Participatory Understanding of Groundwater Dynamics: Threats and Responsive Management [ອິນເດຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Pratik Ramteke
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
CDVI 3D Model
approaches_7555 - ອິນເດຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Yadav Ankita
ankita.yadav@wotr.org.in
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
ອິນເດຍ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Ghodake Navnath
navnath.ghodake@wotr.org.in
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
ອິນເດຍ
ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) - ອິນເດຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
30/04/2021
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
CoDriVE-VI is a participatory approach that integrates local knowledge with scientific data through 3D visual modelling to assess groundwater vulnerability and support sustainable, community-based groundwater management. It overlays surface and subsurface features, enabling villagers to visualize aquifer systems and develop informed water use plans.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
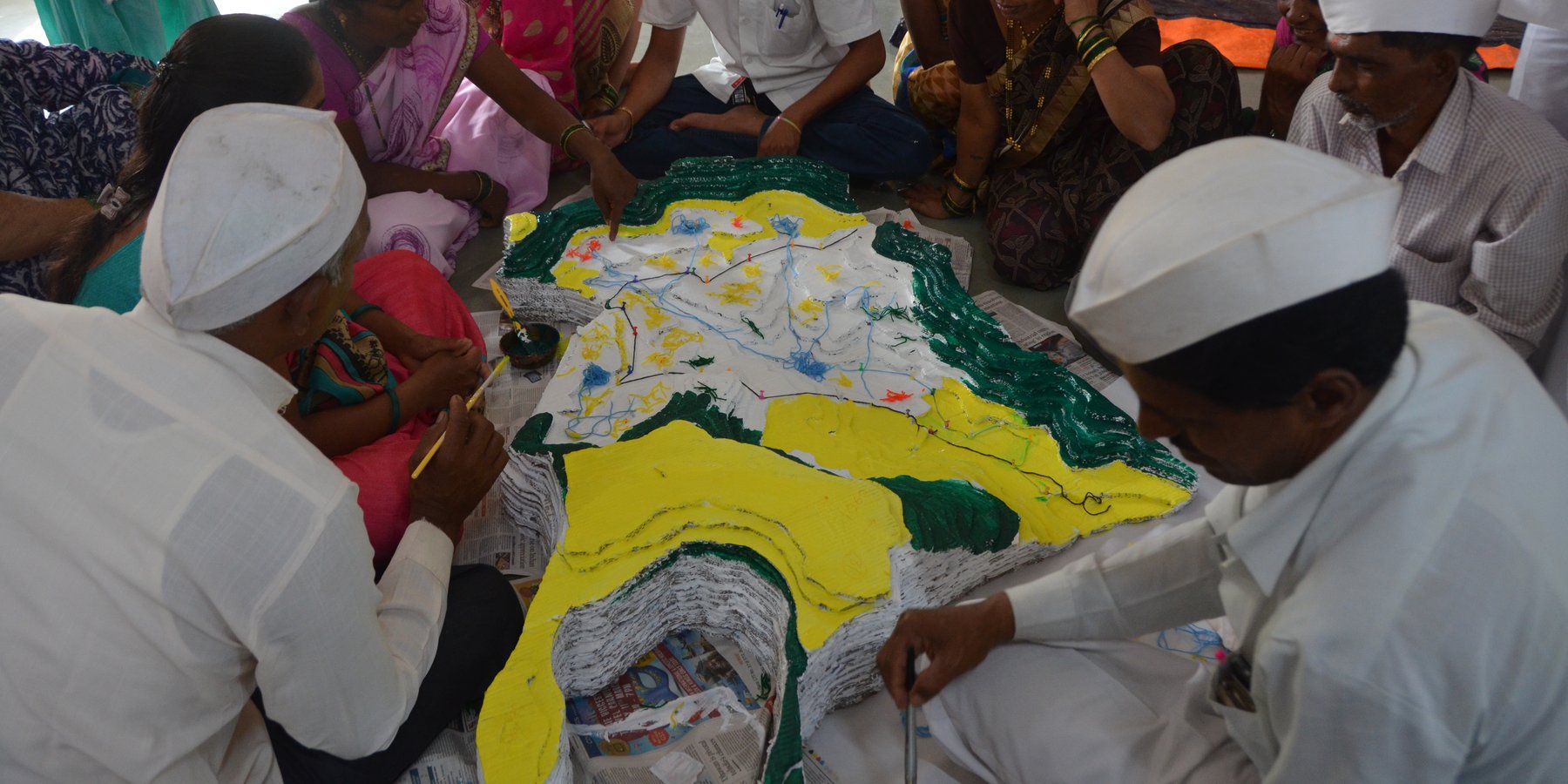
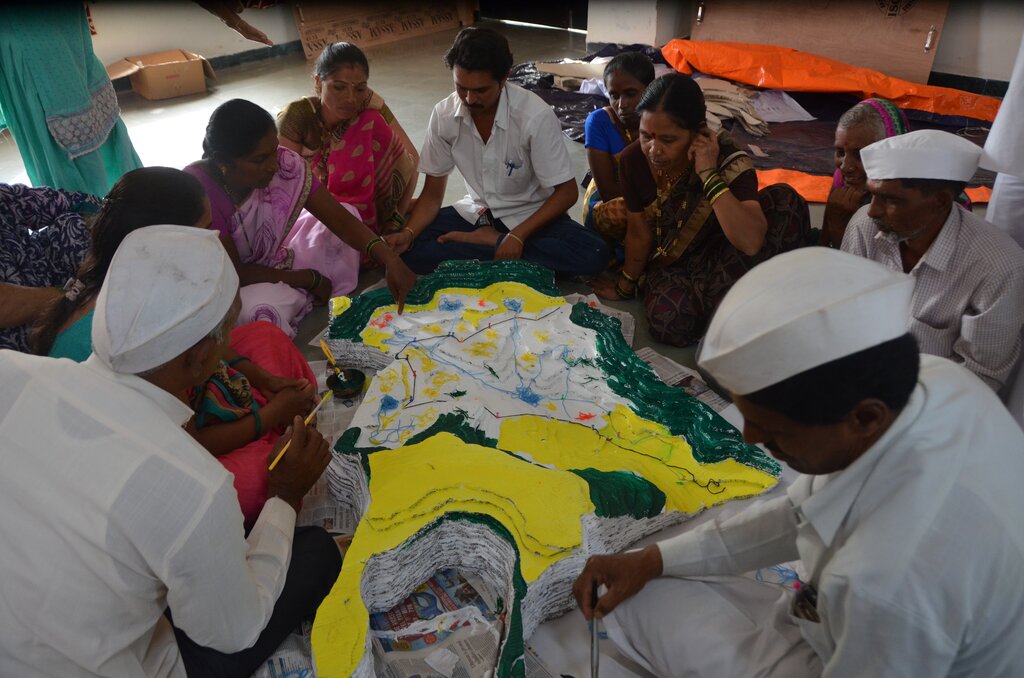
CoDriVE-VI (Community-driven Vulnerability Evaluation – Visual Integrator) is a participatory approach developed by the Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) to support sustainable groundwater management. It aims to demystify the invisible subsurface and make aquifer systems understandable to rural communities by combining scientific tools with local knowledge in a hands-on, visual format. While the process is facilitated by WOTR, communities are placed at the center of the process, contributing traditional insights, assisting with data collection, and actively participating in constructing and interpreting the 3D model. Thus, the approach is best described as participatory, with strong elements of community ownership and engagement.
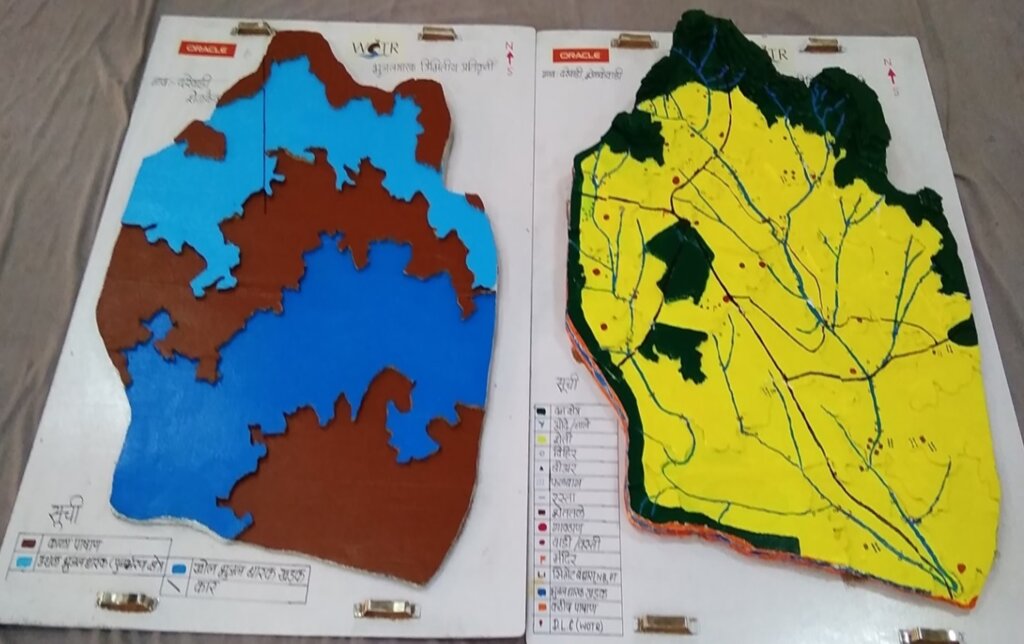
The “Visual Integrator” refers to the integration of both surface and subsurface data—such as topography, drainage, geology, well inventory details, and geophysical survey results—into a tangible, scaled three-dimensional model. This participatory 3D modelling (P3DM) process helps communities visualize how aquifers relate to the landscape, showing key features such as recharge zones, discharge points, and areas of intensive groundwater extraction.
“Vulnerability evaluation” is carried out through the community’s participatory analysis of the model. Using the integrated visual platform, villagers can identify zones that are more vulnerable to depletion—such as those with low recharge, high borewell density, or historically declining water tables. While a formal vulnerability matrix is not used, the 3D model serves as a practical vulnerability map. It guides discussions and decisions around water budgeting, aquifer recharge, crop-water planning, and the development of informal rules for responsible groundwater use.
The methodology combines participatory rural appraisal with hydrogeological and geospatial techniques. After an initial orientation and trust-building phase, communities help map surface features. Subsurface data is then collected through geological mapping, well inventory surveys, and geophysical methods like Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES). The data are analyzed using GIS tools and inverse slope modelling. The 3D model is then constructed using layered cardboard sheets, with communities contributing throughout the process—cutting, assembling, painting, and validating the layers.
The CoDriVE-VI process unfolds in several stages: community mobilization and planning; surface and subsurface data collection; model building in participatory workshops; and result interpretation and management planning. Key stakeholders include community members, WOTR facilitators, technical experts (geologists and GIS specialists), and local governance representatives.
Participants found the visual models highly effective in helping them grasp aquifer dynamics, leading to a shift in perception—from seeing groundwater as an individual entitlement to recognizing it as a shared resource. This in turn fostered collective decision-making. The approach has also contributed to improved groundwater literacy, informed water budgeting, and motivated some villages to initiate local groundwater governance practices.
While climate change is a key driver of groundwater stress, the approach also acknowledges other socio-economic and environmental pressures—such as population growth, land-use change, deforestation, and the uncontrolled proliferation of borewells—as critical factors influencing groundwater vulnerability. By visualizing these interconnections, CoDriVE-VI supports more holistic and sustainable groundwater management at the community level.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ອິນເດຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Maharashtra
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Darewadi,Post. Kauthe Malkapur Tal. Sangamner, Dist. Ahilyanagar, Maharashtra
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2017
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The tool was developed based on experiences from multiple village-level implementations in Maharashtra. The approach is ongoing.
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
1. To build the capacity of rural communities to understand groundwater systems, including aquifer behavior and climate and non-climate stressors affecting groundwater availability.
2. To make subsurface aquifer characteristics visible and comprehensible through participatory 3D modelling that integrates scientific and local knowledge.
3. To foster collective ownership and sustainable management of groundwater as a shared, finite resource.
4. To support community-led evaluation of groundwater vulnerability and guide responsive actions such as water budgeting and recharge planning.
5. To document, preserve, and apply indigenous spatial knowledge related to land use, topography, and local water systems.
6. To enable informed decision-making by facilitating the transfer of community-generated insights to local governance bodies and development agencies.
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ສັງຄົມ / ວັດທະນະທໍາ / ມາດຕະຖານ ແລະ ຄຸນຄ່າທາງສາສະໜາ
- ອໍານວຍ
The participatory nature of CoDriVE aligns well with community-based traditions and values. Villagers appreciated visual models and collective dialogue.
ມີຄວາມສາມາດ / ເຂັ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Physical model preparation and technical surveys (like geophysical VES) require resources. Financial constraints can limit replication or scaling.
ການກໍ່ຕັ້ງສະຖາບັນ
- ອໍານວຍ
Support from institutions like WOTR and local governance structures helped facilitate workshops and technical assessments.
ການຮ່ວມມື / ການປະສານງານຂອງຜູ້ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
- ອໍານວຍ
Strong collaboration between communities, facilitators, technical experts, and local leaders enabled smooth implementation
ກ່ຽວກັບກົດໝາຍ (ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ, ສິດນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ)
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Customary laws viewing groundwater as private property can hinder the recognition of aquifers as shared resources.
ນະໂຍບາຍ
- ອໍານວຍ
National and state-level programs like Atal Bhujal Yojana and Maharashtra Groundwater Act 2009 support aquifer-based planning and groundwater literacy.
ການປົກຄອງທີ່ດິນ (ການຕັດສິນໃຈ, ການປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ຂໍ້ບັງຄັບ)
- ອໍານວຍ
Local institutions and village-level bodies were engaged in discussions and planning.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ອໍານວຍ
Technical support from WOTR and use of local knowledge supported learning and capacity building
ຕະຫຼາດ (ໃນການຊື້ວັດຖຸດິບ, ຂາຍຜະລິດຕະພັນ) ແລະ ລາຄາ
- ອໍານວຍ
ວຽກ, ມີກໍາລັງຄົນ
- ອໍານວຍ
Community enthusiasm and involvement were high during workshops and model building.
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Manual preparation of 3D models requires time and coordination, which may be demanding in some villages.
ອື່ນໆ
- ອໍານວຍ
Visual and tactile tools helped bridge the knowledge gap between experts and villagers.
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
Initial complexity of scientific terms (e.g., aquifer, resistivity) required careful facilitation and adaptation
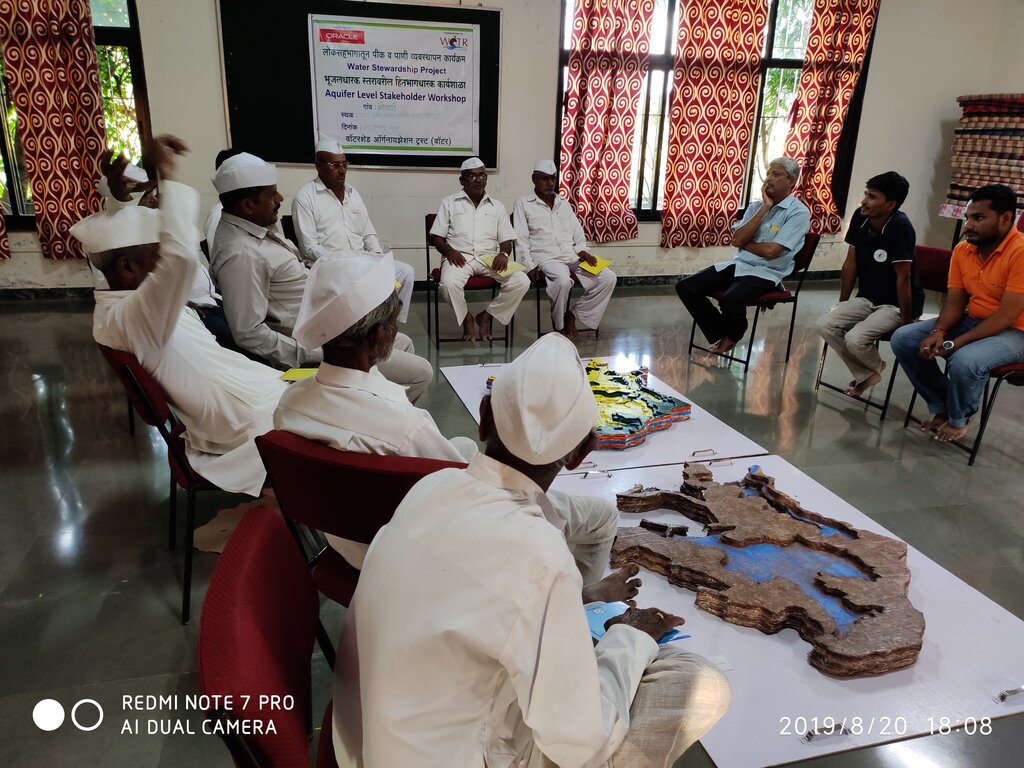
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Villagers and farmers from Ahilyanagar and Jalna districts, Maharashtra
They participated actively in the mapping exercises, provided indigenous knowledge on topography and land use, contributed to well inventory and aquifer-related insights, and were directly involved in building the 3D models. Their engagement was central in interpreting subsurface information and applying it to groundwater planning.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ພາຍໃນຊຸມຊົນ
Village Water Management Committees, Water Stewardship groups
Helped mobilize community members, facilitated communication between villagers and technical teams, and supported local-level planning and rule-setting for groundwater use.
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
WOTR technical staff and hydrogeology facilitators
Provided scientific inputs on geology and hydrogeology, conducted well and geophysical surveys, interpreted data, supported the construction of groundwater potential maps, and trained community members in groundwater management
- ນັກຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
Researchers and field investigators from WOTR and contributing institutions
Developed the methodology, documented experiences, synthesised scientific and community knowledge, and analysed feedback for continuous improvement of the tool.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຂື້ນກັບລັດຖະບານ
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR)
Lead agency responsible for conceptualizing, facilitating, implementing, and documenting the approach. Conducted workshops, managed technical assessments, trained field teams, and engaged communities.
- ພາກເອກະຊົນ
HSBC Software Development India (as supporter)
Provided financial support for printing and disseminating the CoDriVE-VI manual.
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Gram Panchayat members, Sarpanches
Participated in workshops, helped validate maps and data, encouraged community participation, and supported local rule-making for sustainable groundwater use.
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
Indirectly linked via supportive policies (e.g., Atal Bhujal Yojana, National Aquifer Management Project (NAQUIM))
Although not directly involved in implementation, national policies provided support for the overall context and justification of aquifer-based participatory planning and water budgeting.
- ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ ສາກົນ
ProSoil project (GIZ)
Supported in publishing and promoting the CoDriVE-VI manual, including showcasing it at UNCCD COP14
ຖ້າຫາກມີຫຼາຍພາກສ່ວນທີ່ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ອົງການທີ່ເປັນຫຼັກ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR)
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Local villagers in the project areas (e.g., Ahilyanagar and Jalna districts) were engaged early through orientation sessions. While the initiative was introduced by WOTR, community members showed interest and contributed knowledge from the beginning, especially around their water challenges and local hydrogeology. |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Villagers participated in identifying key features for surface mapping, shared traditional knowledge of aquifers and land use, and were involved in selecting locations for surveys. Their inputs shaped both the design and scale of the models. |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | Community members took part in well inventory surveys, guided geological observations, and actively built the 3D physical models. They also helped colour-code aquifer zones under facilitators’ guidance, and validated the data presented. |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | During workshops and feedback sessions, villagers evaluated the accuracy of models, reflected on the implications of subsurface characteristics, and discussed how to use the insights for water budgeting and community planning |
| research | Community knowledge directly contributed to the research process by enriching scientific interpretations with local hydrogeological understanding. Their experiences and reflections were documented and used to improve the approach. |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
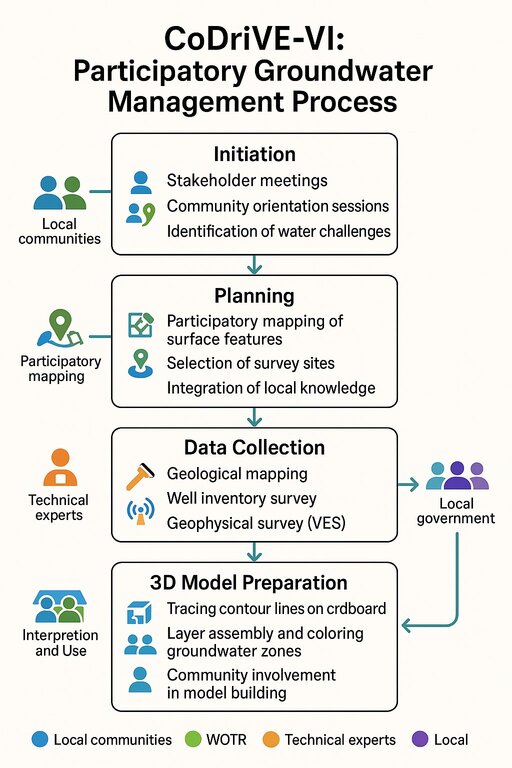
The visual summary illustrates the four key stages of the CoDriVE-VI approach
Initiation
-Stakeholder meetings and community orientation sessions are conducted.
-Local water-related challenges are identified.
-Builds a foundation for participatory engagement and problem recognition.
Planning
-Participatory mapping of surface features is carried out.
-Survey sites are selected based on local inputs and technical feasibility.
-Local knowledge is integrated with scientific planning.
Data Collection
-Technical experts conduct geological mapping and well inventory surveys.
- Geophysical surveys (e.g., Vertical Electrical Sounding - VES) are performed.
- Scientific data on groundwater systems is gathered for model development.
3D Model Preparation
-Contour lines are traced on cardboard to build physical models.
-Groundwater zones are assembled and color-coded.
-Communities are actively involved in model building and interpretation for better understanding and use.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Pratik Ramteke
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທັງໝົດ, ເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ຂອງວິທີທາງແບບມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
ອະທິບາຍ:
The selection and design of the CoDriVE tool was done through participatory processes involving local communities, WOTR facilitators, and technical experts. Villagers contributed local knowledge and needs, while experts provided scientific input, ensuring collective decision-making.
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- ປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ຫຼັກຖານທີ່ຊ່ວຍໃນການຕັດສິນໃຈ)
- ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ປະສົບການສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແລະ ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ທີ່ບໍ່ເປັນເອກກະສານ)
- Decisions were based on field experiences from over 25 villages, scientific methods (e.g., VES surveys, GIS analysis), and documented evidence on aquifer-based planning. Local knowledge and experiential insights also guided model design and validation.
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.1 ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ພາກສ່ວນກ່ຽວຂ້ອງອື່ນໆ ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ພະນັກງານພາກສະໜາມ / ທີ່ປຶກສາ
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເພດ, ອາຍຸ, ສະຖານະພາບ, ຊົນເຜົ່າ, ແລະ ອື່ນໆ:
Training involved both male and female community members, including farmers, youth, and local leaders from diverse socio-economic backgrounds in the villages. Inclusive participation was encouraged throughout
ຮູບແບບຂອງການຝຶກອົບຮົມ:
- ການເຮັດຕົວຈິງ
- ຕົວຕໍ່ຕົວ
- ເນື້ອທີ່ສວນທົດລອງ
- ກອງປະຊຸມ
ໃນຫົວຂໍ້:
•Basic concepts of hydrogeology and aquifers
•Groundwater vulnerability and common pool resource concepts
•Surface and subsurface mapping
•Use of Participatory 3D Modelling (P3DM)
•Groundwater budgeting
•Climate change impacts on water resources
•Community-led planning and rule-setting for water use
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ
- ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
WOTR provided technical assistance through facilitators and hydrogeology experts. These acted as advisors, guiding communities in surveys, model interpretation, and decision-making.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ອະທິບາຍ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ, ພາລະບົດບາດ ແລະ ໜ້າທີ່ຮັບຜິດຊອບ, ສະມາຊິກ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Village Water User Groups (VWUGs) and local governance committees were strengthened to coordinate groundwater management activities. Their roles included planning water use, monitoring aquifer health, implementing community water rules, and facilitating knowledge sharing. Members typically included local farmers, community leaders, and field facilitators
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ການສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດ / ການຝຶກອົບຮົມ
- ອຸປະກອນ
ໃຫ້ລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມ:
The strengthening focused on enhancing institutional capacity to support community-driven water resource management. Training sessions improved leadership and technical skills, enabling institutions to take ownership of groundwater sustainability. Equipment such as GPS units and simple monitoring devices were provided to aid local data collection and verification.
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Monitoring was integrated through periodic community workshops, feedback sessions, and participatory verification of groundwater models. Evaluation focused on assessing the accuracy of aquifer mapping, effectiveness of capacity building, and impact on local water management practices.
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ເອກກະສານສະບັບນີ້ ແມ່ນໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຕິດຕາມ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This documentation serves as a reference for tracking the implementation process, assessing community engagement, and evaluating outcomes. It can be used to guide adaptive management and inform replication in other regions.
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ສັງຄົມ
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- Hydrogeology and participatory modelling
ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ແລະ ກໍານົດ ຜູ້ໃດເຮັດການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ:
Research was integral to developing and refining the CoDriVE methodology. Hydrogeologists and social scientists collaborated with local communities to understand groundwater systems and social dynamics influencing water use. Technology research focused on participatory 3D modeling tools and groundwater budgeting techniques. WOTR staff, partnered with academic institutions and experts in hydrogeology, led the research activities. Community feedback was also systematically documented to improve approaches.
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັດງົບປະມານທີ່ແນ່ນອນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານເອົາ:
- 10,000-100,000
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Funding mainly came from government development programs and international donor agencies supporting WOTR’s groundwater management initiatives. Major donors included state water departments and NGOs focused on sustainable water use.
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ, ເງື່ອນໄຂ ແລະ ຜູູ້ສະໜອງ (ຫຼາຍ):
Material support included provision of tools and equipment such as GPS devices and monitoring kits, provided free or at subsidized cost by project partners. Some minor financial incentives were given as stipends during training sessions. Support was conditional on active participation in capacity-building and water management activities. Providers included WOTR and partner NGOs.
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
- ແຮງງານ
| ທີ່ຂອບເຂດ | ລະບຸ ການອຸດໜູນ |
|---|---|
| ງົບປະມານບາງສ່ວນ | Labour costs for technical support and community mobilization were partly supported by the implementing agency or development partners |
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Most of the labour contributed by land users and local communities during planning, mapping, and 3D model building was voluntary. In some cases, key technical or facilitative roles were partly supported by the implementing agency. No direct subsidies were provided for equipment, tools, or construction inputs under this approach
5.4 ສິນເຊື່ອ
ໄດ້ປ່ອຍສິນເຊື່ອ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ພາຍໃຕ້ ວິທີການສໍາລັບກິດຈະກໍາ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນນຍົງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ສິ່ງຈູງໃຈ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອງມືອື່ນໆ
ການສົ່ງເສີມ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ໄດ້ສະໜອງສິ່ງກະຕຸກຊຸກຍູ້ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ:
Supportive policies included local water governance regulations encouraging sustainable groundwater use and community rule enforcement. NGO advocacy helped secure government backing for participatory water management.
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ວິທີທາງ ຊ່ວຍຊຸກຍູ້ ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນທ້ອງຖີ່ນ, ໃນການປັບປຸງ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ຂອງຜູ້ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The participatory 3D modelling process directly involved villagers in mapping and decision-making. It created a sense of shared ownership over groundwater resources, enabling community-level rule-making and active participation in groundwater governance
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ດັ່ງກ່າວນີ້ ສາມາດເປັນຫຼັກຖານ ທີ່ສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໃຫ້ການຕັດສິນໃຈໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Scientific tools such as geophysical surveys, geological mapping, and GIS-based groundwater potential maps enabled villagers to base water management decisions on accurate data integrated with traditional knowledge
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
By making aquifer dynamics visible, the approach supported sustainable agricultural planning and water budgeting, which are part of SLM practices, although it focused more on literacy and awareness than direct technology implementation
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການປະສານງານ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ທີ່ມີປະສິດທິພາບ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
It fostered collaboration among community members, local institutions, and technical experts, creating alignment in groundwater-related decisions.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດລະດົມ ຫຼື ປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງຊັບພະຍາກອນ ການເງິນ ສໍາລັບການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The approach was low-cost and supported by NGOs and donor funding.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືດຍົງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The process enhanced groundwater literacy, built capacity for aquifer-based planning, and enabled villagers to understand recharge/discharge zones and water budgeting.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Local government representatives and NGO facilitators gained insights into how to communicate complex hydrogeological data using participatory tools, enhancing their capacity to support SLM.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃຫ້ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ, ການຮ່ວມມື ລະຫວ່າງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Village Water Committees and informal community groups were strengthened through workshops, joint planning, and shared understanding of groundwater resources
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
By visualizing the shared nature of groundwater resources, it reduced the perception of groundwater as private property and encouraged collective action, which can mitigate user-level conflicts.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The approach was inclusive and community-wide. Women’s participation was specifically encouraged, though economic empowerment was not a primary focus.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ຄວາມສະເໜີພາບ ຂອງບົດບາດ ຍິງຊາຍ ແລະ ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງໃຫ້ຜູ້ຍິງໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Women were involved in workshops and discussions, recognizing their central role in water use.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊຸກຍູ້ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນທີ່ເປັນຊາວໜຸ່ມ / ຄົນລຸ້ນໃໝ່ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The participatory and educational nature of the tool could be adapted for such use.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ປະເດັນການຖືຄອງທີ່ດິນ / ສິດທິໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The approach challenged the perception of groundwater as an individual property, promoting a common-pool perspective.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການຄໍ້າປະກັນສະບຽງອາຫານ ຫຼື ປັບປຸງໂຄສະນາການໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
While not directly linked, improved water planning and sustainable groundwater use could contribute indirectly to more reliable irrigation and reduced crop failure.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງຕະຫຼາດໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການເຂົ້າເຖິງນໍ້າ ແລະ ສາຂາພິບານໄດ້ບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
By improving groundwater management and awareness, the approach contributed to more sustainable access to water for drinking and agriculture.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການນໍາໃຊ້ແຫຼ່ງພະລັງງານ ແບບຍືນຍົງຫຼາຍຂື້ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມອາດສາມາດໃຫ້ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນການປັບຕົວ ຕໍ່ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຫຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງທາງໄພພິບັດໄດ້ບໍ? :
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The tool helped communities understand climate variability's impact on aquifers, supported water risk assessment, and promoted resilience through informed water use planning.
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ປັບປຸງ ການຈ້າງງານ, ໂອກາດ ໃນການສ້າງລາຍຮັບບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Indirect employment through training, facilitation, and workshops was possible.
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງຂອງໄພພິບັດ
By understanding groundwater vulnerability and recharge/discharge zones, communities became more aware of water-related risks (e.g., drought, borewell failure) and were motivated to manage aquifers collectively.
- ກຽດສັກສີ, ຄວາມກົດດັນທາງສັງຄົມ / ການຕິດຕໍ່ກັນທາງສັງຄົມ
As the model was collectively built and discussed in village workshops, peer learning and mutual accountability encouraged participation and collective rule-making.
- ລວມເຂົ້ານໍາກັນກັບການເຄື່ອນໄຫວ / ໂຄງການ / ກຸ່ມ / ເຄືອຂ່າຍ
Community involvement in WOTR’s Water Stewardship Initiative and other participatory planning efforts created a sense of belonging and continuity with ongoing development processes.
- ຄວາມຮັບຮູ້ ທາງສີ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
The process helped villagers visualize aquifers as finite, shared resources, leading to increased awareness of groundwater overuse and its ecological consequences.
- ພາສີ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊື່ອຖື, ສົມບັດສິນທໍາ
The participatory nature respected local knowledge systems, and community values around fairness and shared responsibility played a motivating role
- ການປັບປຸງ ຄວາມຮູ້ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Through participation in surveys and the creation of 3D models, communities gained knowledge about geology, aquifers, and sustainable groundwater use.
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
A visual understanding of shared aquifers helped reduce tensions among farmers and shifted the perspective from private groundwater ownership to common-pool resource management.
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ແນ່ນອນ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
While the approach may be effective, its long-term viability or replication across other areas could be "uncertain" because:
It relies on external scientific expertise (e.g., geophysical surveys, 3D model building).
There are financial implications (e.g., cost of equipment, facilitation, training).
Communities might not be able to independently replicate or sustain it without ongoing support.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Enhanced groundwater understanding: The 3D model helped farmers visualize aquifer connectivity, which improved their awareness of water scarcity and led to better planning |
| Collective decision-making: The approach promoted social cohesion and encouraged joint management of groundwater as a common resource. |
| Practical application: Enabled decisions on water budgeting, cropping patterns, and site selection for recharge structures |
| Inclusiveness: Encouraged participation of all sections of the village including women and marginal landholders |
| Created a visual tool that villagers could present in Gram Sabha meetings and discussions with local authorities |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Bridges science and local knowledge: CoDriVE-VI effectively demystifies hydrogeology by integrating local understanding with technical surveys |
| Low-cost and replicable: Uses locally available materials (e.g., cardboard) and community manpower. |
| Supports policy alignment: The approach aligns with national programs like NAQUIM and Atal Bhujal Yojana, enabling scale-up |
| Encourages behaviour change through experiential learning—participants shift from individual to community-centered groundwater thinking |
6.5 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງແນວທາງ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂໃຫ້ເຂົາເຈົ້າ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມູມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Time-consuming model preparation: Building the physical 3D model takes effort and coordination. | Train local youth/facilitators to manage the model-building steps and streamline the process |
| Initial difficulty in understanding hydrogeological concepts: Terms like "resistivity" or "aquifer" were hard to grasp | Use simplified language, analogies, and step-by-step facilitation. |
| Models can be physically damaged over time | Store models in safe, community-designated spaces or digitize versions where feasible. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ເສຍ ຫຼື ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນມຸມມອງຂອງ ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Limited scalability without facilitation support: While the model is low-cost, initiating the process requires trained facilitators | Create a cadre of local groundwater ambassadors trained in CoDriVE-VI. |
| Not linked directly to economic incentives: Without immediate financial benefits, long-term engagement may decline. | Integrate with livelihood programs (e.g., water-efficient cropping, irrigation advisories). |
| Not institutionalized within local governance systems | Advocate for formal integration into Gram Panchayat and watershed planning protocols. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
15
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
5
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Chemburkar S., Kale E., 2021. Making the Invisible, Visible: Manual for preparing Co-DriVE - Visual Integrator to o
7.3 ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ອອນໄລນ໌
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Manual for preparing CoDriVE
URL:
https://wotr-website-publications.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/156_Making_the_Invisible_Visible_A_Manual_for_Preparing_the_CoDriVE_Visual_Integrator.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Report
URL:
Chemburkar S., Kale E., 2021. Making the Invisible, Visible: Manual for preparing Co-DriVE - Visual Integrator to overlay surface and sub-surface characteristics for sustainable groundwater management, WOTR
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ