Solar Mobile Dryer (SMD) [ប្រទេសអេមីរ៉ាតអារ៉ាប់រួម]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Joren Verbist
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7197 - ប្រទេសអេមីរ៉ាតអារ៉ាប់រួម
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
Principal Natural Resources Economist:
Dhebibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
Food and Feed Processing Scientist:
Hilali Muhi El-Dine
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសហ្ស៊កដានី
Activities Coordinator Officer:
Nejatian Arash
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសអេមីរ៉ាតអារ៉ាប់រួម
Regional Coordinator APRP:
Niane Abdoul Aziz
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ប្រទេសអេមីរ៉ាតអារ៉ាប់រួម
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - ប្រទេសលីបង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
The innovative Solar Mobile Dryer (SMD) developed by ICARDA addresses climate change challenges for date palm growers in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries by improving fruit quality, reducing waste, saving energy, and enhancing profitability, thereby supporting sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
In the Middle East, the date palm is an essential crop with significant cultural and economic value, thriving in dry, arid, and hot climates. However, climate change is exacerbating production challenges, with higher temperatures, heatwaves, water scarcity, harsh winds, leading to poor pollination, and increased pests amongst other issues. Small-scale date palm producers in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries face additional problems of managing unsold or excess produce. Short harvesting periods and high deterioration rates of some date varieties make the situation worse. A common solution to extend shelf life is freezing. However, this has several drawbacks including storage and handling difficulties, nutrient and flavour degradation, and high energy costs.
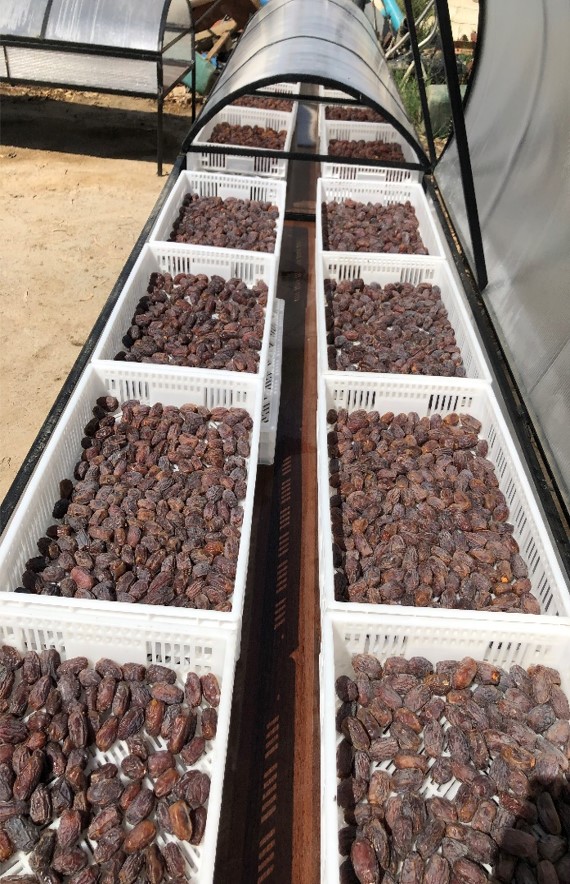
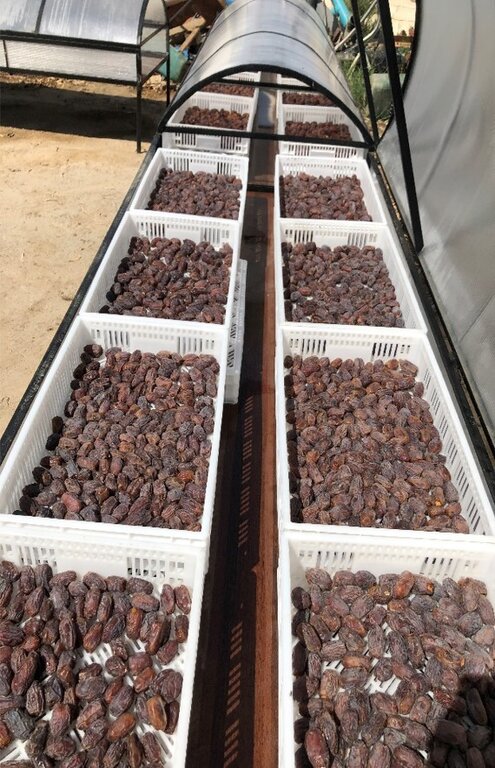
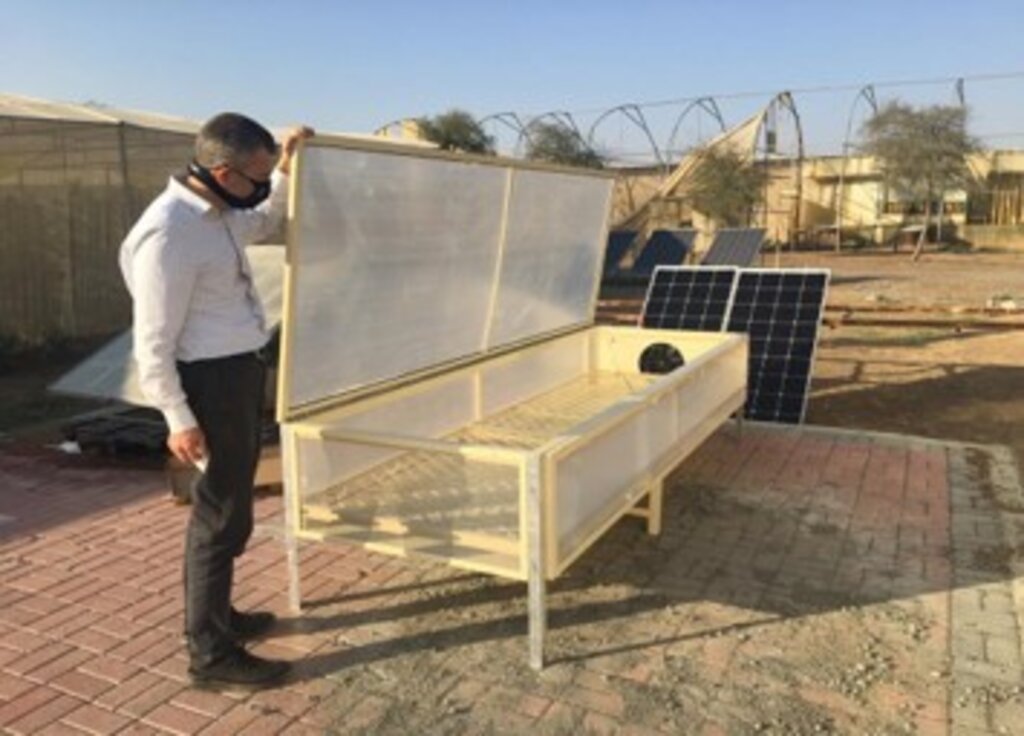
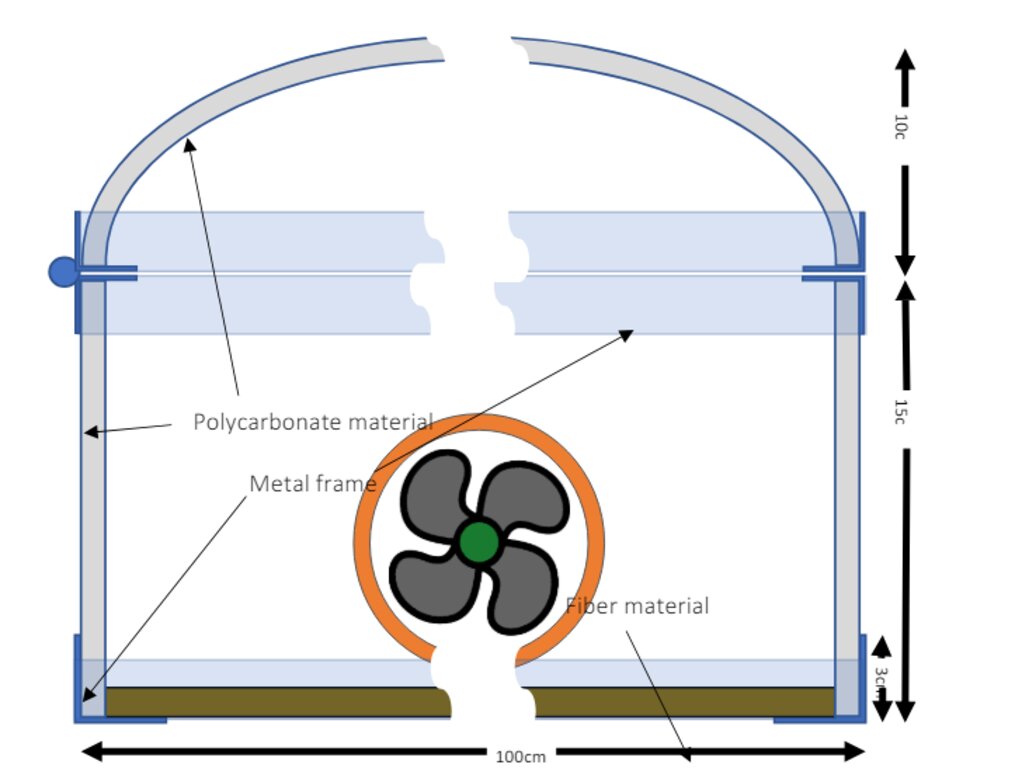
To tackle these post-harvest challenges, the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) developed an innovative Solar Mobile Dryer (SMB) for drying dates, achieving the desired colour for marketing while shielding the produce from dust and rain. The mobile solar dryer includes tables with polycarbonate covers forming a tunnel. Each table is 3 meters long, 1 meter wide, with walls 15-30 cm high, and raised 40 cm off the ground on metal legs. Dates are placed on a mesh for enhanced air flow and drying. Temperatures are kept at 70 degrees Celsius, the same as industrial date drying, to avoid textural changes, hardness, and colour alteration. Two versions of the tables have been produced.
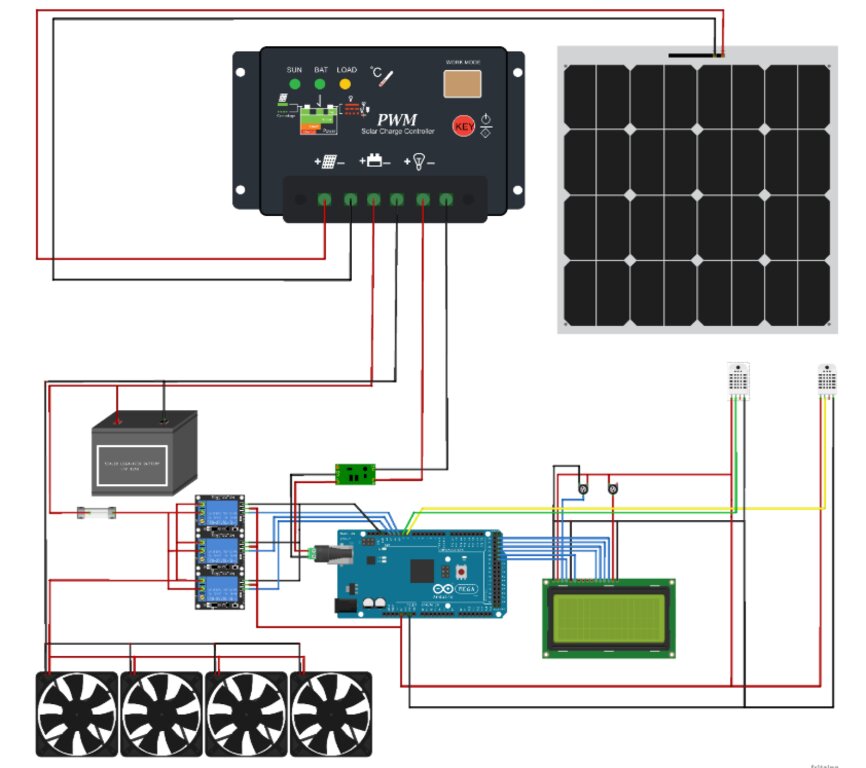
The Jordan version, uses an iron frame and includes four tables that can form a 12-meter tunnel. This dryer has a 12V 40W DC fan, with a control unit and solar panel system, providing 6 hours of operation during the day and 2 hours at night, controlled by a temperature sensor.
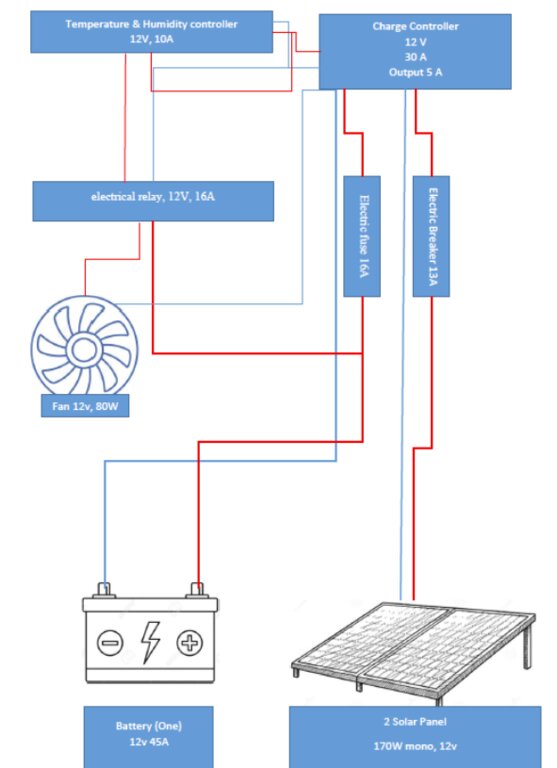
The second version was developed in United Arab Emirates (UAE) and features a lighter aluminium frame and a 12V 80W fan fixed on one table. It includes temperature and humidity sensors, two solar panels, and a 20A charging controller.
The advantage and disadvantages of the SMB are as follows:
Advantages:
+ Improves fruit quality, especially in humid areas. Produce dried in greenhouses are often higher quality than those sun-dried.
+ Prevents contamination by insects, birds, dust, and rain.
+ Saves energy and drying time, improves product quality, and increases process efficiency.
+ Solar drying systems have low operation and maintenance costs.
+ Reduces waste and loss rates.
+ Reduces air pollution and greenhouse gases from fossil fuels.
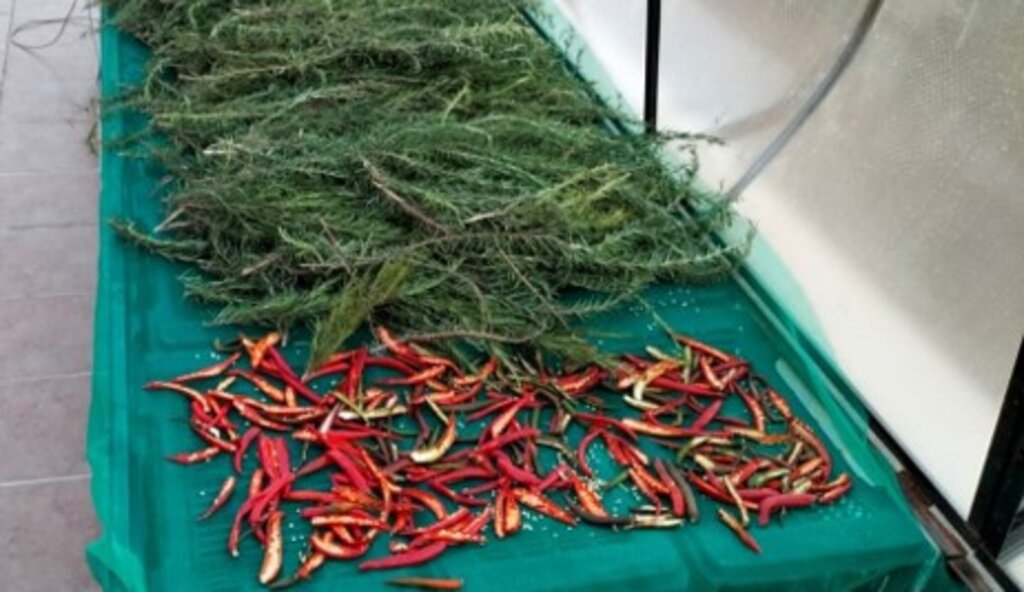
+ Can be used for other products (e.g., fruits, vegetables, medicinal, and aromatic plants).
Disadvantages:
- Drying is limited to sunny days unless integrated with conventional energy systems. Drying without sunshine depends on the humidity difference between inside and outside the chamber.
- Solar drying is slower than conventional fuel or electricity-based dryers.
- Requires large land areas and long drying times, subject to solar radiation and temperature fluctuations.
- Farmers may lack maintenance knowledge for the system.
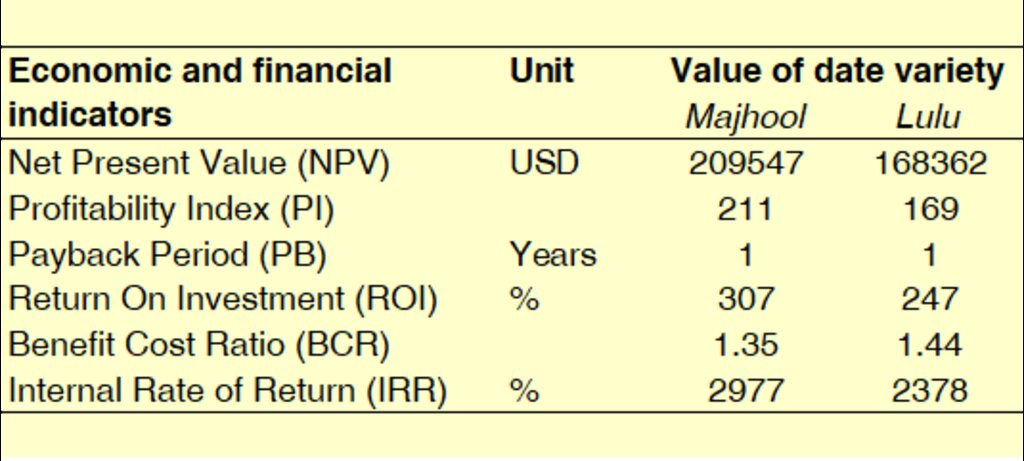
Economic evaluations of the SMD for two date varieties, Majhool and Lulu, demonstrate high profitability. The initial investment in the SMD is approximately 1,000 USD, with an estimated lifetime of about 10 years. The drying process takes between 1 and 3 days. The SMD has a capacity to dry between 6 and 12 kilograms of dates per square meter of drying surface in the SMD, resulting in production of around 5-10 kilograms of dried dates. Maintenance costs are estimated at 25% of the initial investment, while variable costs such as labour, packaging, and transportation are around 500 USD per month. Based on these figures, the net income per kilogram of dried dates is approximately 2.7 USD. Depending on the date variety, the return-on-investment ranges between 240% and 310%, with a payback period of about 4 months. These numbers indicate that the innovation is highly profitable for farmers.
The SMD is a crucial ICARDA initiative for smallholder date palm growers in the GCC countries, offering energy savings, waste reduction, and post-harvest loss prevention, enhancing the competitiveness of modern agriculture in high date production areas.
We express our sincere gratitude to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Secretariat for funding this research under the "Development of sustainable date palm production systems in the GCC countries of the Arabian Peninsula" project. We are grateful to the Ministries of Agriculture, Agricultural Authorities, and Agricultural Research Institutions and Universities in the GCC countries for their continuous support and collaboration in implementing project activities.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអេមីរ៉ាតអារ៉ាប់រួម
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2020
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- កាលបរិច្ឆេទ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- វិធានការក្រោយការប្រមូលផល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការផ្សេងៗ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
This is a post-harvest and technological innovation.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
This innovation increases the income of the farmers per unit area i.e., increased economic land productivity. This allows farmers to reduce pressure on the land and/or to manage their land more sustainable.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
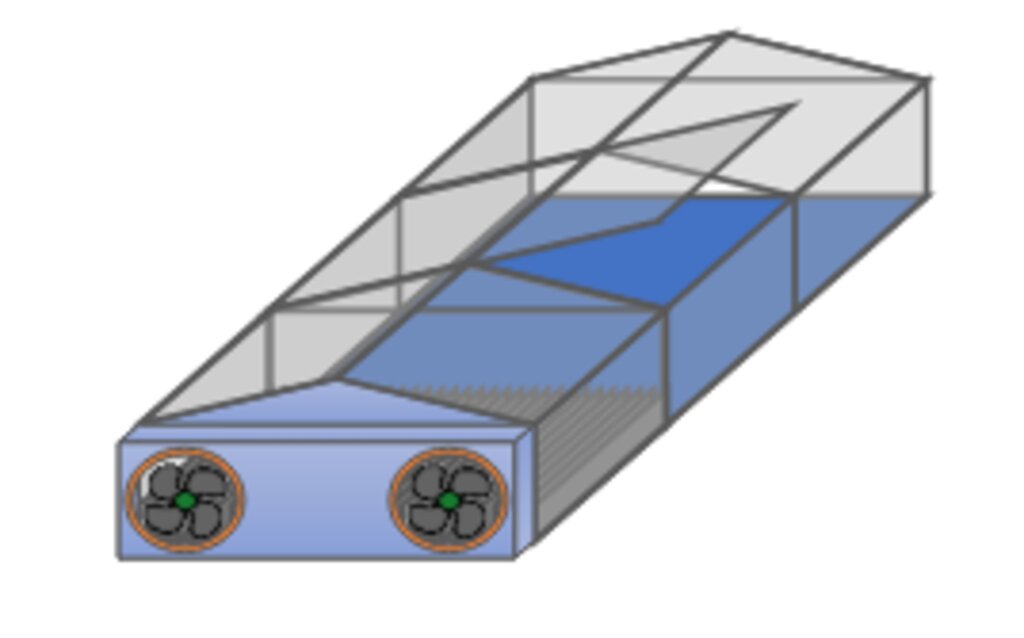
Schematic view of the SMD
Fans blow air to control humidly and temperature. Top windows can be open to store and collect dates, but also for manual control of temperature etc.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Side view dimensions of the SMD.
Plastic (poly-carbonate) sheets are held up by an iron frame. The product lay on a plastic net to also support vertical airflow.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical schematic overview of the SMD
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Electronic parts and connections overview of the SMD
Drawn using Fritzing software, www.fritzing .org
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Net Present Value (NPV)
NPV evaluates an investment's profitability by calculating the difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows. A positive NPV indicates a profitable investment, while a negative NPV signals a potential loss.
Profitability Index (PI)
PI measures the relative profitability of an investment by comparing the present value of future cash inflows to the initial investment. A PI greater than 1 indicates a good investment, whereas a PI less than 1 suggests it may not be viable.
Payback Period (PB)
PB is the time it takes for an investment to recover its initial cost through cash inflows. A shorter PB is preferred as it indicates quicker recovery, though it doesn't account for the time value of money or cash flows after the payback period but provides implication for risk.
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI assesses the efficiency or profitability of an investment by comparing the net gain to the cost. A higher ROI indicates a more profitable investment.
Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR)
BCR evaluates the value for money of a project by comparing the present value of benefits to costs. A BCR greater than 1 suggests benefits exceed costs, making the project worthwhile, while a BCR less than 1 indicates the opposite.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV of all cash flows from an investment equals zero. If IRR exceeds the required rate of return, the investment is considered good. It's useful for comparing projects.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Schematic drwing of the SMD as used in Jordan
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICARDA
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2024
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Charger control 1 (off grid, 12v 20A) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Fuse (10A) | 2,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Switch (10A) | 2,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | DC relay (16A) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Sensors (temperature and humidity) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Arduino micro processor | |||||
| សម្ភារៈ | LCD screen (2x20) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | DC relay (4 relay module) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Polycarbonate board (8-10mm) | 2,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Dark fiber board (6mm) | 2,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Metal bars (3cm x 3cm x 10mm) | 20,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Metal bars (2m x 2m) | 10,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Metal hinges (small, <10mm) | 8,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Fan (12v 40-80W) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Battery (12v 55A) | 1,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Solar panel (170W 12v) | 2,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Voltage regulator (1-40v) | 1,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Plastic terminal box (30cm x 40cm) | 1,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Clock module (5v) | 1,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | SD card module (5v) | 1,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | BCP board | 2,0 | ||||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Total costs | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1000,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើមិនអាចបំបែកតម្លៃដើមក្នុងតារាងខាងក្រោមទេ សូមផ្តល់នូវតម្លៃប៉ាន់ស្មានសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសនោះ:
1000,0
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ផ្សេងៗ | Maintenance | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | ||
| ផ្សេងៗ | Variable (use) cost | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 750,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 750,0 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Material costs for drying such as packaging appeared to be a major cost.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
- ស្ងួត
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទាំងទឹកក្រោមដី និងលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Because the SMD is mobile and processes the harvest, the natural situation is not that essential. However, ideally, it should be placed in warm and sunny areas.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
- មនុស្សចាស់
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
(Economic) Productivity increases because post-harvest losses decrease and selling prices increase
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Because of the drying, products are considered higher quality
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
To reach the higher selling prices additional expenses on the SMD and packaging is required.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Dried products have longer shelf life and less vulnerable to mold and pests.
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
SMD is so designed that it can be easily shared, so that costs for individual smallholder farmers are relatively low.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The SMD only uses solar, so overall less greenhouse gasses are emitted, within the chain, compared to the current situation.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ផ្សេងៗ (សូមបញ្ជាក់):
other inputs
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Experiments are done with other products such as vegetables, fruits, and spices.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Increased farm income |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Improvement of the fruits’ quality |
| No contamination of dates by insects, birds, dust and rain |
| Energy and drying time saving |
| Waste and loss rate reduction |
| Air pollution and greenhouse gases reduction |
| Multiuse purposes (vegetables, medicinal and aromatic plants-MAPs, etc.) |
| Production of the SMD can result in (local) employment opportunities |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Drying can be performed only during sunny days unless the system is integrated with a conventional energy-based system | |
| Solar drying process is slow in comparison with dryers that use conventional fuels | The avoidance of costs to fuel may compensate this. |
| Solar drying requires larger land areas and longer drying times | |
| Fluctuations in solar radiation and ambient temperature | |
| Farmers lack of knowledge for the maintenance of the system | Capacity building programme or training when buying the SMD |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Muhi El-Dine Hilali, Arash Nejatian. (15/9/2023). Economic and Financial Evaluation of a Low-Cost Portable Solar Dryer for Maturing and Drying of Dates: Business for Development (B4D) Report.
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68749
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Muhi El-Dine Hilali, Arash Nejatian, Abdoul Aziz Niane, Mohamed Ali Bob. (30/11/2023). دليل تصنيع و تشغيل المجفف الشمسي المتنقل. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69302
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Muhi El-Dine Hilali, Arash Nejatian. (28/3/2021). Developing solar drier for maturing and drying of dates in the Arabian Peninsula. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
វេបសាយ:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12826
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល