Community tradition [ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: William Critchley
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2625 - ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Van der Merwe Rinda
rinda@arc.agric.za
Institute for Soil, Climate and Water
P/Bag x79, 0001 Pretoria, South Africa
ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Institute for Soil, Climate & Water - ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ (ຫຼາຍ) ກັບແບບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ

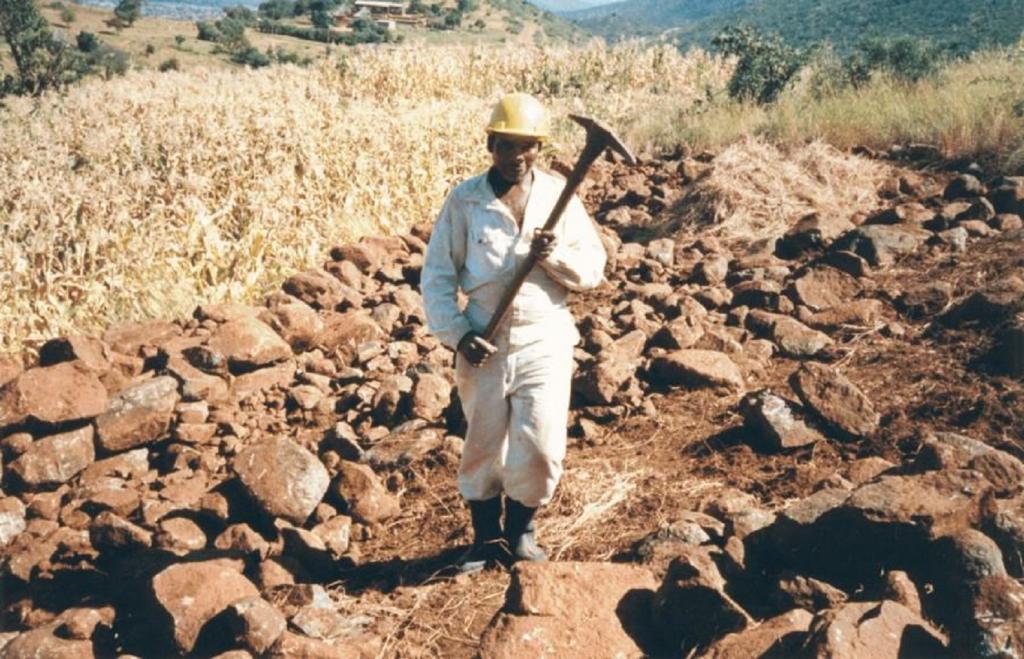
Traditional stone wall terraces [ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້]
Stone walls built on sloping fields to create terraces for cultivation and conservation: both ancient and contemporary.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: William Critchley
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Inherited, and still practiced, tradition of stone terracing - passed down from generation to generation.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
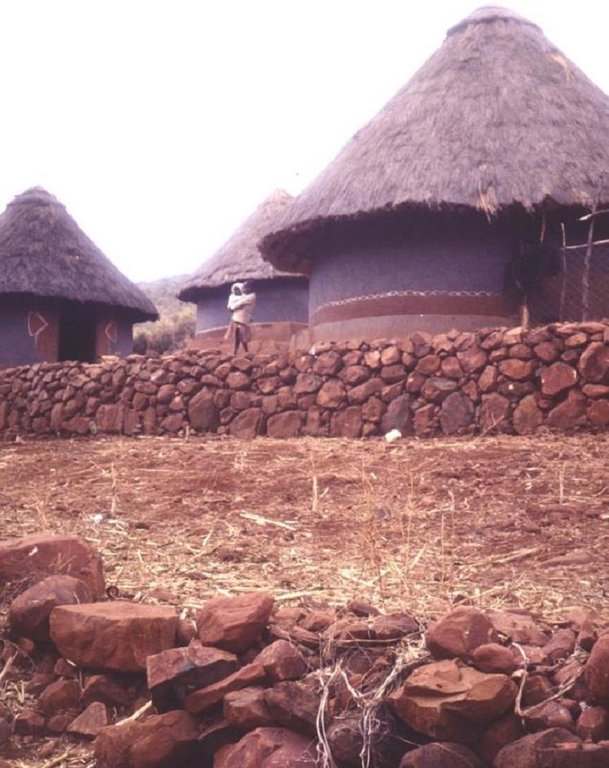
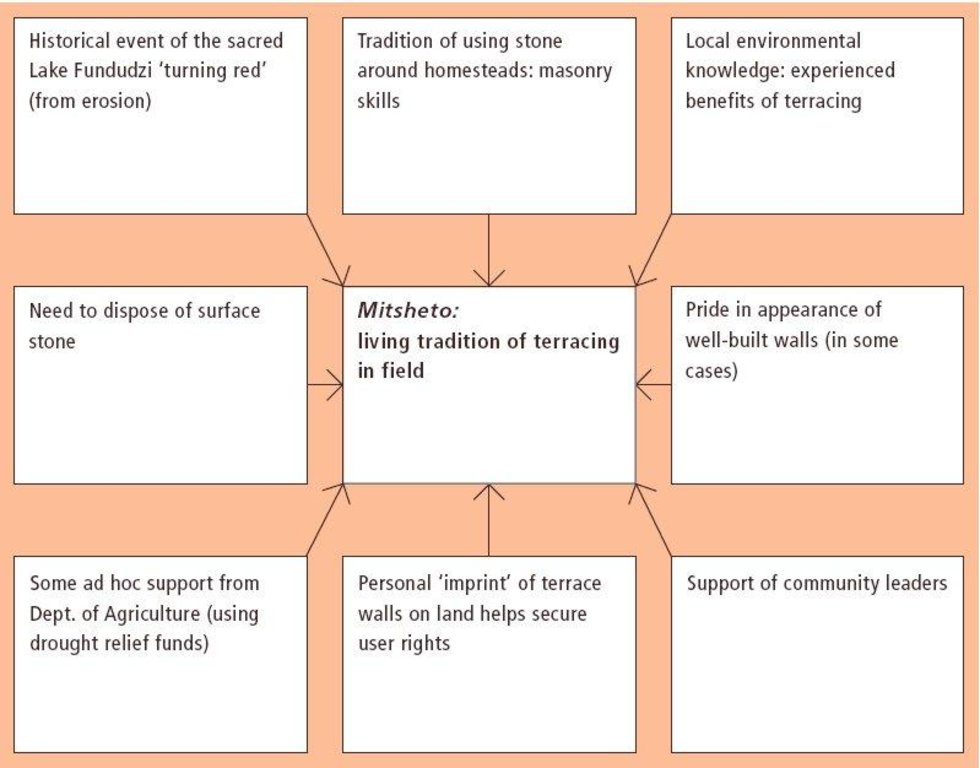
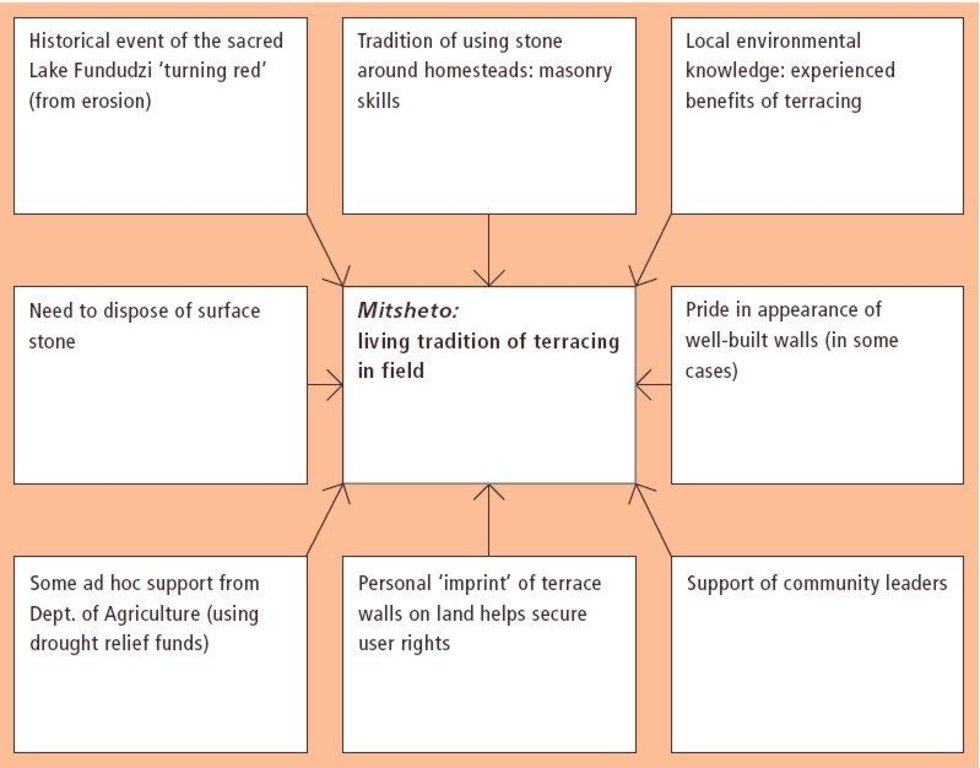
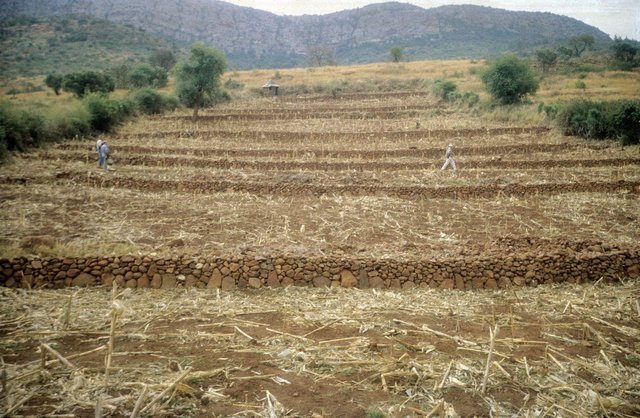
Aims / objectives: The VhaVenda people of Limpopo Province in South Africa have a tradition of building with stone which has been passed down from generation to generation. They construct stone walls around their houses for example, taking a pride in the appearance of their homesteads. There is a historical monument nearby, the stone-built kraal at Dzata, the ruins of which are situated within a few kilometres of the study location. There may even be some evidence that the VhaVenda came originally from the area of the Great Zimbabwe (the famous stone-built fortress in Zimbabwe). It is not surprising therefore that the VhaVenda have used their masonry skills to build terraces in fields to counter erosion and simultaneously to make cultivation - along the contour by oxen - possible. This tradition has been passed down through the ages: it is institutionalised in the community and is practised together by men, women and children on a family basis. It is encouraged by community leaders: a particular example of this was in the 1960s when local chiefs were concerned at the sacred Lake Fundudzi 'turning red' - with sediment eroded from the land - and as a result they launched a conservation campaign to prevent soil wash into the lake. There has been modest and occasional support by the Department of Agriculture, in the form of ad hoc drought relief funds. There is quite a range of technical ability/care taken in terracing. Some walls are meticulously built; others are merely piles of stone across the slope. One of the reasons for this is that work tends to be done on an individual basis. Another result is that fields may take two years or more to be fully terraced. What is evident is that the land users - as well as being experienced masons -appreciate the benefits of the terraces they construct. An investigation of local environmental knowledge and conservation practices has demonstrated this clearly (see reference).
Methods: The causes of erosion were explained by the interviewees as being part natural (rainfall, slope etc) and part anthropogenic (poor road building, up and down ploughing, burning of grassland etc). The main negative impact of erosion was considered to be loss of soil fertility: hence terracing for protection. This indigenous knowledge also extends to soils: eight local soil types and their differences in terms of texture, fertility and erodibility are recognised in the study area.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Limpopo Province
Map
×2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພື້ນເມືອງ / ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The objective of the local people is simply to continue making cultivation possible and sustainable, through the local tradition of using stone walls to create terraces and to remove abundant stones from the field.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - the tradition presumably arose as a spontaneous local response to degradation: it remains well entrenched - underlying problems of no flat land to cultivate, soil erosion/fertility decline on sloping fields, and loose stone and rocks impeding animal-draw ploughs
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ອື່ນໆ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
labour: High labour demand to remove stone from inhibiting cultivation.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Traditional teaching that such stone can be used constructively to improve conservation and yield benefits.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ | passing on knowledge; passing on of knowledge from generation to generation |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ | |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການນໍາໃໍຊ້ເອງ | family-based (or individual) construction |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ບໍ່ມີ | |
| Research | ບໍ່ມີ |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນຜູ້ດຽວ (ການລິເລີ່ມດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ)
ອະທິບາຍ:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
There was/is no formal training - just father to son/mother to daughter.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Key elements: Some encouragement from Department of Agriculture especially during soil and water conservation campaigns/drought relief periods.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
support for SWC campaigns from local leaders
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 5.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 95.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Almost entirely voluntary: some small support (approx 5% of the sample monitored) through Government during times of food scarcity with paid relief work.
A (very) small amount of drought relief in recent years from Government
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Great: as part and parcel of the local tradition - for example contour ploughing is facilitated by the fact that the stone lines are on the contour, making this type of ploughing easier.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Only within this small pocket of Thohoyandou District (as far as known).
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າ ໄດ້, ອະທິບາຍເຫດຜົນ:
The VhaVenda have built terraces for generations so far, so no reason to think that things will change.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Traditional approaches have the potential to endure (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Acknowledgement and encouragement by the Government and/or NGOs will help this.) |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| This tradition was largely unrecognised until recently: therefore an opportunity was lost to encourage people and help the approach spread | Publicise widely and carry out farmer-to-farmer/community-to-community visits to further its spread and the spread of local SWC knowledge more generally. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Critchley W and Netshikhovehla E (1998) Conventional views, changing paradigms and a tradition of soil conservation.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Traditional stone wall terraces [ອາຟິກກາໃຕ້]
Stone walls built on sloping fields to create terraces for cultivation and conservation: both ancient and contemporary.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: William Critchley
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ