Riverbed reclamation & silt trapping for sugarcane [ເຄັນຢາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Kithinji Mutunga
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff
Kyanda (Kikamab)
technologies_1096 - ເຄັນຢາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Ngati Mbuvi
MOARD
ເຄັນຢາ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Mwendwa Linus
MOARD
ເຄັນຢາ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
17/04/2000
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
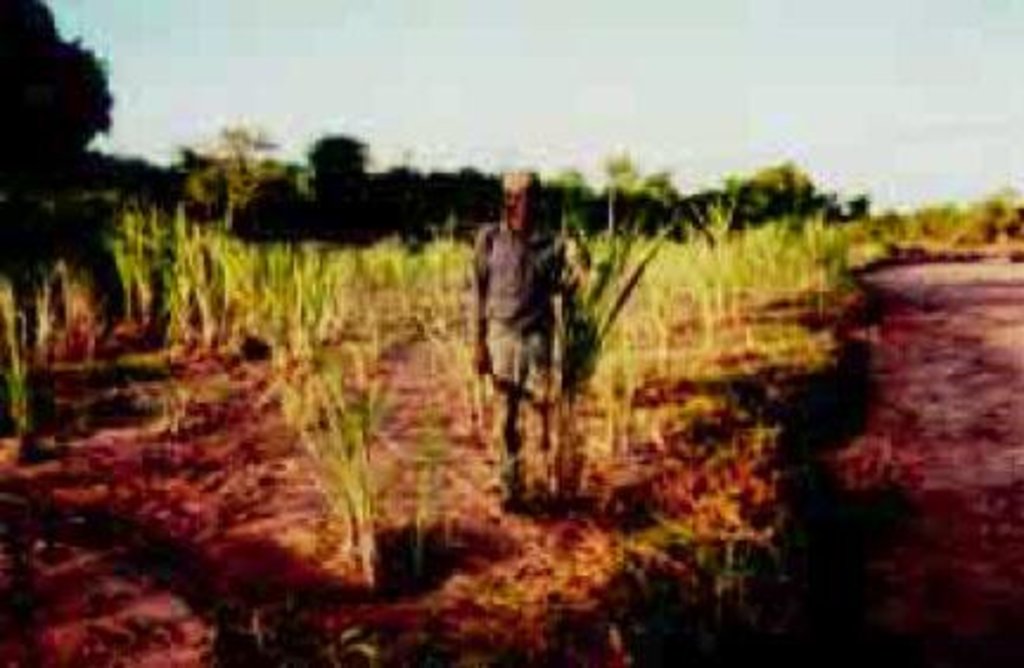
Silt harvesting on riverbeds to maximise sugarcane growing in semi arid area
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
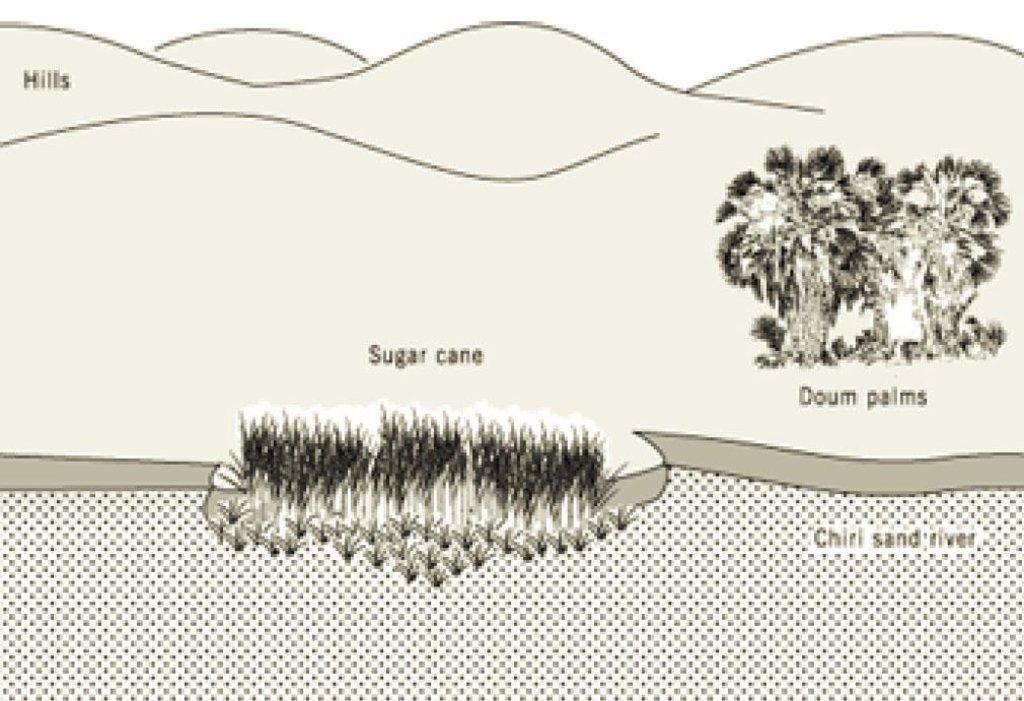
The technology first involves fencing off part of a riverbed with cut thorn scrub in order to keep livestock away. The enclosed area is then mulched with brushwood and herbaceous materials in places. Sugar cane is planted and harvested piecemeal when mature. Kamuti plants a perennial grass (Cynodon dactylon) between the canes to help bind the sand. This exercise has been done, incrementally, over a series of seasons, enclosing an increasingly large area. When the rains return and the river flows, floodwater passes through and over the sugar cane and silt is deposited as the flow is slowed.
Purpose of the Technology: This initiative is categorized as an agronomic/vegetative measure, for reclamation of land. Its purpose is to increase water stored in the soil and to increase fertility by sediment harvesting, as a way of making land productive, while simultaneously addressing riverbed erosion. Farm income increase from the sale of sugar cane is the main production/ socio-economic benefit, while the ecological benefits include sediment accumulation, soil (ie riverbed and bank) loss reduction, soil cover improvement, increase in soil moisture and increase in soil fertility.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The action involves cutting tree branches, trimming pegs about 1m long, and hammering these pegs into the bed of the sand river, parallel to the bank, enclosing a long narrow strip. This initial strip may be 10 metres wide in a riverbed of 100 meters wide. The tree branches and trimmings are used to form a brushwood-netting barrier, which protects the area from livestock, and simultaneously slows the river flow and traps sediments. To further strengthen the barrier, star grass (Cynodon dactylon) is planted along the line of the fence. Inside the fenced-off area, sugar cane cuttings are buried at a depth of 0.4 m, and the same grass planted between the canes. The area is mulched with brushwood, which rots down to increase organic matter in the soil. These cuttings sprout and an intercrop of grass and sugar cane is the result. Maintenance comprises repairing the fence and cutting grass for mulching. No special tools are required. To be effective, the technology requires mulching every season, as the old mulch is covered by the silt load during the rainy period. The perimeter fence is maintained seasonally and requires considerable material. Occasionally when the rainfall is heavy, the sugar cane is swept away by floods and needs replacing.
Natural / human environment: The farm on which this technology is applied is in the arid far-north of Mwingi District. During the rainy season the farm can be inaccessible. The farmer, who is over 60 years of age, lives with his wives and children in what effectively forms a mini-village. The annual average rainfall in this area is barely 500 mm, and famine years are common. Temperatures are consistently high. The farm borders a dry sand riverbed.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຄັນຢາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Farmer own intiative
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Extensive grazing of animals/unit area, uncontrolled felling and burning of tree in land preparation, low soil fertility due to continous cultivation without conservation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yields hence opening of large areas for cultivation. Difficult soils, hence ploughing during the rains. Infertile soils.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 75 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Dec
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
- ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 m2.
This technology is along a riverbed and it is not adapted by other farmers
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A6: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S6: ແລວກັນເຈື່ອນ, ຮົ້ວ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
Reclaiming part of sand river bed with Sugar cane
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: grasses
Quantity/ density: 2
Remarks: grass scattered
Grass species: stargrass
Change of land use type: fencing off portion of river bed
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Kenya shilling
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
70.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
1.50
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | after rains |
| 2. | mulching with bushes | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | before rains |
| 3. | planting of sugarcane | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | dry season |
| 4. | cuting grass for mulch | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | rainy season |
| 5. | fencing riverbed to keep off animals | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after rain |
| 6. | planting grass | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after rain |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | ພືດ | dry season / when height goes down |
| 2. | mulching with trash | ພືດ | dry '' / after clearing |
| 3. | grass planting | ພືດ | dry / before rains |
| 4. | sugarcane planting | ພືດ | wet / end of rain |
| 5. | collection of mulch | ພືດ | dry / biannual |
| 6. | fencing | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | after rain /biannual |
| 7. | cutting grass for mulch | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | rainy /biannual |
| 8. | scatterin thorn bushes | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | during rain /biannual |
| 9. | fencing | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after rain / each cropping season |
| 10. | spreading brushwood | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after / annual |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: oxen plough, 2 pangas , 2 hoes
the above cost were calculated in terms of purchase of tools,material and manday used.
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
labour affects cost as it is required in large quantities
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
- ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Topsoil organic matter: Becomes medium after the technology
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is very low - medium
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 33% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 12% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 8% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 21% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: most of harvest are low and hence dependent on off farm income.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction is used for assembling the thorny bushes and for marking farrows
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Sugar cane
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Sugar cane
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
60
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
20
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
12
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
5
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
30 households (1% of the area stated)
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 90-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: after farmer tour organised by the PFI most are attempting. At least five farmers had adopted the innovation by the beginning of 1999 (exact figures not available). This is a particularly site-specific system, and thus wide replication is simply not possible. It is only relevant to those who have farms bordering sand rivers with wide beds.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| This innovation demonstrates how productive use can be made of sub-surface moisture in sand rivers in arid areas while simultaneously protecting the riverbed and bank from erosion |
| Farm income increase through land reclamation |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
|
Planting within a riverbed is, strictly speaking, against regulations. |
Such technologies should not be attempted without consulting the local agricultural office. |
| The fence is constructed with thorn bush cuttings which have to be constantly replenished |
A live fence is recommended as an alternative to constantly having to replenish the fence with cut thorn bush. The fence is required to avoid grazing of the cane by domestic livestock. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Farm management Guidelines. 1989.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
MOA, Nairobi
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ