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Fertilisers and pesticides not transported with eroded soil, better soil structure + biodiversity slow + improve metabolism of chemicals in the soil
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 90-100%
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Currently 40% of UK farmers practice non-inversion tillage mainly for economic reasons
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Timely crop establishment + good work rate How can they be sustained / enhanced? good planning |
|
Lower costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increased acreage to spread costs |
|
Increased contractor income How can they be sustained / enhanced? as above |
|
improved soil structure - higher organic matter and provision of a better seed bed to drill into How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue with practice |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
cost effectiveness How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase ares under cultivation (economy of scale) |
| increased work rate |
|
improved soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? continuation of current soil management principles |
|
increased biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? price premium for biodiversity-friendly products |
|
improved water quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? no option. The EU Water Framework Directive requires watercourses to be of good status by 2015 |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| narrow weather window | drill non-inversion tillage fields first |
| grass weeds | crop rotation; new herbicide modes of action |
| slug management | monitoring slug populations |
| large acreage required to justify cost of machinery | consider not cropping headlands |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Grass weed control | New herbicide modes of action, more integrated management options |
| Untidy appearance of field (due to crop residue) | Familiarity with the technology |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Guide to managing crop establishment, SMI
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
www.smi.org.uk
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Improved soil management for agronomic and environmental gain, SMI
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
www.smi.org.uk
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
ECAF website
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
www.sowap.org
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Participatory on-farm demonstration in UK arable cropping: Loddington [ចក្រភពអង់គ្លេស]
Provision of expert knowledge in appropriating equipment and setting up small scale on farm trials in collaboration with the land manager
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Ceris A. Jones
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល