Self-help groups [ເຄັນຢາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Frederick I. Kihara
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2357 - ເຄັນຢາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Kiteme Boniface
+254-62 31328
b.kiteme@africaonline.co.
CETRAD - Centre for Training and Integrated Research in ASAL Development
PO Box 144, Nanyuki
ເຄັນຢາ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Centre for Training and Integrated Research in ASAL Development (CETRAD) - ເຄັນຢາຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
University of Bern, Institute of Geography (GIUB) - ສະວິດເຊີແລນຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Agronomica - ລາຊະອານາຈັກອັງກິດ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
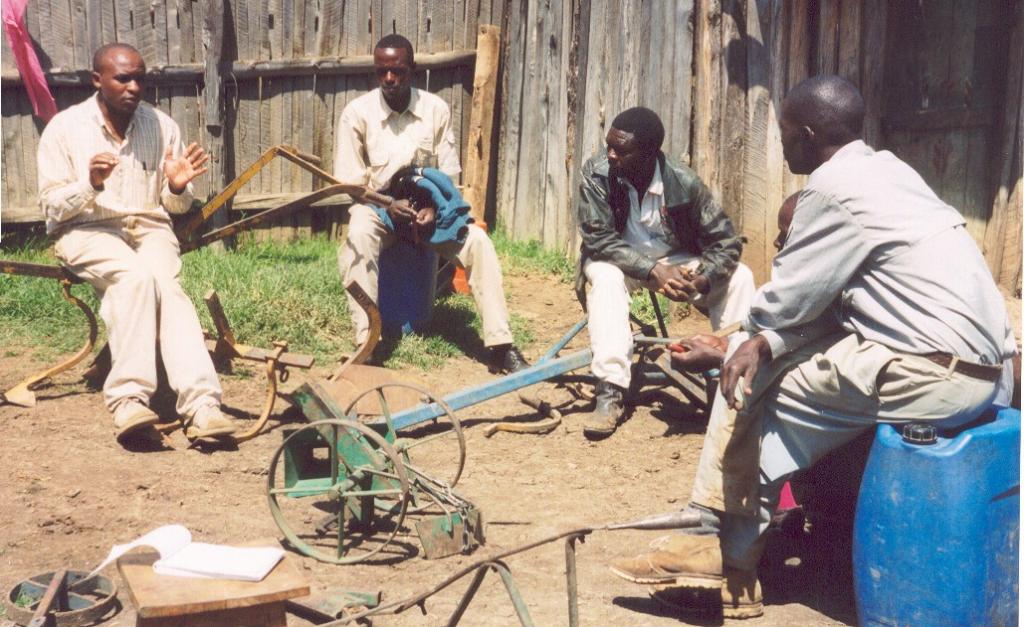
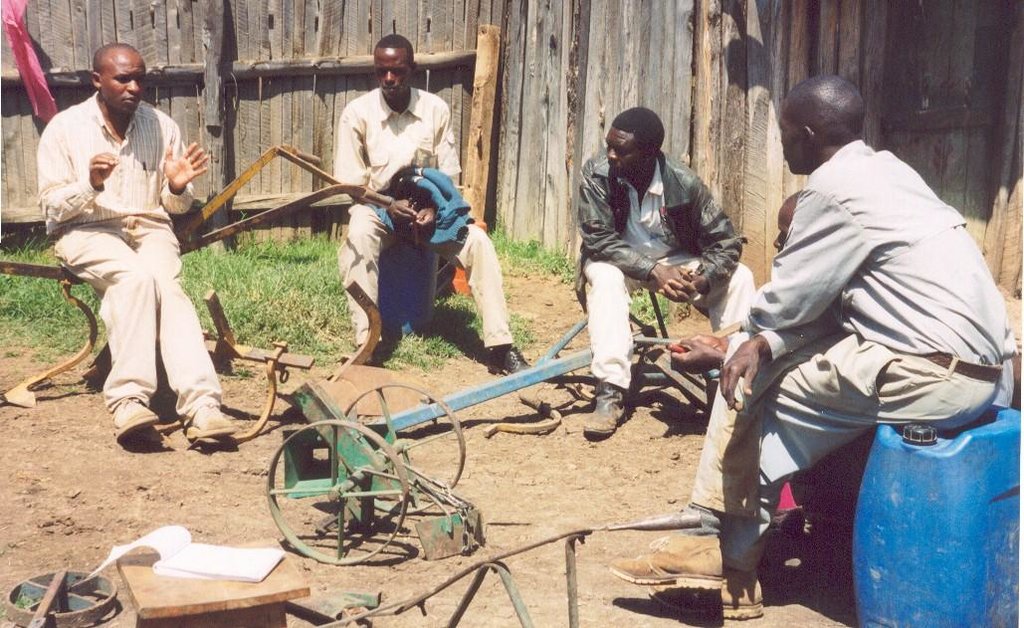
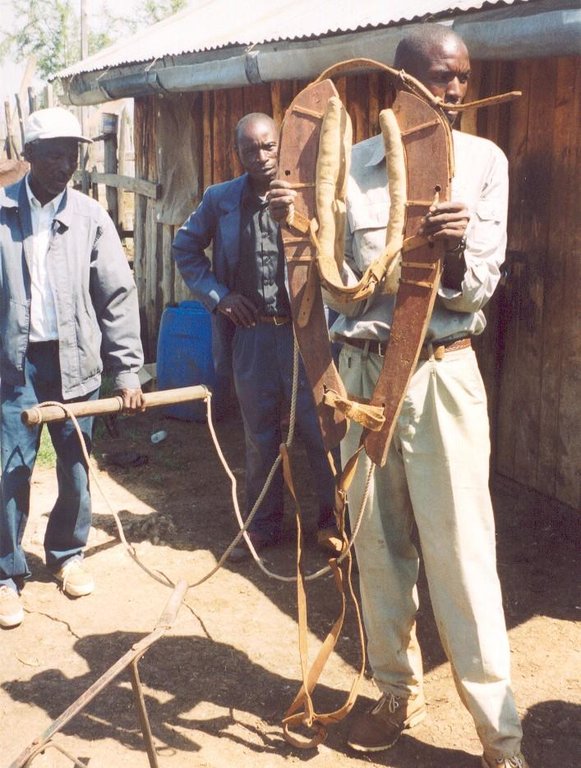
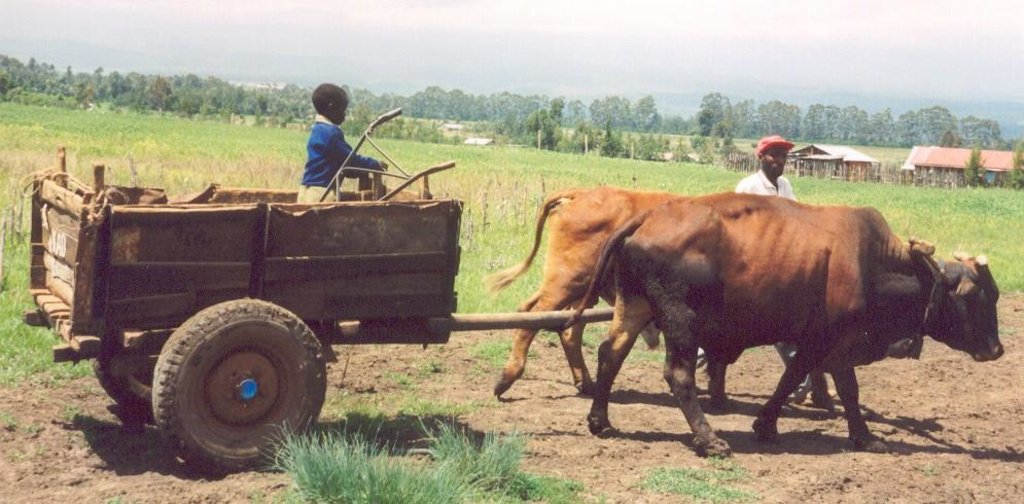
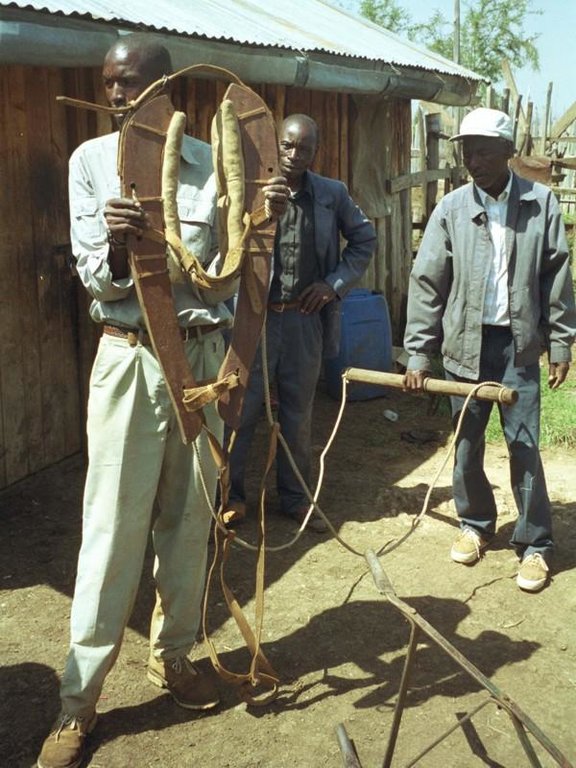
Small-scale farmers forming self-help groups to provide mutual support for adopting and promoting conservation agriculture.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
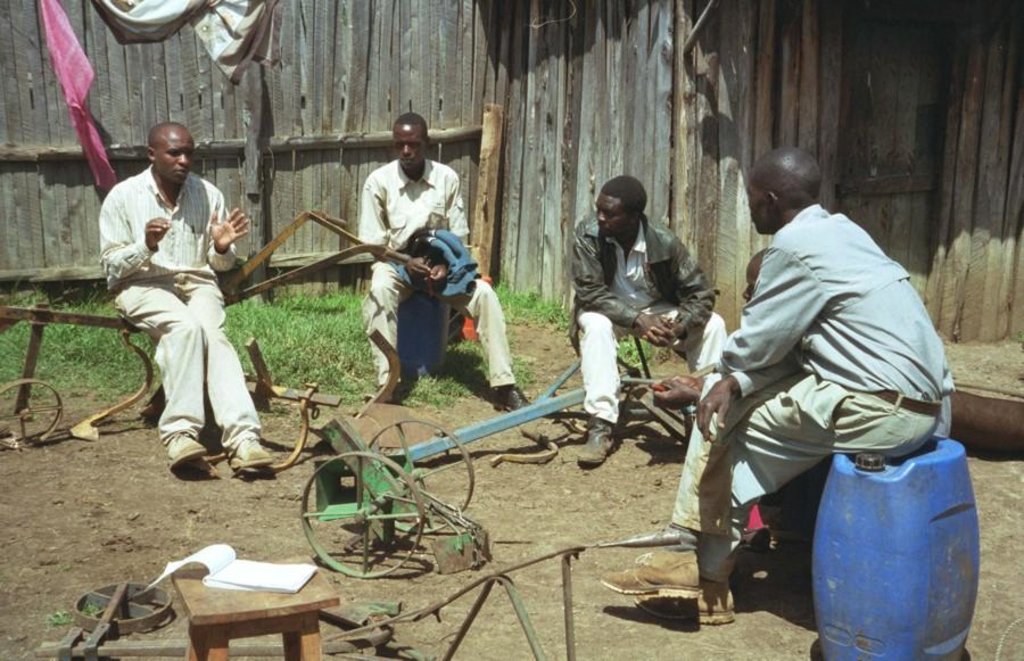
Aims / objectives: The self-help group approach described here is an initiative which grew from the local land users themselves. Farmers with common interests and goals came together, formed and registered groups and developed constitutions. Conservation agriculture groups started forming in 1997: within two years, five groups had been set up in the study area with over 150 members. The Ministry of Social Services facilitated the registration process. Groups have liased with technology promoters from the Ministry of Agriculture, KENDAT (Kenya Network for Draught Animal Technology), and research and development projects, to gain access to technical knowledge. These organisations have set up research and monitoring projects to assess the impact of conservation agriculture in this area. The groups receive more attention from local development partners than individuals would. The overall purpose behind the formation of the groups is to improve household food security and raise income. More specific objectives include: (1) mutual adoption of the technology, enabling group members to improve their farm operations and yields, and thereby; (2) creation of opportunities for additional income to help and support each other; (3) sharing knowledge, and conservation tillage equipment.
Role of stakeholders: Groups involve themselves in farmer-to-farmer training. They develop training modules which cover all aspects of conservation agriculture as well as practical training of the animals. Meetings are held once a month to plan group activities. The groups also solicit loans from local development partners for equipment, and they access training on technology from national institutions. Further collaboration with national institutes is planned to facilitate availability of droughttolerant crop varieties. The members of the self-help groups make various contributions including time, money, animals and some equipment - for joint group activities. Farmers with equipment contract their services to those without, but this is provided at a 20% discount to members.
Other important information: High adoption levels of conservation agriculture have been achieved through the self-help groups, due to the sharing of resources for technology development and mutual support. The interest in conservation agriculture and demand for equipment is high and growing. Group members are also diversifying their activities into, for example, agroforestry, water harvesting and bee-keeping.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ເຄັນຢາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Rift Valley
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
1997
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (poverty alleviation, collective bargaining for procuring services, joint produce marketing, on-farm diversification, off-farm opportunities)
- increase household food security and raise income within the group. - provide mutual support and thereby develop collective bargaining power - an example is the ability to attract technology training from national organisations. - seek possible ways of acquiring equipment for all members of the group, through securing donor support or sponsorship. - all cropland to be under conservation tillage, with all members being fully trained in the technology and having the necessary equipment
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - insufficient individual resources to invest in/or learn about new technology. - underlying problems of (1) food security and (2) insecure water supply for rainfed crop production due to insufficient and poorly distributed rainfall
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Use of draught animals seen as backward and non-progressive and gender-bias (technical operations and animal ownership traditionally male activities)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The number of practising farmers providing mutual support able to neutralise such thinking and the group approach has created an avenue for women to participate
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Equipment is costly and generally cannot be afforded by many
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Ability to hire services from farmers in the group who have equipment
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Small land size can hinder adoption of the technology: the group approach can help to overcome this limitation. Those with small land parcels can access and afford the technology without having to keep animals.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Technology wsa new and initially not well understood
Treatment through the SLM Approach: As an organised group, the members were able to attract technical training from experts (eg KENDAT, KCTI)which was paid by local development partners and also learnt from more experienced members of the group
ອື່ນໆ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Organisational. Group formation and group dynamics
Treatment through the SLM Approach: 2-3 enthusiastic, visionary individuals ensures success
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Farmers, with common interests and goals, formed the group, registered and enacted their constitution. Government Ministry of Social Services facilitated the registration process. Group members liaised with technology promoters to access technical knowledge.
Working land users were work equally divided between men and women (The group has mixed membership but men tend to dominate field operations). Men traditionally own animals and have easier access to investment capital to purchase equipment than women. However, this is changing. In addition, in one group, the treasurer is a woman. The group also trains women how to use the technology. Within the first year, one woman had obtained the whole set of equipment plus a pair of oxen.
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
The group mobilises itself but with some support from Ministry of Agriculture extension workers.
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | public meetings; Creating awareness of technological development through open forums undertaken by agricultural extension staff. Meetings were held to plan organisational development . Farmers received information about an innovation that could be beneficial to them; they then mobilised themselves |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | public meetings; The group plans its own agenda in meetings |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | responsibility for major steps; The group is responsible for procuring equipment and inputs; they train their animals, while training on technology is provided by specialists |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ | Mainly: measurements/observations; partly: public meetings; Group members keep yield records which are reported and discussed at meetings (without participation of specialists) |
| Research | ການຮ່ວມມື | on-farm; Farmers themselves compare cultivation methods; in addition, some research plots by KENDAT, the extension services (MoA) and students have also been set up in farmers' fields. |
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Supported by the National Soil and Water Conservation programme under the Ministry of Agriculture (MoA). SWC specialists created awareness of the technology in the local community, with land users independently deciding to adopt.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). Farmers adopted the technology with modifications so that they could use their animals for draught power. However, there was a degree of follow-up by SWC specialists.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- group members, SWC specialists (2), extensionists/trainers (3)
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
- ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
- ຫຼັກສູດ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
The main element is farmer-to-farmer training within the group on use of appropriate equipment, equipment maintenance, animal health and care. Members attend training courses organised by extension staff and NGOs including KENDAT and Operation Comfort (from Central Kenya). Apart from courses, there are demonstration areas on research sites and group plots, as well as farm visits amongst and betwee
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: Innovative farmers support; Key elements: Identify innovative farmers in an area, Supporting them to come together, Providing new technology training; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: Other: governmental, non-governmental and group members 2) Advisory service was carried out through: Other: governmental, non-governmental and group members; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Training on use of appropriate equipment, equipment maintenance, animal health and care etc
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The performance of the technology is very impressive and rapidly adopted by group members. However this is dependent on the group ie 2-3 enthusiastic and innovative members are required for a successful group. Further expansion is limited by weak extension support.
Extension is carried out through governmental and non-governmental specialists, equipment sales person and well-informed group members. This is facilitated by the way groups formed and tapped into the extension advice, and also shared information amongst themselves.Extension is carried out through governmental and non-governmental specialists, equipment sales person and well-informed group members. This is facilitated by the way groups formed and tapped into the extension advice, and also shared information amongst themselves.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored. Indicators: work undertaken
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored. Indicators: rate of adoption, attitudinal changes
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: yield/area with the data from research station being occasionally analysed and results shared out
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: acreage
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: as membership feedback af meetings
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The success of the technology - conservation agriculture - has strengthened group collective bargaining power to attract further extension input support, regular visitation and advice on best agronomic practices. There has also been a move to encourage women's uptake of the technology.
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
On-farm research is carried out by KENDAT, who conduct field trials to investigate the best technological practices. The data is collected in collaboration with participating farmers. The field research activities have included long-term experiments, demonstration sites and field days.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- < 2,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (Self-help group members): 100.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ, ເງື່ອນໄຂ ແລະ ຜູູ້ສະໜອງ (ຫຼາຍ):
Two year loans are available from international development partners (SNV).
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | 2 year loan possible |
- ອື່ນໆ
| ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ) | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| Technical training and back up | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເງື່ອນໄຂກໍານົດ (ອັດຕາດອກເບ້ຍ, ຈ່າຍຄືນ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ) :
Two year loans are available from international development partners (SNV). Generally 50% is repaid in the 1st year, 50% in the 2nd year. These loans are used to purchase equipment, with group members acting as guarantors for each other.
ລະບຸ ການໃຫ້ບໍລິການ ການປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ:
The community contributed a considerable percentage (through labour and time). KENDAT (NGO,Kenya) mainly provided training and extension, whereas SNV (NGO, Netherlands) gave credits. Details of the breakdown are not available.
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
These improvements include in situ moisture conservation (reduced evaporation and runoff), water harvesting, increased soil fertility and reduced soil loss.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Many self-help groups have arisen and are addressing their particular problems related to conservation agriculture.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງຂອງໄພພິບັດ
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າ ໄດ້, ອະທິບາຍເຫດຜົນ:
Land users can continue group formation and the associated activities without external support because they can seek technical support for the specific activities.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Collective bargaining power is achieved through good accounting and positive group financial status. This tends to attract donor support for further collective activities. |
| Sharing of technological knowledge, as well as equipment, within the groups and exchange between groups. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Easier for extension services to target a group of like-minded farmers than individuals (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Encourage further self-help group formation) |
| Self-help groups are self-sustaining (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ensure continual success by providing refresher courses on technology by extensionists, introduce innovations to keep group interest alive.) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Greater time and energy input from the innovative farmers, because they pass on their knowledge without direct reward | Farmers gain confidence and status in the group or area as leaders. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Self-help groups are not optimal where some individuals are relatively poor and cannot afford contributions | modify arrangements to permit higher contributions by more financially able members who then get a greater share of the profits. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Liniger HP and Thomas DB (1998) GRASS - Ground Cover for Restoration of Arid and Semi-arid Soils. Advances in
Ngigi SN (2003) Rainwater Harvesting for improved land productivity in the Greater Horn of Africa. Kenya
Mutunga CN (1995) The influence of vegetation cover on runoff and soil loss - a study in Mukogodo, Laikipia district Kenya. MSc
Kihara FI (1999) An investigation into the soil loss problem in the Upper Ewaso Ng'iro basin, Kenya. MSc. Thesis. University of
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ