A Decision Support Tool for integrating stakeholder perspectives through WEFE Nexus [ອູເບກີສຖານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Joren Verbist
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_7356 - ອູເບກີສຖານ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- A Decision Support Tool for integrating stakeholder perspectives through WEFE Nexus: Nov. 25, 2024 (inactive)
- A Decision Support Tool for integrating stakeholder perspectives through WEFE Nexus: July 9, 2025 (inactive)
- A Decision Support Tool for integrating stakeholder perspectives through WEFE Nexus: Aug. 8, 2025 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ (ຫຼາຍຄົນ)
Senior Scientist:
Akramkhanov Akmal
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ອູເບກີສຖານ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ຂອງໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນດ້ານແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - ລີບານອນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
2024
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
The Decision Support Tool helps decision-makers prioritize sustainable land management practices using the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem Nexus, fostering collaboration, facilitating social learning, and balancing diverse stakeholder interests.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
Land management and agricultural production often face diverse and conflicting interests from various stakeholders. The Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem (WEFE) Nexus offers a framework for addressing these challenges. Under the CGIAR Nexus Gains Initiative, the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) developed a Decision Support Tool (DST) designed to help decision-makers balance stakeholder interests within the WEFE Nexus. The DST’s main objective is to enable comparison and thus prioritization of sustainable land management (SLM) technologies based on specific criteria and stakeholder-assigned weights.
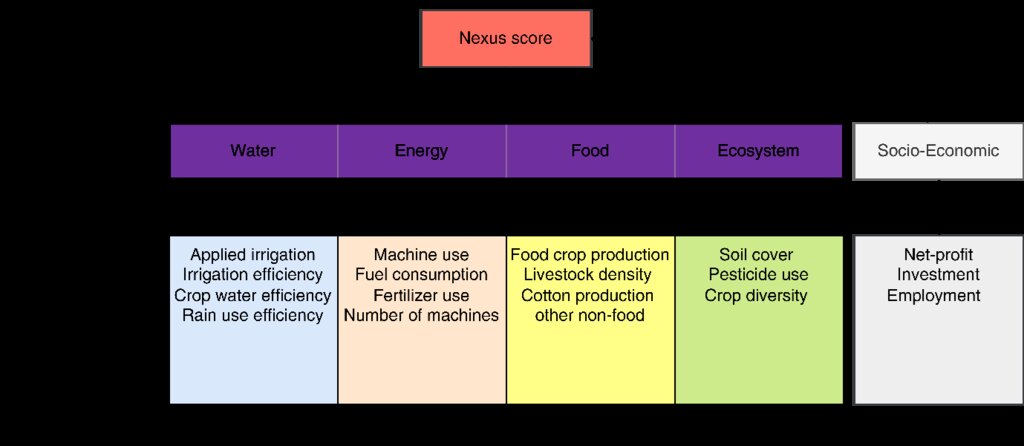
The DST applies a multi-criteria analysis (MCA) framework combined with the Best-Worst Method (BWM) to capture stakeholder preferences and assign weights to different criteria. The MCA follows a hierarchical structure: the overarching goal of SLM is divided into sector-specific objectives for water, energy, food, and ecosystem health. Each is assessed through specific indicators, with stakeholder interviews used to derive weights and calculate a "Nexus Score"—a weighted average reflecting preferences for different SLM practices.
The tool’s development involved two field campaigns:
* The 2023 campaign gathered indicator values for SLM practices through field visits and interviews with farmers, ensuring data reflected field-level conditions. It concluded with a validation workshop leading to adjustments in the ranking system.
* The 2024 campaign focused on collecting stakeholder weights for indicators within the WEFE Nexus through key informant interviews. A workshop gathered stakeholders from ministries and research institutions, and updated participants on the DST’s development and preliminary findings, while collecting feedback.
Using the DST involves the following steps:
Identify Area: Define geographic boundaries, consult local SLM experts for technical validation, and engage stakeholders at local and regional levels.
Use the Tool: Download the DST, compile an inventory of local SLM practices, gather stakeholder weights, review and complete indicator values, generate results, and refine inputs.
Social Learning: Hold validation workshops with stakeholders to review DST outputs, foster knowledge sharing, and address concerns to build consensus.
Implementation: Based on validated DST outcomes and stakeholder input, implement agreed SLM practices.
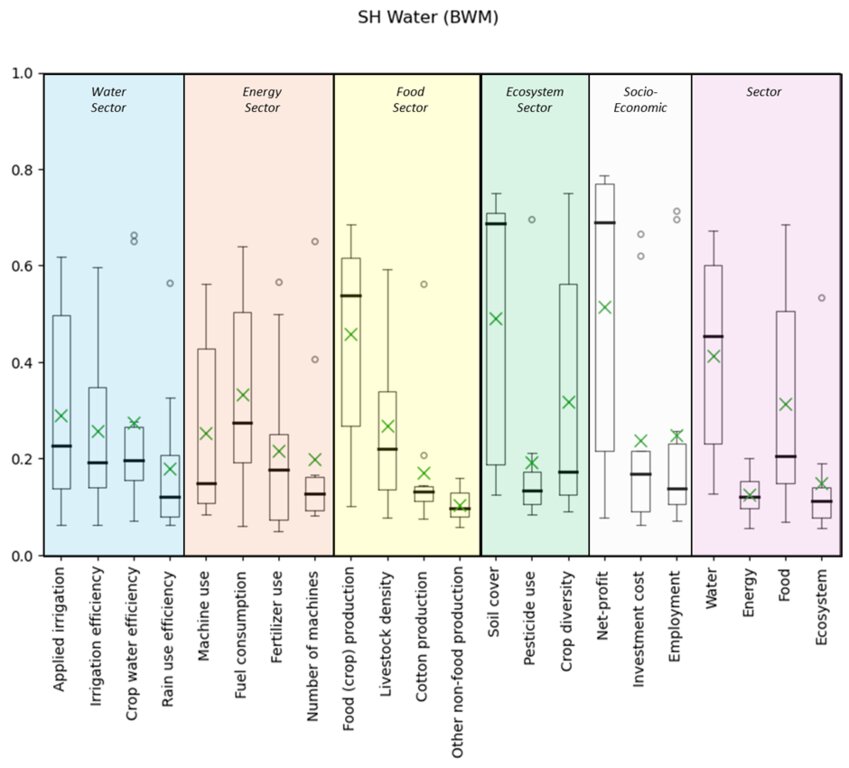
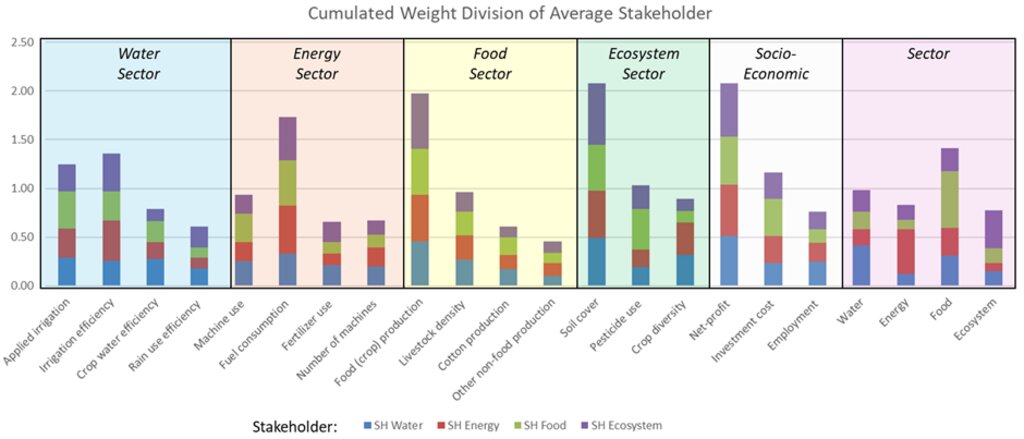
Overall, the DST aims to unite stakeholders in a shared understanding of land management decisions while addressing conflicting interests and policies. Findings reveal that departments often weigh indicators differently. Cross-departmental weight comparisons indicate shared priorities for certain criteria and highlight gaps in others, paving the way for interdepartmental collaboration.
The results of the weight survey provided notable insights. Within departments, responses exhibit a wide spread, indicating no collective priority. Across departments, certain criteria—such as reducing fuel consumption, food production, and net profit—are prioritized by all. Conversely, criteria like rain use efficiency, non-food production, and employment opportunities are collectively deprioritized.
This work was conducted under the CGIAR Initiative on Nexus Gains, with gratitude to the CGIAR Trust Fund contributors (www.cgiar.org/funders). The DST and approach are inspired by the thesis of J. Verbist, titled “Perspectives on the Economic Feasibility of Increasing Soil-Based Ecosystem Services on Arable Farms in The Netherlands” (2022), conducted at the Business Economics (BEC) Group of Wageningen University under the supervision of Professors H. Saatkamp and M. Kik.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດໂດຍທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຮູບພາບ:
More elaboration on the figures and the figures for the other departments can be found in the final report (see references).
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ອູເບກີສຖານ
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Tashkent (Uzbekistan)
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2022
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Tool was developed in 2022, with a literature review and followed by initial design, data collection and two validation workshops. The tool is downloadable via repo MEL (ICARDA knowledge repository).
2.7 ປະເພດຂອງແນວທາງ
- ພາຍໃຕ້ໂຄງການ / ແຜນງານ
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The objective of the DST is scale Sustainable Land Management through improved stakeholder engagement and integrated Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem Nexus management.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Institutional setting is relatively set in silos so departments and ministries generally do not mix and exchange ideas optimally.
ການຮ່ວມມື / ການປະສານງານຂອງຜູ້ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
- ອໍານວຍ
All of the interviewed and collaborated department and ministries were willing to support and attend the workshop, closely following the developments of the DST.
ນະໂຍບາຍ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Policy in general often reflect the objective of a specific ministry, which can create conflicting policies.
ການປົກຄອງທີ່ດິນ (ການຕັດສິນໃຈ, ການປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ຂໍ້ບັງຄັບ)
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Land governance is characterized by a strong push for productivity and land tenure over ownership.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Farmers were interviewed to understand their preference and to quantify indicator values (e.g., how much fuel does their current practice consume)
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
Experts from the four WEFE departments
They were interviewed to get weights for indicators.
- ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ICARDA
ICARDA developed the DST based on Multi-Criteria-Decision-Making (MCDM) literature.
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
Four WEFE departments
These stakeholders implement and formulate policies for land management.
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
ICARDA developed the DST and organized the field campaigns and workshops.
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ບໍ່ມີ | SLM specialist, as user of the DST, should identify a working area and identify relevant stakeholders and locally available good practices. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | When indicator data is retrieved and study area is known, weights for the different WEFE indicators should be given by the stakeholders. Based on that a workshop should be organized where stakeholders can discuss the outcome of the DST and move towards implementation. |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Once stakeholder agree on the outcome of the DST, the resulting SLM Technologies can be implemented |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | The DST can be used for MEL as well. Stakeholders can interviewed to see if preferences have changed over time and to validate indicator values when data becomes available. |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
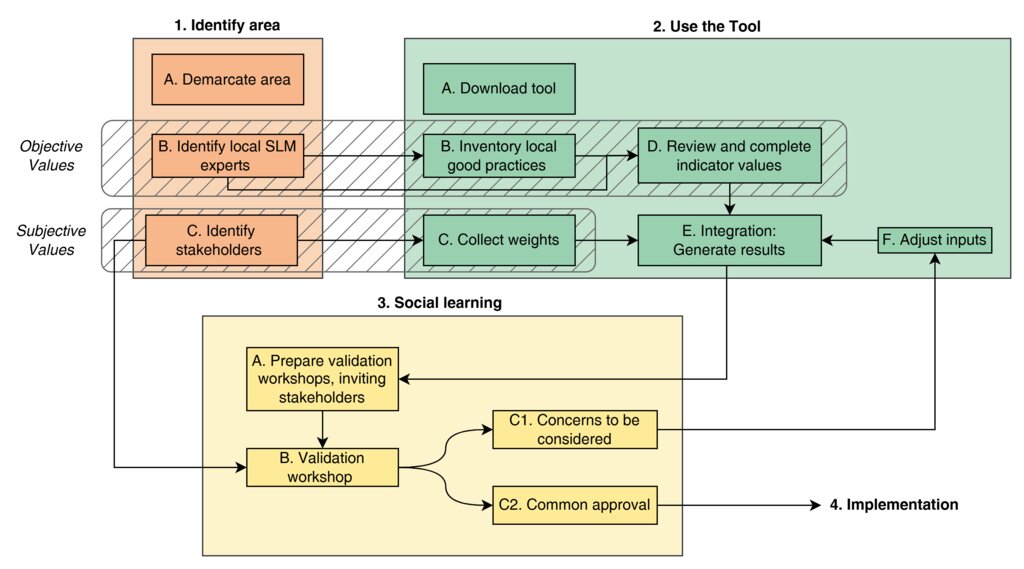
The Decision Support Tool (DST) facilitates the planning and implementation of Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices through a structured process. The flow chart illustrates the four main phases of using the DST: identifying the area, utilizing the tool, promoting social learning, and implementing the plan. Each phase involves specific steps to ensure the tool’s effective use and stakeholder collaboration. The following guidelines provide a detailed explanation of these steps, guiding users from initial planning to final execution.
Objective Values: The first distinct process within the framework of the DST is the incorporation of objective values. These values are derived from measurable and verifiable data such as yield, fertilizer use, irrigation efficiency, and net-income. The DST leverages this quantitative information to assess how well different interventions perform across a range of technical criteria.
Subjective Values: The second process addresses the integration of subjective values, which stem from the perceptions, priorities, and preferences of stakeholders. These values are gathered through weighing, such as Direct Ranking or the Best-Worst Method (BWM), to reflect stakeholders’ interests, but also reflecting social and cultural dimensions. Incorporating subjective values ensures that the tool aligns with the needs and interests of the communities and stakeholders involved, fostering greater acceptance and ownership of the chosen SLM practices. This process emphasizes the importance of balancing technical efficiency with social relevance, resulting in a more holistic and inclusive decision-making process.
1. Identify Area
A.Demarcate Area: Define the geographical boundaries at the farm and watershed levels. These scales are suitable for applying the DST because the DST focusses on land management rather than more abstract national and policy levels.
B.Identify Local SLM Experts: Engage local experts in SLM early in the process to leverage their knowledge about the area’s specific practices and challenges. They are the right people to validate technical aspects of land management, which is invaluable regarding the indicator values.
C.Identify Stakeholders: Identify relevant stakeholders across different levels, including local authorities, farmers, and regional organizations. Even if broader-scale stakeholders (e.g., national ministries) are involved, focus on local or regional branches that directly influence the area.
2. Use the Tool
A.Download the Tool: Access the DST from ICARDA's Monitoring, Evaluation, and Learning (MEL) platform after defining the area and identifying stakeholders.
B.Inventory Local Good Practices: Review existing SLM practices and identify those most relevant for the area. The DST comes with predefined options, but additional practices can be added to reflect the local context.
C.Collect Weights: Gather weights for different indicators from stakeholders using methods like the Best-Worst-Method (BWM) or direct ranking. These weights will be used to reflect stakeholder preferences in the evaluation.
D.Review and Complete Indicator Values: Assess and adjust the default indicator values within the DST to better reflect local conditions, considering factors like soil properties, rainfall, and market conditions. In addition, when local SLM practices are added, these indicators values should also be given.
E.Generate Results: Use the weighted indicators to run the DST and produce visualizations and evaluations of various SLM options.
F.Adjust Inputs: If necessary, refine the input data based on insights gained during the tool’s use, allowing for recalibration of indicator values, weights, or additional local practices.
3. Social Learning
A.Prepare Validation Workshops, Inviting Stakeholders: Organize workshops with identified stakeholders to validate the DST’s outputs. Ensure that all relevant voices are heard, and prepare to address any concerns raised.
B.Validation Workshop: Facilitate a structured workshop where stakeholders can review and discuss the tool’s results. The workshop should encourage knowledge sharing and foster social learning. The DST is a mean to create common understanding and appreciation among WEFE stakeholders for sustainable land management.
C.Iterate:
C1. Concerns to be Considered: Document and address any issues or concerns raised by stakeholders during the workshop, potentially revising the DST inputs or methodology.
C2. Common Approval: Aim for a shared understanding and acceptance of the results, incorporating feedback from the validation process.
4. Implementation
Once the results are validated and any necessary adjustments have been made, proceed to implement the agreed-upon SLM practices. The plan should reflect the insights gained through the DST analysis and stakeholder feedback, ensuring that the execution phase aligns with the validated recommendations.
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທັງໝົດ, ເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ຂອງວິທີທາງແບບມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
ອະທິບາຍ:
The rationale behind the DST as an Approach is that there is somewhat consensus on which SLM Technologies are implemented.
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- ປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ຫຼັກຖານທີ່ຊ່ວຍໃນການຕັດສິນໃຈ)
- ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ປະສົບການສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແລະ ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ທີ່ບໍ່ເປັນເອກກະສານ)
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
- WEFE Departments
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຫຼັກສູດ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
A short course on the WEFE concept and its relation to land management was conducted, to build a common understanding.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ມີ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
ME is not necessarily part of the DST, the process of intermediate feedback is more seen as the process rather than monitoring. ME implementation depends on what is in place by local authorities and land users.
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
A publication in Operations and Research was done. This paper elaborated on the need, concept, and use of the DST.
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
The main objective was to make a DST so not to implement SLM Technologies. DST is programmed in excel exactly for the reason to have no ongoing finance for IT. The Tool is downloadable through the institutional knowledge management of ICARDA (repo MEL). Costs are expected for implementing/constructing the SLMs or for holding the workshops.
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ບໍ່ມີ
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ການສົ່ງເສີມ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ໄດ້ສະໜອງສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ດັ່ງກ່າວນີ້ ສາມາດເປັນຫຼັກຖານ ທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໃຫ້ການຕັດສິນໃຈໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The DST requires input data such as indicators value and weight of these indicators. Therefore, the DST is also framework to elaborate decision and priorities in SLM/WEFE, increase evidence-based DM.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການປະສານງານ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ທີ່ມີປະສິດທິພາບ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The DST shows where stakeholders can work together and where their action contradict, knowing this can lead to more cost-effective policies and improve coordination.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The DST revolves around WEFE Nexus, hence when presenting the DST, WEFE is also automatically considered as well, which enhanced the knowledge of the stakeholders.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃຫ້ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ, ການຮ່ວມມື ລະຫວ່າງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The DST should lead to cross-department collaborations.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Integrated Analysis Across Multiple Sectors: The DST incorporates the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem (WEFE) Nexus, enabling a holistic evaluation of Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices. This allows stakeholders to assess potential trade-offs and synergies across sectors, promoting balanced, multi-faceted decision-making. |
| Stakeholder-Driven Approach: By gathering weights from stakeholders through methods like the Best-Worst Method, the DST reflects diverse priorities and values. This inclusivity fosters greater acceptance and ownership of SLM decisions, enhancing alignment with local needs and contexts. |
| User-Friendly and Adaptable Design: The DST is designed to be intuitive and compatible with common spreadsheet software, reducing the need for specialized training. Users can also adapt the tool by adding local practices and adjusting parameters, ensuring it remains relevant across varying contexts. |
| Support for Social Learning and Collaborative Decision-Making: The DST’s framework encourages stakeholder validation workshops, which facilitate knowledge sharing and collaborative refinement of the tool. This social learning process enhances mutual understanding among stakeholders and builds consensus on SLM priorities. |
| Visual and Quantitative Decision Support: By translating data into weighted scores and visual representations, the DST provides clear, actionable insights into SLM options. This visual aid helps decision-makers quickly identify win-win solutions or understand potential trade-offs, aiding more informed and efficient planning. |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Dependence on Stakeholder Involvement: The DST’s effectiveness relies heavily on active engagement from a diverse set of stakeholders to provide accurate weighting and feedback. If stakeholders are unwilling to participate or lack interest, the tool’s output may not fully reflect local priorities and needs. | If stakeholder involvement is limited, their weights can be estimated based on previous studies or similar contexts to approximate their likely priorities. Alternatively, you can demonstrate the DST’s relevance by showcasing how it supports their specific goals or decision-making processes, encouraging them to see the value of their input. |
| Oversimplification of Indicator Values: The DST may reduce complex, multi-faceted indicators to single values, which can overlook important nuances, such as temporal variability or site-specific conditions, potentially leading to decisions that don’t capture the full reality. | This can be considered during the proposed workshop and may result in change of indicator values. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Two surveys were doen. First, one was done to talk to farmers in order to get the values related to the WEFE indicators. Then a second was done to obtain weights of indicates given by the WEFE departements.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
Interviews to understand how they implement their practice, to fill in indicator values. We have surveyed 20 practices with three farmers each.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Two workshops were held to validate the developments of the DST and the collected data. The participants can be considers experts and researched.
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
Numerous
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Verbist, J., & Akramkhanov, A. (2024). A decision support tool for stakeholder engagement in sustainable land management using the WEFE Nexus: A simulation for the Aral Sea Basin stakeholders. Lecture Notes in Operations Research.
7.3 ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ອອນໄລນ໌
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Joren Verbist, Ulugbek Sadullaev, Ruhangiz Nurbekova, Akmal Akramkhanov. (18/12/2023). DSS for WEFE Nexus: Balancing Stakeholder Priorities for Sustainable Land Management and survey results on SLM practices.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69182
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Akmal Akramkhanov, Joren Verbist, Shakhzoda Umarova. (18/12/2023). Report on the validation of "Sustainable land use practices: increasing soil fertility, effective use of water resources, and increasing the efficiency of agrotechnical activities" workshop.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69038
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Support Tool for Stakeholder Engagement in Sustainable Land Management using the WEFE Nexus: A simulation for the Aral Sea Basin stakeholders.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69569
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Joren Verbist, Akmal Akramkhanov. (25/9/2024). A Decision Support Tool for Stakeholder Engagement in Sustainable Land Management using the WEFE Nexus: A simulation for the Aral Sea Basin stakeholders. BWM conference in Delft university.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69567
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Akmal Akramkhanov, Joren Verbist. (25/9/2024). Decision Support Tool for Sustainable Land Management: Integrating Stakeholders and WEFE Nexus. Landscape 2024 conference Humboldt university.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/69568
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Joren Verbist, Akmal Akramkhanov. (1/12/2023). Progress Report 2023: Decision Support System for WEFE Nexus to balance stakeholder priorities in sustainable land management.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68947
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ