Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production [ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
"Tipid Saka"
technologies_1021 - ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
Jasper Manalo
Monsanto Philippines
ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Edicer Ocampo Jr
FSSRI, http://www.uplb.edu.ph/research/research-centers
ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los (Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los) - ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីនឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Monsanto Philippines Inc. - ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
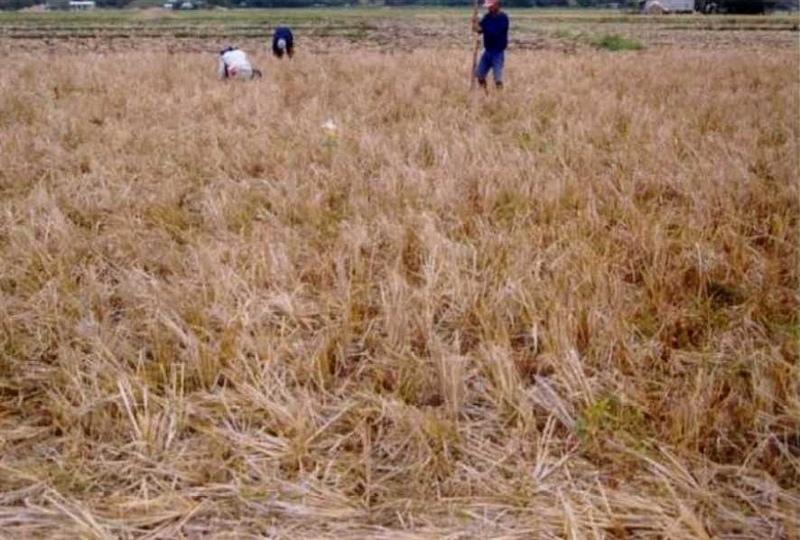
Conservation Tillage Technology (Zero Tillage) or "Tipid Saka" - A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Brief Description about Conservation Tillage Technology
Conservation tillage is the practice of planting seeds through the stubble of last season’s crop, rather than plowing and disking the field. The stubble protects topsoil against loss to wind and rain and reduces chemical run-off to streams. By not plowing, farmers also conserve soil moisture, which can reduce irrigation demands. Farmers can save fuel by reducing the number of farm machinery passes across their fields. In simple terms, Conservation Tillage can be said to lie along a continuum of two other techniques:
Minimum Tillage - mouldboard plowing is replaced by light tillage with tined implements, with or without a low toxicity non-residual herbicide to eliminate both perennial and annual weeds. 30% or more of the soil surface is kept covered by soil residues until final seedbed preparation. Conventional planting equipment can normally be used. Zero Tillage - planting is normally conducted without any preparatory tillage, or seedbed preparation. Normally, this technique requires specialized machinery for planting which can displace residues from the previous crop. A low toxicity non-residual herbicide application is recommended where growing weeds are present. There are numerous potential advantages of conservation tillage:
Farming Benefits
For farmers the primary benefits of CT, achieved with any loss of yields, include:
- More sustainable farming due to dramatic reductions in soil erosion caused by water or wind
- More efficient conservation and utilization of water under dryland conditions
- Improved energy efficiency as a result of reduced fuel requirements associated with fewer field operations
- Greater crop and farm profitability through reduced direct and indirect costs for chemicals, fuel and labor.
Environmental Benefits
At the same time, CT offers a number of significant benefits to the environment, these include:
- Greater biodiversity than with standard cultivation practices where the surface has no crop residues
- Reduces the build-up of soil sediments in reservoirs, drainage, ditches, etc. caused by soil erosion
- Less pollution of drinking water sources caused by run-off of soil, fertilizers and pesticides
- Reduced CO2 emissions due to increased soil organic matter level
Furthermore, crops grown without tillage use water more efficiently, the water-holding capacity of the soil increases, and water losses from runoff and evaporation are reduced. For crops grown without irrigation in drought-prone soils, this more efficient water use can translate into higher yields. In addition, soil organic matter and populations of beneficial insects are maintained, soil and nutrients are less likely to be lost from the field and less time and labor is required to prepare the field for planting. In general, the greatest advantages of reduced tillage are realized on soils prone to erosion and drought. Also achieved are greater water-stability of surface soil aggregates, higher microbial activity and earthworm populations and higher total carbon. Soil loss is less from sprinkler irrigation than in the plow treatment.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសហ្វីលីពីន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Laguna
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
San Jose, Abra de Ilog, Sta. Cruz, Sablayan
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
100,0
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 100-1,000 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
"Tipid Saka" is being practiced by farmers in the sites of San Jose, Mindoro Occidental since the dry season cropping (1999-2000) with the entry of UPLB Corn project and Monsanto Philippines, Inc.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 km2.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Although the technology has long been practiced by farmers particularly in the upland areas, zero tillage practices for corn production after rice was introduced in the SWC sites of Mindoro Occidental by the UPLB Corn project through the "Tipid Saka technology of Mosanto Philippines, Inc.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ថ្នាំជក់
- បន្លែ - ផ្សេងៗ
- rice
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែឈើផ្សេងៗ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
មតិយោបល់:
Major cash crop: rice, corn
Major food crop: rice, vegetables
Other: fruits, tobacco
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Continuous salinization due to intrusion of salt water and soil fertility decline. Loss of topsoil by water erosion seriously affects soil productivity, degrades water quality and causes costly sedimentation problems.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain and increase crop yield.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Generally, first crop of rice is planted in early part of June nad harvest in mid October. Followed by green corn and/or vegetables in November and harvested in February. Yellow corn is planted in December and harvested in March to April.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated is common but less used than rainfed
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
- cost reduction
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
A3: ប្រព័ន្ធភ្ជួររាស់ខុសៗគ្នា:
A 3.1: មិនភ្ជួររាស់
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Ha: aridification
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
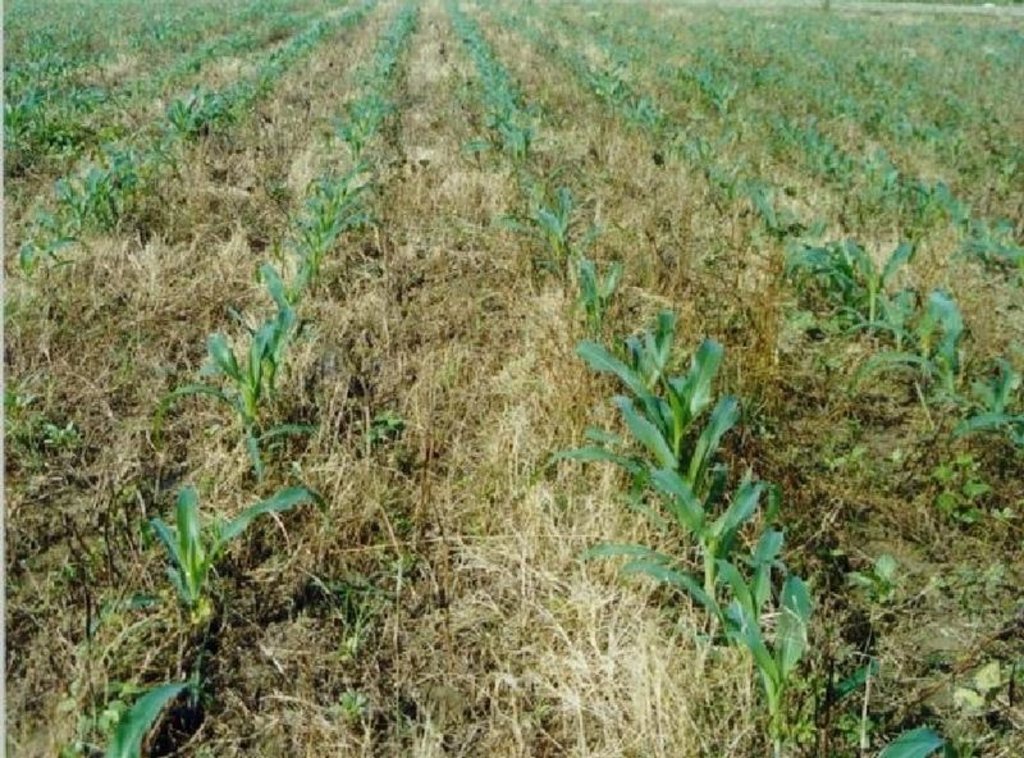
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residues, rice stubbles
Remarks: crop residues serve as mulching materials once killed by POWER herbicide
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: application of POWER herbicide 7-10 days after irrigation
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
5.00
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour vouluntarily and paid | ha | 1,0 | 147,6 | 147,6 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | post harvest | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seed | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 1,6 | 1,6 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | BIO-N | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | man person days | ha | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | marketing: transportation | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | marketing: packaging | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 541,2 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 541,2 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st side dressing, Release of trichogramma | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 2. | 2nd side dressing, Off-barring and hilling-up | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 3. | Detasseling | late vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 4. | Spray POWER herbicide, Planting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Retouch application of POWER herbicide, Replanting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: plow, harrow, hand tractor
Per hectare of land
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Land cultivation- zero tillage offset the costs incurred during land preparation. Labor costs for hand tractor and carabao-drawn plows are substituted by costs of spraying POWER herbicide which is significantly less expensive
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
450,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Landfroms: Area has generally flat topography located along wide plains.
Slopes: Small isoloated areas have slope of 0-2%
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil texture is medium andtextural analysis of samples show that the soils are silt loam.
Soil feritlity is low and the areas have high potential soil salinity problem.
The soil water storage has a capcity of 53.66% to 77.53%.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 15% of the land.
5% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, plumbing, business, offer of labor services to neighbors
Market orientation of production system: mixed (subsistence and commercia (Corn)l: Sold to feed millers, surplus is kept for next cropping.
Level of mechanisation: Rich farmers can afford to rent trators but Carabao-drawn plow is still dominant among averaged income farmers.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
2-5 ha also common but lowest ranked
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
input constraints
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
10
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
2
ដីហាប់
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
soil fertility
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
300 households
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
300 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Multinational company such as Monsanto Philippines, Inc. Continuously disseminate the technology through promotion of POWER herbicide
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| Increase soil water storage |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Labios, R.V. Et al. 200-2002," Conservation Tillage Practices in Corn Production After Rice: A Case in San Jose, Mindoro Occidenta"l. Pamhplet published by UPLB, DA-BAR, and National Corn RDE Network. P33
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Labios, R.V., Robles, A.Y., Javier, P.A., Garcia, M.U., Gonzales, P.G., Luis, E.M., Labios, J.D., Medina, C.M., Valencia, G.Z., Tamisin, L.L., Ocampo, E.P. Jr., Miciano, D.M. 1999. Annual Report. Enhancing Adaptation and Utilization of Location Sp
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Manalo, J.O. 2000. Tipid Saka Technology. Monsanto Philippines, Inc. 7th Floor Ayala Life FGU Center, Madrigal Business Park, Alabang, Muntinlupa City.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល