Comprehensive watershed development [ອິນເດຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: David Gandhi
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2374 - ອິນເດຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Desai Nilesh
SAMPARK, Raipuria, Tehsil- Petlawad, Distt. Jhabua (MP)
ອິນເດຍ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Bhattacharya Tapan
Lok Biradari Trust, Indore (MP)
ອິນເດຍ
ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur (Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur) - ອິນເດຍຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Lok Biradari Trust - ອິນເດຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Aims / objectives: The approach adopted under the Comprehensive Watershed Development Project (CWDP) is intended to ensure sustainability of development interventions. This can only be achieved through creating a sense of 'ownership' amongst users, which means involving the community in planning, implementation and management of the interventions. A further, specific objective is to benefit vulnerable sections of the community.
Methods: Various methods are employed to achieve these goals. There is, first of all, awareness generation within the community through exposure visits outside the area, street theatre and video shows. After this comes the formation and capacity building of village level institutions, in particular the Village Watershed Development Committees (VWDCs). Users' groups are also formed. Micro-planning (under a 'village development plan') using participatory rural appraisal (PRA) follows. There are arrangements to ensure participatory execution of the plan, specifying cost and benefit sharing (on average 75%-90% of the work is paid for in cash under this approach). Another important element is to ensure user rights to resources. This entails negotiation with government for rights to produce from common land. Eventually, after initial implementation, management becomes the task of the users' groups: this includes maintenance, distribution of benefits and conflict resolution. The whole process involves NGOs along with government staff in order to achieve better communication all round. The participants have different roles. Government staff (at various levels) provides technical and financial support, as well as assistance towards gaining user rights over resources. NGOs are particularly important in awareness generation and mobilisation, capacity building of village level institutions, and in the process of negotiation with the Government.
Role of stakeholders: The village committee is central in planning and implementation of the village development plan, and in overseeing users's groups. Users's groups are involved in planning, implementation and then resource management. The village assembly helps to identify beneficiaries and users, and to give overall support to the VWDC. An external international donor, DANIDA of Denmark, supports the Comprehensive Watershed Development Project.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
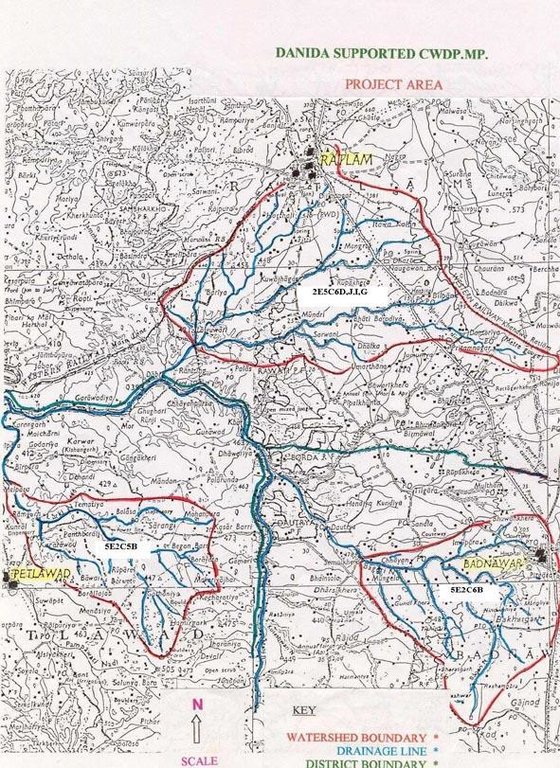
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ອິນເດຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
1997
ປີທີ່ສີ້ນສູດ (ຖ້າຢຸດບໍ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ):
2007
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (1- Capacity building of communities, 2- Production system)
- create a sense of ownership amongst users. - ensure sustainability of technical and social interventions. - benefit more vulnerable sections of the community, including the poor and women. - involve the community in planning, implementation and management interventions
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: previous lack of consultation/involvement with the community in planning, implementation and management of watershed development interventions
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of awareness and mobilisationon improvement of production systems.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Intensive programme for awareness generation and mobilisation of community
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Lack of effective institutions at village level to take responsibility for the development process.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Formation & capacity building of VLI (VWDC,UG) with assistance of NGOs.
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Uncertainity fover rights to access to resources
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Negotiations facilitated by NGOs
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation While treatment of privately owned land did not face a problem, encroachment on Govt. land was an obstacle which discouraged land users from implementing SWC on these lands. Furthermore it was not possible to obtain users rights on lands under the Forest Department, which resulted in their exclusion from SWC in most cases. The NGOs involved however acted as intermediaries in negotiations.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
High cost water harvesting measures.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Demonstration of low cost alternatives such as the doh (sunken structure in dry riverbed to increase infiltration of runoff, which replenishes wells for irrigation: see 'related technology').
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
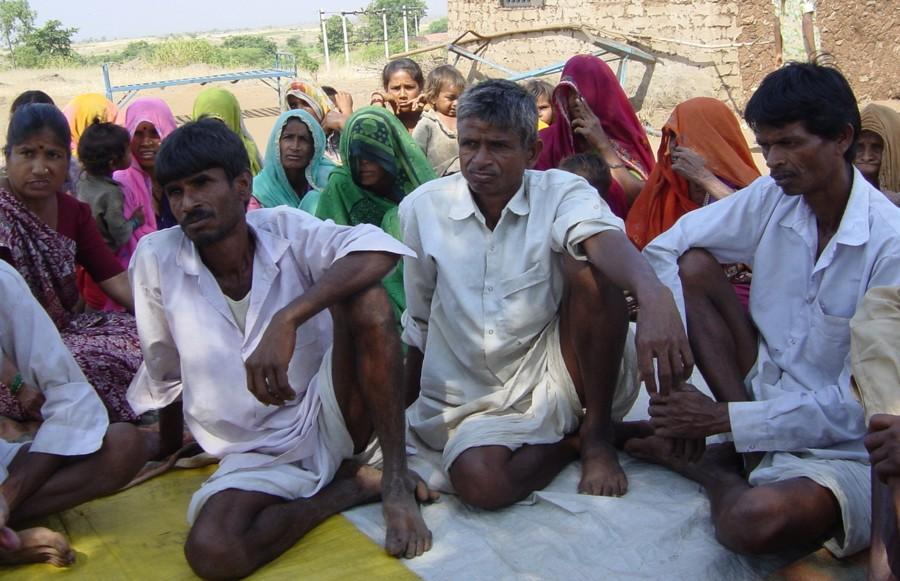
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Specific ethnic groups: While the main group were Bhil tribal, other groups included Gujars, Patidars etc.
Due to social factors, traditionally decision making largely done by men. However, the project has worked towards involving women in all aspects of the project. Participation of women in decision making bodies such as village committee is restricted . Participation of women is good in implementation, self-help groups etc. The project is active in neediest & most degraded villages which are fairly homogenous in nature. Furtherore efforts are made to identify and benefit poorest households.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Village Watershed Development Committee, Users Group.
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
Govt. of India/ Govt. of Madhya Pradesh, Department of Agriculture.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ
Danida
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The broad approach was developed by national and international specialists at the time of project appraisal. The detailed pedagogy was developed by the project in consultation with NGO partners and consultants.
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Mainly:public meetings; partly: awareness generation; Community meeting for discussion. Street plays, exposure visits for awareness generation. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Mainly: rapid/participatory rural appraisal; partly: group meeting; Preparation of village plan. Discussion on village plan. Negotiation, Decision making. |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | responsibility for minor steps; Landusers provide labour, partly subsidized by project. VWDC members involved in supervision & payments. |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | measurements/observations; Water levels, migration rates monitored by community with project staff. Gram sabha (Village assembly) meets every 3-6 months to discuss project activity. VWDC meets monthly to take stock. |
| Research | ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ | on-farm; studies carried out by project staff. |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
CWDP-MP: Comprehensive Watershed Development Project in Madhya Pradesh PIP: Project Implementation Plan VWDC: Village Watershed Development Committee
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ:
exposure visits' to outside demonstration sites are used as a tool for sensitisation, motivation and awareness raising.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Discussion with VWDC,UG.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- SWC specialists, extensionists/trainers
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
- ຫຼັກສູດ
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- exposure visits
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
1- Training for VWDC, UG, SHG's to conduct meetings, accounts and book-keeping. 2- Technical trainings. These are provided by government and NGO staff. Training concentrates on participatory approaches and low cost technologies. Capacity building for community groups and land users enables them to participate better in projects and to take ownership of assets.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: Multi Disciplinary Teams; Key elements: Field staff drawn from different Govt. line deptt. and NGO's., Village level workers selected locally, paid by the Project through NGOs., Formation, capacity building of village level institutions and farmers.; 1) Advisory service carried out through: non-governmental agency, projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: Govt.+ NGO employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Capacity building of village institutions, demonstration of SWC measures, production
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The state policies now emphasise the participatory approach. However, aspects like GO-NGO cooperation need to be instutionalised.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: general parameters
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: water levels in some wells
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: migration
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: yield
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: hectares treated
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: attendance at meetings
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Several technological changes have taken place as a result of a review: for example feedback on yield data led to crop variety recommendations. Levels of water in wells confirmed impact of the 'sunken structures' (dohs).
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- 100,000-1,000,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 5.0%; international (-): 85.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour): 10.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
- ກະສິກໍາ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ແນວພັນ, ແກ່ນພັນ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
| Seedlings | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນສົດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
As is common in Indian watershed development initiatives, there is a substantial subsidy towards labour involved. under this approach 75-90% of labour input is paid for in terms of cash: the remainder is voluntary contribution
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The participatory approach has been fairly successful in demonstrating SWC technologies such as Silvi Pasture, Sunken Structures which have been adopted/maintained by the land users.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
By using the approach, the project was able to win the confidence of most land users.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The pilot project which has tested the approach over past 3-4 years is implemented by the Department of Agriculture. The State Department of Agriculture has now expanded the approach to its other projects eg. NWDPRA.
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ແນ່ນອນ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
1- NGO's will contrinue to visit villages where project has completed bio-physical activities for a period of 2-3 years with a view to provide support and further training to VLI's & communities. Hence it is pre-mature to comment at this stage.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Awareness about SWC increased through street plays, exposure visits. Use of drama preferred to verbal communication. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue, and include visits to successful income generating projects.) |
| Participatory planning has led to better understanding of resources and possibilities (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The entire village plan should be implemented in defined stages to allow impact to be noted/felt.) |
| Cost-sharing increases feeling of ownership. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Community contribution should be deposited in the village fund to enable further activities after project moves out.) |
| Due to village institutions, there is greater decentralisation of ressponsibility and more people are actively involved. |
| As a result of village fund, interest component remains within the village. |
| Increased transparency as a result of GO-NGO cooperation. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Less rigidity in roles of GO/NGO staff.) |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Marginalised groups have been identified and given a 'say' (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: NGOs should continue to advise/guide/monitor activities) |
| Systematic approach to strengthen community participation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Detailed 'process documentation' to be continued.) |
| Leadership developed at village level. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: NGO's continue to advise/guide/monitor activities in the village.) |
| Land users develop a strong sense of ownership of the assets created. (in terms of cost-sharing, a local contribution of up to 25% is high in Indian contexts) (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: There needs to be continued support for 2-3 years after phasing out of bio-physical watershed development activities; also important to build up village funds through a 'community contribution' charge deducted from wages.) |
| Government system can be strengthened by co-operation with NGOs in watershed management projects (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue dialogue between partners at various levels..) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Formation of User group creates conflict with surrounding villages. | |
| Segregation of responsibilities of GO-NGO staff viz. NGO role restricted to community organisation while GO staff deal with technical asspects. | Better integrated teamwork should be the goal. |
| A 'community contribution' charge is currently deducted equally from all villagers by the project from wages paid | Contribution to be deposited in village fund., Should be a greater voluntary contribution from the richer farmers. |
| Participation in various meetings at village level is cumbersome for women, resulting in increased pressure from male family members and loss of wages. | |
| Project duration for planning and implementation too short | Increase the timespan to 3 years or more. |
| Women not adequately involved in exposure visits. | Correct this imbalance/arrange separate visits for women. |
| Exploitation by middlemen when small farmers market produce not addressed by the project. | Group marketing of produce. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Because of low literacy levels NGO support to village level institutions is required for more than just short-term | Adult literacy classes of sufficient duration are needed. |
| PRA brings out many social factors that are beyond the scope of the project to influence eg the feudal system | NGOs need to have broadbased activity platforms that can address these issues as they arise. |
| Shortage of female staff restricts contact with women land users. | Gender sensitization, training for project staff intensified. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
'Participatory approaches in watershed management- successful experinces' David Gandhi 2002
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Indian Association of Soil Conservation, Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Insti
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ