Strip mine rehabilitation [ប្រទេសអាហ្រ្វិកខាងត្បូង]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Kirsten Mahood
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli
technologies_970 - ប្រទេសអាហ្រ្វិកខាងត្បូង
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
University of Stellenbosch (University of Stellenbosch) - ប្រទេសអាហ្រ្វិកខាងត្បូង1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Rehabilitation of areas degraded by strip mining, through returning stockpiled topsoil and transplanting of indigenous species, to promote revegetation.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
In contrast to the land degradation commonly caused when ‘strip mining’ is carried out, a land rehabilitation technology, which was first developed experimentally, is now routinely applied by mining companies on the west coast of South Africa. Indeed it is now a legal requirement in South Africa for mining companies to rehabilitate mined areas to a condition and productivity equivalent to the pre-mining situation.
The primary purpose of the technology described here is to achieve this result – thus allowing the site to be used again for extensive grazing by sheep and wild animals. Revegetation also reduces wind erosion. The technology further contributes to increasing biodiversity, as particular attention is given to planting a range of locally endemic and other indigenous species.
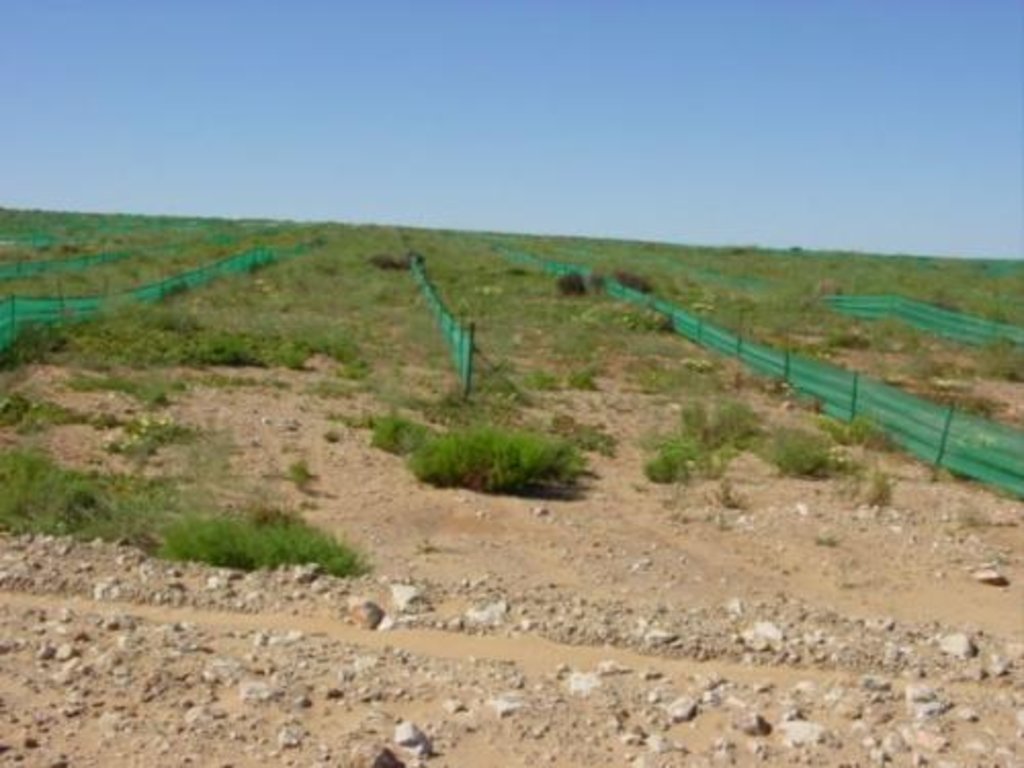
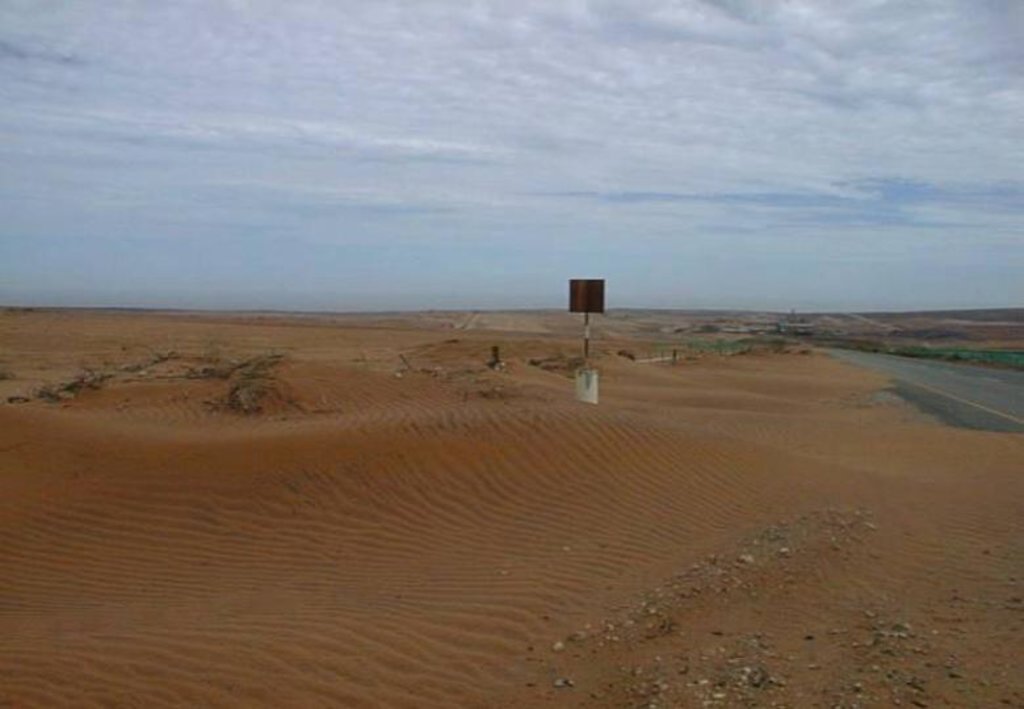
The sequence of operations is as follows: during strip mining operations the topsoil is pushed to one side by bulldozer, and stockpiled. The substrata is then excavated mechanically, removed by tipper truck, and processed to extract the heavy metals. The tailings (waste materials) are returned by tipper truck to the area from which they were mined, and then levelled by bulldozer. The stockpiled topsoil is returned and spread by bulldozer over the levelled tailings. Indigenous succulents and other plant species are dug out by hand, with a spade, from either the surrounding areas of natural vegetation, or from the piles of topsoil (where plants may have naturally established) and transplanted manually into the newly spread topsoil. The planted areas are protected from wind erosion by erecting fine mesh nylon netting as windbreaks. These are 0.8 metre high and 5 metres apart. The nets are usually installed for a period of up to 2-3 years. Subsequently they are removed, once the vegetation has successfully become re-established, and they may be re-used at the next rehabilitation site. Maintenance activities continue for a few years – until the site is rehabilitated. An individual mine strip is usually about 1 km long and some 100 m wide.
This form of strip mine rehabilitation has been in operation since 1990, and costs on average just over US$ 200 per hectare, with all expenses met by the mining company. This particular approach was developed for the Anglo-American subsidiary – ‘Namaqua Sands’. A similar approach was adopted by ‘PBGypsum Mines’ located further inland, where rehabilitation is also conducted on several hundreds hectares of mined land. Not all mining companies use the same technology, however.
Purpose of the Technology: Establishment activities:
Mining activities (not part of technology)
1.Removal and stock piling of topsoil
2.Excavation, removal and processing of substrata to extract heavy minerals
3.Return and levelling of the mine tailings
4.Return and spreading of topsoil Technology activities
5.Collection/digging up of indigenous plants
6.Transplanting into returned topsoil
7.Erection of fine mesh nylon net windbreaks Activities 1-4 are a continuous process associated with the speed of mining activities and involve the use of heavy earth moving machinery (bulldozers, front end loaders, tipper trucks). Activities 5&6 take place immediately prior to the onset of the rainy season and involve hand labour for collection and transplanting and tractor and trailer for transporting collected plants. Activity 7 can take place at any time of the year involving hand labour for erection of the nets and tractor and trailer for transport.
Maintenance / recurrent activities per year:
Maintenance activities restricted to:
1.Ensuring the nylon nets remain upright
2.Supplementary watering during the winter months, when rainfall inadequate, to support plant growth
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាហ្រ្វិកខាងត្បូង
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Western Cape
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Brand-se-Baai, Western Cape
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 1-10 គម2
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Developed at University of Stellenbosch
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
ឧស្សាហកម្មទាញយករ៉ែ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Aridness and climate change. Erratic rainfall/climate. Frequent drought.
Ranching: Yes
Constraints of mines and extractive industries: Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Aug
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
A3: ប្រព័ន្ធភ្ជួររាស់ខុសៗគ្នា:
A 3.1: មិនភ្ជួររាស់

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V5: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S11: ផ្សេងៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Specification of other vegetative measures: translocation of indigenous plants
Specification of other structural measures: land levelling, artificial windbreaks
Type of agronomic measures: zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pu: បាត់បង់នូវផលិតភាពជីវៈដោយសារសកម្មភាពផ្សេងៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 2000
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Other species: Succulent plants
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
Structural measure: silt fence
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Construction material (other): nylon net - small grid size
Silt fence: all 5m and height of 0.8m
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Kirsten Mahood
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Rand
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
9,07
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
12.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of plants from natural vegetation | Pre-rainy season |
| 2. | Collection of plants from topsoil stockpiles | Pre-rainy season |
| 3. | Transport plants to rehabilitation area | Pre-rainy season |
| 4. | Plant all plants | Pre-rainy season |
| 5. | Insert droppers into net pockets | all year |
| 6. | Spread nets over topsoil areas | all year |
| 7. | Erect nets and hammer in droppers | all year |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | hectare | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | machine hours | 0,5 | 134,0 | 67,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Nylon net | ha | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 212,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 23,37 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topsoil pushed into stockpile | all seasons / continuous |
| 2. | Subsoil removed and processed | all seasons / continuous |
| 3. | Processed subsoil returned to mined area and levelled | all seasons / continuous |
| 4. | Stockpiled topsoil spread over processed subsoil | all seasons / continuous |
| 5. | Plants transplanted onto spread topsoil | just before rainy season / late autumn/winter |
| 6. | Ensure nets remain upright | all year/continuous |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 37,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 4,08 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Per hectare
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Labour costs
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- ស្ងួត
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
soil fertility: very low, soil drainage / infiltration = low, soil water storage capacity = low
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Most of income from mining
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
vegetation, establishment
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Land can be used again for extensive grazing after mining
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
improved conservation / erosion knowledge
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
restoration of bio-productive function
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
biodiversity enhancement
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced wind velocity
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Low establishment costs and very low maintenance costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make use of whatever resources and potentials are naturally available (such as micro-catchments to trap rainwater and improve soil moisture conditions for plants) to lower establishment costs. |
|
Costs are met by the mining company – no costs are transferred to those who subsequently use the land for grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular monitoring of soil and vegetation conditions. |
|
Land productivity is restored and biodiversity increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Seeding as well as transplanting. |
| Wind erosion minimized. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Rehabilitation is an extra cost for the mining company. | Ensure mining company meets the costs through enforcing legislation. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល