Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Celeste Coelho
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Zona de Intervenção Florestal (Portuguese)
approaches_2588 - ປໍຕູໂກລ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - ປໍຕູໂກລ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
10/02/2009
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ

Prescribed fire [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
Use of prescribed fire (or ‘controlled burn’) to reduce the fuel load in the form of live and dead plant material and thus to prevent the likelihood of more damaging wildfire.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Manuela Carreiras

Primary strip network system for fuel management [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Celeste Coelho
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) is a territorial unit, where the main land use is forestry. This approach assembles and organizes small forest holders and defines a joint intervention for forest management and protection. Defined by law in 2005, and revised in 2009, each ZIF of private forest has to include at least a contiguous area of 750 ha, 50 landowners and 100 forest plots, and has to be managed by a single body, defined by ZIF members.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Aims / objectives: The ZIF overall objective is to promote the efficient management of forest and to mitigate current constraints of forest intervention (e.g. land size and tenure). Other objectives are to develop structural measures for fire prevention, to integrate local and central administration actions and to implement the national and regional forest management policy at the local level. The final purpose of ZIF areas is to improve productivity in rural forest areas, contributing to rural development
Methods: The idea emerged after the catastrophic wildfires of 2003 and was developed and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, City Council, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries. The ZIF approach was legislated by Law 127/2005, and revised under Law 15/2009. Each ZIF assembles small properties, which will be jointly managed by a single entity, which can be a non-profit-making and voluntary organization or some other group of people approved by the forest owners. Each ZIF will have a Forest Management Plan (PGF), where the forestry operations and activities for ZIF area are defined accordingly to the guidelines of the Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning (PROF), and a Specific Plan to Forest Protection (PEIF), which includes actions to protect forest against biotic and abiotic risks. The management entity should have a team with qualifications and experience in forestry and with technical ability to design these plans.
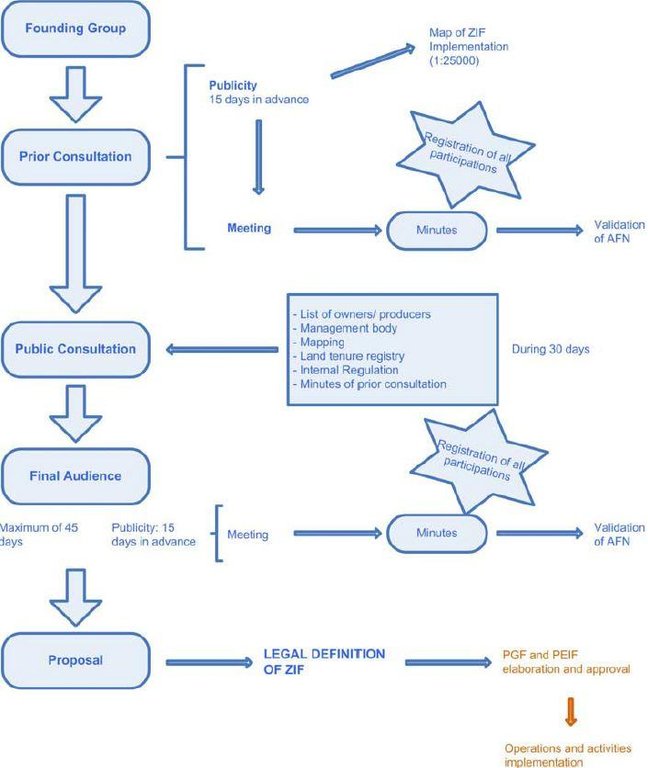
Stages of implementation: The legal constitution of ZIF includes six mandatory steps, namely the constitution of the founding group (group of landowners with at least 5% of a continuous area inside the ZIF), the prior consultation meeting, the public consultation, the final audience meeting, the proposal submission to the National Forest Authority (AFN) and legal publication of each ZIF (already done). After these procedures, the PGF and PEIF of each ZIF will be designed by the management entity and evaluated and approved by AFN. The implementation activities can then be implemented by the management entity or by individual landowners following the rules described on the plans. PEIF validity is five years and PGF validity is 25 years (still in preparation). [See figure below].
Role of stakeholders: The founding group is mainly composed of forest owners and producers and is the starting point for creating a ZIF. The management entity administers the ZIF in order to achieve their main purposes and the aims defined on the plans. AFN will support and monitor ZIF activities. ZIF non-supporting landowners are obliged to have a PGF for their land, as well as to accomplish the PEIF of the ZIF.
Other important information: The landowners inside the ZIF who are non-supporters do not have a clear role. Based on PROF - Plano Regional de Ordenamento Florestal (Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning), for ownerships of > 25 ha, the owners are obliged to have a PGF - Plano de Gestão Florestal (Plan for Forestry Management) for their property.
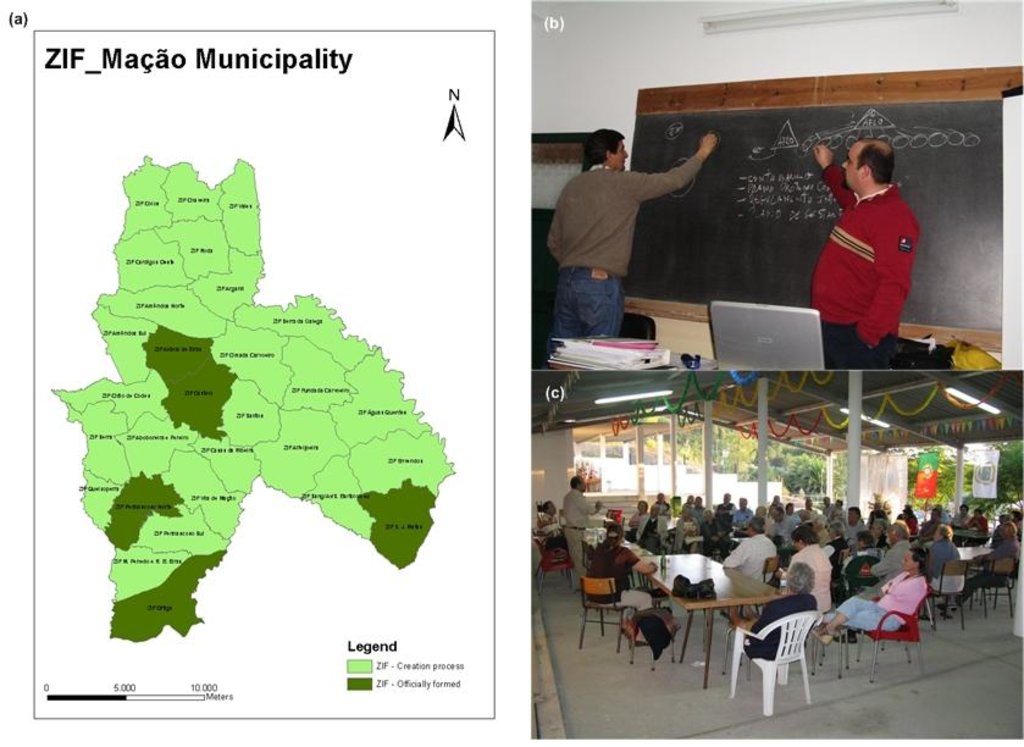
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ປໍຕູໂກລ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Santarém
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Mação
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2003
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (The main objective is to increase land management and profitability)
- To promote the sustainable management of forest; - To coordinate the protection of forest and natural areas; - To reduce the conditions to fire ignition and spread; - To coordinate the recovery of forest and natural areas affected by forest fires; - To give territorial coherence and effectiveness to the action of local administration and others actors.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - lack of forest planning and management, forest fires, land structure and tenure, land abandonment, rural depopulation and ageing.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Social resistance to this approach. Landowners fear to lose tenure rights. Difficult to reach and find owners due to inheritance and out-migration. Rural depopulation occurred in the last decades.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Financial support, creation of new job opportunities in rural areas.
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
High implementation cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Governmental incentives
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Scepticism about the practical effects of this approach. Very high costs for implementation and lack of private investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: ZIF pilot areas will motivate implementation and investment into other ZIFs.
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Land structure and tenure (private holdings)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Minimum area to constitute a ZIF is 750 ha
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation The ZIF join small properties and their management is undertaken as a single property, guide by a forest management plan. This entity can be a non-profit and voluntary organization or an other group of people approved by the forest owners and/or producers.
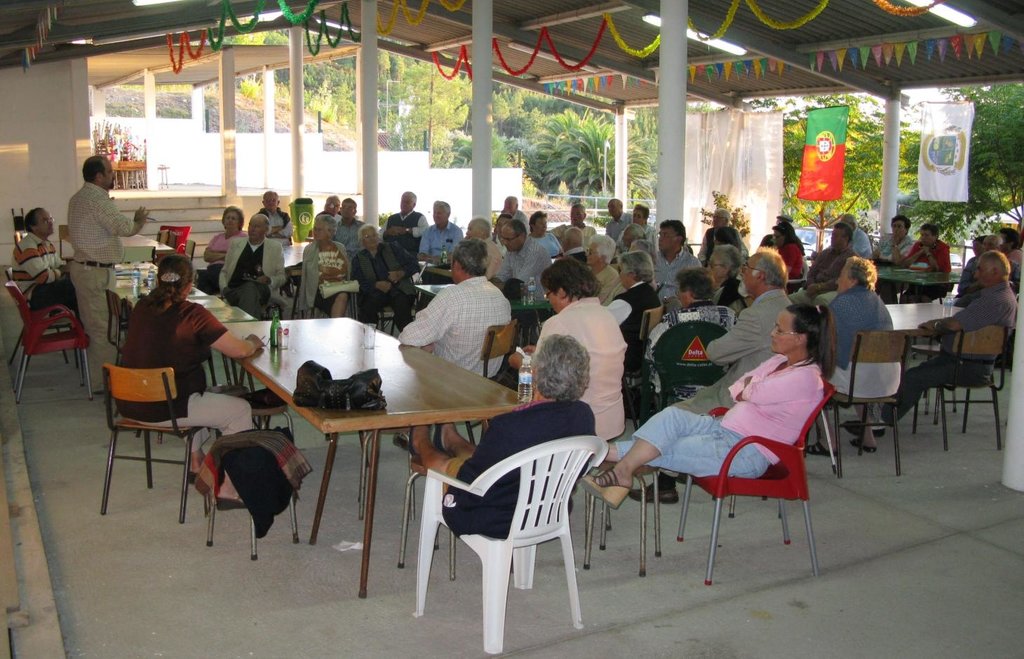
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Gender: mixed, Age: 50 years old
The majority of forest owners are usually pensioners, with low incomes
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
AFLOMAÇÃO technicians
- ພາກເອກະຊົນ
Private organizations
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
Municipality
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Based on an initial idea from Mação local specialists; the national ZIF legislation emerged in 2005 and was revised in 2009
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Balance alternatives and take decision to test the agave forestry information sessions about ZIF approach; informal contacts, door-to-door approaches and formal agreement of the landowners to become ZIF members. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ | information sessions to present the ZIF plans (PGF and PEIF). |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | management activities can be made by the land owners or by the ZIF management entity. Regular meetings with ZIF members |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | not defined yet |
| Research | ການຮ່ວມມື | on-farm research, good practice demonstration and collaboration with research projects. |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
Legal process related with the ZIF constitution (blue)
Elaboration and approval of the ZIF plans (orange)
Implementation of the plans (orange)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ຫຼັກດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ມີການຕິດຕາມປຶກສາຫາລືກັບຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Users’ perceptions and expectations were also considered.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by SLM specialists alone (top-down)
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
- opinion leaders
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
information sessions and individual contacts with opinion leaders
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Name of method used for advisory service: Information sessions; Key elements: ZIF process, Explaining rational of ZIF for specific municipality and its conditions like depopulation, forest fires, etc, Elaboration of the ZIF plans; The extension system is well set up to ensure follow-up activities
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
City council supports the forest association activities.
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
There were None changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: (* The monitoring procedures are not structured yet)
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ສັງຄົມ
- ເສດຖະສາດ / ການຕະຫຼາດ
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
- forestry, politics
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
The approach includes technical and local knowledge. The idea was prepared and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries and legislated by the Law n. º 127/2005, 5 August.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- > 1,000,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Permanent Forest Fund): 100.0%; local community / land user(s) (ZIF implementation activities: National Strategic Reference Framework (60%), Land users (40%))
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ອຸປະກອນ
| ໃຫ້ລະບຸໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າຫຍັງແດ່ | ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|---|
| Printer, toners, map production | ງົບປະມານເຕັມສ່ວນ | |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Landowners can work on their properties or can be substituted by the ZIF management entity. Some activities, such as the implementation of the Primary Strips Network System for Fuel Management can be supported by the municipality services.
1-technical, fully financed (FFP).2- preparation of PGF,partly financed. 3-implementation,partly financed.
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Reduction of the number and likelihood of forest fires.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
It is expected that the increase in land productivity through the implemented technologies will help to improve the socio-economic situation of these rural groups.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The initial social resistance to the approach will diminish through the existence of a successful ZIF.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
It is expected that the implementation of this approach will contribute to the improvement of rural socio-economic conditions through productivity increase, creation of employment and promotion of local products.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກົດລະບຽບແລະລະບຽບການ (ລະອຽດ) / ການບັງຄັບໃຊ້
- ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
- aesthetic
- forest fires
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ມີ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
The forest owners do not have the financial capacity to apply and support these activities by themselves.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Social conscience (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: through awareness campaigns and information sessions provided at national and local level.) |
| Prevention of forest fires (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: the increase of forest management will contribute to the decrease of large forest fires. The implementation of integrated and global measures to fire prevention will be suitable within the ZIF approach.) |
| Restoration of burnt areas (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The use of forest species to enable the protection and recovery of degraded soils or soils with high erosion risk has a very positive influence on the rehabilitation of burnt areas. However, many of these species are not economically attractive at short or medium term. The management of the land using ZIF model will allow the definition of the most affected areas for an urgent intervention.) |
| Increase productivity (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: present land tenure and structure of forest holdings constitute a bottleneck for forest productivity. The integrated management of the ZIF will allow a better management and use of the land, increasing the exploitation of timber and non-timber products and also increasing the resilience to wildfires.) |
| Improve forest management (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: promotion of the planting of more fire-resilient species which are better adapted to the local conditions. AFN should: (i) provide information about the guidelines; (ii) develop new policies and tools, which are more suitable to the local level; (iii) support and implement public awareness campaigns about forest values and services, and (iv) provide financial support to ZIF constitution and implementation activities.) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Unattractive investment (low public support and lack of private support) | the need to review and reform the existing QREN or provide others means of support. Incentives to private initiative or donors should be found. |
| Highly bureaucratic nature of the ZIF approach | simplification of the bureaucratic process |
| Rather complex process: unclear role for the non-adherent landowners within the ZIF; ZIF has to follow many laws and plans; control and monitoring activities still not defined | clarification and simplification of the bureaucratic process of the ZIF |
| Costs related to the approach | major financial support from the government needs to be provided. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Decree- Law 127/2005, 5 August. Official Gazette n. 150 - I series A.: 4521-4527Decree-Law 15/2009, 14 January. Official Gazette n. 9 - I series: 254-267AFN (2011). Caracterização das Zonas de Intervenção Florestal. Lisboa, Autoridade Florestal Nacional: 54
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Prescribed fire [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
Use of prescribed fire (or ‘controlled burn’) to reduce the fuel load in the form of live and dead plant material and thus to prevent the likelihood of more damaging wildfire.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Manuela Carreiras

Primary strip network system for fuel management [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Celeste Coelho
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ