INTEGRATED AGRICULTURE-BASED LAND USE IN AREAS WITH SALINE SOILS [ប្រទេសថៃ]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Laksamee Mettpranee
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7276 - ប្រទេសថៃ
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Siangsunthia Mana
ប្រទេសថៃ
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
co-compiler:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - ប្រទេសថៃ1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Salinity and associated land degradation in parts of the Northeast of Thailand limits production. Knowledge of saline soil management was integrated into an organic agriculture system: dolomite application adjusted pH levels, manure increased the soil's organic matter, while fermented bio-extracts stimulated root systems. Yields of chili pepper and parsley improved greatly.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
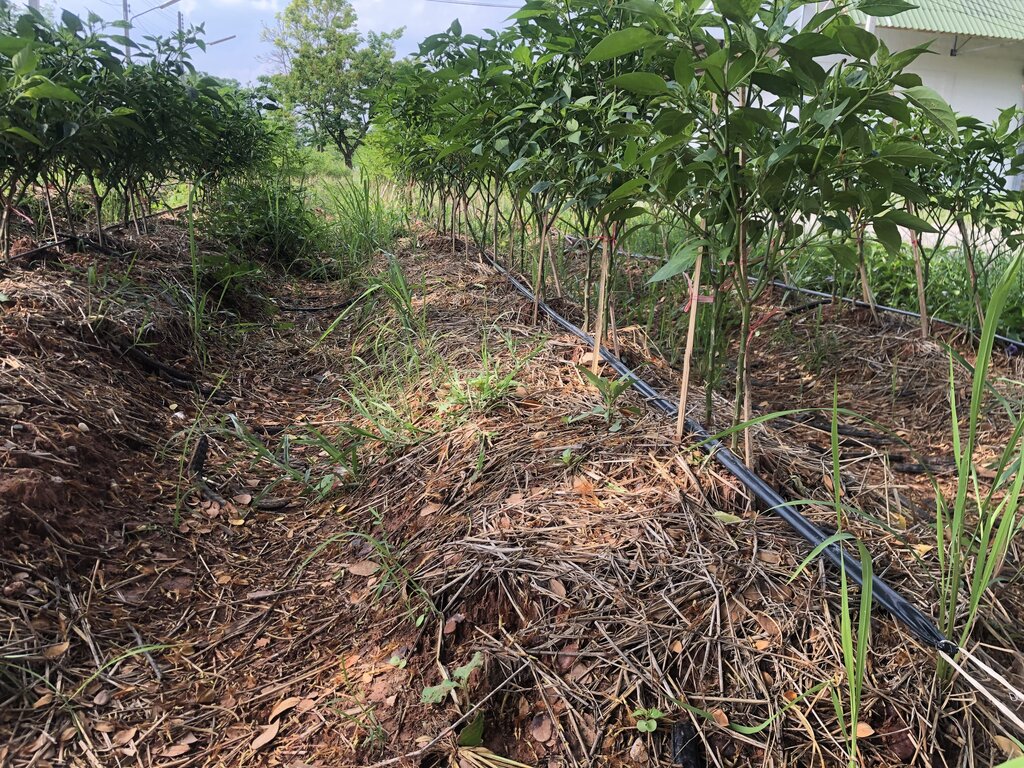
The problem of soil degradation in regions with saline soil such as parts of the Northeast of Thailand shows up as chemical and physical deterioration and low fertility, which are significant limitations to land use. These issues are exacerbated by water shortages in the dry season and excessive rainfall during the cropping season.
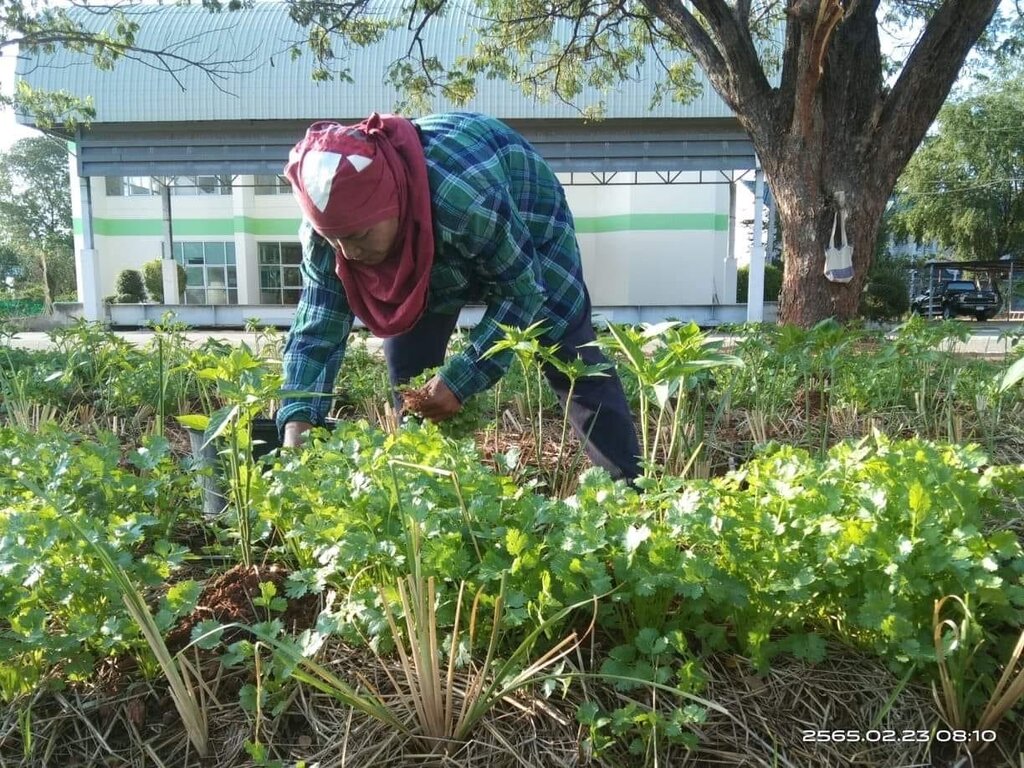
To address this, a group of farmers interested in learning effective soil management strategies has formed. Their aim is to mitigate the effects of salinity and improve crop productivity on their farms. The group has received support in the form of production inputs, including microbial activators for producing organic fertilizers and bio-fertilizers, vetiver grass of the Songkhla 3 variety, and dolomite. Additionally, they have implemented guidelines based on learning, observation, and trial and error to develop a 0.04-hectare vegetable plot.
Previously, this area was characterized by low soil fertility and salinity, which resulted in reduced crop yields. The sandy clay loam soil, though slightly saline, had very low moisture content during the dry season. Furthermore, the area lay outside the irrigation zone. To answer these questions, farmers in the community of Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai Sub-district, collaborated to develop sustainable farming practices. With support from the Land Development Department, they integrated knowledge of saline soil management into an organic agriculture system.
This technology began with soil analysis and appropriate measures for managing saline soil before land preparation. Farmers combined their wisdom with Land Development Department technologies, such as dolomite application to adjust pH levels and eliminate pathogenic microorganisms affecting chili pepper growth. Manure was applied to increase the soil's organic matter, while fermented bio-extracts containing beneficial microbes stimulated root systems.
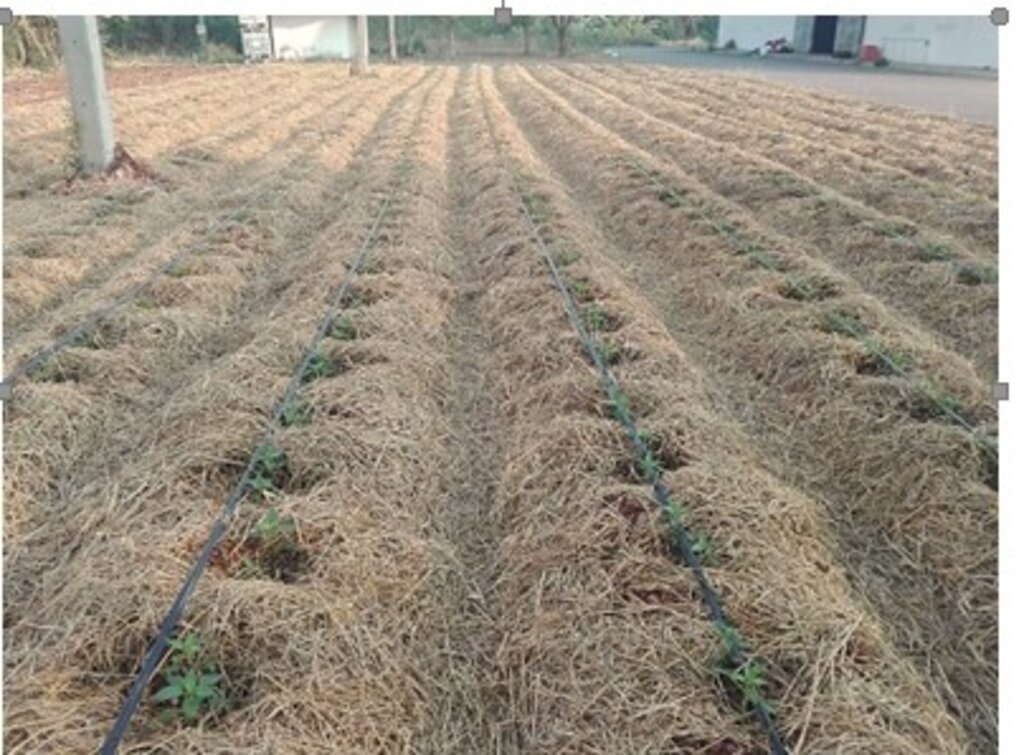
To conserve soil moisture, drip irrigation technology was installed in the chili planting plots, and the soil was covered with straw. Vetiver grass was also used to further conserve moisture as a grass barrier strip. After these soil amendments, the soil structure improved, becoming friable and suitable for planting chili peppers—specifically the Amphawa Gold variety, which has a high market demand.
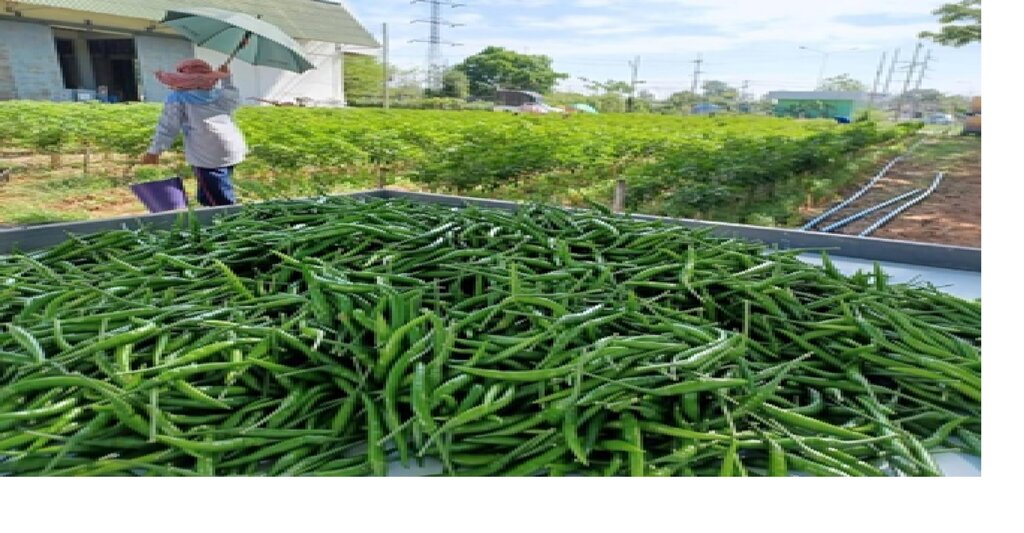
Additionally, parsley was intercropped between plots to optimize land use. On average, the chili pepper yields reached 400 kilograms per 400 square meters over 180 days, with a market price of about 2.50 USD per kilogram. Parsley, as a by-product of watering the chili pepper plants, produced just over 100 kilograms per 400 square meters per production cycle of chili peppers.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសថៃ
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Nakhonratchasima
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 100-1,000 គម2
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2022
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Farmer groups in Non Thai Subdistrict and nearby areas transfer knowledge through the volunteer soil doctor network.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- បន្លែ - ផ្សេងៗ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
The area is outside the full irrigation zone and has a local or community small size water sources.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- បញ្ចូលការគ្រប់គ្រងសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺតាមបែបចម្រុះ (រួមទាំង កសិកម្មសរីរាង្គ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A5: ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រាប់ពូជ បង្កើនប្រភេទពូជ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cs: សារធាតុប្រៃ/អាល់កាឡាំង

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
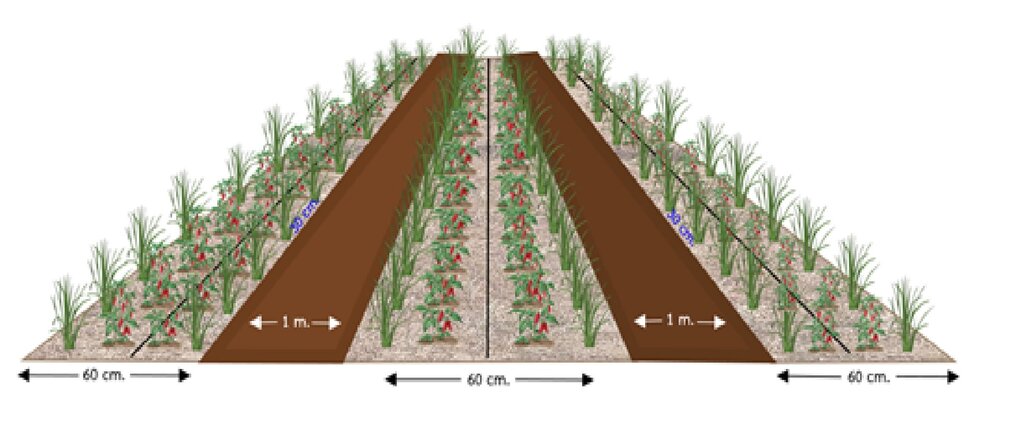
Cultivation plot preparation
1. Plough and harrow the soil, then plough again using a 65 HP tractor and a small Kubota tractor for further tilling.
2. Raise ridges to 30 cm high and 60 cm wide, with 1-meter spacing. Burn plant residues to kill bacteria and fungi, then water to extinguish the blaze.
3. Apply dolomite at 156.25 kg/hectare and bioslurry (100 kg/rai) after fermentation. Mix in bio-extract (2 spoons per 20L water) to improve soil and stimulate root growth.
4. Mix soil with 3 handfuls of soil and 1 handful of dung.
5. Dry the soil for 7-14 days, then place a 10 cm banana stem at the bottom of the planting hole before planting.
Planting and maintenance
1. Plant 35-day-old Amphawa Gold chili peppers, sprinkle parsley around the plot, cover with rice straw, and plant vetiver around the edges.
2. Water in the morning and use fermented Indian Laburnum pod extract (2 spoons per 20L water) in the evening. Spray wood vinegar weekly to prevent fungi.
3. When buds appear, spray LDD 2 every 5 days in the evening.
4. Set up a drip system for backup watering in case of labor shortage.
5. If anthracnose occurs, remove affected chili peppers. For aphids, spray plain milk on the affected areas, leave for 20 minutes, then wipe off.
6. Remove old leaves at 45-50 days to expose the trunk to sunlight, promoting better growth and higher yields
Harvesting yields
1. Harvest the first generation of chili peppers at 65 days, then harvest every 5 days for the next 6 months.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Ms. Nisa Sahoh
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/04/2025
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1.12ha
បើសិនប្រើឯកតាតាមតំបន់ សូមបញ្ជាក់តម្លៃបម្លែងវាទៅជាហិកតា (ឧ. 1 ហិកតា = 2.47 អា)៖ 1 ហិកតា =:
6.25rai
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
8.82 USD
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Drip irrigation system installed | Before mulching/ cropping (March) |
| 2. | None | |
| 3. | None |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Drip lines | metre | 4,6 | 1,76 | 8,1 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | PVC tubes | metre | 10,0 | 0,59 | 5,9 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | 1000 litre tank | piece | 1,0 | 67,65 | 67,65 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | None | None | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 81,65 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 81,65 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cultivation plot preparation | |
| 2. | Planting and maintenance | |
| 3. | Harvesting yields | |
| 4. | In case of an anthracnose epidemic, destroy the chili pepper stricken with the disease. During an outbreak of aphids, spray with plain milk at the point of the outbreak. Leave it for 20 minutes and then wipe it off. | |
| 5. | Remove leaves of the chili peppers when they are 45-50 days in order to make the trunk expose to the sun. This helps chili peppers grow well and increase their yields. |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Ploughing to prepare plot | Person days | 1,0 | 8,08 | 8,08 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Soil preparation | Person days | 1,0 | 4,41 | 4,41 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Cultivation, watering, plot maintenance | Person days | 1,0 | 24,25 | 24,25 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Harvesting | Person days | 1,0 | 137,64 | 137,64 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tractor/ cultivator maintenance | Fuel etc | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Chili peper plant | plant | 1200,0 | 0,029 | 34,8 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Parsley seeds | gram | 600,0 | 0,01 | 6,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Rice straw | kilogram | 180,0 | 0,1 | 18,0 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Fermented bio-extracts | liter | 120,0 | 0,29 | 34,8 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Dolomite | kilogram | 13,6 | 0,73 | 9,93 | |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Dung | bag | 35,0 | 2,5 | 87,5 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Drip line | meter | 4,6 | 1,76 | 8,1 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | PVC tube | meter | 10,0 | 0,59 | 5,9 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | 1,000 liter bucket | bucket | 1,0 | 67,65 | 67,65 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 522,06 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 522,06 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Drip irrigation systems have no maintenance costs but they are replaced after 2 to 3 years.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
1. Labour costs
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
ផ្ទៃខាងលើ
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- ច្រើនជាង 50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- មនុស្សចាស់
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Degraded soil, and poor fertility
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Soil amendments make the soil better
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
គុណភាពដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Plants could not grow
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Plant thrive and give good quality yields continuously.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Plants cannot be planted.
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Integrated cultivation, namely chili peppers, parsley and vetiver for soil amendment
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
There was no cultivation.
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
The quantity of products can be sold and exported.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
--
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Studied how to solve problems by themselves
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
There was no knowledge propagation
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Farmers in the area accept the technology and gather together to learn methods of soil management so that they can grow plants and implement them in their own areas.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Mulching with plant debris, rice straw and growing plants.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Information from a questionnaire
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
--
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Nutrients increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etcnts increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Using a questionaire
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
--
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Using a questionaire
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
--
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Using a questionaire
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Information from a questionnaire
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
Information from a questionnaire
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
Rainfall has decreased due to climate change, a result of global warming.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 11-50%
មតិយោបល់:
The land users are responsible for covering the cost themselves. Supported by agricutural production factors from LDD.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Yes. Use the drip system for morning watering with organic fertilizer.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Farmers manage soil and water and use integrated farming methods, leading to additional income opportunities. |
| Farmers in the area are committed to overcoming challenges and limitations related to soil, water, and environmental conditions. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Support for forming farmer groups in the area to exchange knowledge on soil management for increasing crop yields and addressing local farming issues, as well as developing professions for community farmers. This includes promoting the production of safe, non-toxic crops and creating value for products, leading to increased household income for farmers. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Farmers who use the technology must learn to follow procedures carefully. | Training and experience |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The technology used is precision farming. Farmers who use the technology must pay attention to every step. | Training |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
10
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
10
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
2
មតិយោបល់:
https://lddmordin.ldd.go.th/web/data/Tank_Soilmanagement/Soil_58.pdf
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
វេបសាយ:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល