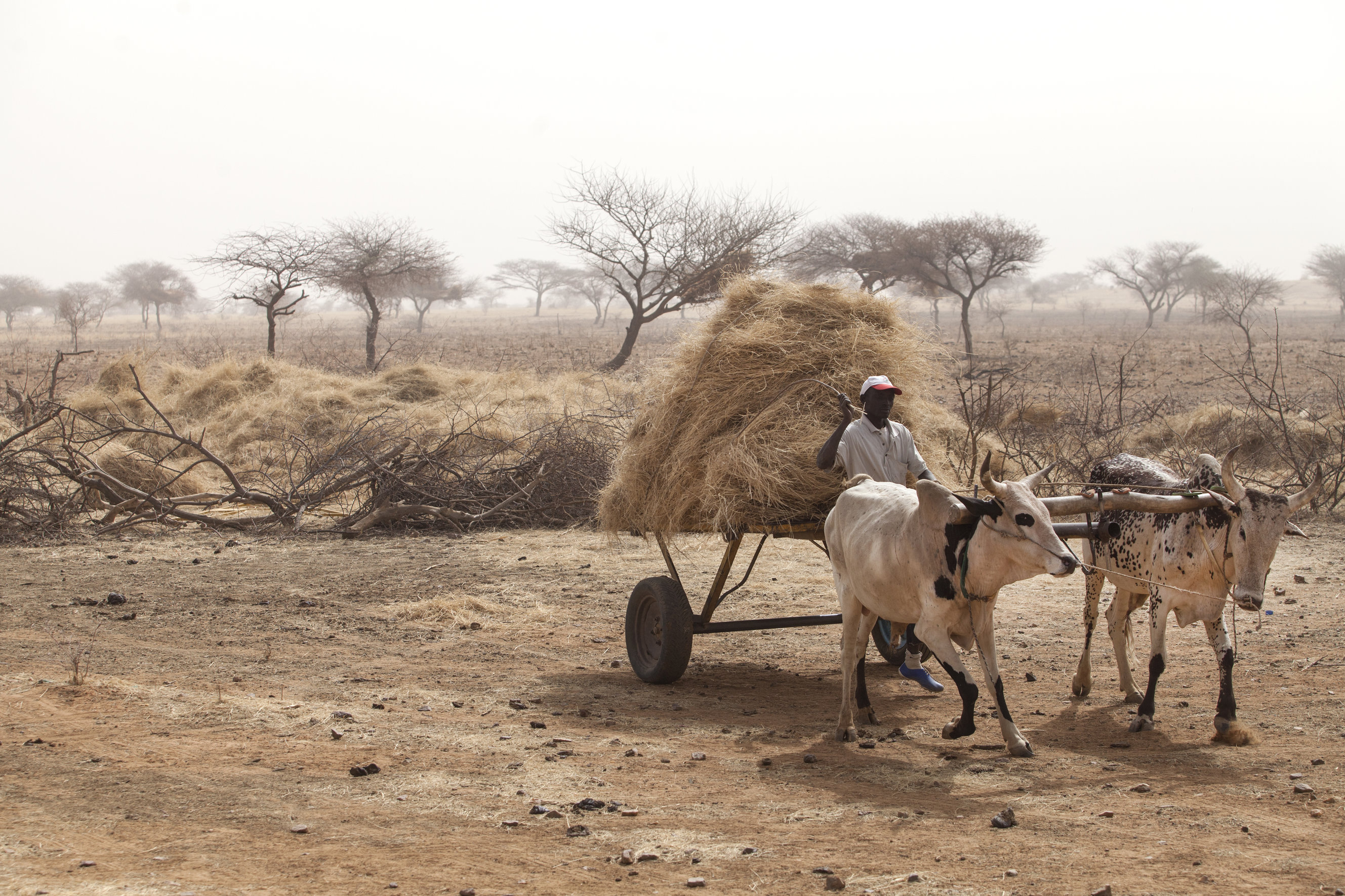
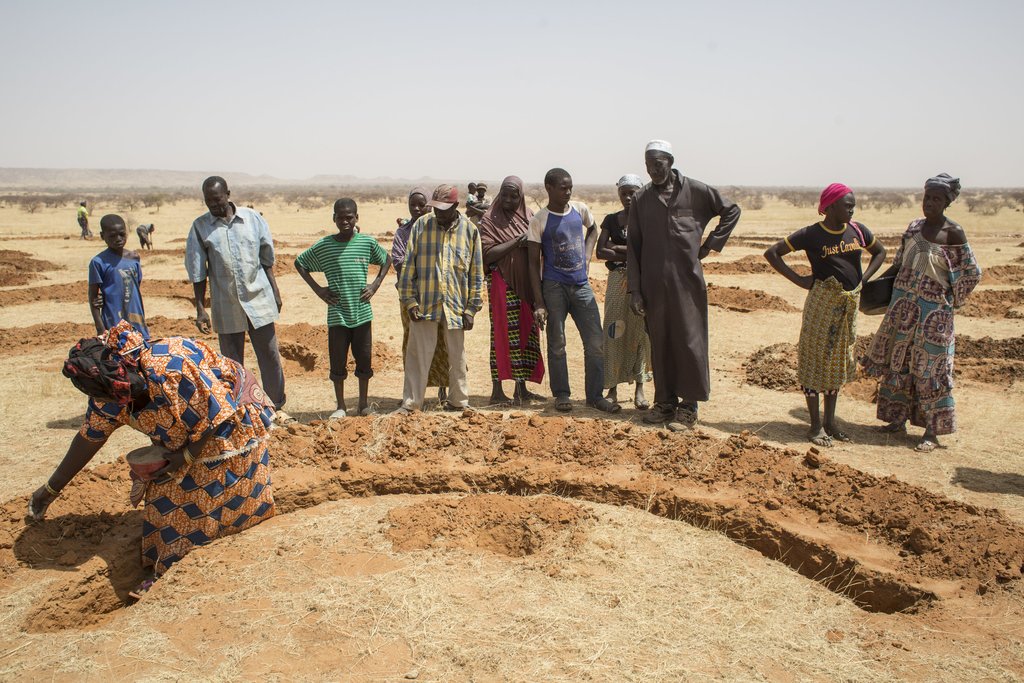
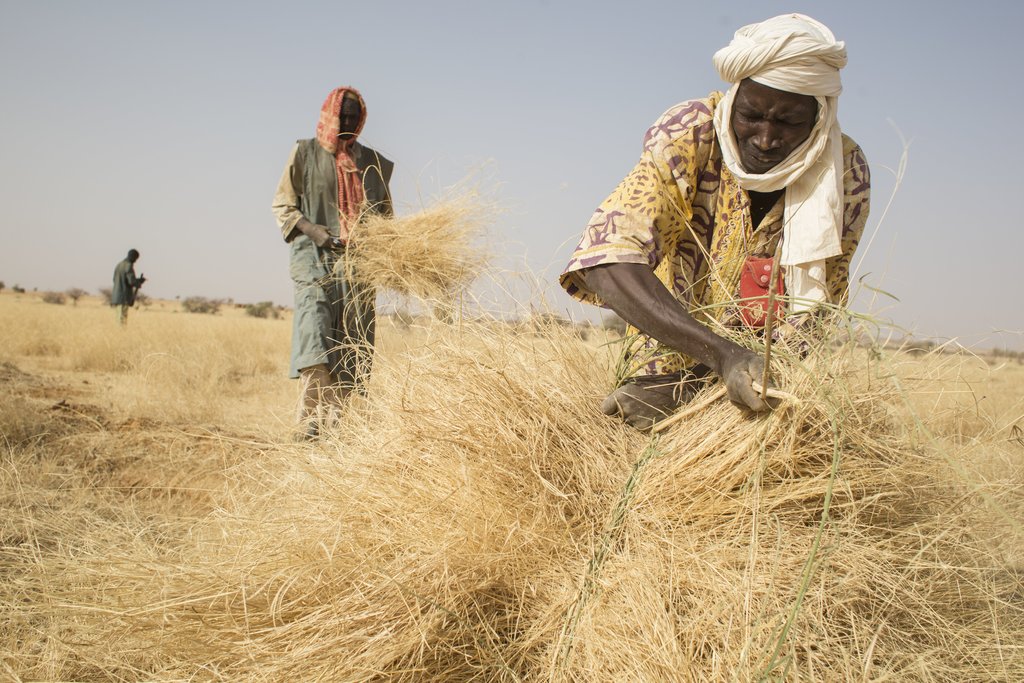
Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa‘s Great Green Wall programme in Niger. [ໄນເຈີ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Vivian Onyango
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_2909 - ໄນເຈີ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa’s Great Green Wall programme: Nov. 2, 2021 (inactive)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa’s Great Green Wall programme: July 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa’s Great Green Wall programme : May 13, 2018 (inactive)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa’s Great Green Wall programme : April 26, 2018 (inactive)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa‘s Great Green Wall programme in Niger.: April 24, 2018 (inactive)
- Community participation in large-scale land restoration for Africa’s Great Green Wall programme: Aug. 21, 2024 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Sacande Moctar
moctar.sacande@fao.org
Forestry Policy and Resources Division (FOA)
ອີຕາລີ
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
FAO-Action Against Desertificationຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) has been implementing a participatory approach to implement large-scale restoration of degraded land in the Sahel, by placing rural communities at the center. In the framework of the Great Green Wall initiative, well adapted useful native species of trees, shrubs, and fodder grasses are planted in agro-sylvo-pastoral land that responds to community needs and preferences and at the same time to the ecological suitability.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
The approach is implemented under FAO's Action against Desertification (AAD) programme in the Great Green Wall for the Sahara and the Sahel (GGWSSI); Africa's flagship initiative to combat the effects of climate change and desertification, and address food insecurity and poverty, bringing together more than 20 African countries with international organizations, research institutes, civil society and grassroots organizations. Through the GGWSSI, the vision is a mosaic of sustainable land use practices and productive landscapes across North Africa, the Sahel and the Horn.
Community participation in the Great Green Wall Restoration is a people-centered approach to rangeland management that puts communities at the heart of restoration efforts and focusses on their needs for useful plant species such as well-adapted native trees, shrubs and fodder grasses with a high resilience to drought and preferences for restoration in support of their livelihoods. Village communities decide on lands and on diverse species that they can use for food, to feed animals, for medical care and to produce economically valuable goods for local, national and even international markets, such as gum Arabic for example. Technically, AAD support the implementation of land restoration activities through provision of necessary equipment and strengthening the technical and functional capacities of individuals, communities, and organizations in restoration techniques and sustainable land management.
The main objectives of this approach are:
a) Poverty alleviation;
b) Ending hunger;
c) Improving resilience to climate change using a landscape approach.
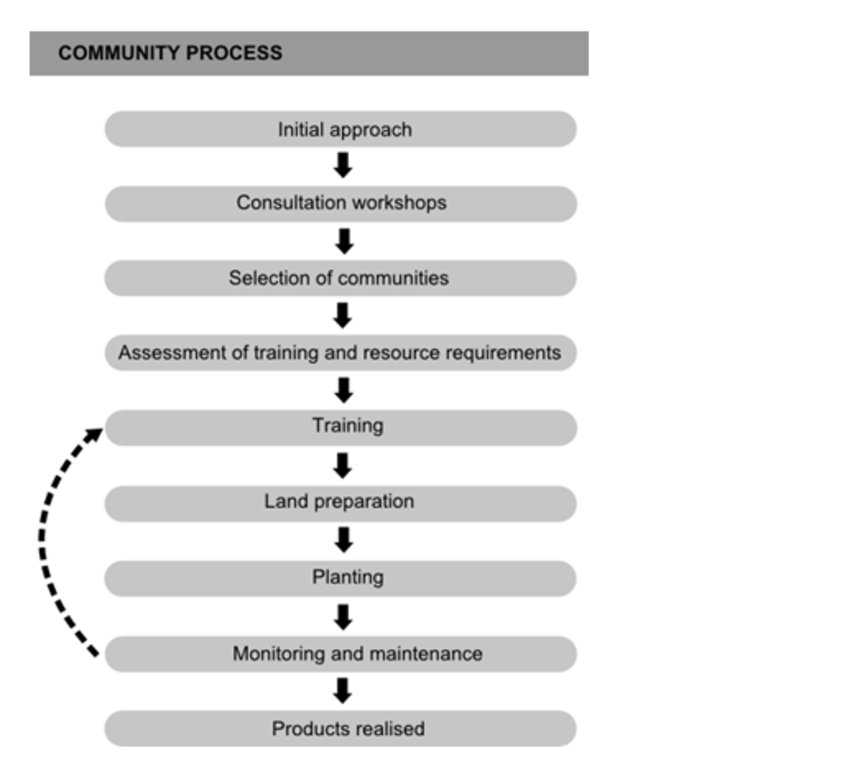
The restoration approach is based on a five-step model:
• Communities: needs and requirements for restoration are determined through in-depth consultations with communities.
• Research: the quality seed is made available for the propagation of economically viable, locally adapted and bio-diverse material.
• Operational procedure: ensuring efficient operational restoration processes, including land preparation and management, assisted natural regeneration and planting.
• Monitoring: evaluating the field performance of species, as well as communal activities such as maintenance and management of restored areas.
• Capacity development: develop village technicians’ capacities in forest seed collecting and nursery techniques, planting, maintenance and management of restored areas, and development of plant products, marketing, and local business management.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດໂດຍທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຮູບພາບ:
The photos were taken under the FAO project GCP/INT/157/EC: Action Against Desertification is an initiative of the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP) to promote sustainable land management and restore drylands and degraded lands in Africa, the Caribbean and the Pacific, implemented by FAO and partners with funding from the European Union in the framework of the 10th European Development Fund (EDF).
2.4 ວີດີໂອ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qVcMSeXZnJI
Over the next decade, 50 million people may be displaced by desertification - the result of climate change and the depletion of natural resources. Action Against Desertification, an initiative of the African, Caribbean, and Pacific Group of States is implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations with the financial contribution of the European Union. It aims to restore the productivity of degraded forests and landscapes and enhance the resilience of people to climate change in 6 Great Green Wall countries in Africa as well as Haiti in the Caribbean and Fiji in the Pacific.
ວັນທີ:
02/12/2015
ສະຖານທີ່:
Rome
ຊື່ຂອງຜູ້ຖ່າຍວີດີໂອ:
© FAO
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=prl1eaSvQCQ&feature=youtu.be
Land restoration in the Sahel is making degraded areas productive again, providing economic opportunities in a region where migration has become a tradition. Under FAO’s “Action Against Desertification” programme, these efforts are being expanded to six African countries. Land degradation around the Sahara is not yet irreversible.
ວັນທີ:
18/07/2016
ສະຖານທີ່:
Rome
ຊື່ຂອງຜູ້ຖ່າຍວີດີໂອ:
© FAO
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ໄນເຈີ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tillabery, Dosso and Tahoua
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
In Niger, the GGW covers all the eight Regions of the countries. Currently FAO’s Action Against Desertification project works in three Regions including Tillabery, Dosso and Tahoua, though the approach is used and expanding to all of the remaining 5 Regions, which are also implementing the GGW restoration programme.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The AAD land restoration approach has been successfully implemented with trans-boundary interventions in Niger, Burkina Faso, and Mali. For this documentation, the focus is on Tera, Niger.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2013
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
Key elements and aim of this approach include:
• That the right species planted in the right place.
• Promote the use of quality native forest and fodder seeds for restoration.
• Ensuring that a wide range of useful plant species is used or made available for use.
• Managing natural regeneration of species and planted areas through village management committees.
• Updating a species database for gene-pool traceability, monitoring, reporting and for future uses of data and information.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ອໍານວຍ
The approach is people centered and builds up on traditional management of land and traditional ecological knowledge and techniques such as half-moon for rain water harvesting that facilitates improved seedling and crop establishment.
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ອໍານວຍ
Individuals can use finances to buy seeds. At community land, finances maybe needed to lease land needed for production of plant varieties needed, for hiring labour to take care of seedlings.
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ອໍານວຍ
Better organization at local level enhances community participation and commitment to realize the interventions at large scale/community level.
ການຮ່ວມມື / ການປະສານງານຂອງຜູ້ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
- ອໍານວຍ
There are various levels of collaboration needed for example in establishing land, in seed selection based on desired needs and also on labour provision.
Fundamentally, collaboration is key to agreeing on desired objectives.
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ອໍານວຍ
Secure access rights to land and water resources is a motivation for investing in reforestration.
ນະໂຍບາຍ
- ອໍານວຍ
national level policies can protect and ensure supply of seeds and seed varieties as well as access to natural resources such as land.
Additionally, policies such as those in support for Great Green Wall activities create an enabling environments on which these activities can be supported and take place.
ການປົກຄອງທີ່ດິນ (ການຕັດສິນໃຈ, ການປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ຂໍ້ບັງຄັບ)
- ອໍານວຍ
Similar to legal framework above.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ອໍານວຍ
Knowledge around SLM contributes to maintenance and management of restored areas thus ensuring sustainability of activities. The programme has integrated existing/traditional SLM activities such as zaï/half-moon in capturing, retaining and saving water thus keeping soils moisturized and giving plants a chance to grow in an otherwise very dry environment.
ຕະຫຼາດ (ໃນການຊື້ວັດຖຸດິບ, ຂາຍຜະລິດຕະພັນ) ແລະ ລາຄາ
- ອໍານວຍ
Market access and increasing economic capacities of communities can enable active involvement in restoration especially when plant products can earn income thus facilitating local business management.
ວຽກ, ມີກໍາລັງຄົນ
- ອໍານວຍ
Availability of labour facilitates activities such as forest seed collecting, nursery techniques, planting, maintenance and management of restored areas. Most of the work is done by women who prepare the soils and lead planting.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Total project beneficiaries are 116,000 people (with over half women)
Age groups varied from 15 to 70 years.
Participants were villages including farmers, herders, traditional healers and herbalists.
Each intervention village has a village management committee set up for the GGW implementation activities. They contribute land and labour and village technicians are trained in large scale degraded land restoration techniques so that they can be self-sufficient at the end of the funding.
1. Defining needs, preferences of species and objectives for land restoration in degraded lands.
2. Trained on collection of seeds and on how to produce seedlings in village nurseries.
3.The involved communities also participated in the regular monitoring and evaluation of plots.
4. Participating in workshops including to agree on work plans
5. Communities were also source of rich traditional ecological knowledge
6. Supporting project through in-kind contributions such as labour and land
7. Representation in the steering committee
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ພາຍໃນຊຸມຊົນ
Each intervention village has a village management committee set up for the GGWSSI implementation activities
- Contibute land, labour and village technicians to be trained on large scale land restoration techniques geared at self-sufficiency at the end of project life.
-Managing intervention sites including products such as fodder
-Collaborating with national and local administration
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
Support to identification of land needed for restoration, seeds and management objectives of restoration.
- ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
National seed centres.
1. Address the availability of good quality seeds for collection
2. Ensuring genetic diversity reflecting original provences of native species.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ
Local NGOs and CBOs.
Local NGO's were trained on land restoration activities.
NGOs were also instrumental in discussions on scaling up the approaches and policy support for mainstreaming sustainable land management .
- ພາກເອກະຊົນ
Supplies of equipment and materials needed for restoration activities.
Mainly business related to procurement of goods and services.
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Local administration and national governments in the respective countries.
1. provide technical management and management if the operational team.
2. Mobilization of communities.
3. Part of the steering committee.
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
1. Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development.
2. National Agency of the Great Green Wall.
3. National Forestry Seed Centre.
4. Local authorities (i.e. Mairies or Town halls) involved in Tillabery, Dosso and Tahoua regions.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ
Royal Botanical Garden, Kew.
Technical support; botanical knowledge and information resources, and identifying priority species for the Great Green Wall.
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Communities local knowledge, needs and aspirations were the back-borne of the project. Communities were extensively consulted on species identification and prioritization based on needs including speed of return of products for the local communities, personal knowledge and inspirations. This was through questionnaires and village workshops. I bigger commitment and buy-in from the community was also a prerequisite for activities to start as they had to commit to contribute land and labour in-kind. As a matter of fact, selection of villages for restoration was based on among other things motivation and commitment by communities to participate in restoration activities. and community based structures and organization. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Extensive planning was done with communities before implementation e.g. to agree on planting time ( at onset of rains), use of traditional techniques and land scarification. |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Implementation was done actively with communities who volunteered traditional knowledge and labour to the activities. This had built on the initiation; where species were selected and prioritized, planning of activities and later labour in preparation of land, setting up nurseries and trans-planting. |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Monitoring and field data collection on survival and growth of seedlings were carried out by trained village technicians in collaboration with the communities and technical institutions. |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທັງໝົດ, ເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ຂອງວິທີທາງແບບມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
ອະທິບາຍ:
This is a local initiative that uses traditional ecological knowledge and multi-purpose plant species (of known benefits to the local communities) for restoration.
Community participation, lifestyles and preferences and a careful analysis of ecological landscapes are carefully considered and then matched to suitable interventions. This similar approach has been applied by other projects in the GGWSSI region however although has not often been formally disseminated to wider audiences.
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- ປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ຫຼັກຖານທີ່ຊ່ວຍໃນການຕັດສິນໃຈ)
- ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ປະສົບການສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແລະ ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ທີ່ບໍ່ເປັນເອກກະສານ)
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເພດ, ອາຍຸ, ສະຖານະພາບ, ຊົນເຜົ່າ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ:
100 small-scale farmers were trained in 2017, in Natural Assisted Regeneration techniques and 40 farmers were trained in forest and fodder seed collection and the production of seedlings in village nurseries and in the management of planted sites.
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຫຼັກສູດ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
Technical training was provided to villages in formal modules on how to collect quality seeds in defined seed zones. The training was provided by the national forest seed centres . The trainings were on seedling production and participatory forest management . Other areas covered included; added-value and the development of plant products (non-timber forest products), marketing and local business management to support income generation.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Apart from the restoration technical areas covered above, additional areas of training included; improving adult literacy, family health and nutritional standards. This was done together with specialized rural sector developers.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- workshops
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
To re-introduce plant for large-scale restoration, effective use of seeds of wild species demands sufficient biological and technical knowledge on a big number of species to allow for collection, storage and germination of seeds and establishment of seedlings. In this approach therefore, the technical know-how of RBG Kew and related partnership with forest seed centres that allowed for collection of quality seeds.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
- ລະດັບພາກພື້ນ
- ແຫ່ງຊາດ
ອະທິບາຍ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ, ພາລະບົດບາດ ແລະ ໜ້າທີ່ຮັບຜິດຊອບ, ສະມາຊິກ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Institutions: National government; NGOs, CBOs,
Support to the national government who is the national agency for the GGW is the entry point. Through them ad based on national objectives, the project moves to a decentralized level. At the national level, capacities have been improved on monitoring and evaluation techniques; seed identification and selection and handling.
Local level: these are the implementing partners and do work on the ground. Their capacities have been improved on seed selection and restoration techniques and on data collection
Regional level: more collaboration, coordination and knowledge sharing on the GGW initiatives as well as peer to peer learning.
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
- ອຸປະກອນ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
Equipment: mainly for land preparation for planting and non-timber forest processing.
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Regular monitoring is carried out by village communities involved in the restoration exercise. The activities include assessing seedling survival and growth and planted surface areas.
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ເອກກະສານສະບັບນີ້ ແມ່ນໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຕິດຕາມ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ສັງຄົມ
- ເສດຖະສາດ / ການຕະຫຼາດ
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
Through a questionnaire, communities define their needs and preferences of species, the objectives of land restoration in their available agro-sylvo-pastoral degraded lands. Results of this consultation are fed back to them after analyses by the project team (researchers, plant expertise, seed centres) for the feasibility, suitability and availability of the requested species. This allows commonly to agree on interventions, priorities and implementation plans with roles and responsibility from the communities as well as from the technical teams.
1. Sociology: prior research was done on social diversity of village communities on areas such as gender, age, profession among others to decide on village selections but also ensure required balance.
2. Economics/marketing: This was multi-faceted on one hand looking at community economic needs and priorities and also on how to value addition to non-timber forest products. The plant-use data received from respondents were classified according to the Economic Botany Data Collection.
These helped in deciding and prioritizing species according to community needs.
3. Ecology: GGW initiative is typically for drylands with challenges such as moisture retention. Thus the ecology of the place was studied to identify suitable plant species that would thrive under these conditions of course in combination with traditional technologies that have been developed to overcome the moisture deficits.
The botany of selected species was further examined in laboratories to first of all check their suitability to dryland environments and thereafter to ensure good quality seeds are used including ensuring genetic diversity
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- 100,000-1,000,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Action Against Desertification is implemented by FAO and partners with funding from the European Union in the framework of the 10th European Development Fund (EDF). The GGWI under AAD in Niger is funded up to around 1.5m USD for the four years of the project.
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ, ເງື່ອນໄຂ ແລະ ຜູູ້ສະໜອງ (ຫຼາຍ):
Finances are needed for purchasing equipment, seeds were also provided, seed testing to establish the desired type/species.
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ແຮງງານ
| ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|
| ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | Local communities shared some tasks such as during planting period the project provided lunch. |
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | Provided such as arable tools, carts for transportation. |
| ເຄື່ອງມື | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | Arable tools for planting. |
- ກະສິກໍາ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ແນວພັນ, ແກ່ນພັນ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | Training was provided on a collection of native forest seeds that were then bought from them (communities thus earning an income for communities). |
| Organic manure | Training to do and collect composts. | |
- ການກໍ່ສ້າງ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| ຫີນ | ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | For storage facilities. |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ອຸປະກອນດ້ານອື່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
In partnership with WFP there was collaboration on food for assets and incentives from the project such as trainings on preparation of vegetable gardens..
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ການສົ່ງເສີມ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ໄດ້ສະໜອງສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ:
Functional capacity building village communities for example in management of restoration sites and development of community forest products
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ວິທີທາງ ຊ່ວຍຊຸກຍູ້ ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນທ້ອງຖີ່ນ, ໃນການປັບປຸງ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ຂອງຜູ້ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The project supports the communities to improve productivity of their land in direct consultation with them while benefiting from trainings with changes recorded in diversity of biomass in community plots and lands.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ດັ່ງກ່າວນີ້ ສາມາດເປັນຫຼັກຖານ ທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໃຫ້ການຕັດສິນໃຈໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Substantial improvement is already recorded on state of land in the last 2 years.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Trainings were provided on various aspects such as seed selection and collection.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການປະສານງານ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ທີ່ມີປະສິດທິພາບ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The project is not funding all aspects yet building sustainability through the direct capacity development and participation by communities.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດລະດົມ ຫຼື ປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນ ການເງິນ ສໍາລັບການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
1. Village technicians have been used by other projects in the area in SLM and also by the government while getting remuneration. 2. Communities are able to sell native restoration seeds to other projects in the region and to the government.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Through trainings and capacity development e.g. on large-scale land preparation for planting and seed selection.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
1. Governments; training of technicians including on specialized tools, training on monitoring and evaluation of SLM and restoration impacts. 2. CBOs and local administrations. regional organizations such as CILSS-Agryhmet were also trained on the above.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃຫ້ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ, ການຮ່ວມມື ລະຫວ່າງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The village technicians and trained seed collectors are now organized in a regional union for restoration seed supply.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
With the increasing of fodder production, pressures on other grazing areas have gone slightly down.
Disadvantaged groups not present at village level.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ຄວາມສະເໜີພາບ ຂອງບົດບາດ ຍິງຊາຍ ແລະ ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງໃຫ້ຜູ້ຍິງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Yes; gender equality is taken into consideration such as women representative in each village management community.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊຸກຍູ້ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນທີ່ເປັນຊາວໜຸ່ມ / ຄົນລຸ້ນໃໝ່ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
As income is coming in from restoration activities, it has been encouraging young people to consider SLM as in income generating opportunity.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Communities now see more value in restoring degraded land previously neglected and there is tenure agreements with local administration. Land tenure had been insecure for local communities but now rights of access and use have been delivered by local administrations to local communities guaranteeing that restoration areas belong to communities thus ensuring sustainability also as a community see ownership of the investments.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການຄໍ້າປະກັນສະບຽງອາຫານ ຫຼື ປັບປຸງໂຄສະນາການໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
1. Farming in restored areas allows for more crop production. 2. Fodder production is feeding livestock improving production of milk and meat.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງຕະຫຼາດໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
1. Seeds and fodder are being sold by local communities to other projects, governments and communities.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງນໍ້າ ແລະ ສາຂາພິບານໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Not within scope.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການນໍາໃຊ້ແຫຼ່ງພະລັງງານ ແບບຍືນຍົງຫຼາຍຂື້ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Out of scope.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດໃຫ້ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນການປັບຕົວ ຕໍ່ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຫຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງທາງໄພພິບັດໄດ້ບໍ? :
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The project aim is to increase resilience of natural capital and people living in drylands while being able to adapt to climate change.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການຈ້າງງານ, ໂອກາດ ໃນການສ້າງລາຍຮັບບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
In seed sales, crop production, income earning from employment of technicians.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
Increased land productivity from restored land.
- ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
Improved yields and harvest.
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ
Restored land provide more opportunities to land users.
- ກຽດສັກສີ, ຄວາມກົດດັນທາງສັງຄົມ / ການຕິດຕໍ່ກັນທາງສັງຄົມ
Restoration of agro-sylvo-pastoral systems promoted cohesion across different user groups and provided benefits.
- ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
Desire to be part of community based organization and through these, management of restored lands is also possible.
- ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
Improved biodiversity, wildlife and link to community cultures and lifestyles was a motivator.
- ພາສີ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊື່ອຖື, ສົມບັດສິນທໍາ
Linked to environmental above; need to protect and preserve wildlife and biodiversity.
- ການປັບປຸງ ຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Project provided technical capacity development such as water harvesting and rice species to plant in right places motivated communities to participate.
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
Increasing biomass in agro-sylvo-pastoral systems reduced conflicts between pastoralists and farmers.
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າ ໄດ້, ອະທິບາຍເຫດຜົນ:
The capacity being developed should help farmers continue without external intervention e.g. training in collecting planting material, planting technique and in managing the plot enable continuity and the capacities developed stay within the community examples; the trained village technicians.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Builds on existing knowledge such as the use of zhai and pit planting. |
| Income generation e.g. from selling of seeds to governments and other land users. |
| Helping achieve communities specifics objectives such as increasing tree cover. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| The consultation process and the mutual trust built over time, which make people buy-in the programme and feel the ownership of the activities on the ground. |
| The technical and scientific feedback answers to priorities and preoccupation of land users in terms of restoration objectives. |
| The involvement of people in monitoring and management of their planted sites as they contribute their lands and labour. |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Inability to adequately influence donor plans. | Frequent consultations. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Inability to address all the needs of the beneficiaries. Such as demand for water supply in dry seasons restoration while project focusses on rainfed restoration. | Increased dialogue on interventions across sectors such as with donors for more systematic and integrated approach. |
| Lack of flexibility in implementation to consider some of the upcoming demands of communities. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
FAO. 2015. Global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands: building resilience and benefitting livelihoods. Forestry Paper No. 175. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
UN-FAO
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Community participation at the heart of Africa’s Great Green Wall Restoration model. Authors: M. Sacande, N. Berahmouni and S. Hargreaves. In Unasylva. Volume 66 2015/3
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
UN-FAO
7.3 ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ອອນໄລນ໌
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Action Against Desertification (FAO)
URL:
http://www.fao.org/in-action/action-against-desertification/en/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Building Africa’s Great Green Wall: Restoring degraded drylands for stronger and more resilient communities
URL:
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i6476e.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Forest and Landscape Restoration Approach
URL:
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5212e.pdf
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ