Gravity Irrigation for enhancing Community-Based Restoration efforts in the degraded forests of Paktya [ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Mohammad Wazir Ahmadzai
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal, Mohammad Mustafa Sahebzada, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi, Megha bajaj
Obu Zakhira
technologies_7481 - ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistanឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
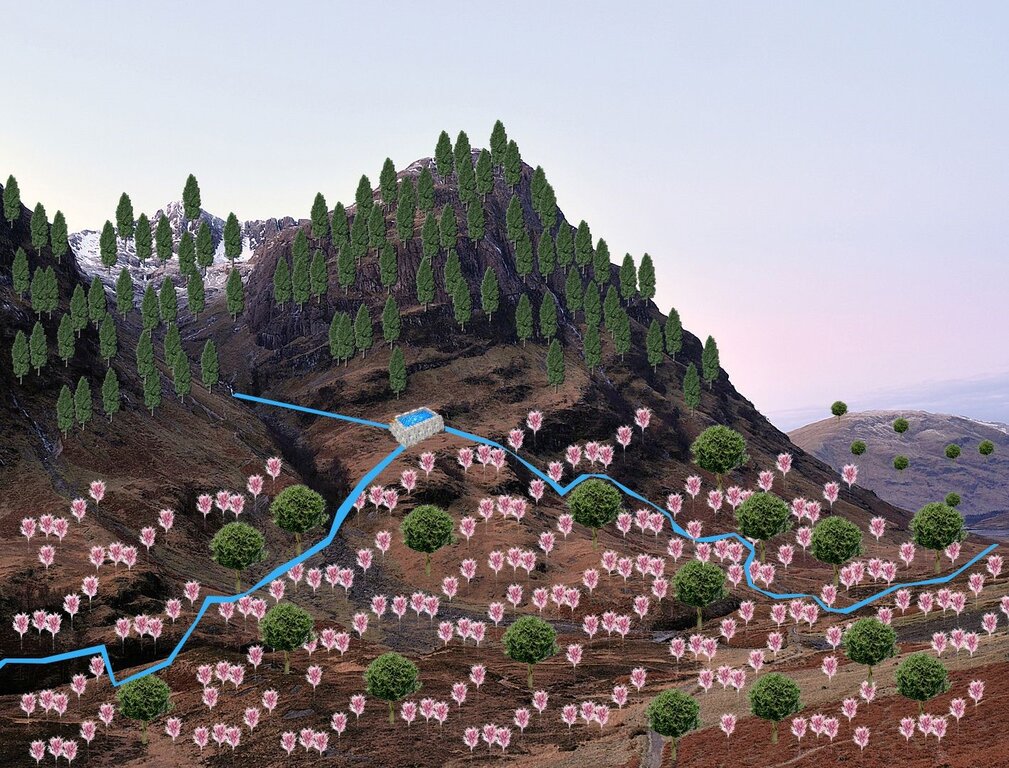
Using a gravity-irrigation system, spring water is diverted to fill reservoirs and then distributed to fields for the restoration of degraded forest areas, with the active involvement of local communities and a focus on the sustainable use of water resources (spring water).
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The Paktya province in Afghanistan, known for its mountainous terrain and rich forests of pine nuts deodar, cedar, and conifers, faces severe challenges. Most water in the province comes from rivers, springs, and tube wells, with high mountains acting as natural reservoirs. Unfortunately, many traditional water sources have been destroyed over decades of conflict and natural drought, forcing farmers to rely on costly tube wells for irrigation.
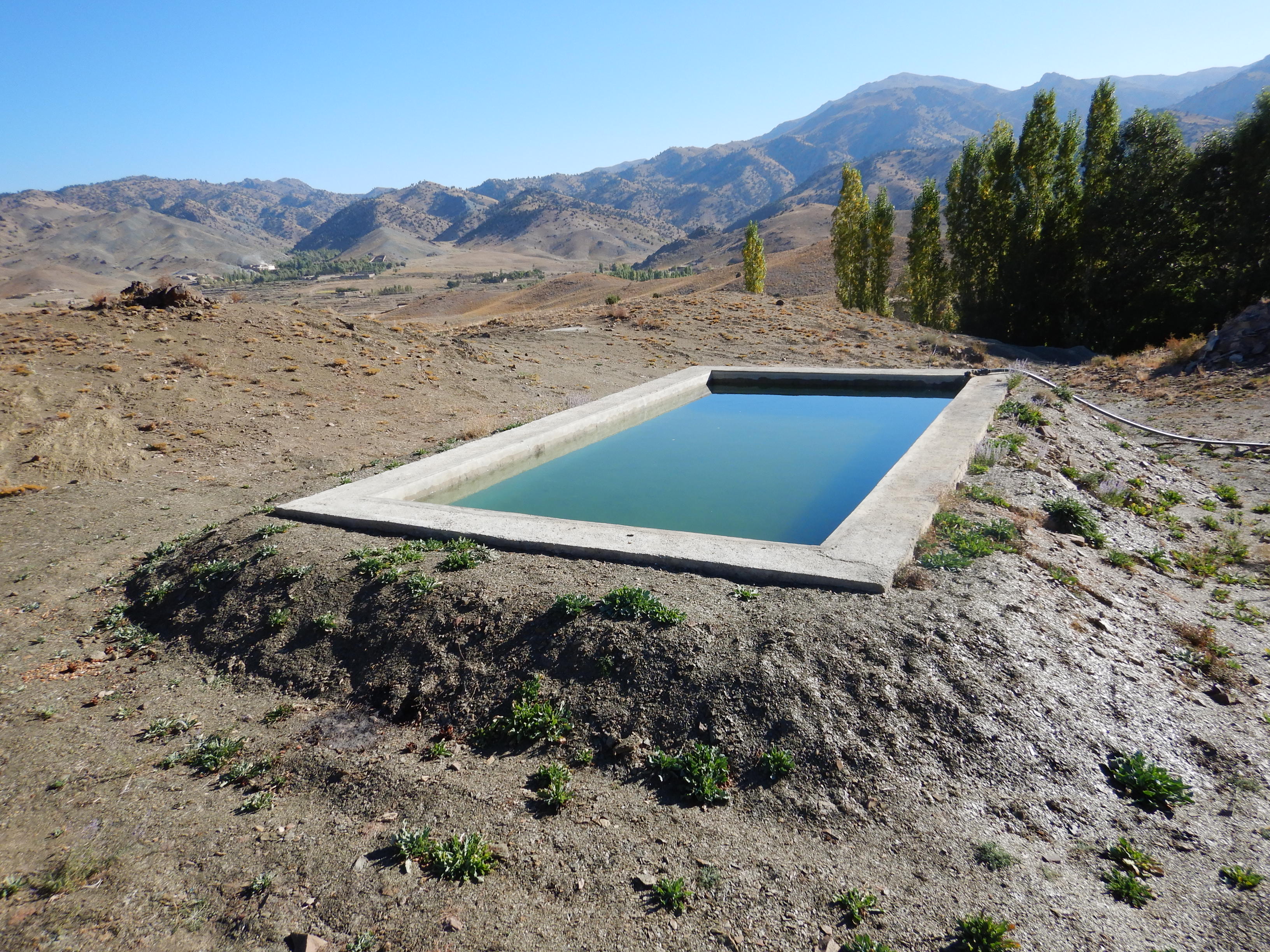
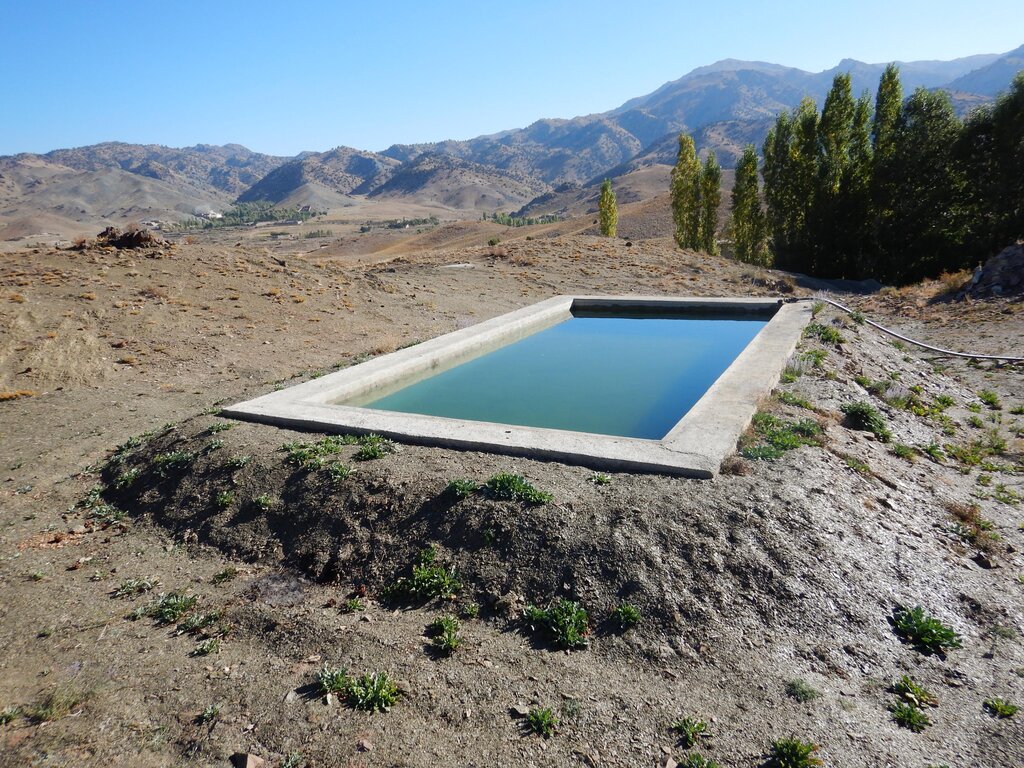
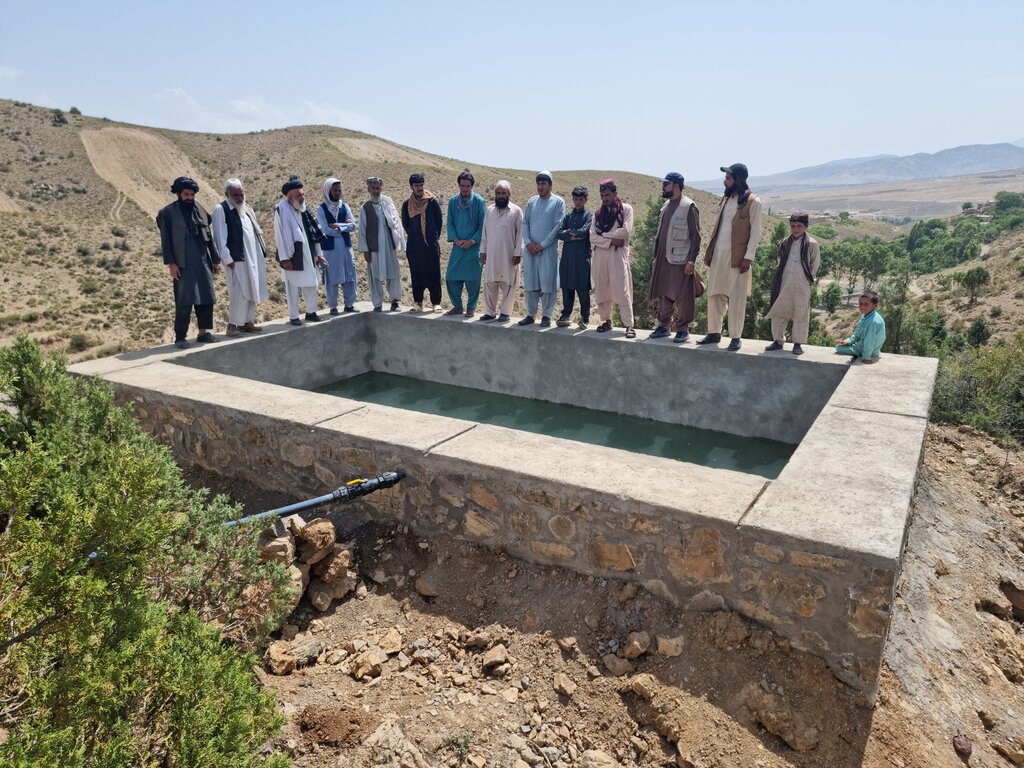
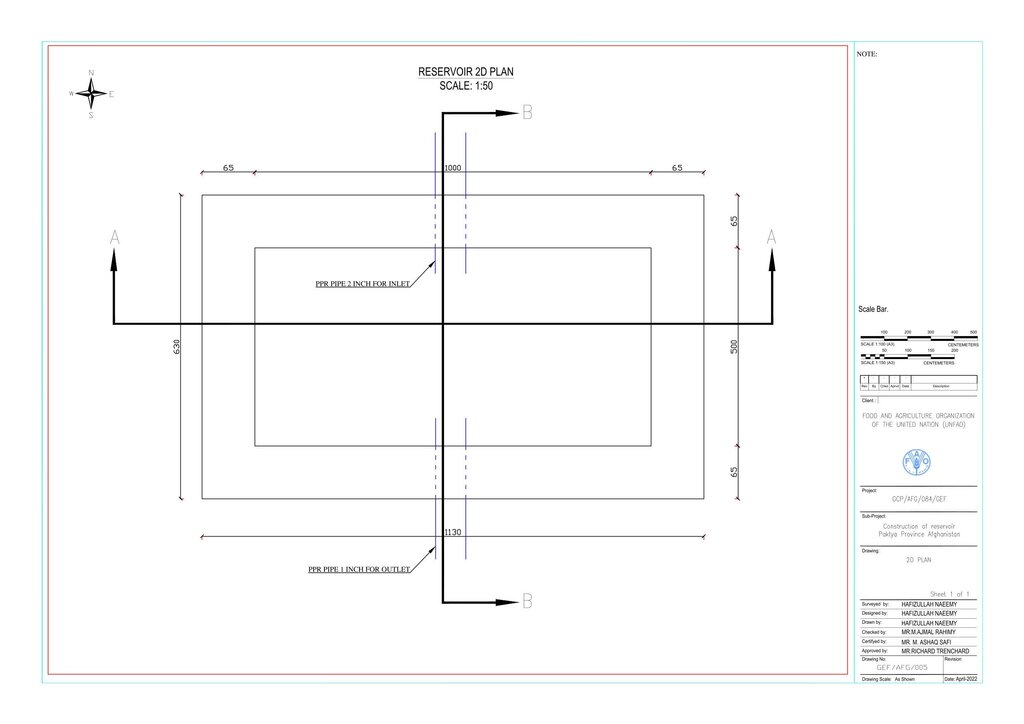
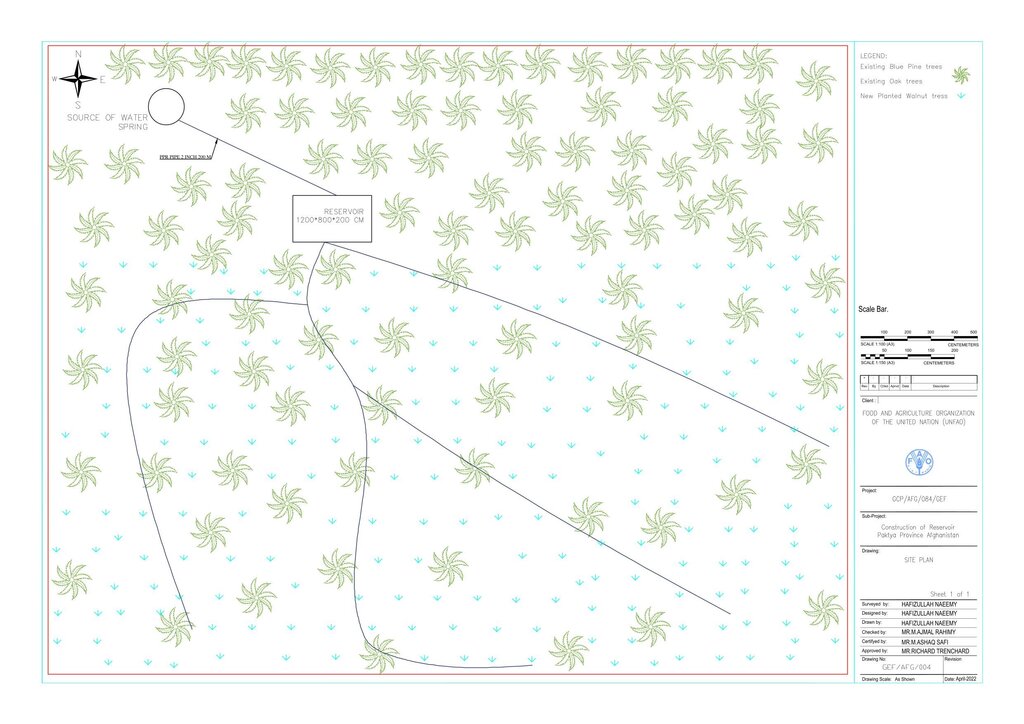
To support sustainable water management in the mountainous areas of Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam districts, 60 water reservoirs with a total storage capacity of 6,000 m³ were constructed. The volume of individual reservoirs varies depending on the availability and flow of upstream spring water ranging from 36 m³ to 192 m³.
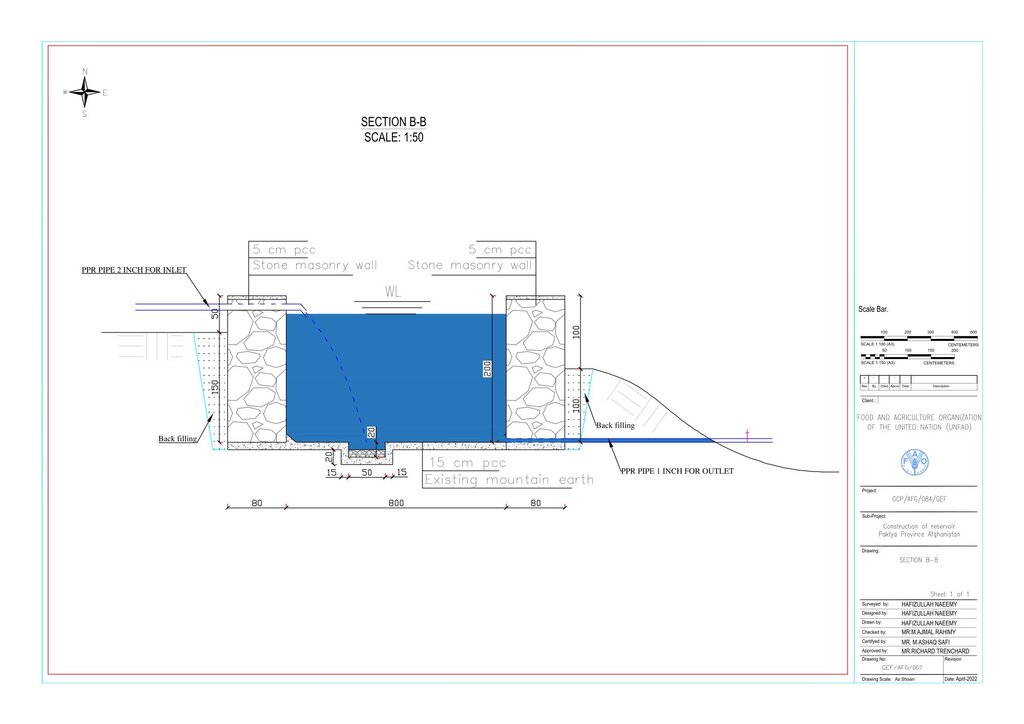
Water is diverted from a small intake near the source and delivered to the reservoir inlet through a 2-inch Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe. For irrigation of the restored areas, the outlets from the reservoirs are connected to 1-inch PVC pipes for distributing water to various plantation sites.
This technology is applied in a natural environment and is designed to support environmental sustainability by recharging the groundwater table, as water is harvested into reservoirs, it can infiltrate through the side walls and bottom. This percolation process contributes to the natural hydrological cycle, harvesting surplus water (water evaporate or percolating into atmosphere or soil) into reservoirs for irrigation of planted saplings, and extending existing forest boundaries.
The system enables the local community to sustainably manage and utilize spring water for gravity-based irrigation of restored areas, while also supporting the expansion of forested land through sapling plantation.
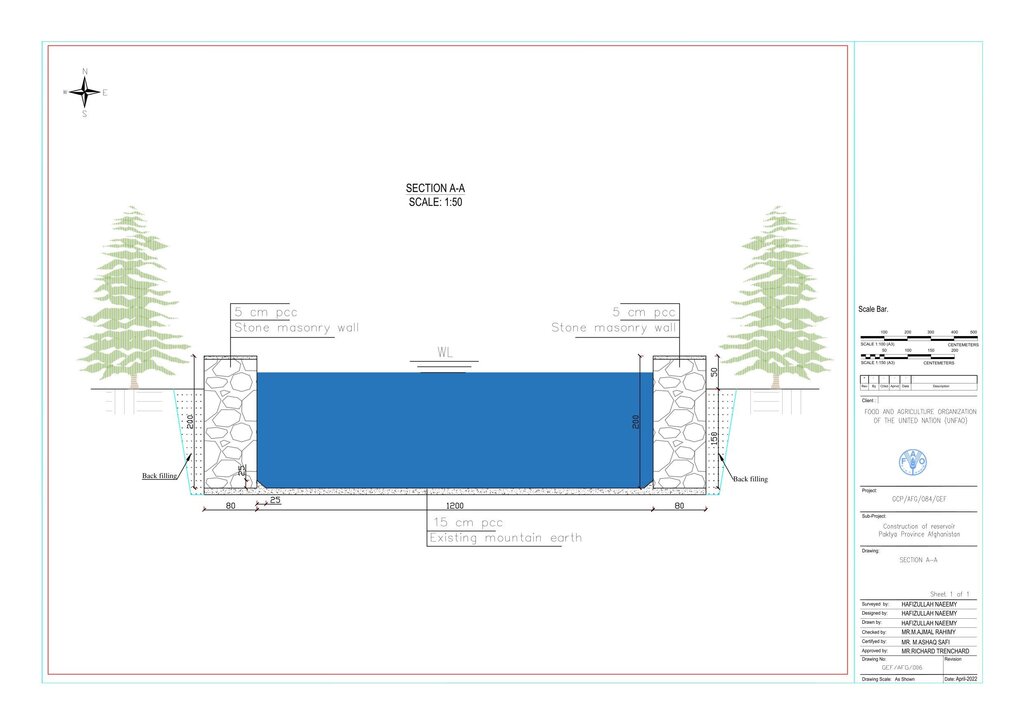
Before constructing the reservoirs, a feasibility survey of the water source (the spring) was conducted to verify the perennial availability of water and to determine the optimal distance between the spring and the designated reforestation sites. The preliminary selection of reservoir locations was based on key criteria including the year-round reliability of the water source, the size of the target reforestation area, and the discharge capacity of the spring. Excavation of the rocky mountain earth was carried out using a hand excavator as per the specified requirements as per technical drawing and approved design. The stone masonry work was completed using random rubble coursed stone with a cement-sand mortar mix (1:2, Type A). As per the design, Plain Cement Concrete (PCC M20) was applied to the top of the stone masonry and on all floors of the reservoirs. A 20 mm thick plastering was carried out on the internal walls using cement-sand mix (1:2). The external walls were backfilled to a height of 1.5 meters.
The benefits of this gravity-fed irrigation technique include increased reforestation rates, reduced water loss due to evaporation and runoff, achieved by using closed piping systems instead of open channels, and improved water use efficiency. These improvements have led to higher sapling survival rates and better growth. Overall, the socio-economic and environmental conditions of rural populations have been improved. Additionally, the implementation of the gravity irrigation system has reduced the cost of restoring degraded forests.
As a low-cost, environmentally friendly technology, it allows for the efficient harvesting of spring water for irrigation, supports sapling planting for carbon sequestration, and helps mitigate the severe impacts of climate change.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Paktya
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ahamd Aba and Sayed Karam district
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
មតិយោបល់:
The technology being applied in various location of forest areas, while in the map only two points highlighted in Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam district of Paktya
However, 46 water reservoirs constructed in Sayed Karam, while 14 water reservoirs constructed in Ahmad Ab
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- កាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ឯកវប្បកម្មដែលប្រើពូជក្នុងតំបន់
ប្រភេទដើមឈើដែលដាំនៅកន្លែងដែលមិនធ្លាប់មានឈើពីមុន :
- ព្រៃស្ងួតដាំតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច - Pinus spp.
ប្រភេទឈើ:
- ប្រភេទស្រល់
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃល្បោះចម្រុះ/ ព្រៃស្រោង
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
- ផ្លែឈើ និងគ្រាប់ធញ្ញជាតិ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ផ្លូវទឹក ផ្ទៃទឹក ដីសើម
មតិយោបល់:
With the implementation of the technology, degraded land has been restored to forested areas through reforestation.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- គ្រប់គ្រងការដាំព្រៃឈើ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកលើដី (ទឹកធ្លាក់ ទន្លេ បឹង សមុទ្រ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical drawing: indicated the details of the dimension of water reservoirs
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Hafizullah Neemy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/03/2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical drawing
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Hafizullah Neemy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
23/03/2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical drawing
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Hafizullah Neemy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/03/2022
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Drawing
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Hafizullah Neemy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
30/03/2022
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
5
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation to build reservoirs | When construction work is possible |
| 2. | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | After construction the reservoir |
| 3. | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | When construction work is possible |
| 4. | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | When construction work is possible |
| 5. | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | When construction work is possible |
| 6. | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | After construction work |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Excavation to build the reservoris | M3 | 62,0 | 10,0 | 620,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | M3 | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | M3 | 6,0 | 14,0 | 84,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | M3 | 42,0 | 14,0 | 588,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | Man-days | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | Man-days | 8,0 | 5,0 | 40,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Shovel | PC | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hammer | PC | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Excavator (taking by rent for excavation) | Cubic meter cost | 192,0 | 10,0 | 1920,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Cement | Package | 75,0 | 6,0 | 450,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Stone | Cubic meters | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Polyethelen pipe 1 inch | Meter | 500,0 | 0,8 | 400,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Polyethelen pipe 2 inch | Meter | 200,0 | 1,0 | 200,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Elbow joint | Piece | 3,0 | 1,0 | 3,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Valves | Piece | 4,0 | 4,0 | 16,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Sand | Cumbic meter | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Transportation | LS | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 5835,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 5835,0 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of pipes to outlet and inlet area of water reservoir | Spring season |
| 2. | Maintenance of reservoir for clearing and unclogging the inlet area | As per requirement |
| 3. | Replacement and installation of valves and elbow joints to prevent water clogging in the pipes | During non-function |
| 4. | The embankment constructed to accumulate the water and put the pipes inside to water for diverting to the reservoir | Spring season |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour for repairing of pipes at outlet and valves | Person | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour for clearing and unclogging | Person | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Valves | PC | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Elbow joint | Pc | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 170,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 170,0 | |||||
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The distance between the spring and reservoir can affect the total cost of technology
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
553,00
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
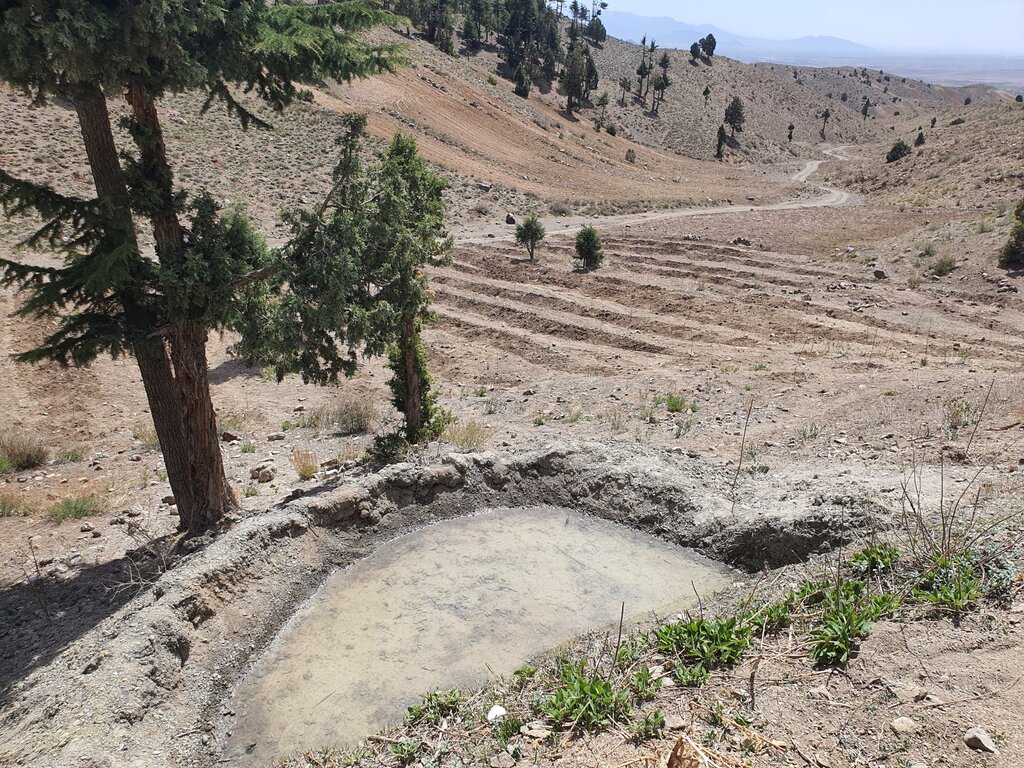
The construction site is situated at an elevation of 2500-3000 meters above sea level, with a terrain slope ranging from 15% to 20%. Photo related to field skitch, indicated that the area of reforestation is around the reservoir.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
លើស
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទាំងទឹកក្រោមដី និងលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
As the water from spring harvesting through pipes and accumulated in reservoirs can reduced the evaporation and stored for 2 or 3 days in reservoirs that can excess the water quantity for irrigation purposes.
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
- មនុស្សចាស់
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
All age group excluding children
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
The small-scale covered the reforestation areas about 10 ha for irrigation, while the medium scale covered about 20 ha for irrigation purposes.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
The water reservoirs were constructed on communal land for use by the local community, allowing shared access for irrigating reforested areas. Access and use are managed through a community-agreed contribution system.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The establishment of woodlots and other forest can increase the fuel wood for heating the house and cooking, fodder for livestock and fruit for home consumption. The established woodlots consist of a mix of fruit and non-fruit tree species.
អនុផលព្រៃឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The non-wood forest productions increased with increasing the area of production through gravity irrigation systems enhanced the community-based efforts in degraded forest.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The production areas of NTFPs have expanded due to the annual planting of saplings in degraded forest areas, supported by water reservoirs that provide irrigation and enable the extension of existing forest boundaries.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកប្រើប្រាស់សម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The irrigation water availability has improved due to efficient management of the spring water. As the spring water gradually decreases from June to December months which considered as dry period, while January to March months is the wettest period that water is excessive and can be harvested for the following dry period.
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As the construction of water reservoirs can significantly improve the water availability during the year both in the wettest period and followed by dry period, by storing the water can balance the demand for the irrigation water.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Households living in rural areas rely on income from non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and agricultural production, resulting in a diversification of their income sources.
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
the workload for the irrigation of reforestation areas reduced with application of technology because the number of days for irrigation done manually reduced and also the cost of irrigation.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
Vegetation Cover
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Vegetation cover has improved each year due to ongoing tree planting and the protection of designated areas through quarantine measures.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការកើនឡើងដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
អាកាសធាតុ
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | ថយចុះ | ល្អណាស់ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | និទាឃរដូវ | កើនឡើង | ល្អណាស់ |
មតិយោបល់:
The forest function for the regulating of climate, rainfall and snowfall. By increasing the forest cover that can help in regulating the annual rainfall.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
The technology adapted well to reduce the severe impacts of the water on the plant growth and development during water scarity situation in summer.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The technology is cost-effective for irrigating afforested areas and is easy to use and conducive to implementation. |
| The workload for irrigating the afforested area has been reduced, resulting in fewer man-days required for irrigation. |
| The harvesting of water from ground spring allows to expand the forest area through plantation of saplings, otherwise it not possible. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The sustainable management of ground water spring contributed to the expansion of restoration efforts in the community level. |
| By implementation of technology at specific point, the soil vegetation cover improved from 10 to 15 percent. |
| The biodiversity enhanced with restoration of degraded forest area, through plantation of native species, regeneration of native bushes, grasses. |
| The unproductive soil converted into productive soil through plantation of bio energy plants to produce fuel wood, fodder and fruit. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital for construction of water reservoir. | Government should provide subsidy for construction of reservoir. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Communities' willingness and technical knowledge for the resource management depends on the component of the project . | Providing supporting from the government side for establishment and technical knowledge. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Sixty field visits were conducted to assess the constructed water systems.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Four land users interviewed using SLM technology questionnaire.
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
Two SLM specialists were interviewed to gather their insights on aspects of the project.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល