Pest management with pheromone insect traps [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Firdavs Faizulloev
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Tajikistan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_1054 - ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Pest management with pheromone insect traps: 15 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2017 (inactive)
- Pest management with pheromone insect traps: 20 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2017 (inactive)
- Pest management with pheromone insect traps: 19 ខែ សីហា ឆ្នាំ 2019 (inactive)
- Pest management with pheromone insect traps: 2 ខែ វិច្ឆិកា ឆ្នាំ 2021 (public)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Urakov Buran
UNDP
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
United Nations Development Program (United Nations Development Program) - ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថានឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management - Multicountry Capacity Building (CACILM - MCB) - ប្រទេសកៀហ្ស៊ីស៊ីស្ថាន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management … [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
Farmer Field Schools (FFS) are held to fill farmer's gaps in knowledge on the use of sustainable agricultural technologies, efficient irrigation water use and prevention of land degradation using trials tailored to local conditions.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Firdavs Faizulloev
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
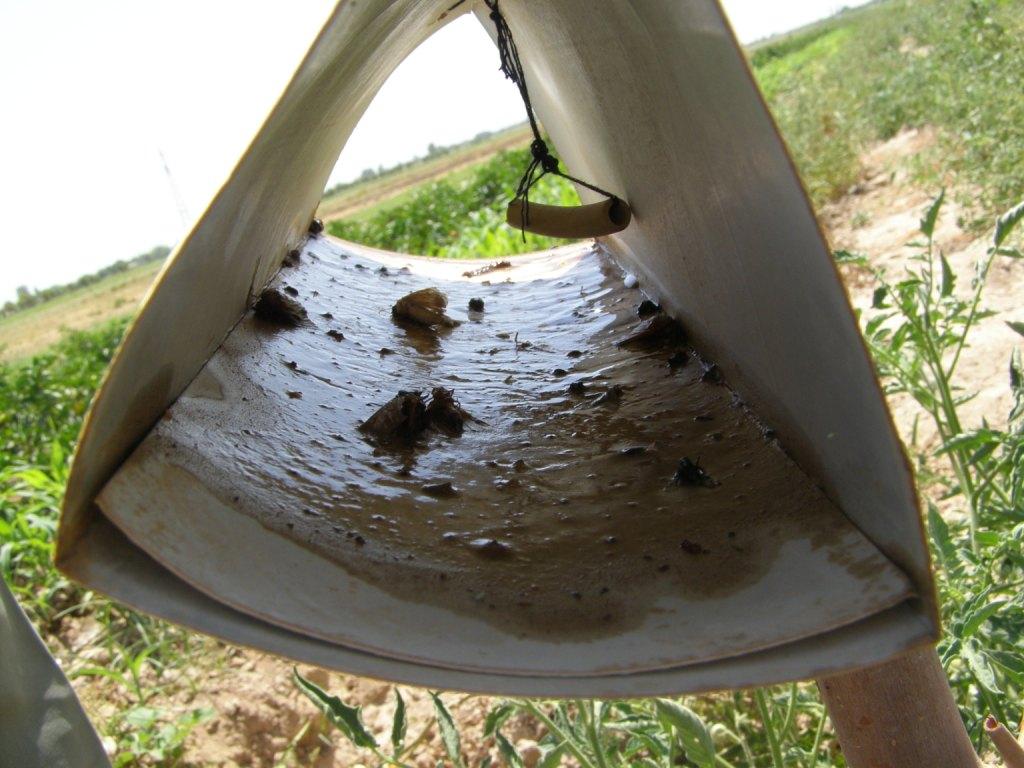
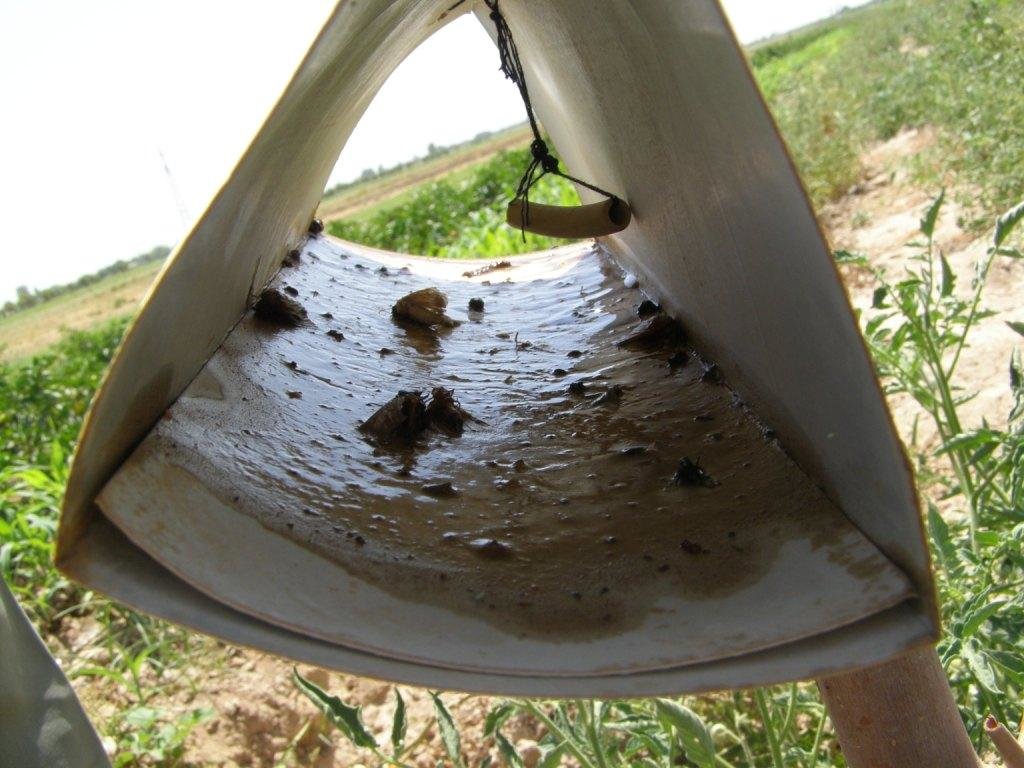
Coloured pheromone traps are set up in agricultural fields to attract and eradicate flying insect pests.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Within the UNDP Farmer Field Schools, farmers were taught about how to use pheromone insect traps to combat insect pests in crop fields. In the past, people used to irrigate their fields in winter with ice-cooled water, or to apply deep ploughing in order to kill pests. According to local people, the winters in the Shaartuz area are getting shorter so it is difficult to apply these practices any more, and they cannot afford to pay for the ploughing devices they need, and therefore pests are spreading.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of these traps is to attract flying insects which might constitute crop pests by sending out pheromones and to kill them once in the trap. The main insect pests against which the traps are used include caradrina and other moths from the Noctuidae family, thrips, aphids, whiteflies and mole crickets.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The trap consists of a wooden body, covered with plastic sheets to protect it from the rain. The exterior is painted in yellow to make it more attractive the insects. Inside the plate, a small tube is fitted which sends out pheromones to attract insects and the floor is covered with a plate covered with a mix of glue and Vaseline to trap the insects. As an alternative to Vaseline, motor oil can also be used. The trap is set up in early May and the sticky plate has to be changed once every two months.
Natural / human environment: This technology is used in fields of tomatoes, watermelon, onion, pumpkin, beans, corn, wheat and sweet pepper. As it is very cheap and simple to establish, there is a strong adoption trend seen among farmers. The pheromone insect traps provide an effective replacement for expensive chemical insecticides. However, the trap is only works for flying insects and methods to combat other arthropod pests still need more testing.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Khatlon
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kabodion
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 10-100 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 60 km2.
Around 160 farmers are using the technology distributed over 4 Jamoats:
Hudoiqulov Jamoat - 2700 ha,
Nuri Vakhsh Jamoat - 1156 ha,
Telman Jamoat -1450 ha,
Jura Nazarov Jamoat -1200 ha
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- reduce cost for inputs
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី (និទាឃរដូវ)
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកមើម (ការ៉ុត ខ្ទឹមបារាំង ឆៃថាវម្យ៉ាង ផ្សេងៗ)
- Tomatoes, Pumpkin, Watermelon, Sweet Pepper, Corn
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March-October
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): wind erosion, aridity, low soil fertility, increasing impacts of climate change, pests
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- បញ្ចូលការគ្រប់គ្រងសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺតាមបែបចម្រុះ (រួមទាំង កសិកម្មសរីរាង្គ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A7: ផ្សេងៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: agronomic measures
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bp: ការកើនឡើងនូវសត្វល្អិត ឬជំងឺ បាត់បង់នូវសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Irrigation with icy water in winter would be required but is not done any longer), change in temperature (warmer winters)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of pests
Agronomic measure: pest control
Material/ species: plastic pheromone traps
Quantity/ density: 4
Remarks: 4 traps per hectare
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Set up insect trap | early May |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Buying traps | pieces | 4,0 | 4,0 | 16,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 16,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 16,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
4 traps per ha
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Change glue on plate | once every two months |
| 2. | None | None |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Change glue on plate | - | 1,0 |
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: plastic plates, yellow colour, glue, vaseline, motor oil, pheromone tube
The costs mentioned apply to the set-up of 4 traps per hectare and include all materials used
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- ស្ងួត
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
poor drinking water (treatment required)= groundwater
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology also 50-100 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
pesticides
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
Livelihood and human well-being
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
| hail | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
a cover could be applied to the trap to protect it from hail
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
160 household in an area of 60 km^2 (density 50-100 persons/km^2)
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
160 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology was shown to the farmers in the Farmer Field Schools, and as a result many adopted the techniques and built traps for themselves.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Effective pest control |
| Very cheap and simple to apply technology |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Biological pest control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Arrange for farmer to farmer visits to disseminate information. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The trap only attracts flying insects, but does not help to kill other types of pests | Develop technologies to control caterpillars etc. |
| The small pheromone tube that is used in the setup of the trap is more and more difficult to find in the local chemist shops |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The trap does not differentiate between flying insects, so it is possible that it will also catch beneficial insects as well as pests. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management … [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
Farmer Field Schools (FFS) are held to fill farmer's gaps in knowledge on the use of sustainable agricultural technologies, efficient irrigation water use and prevention of land degradation using trials tailored to local conditions.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Firdavs Faizulloev
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល