Mobile cultivation beds [ເຢຍລະມັນ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Peter Kirch
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1678 - ເຢຍລະມັນ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Shaw Robert
+49(0)17624332297
rs@prinzessinnengarten.net
Nomadisch Grün gemeinnützige GmbH
Forster Str. 5, 10999 Berlin, HRB 121043 B 3
ເຢຍລະມັນ
Bärich Christian
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Nomadisch grün GmbH - ເຢຍລະມັນຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) - ເຢຍລະມັນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
08/05/2015
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
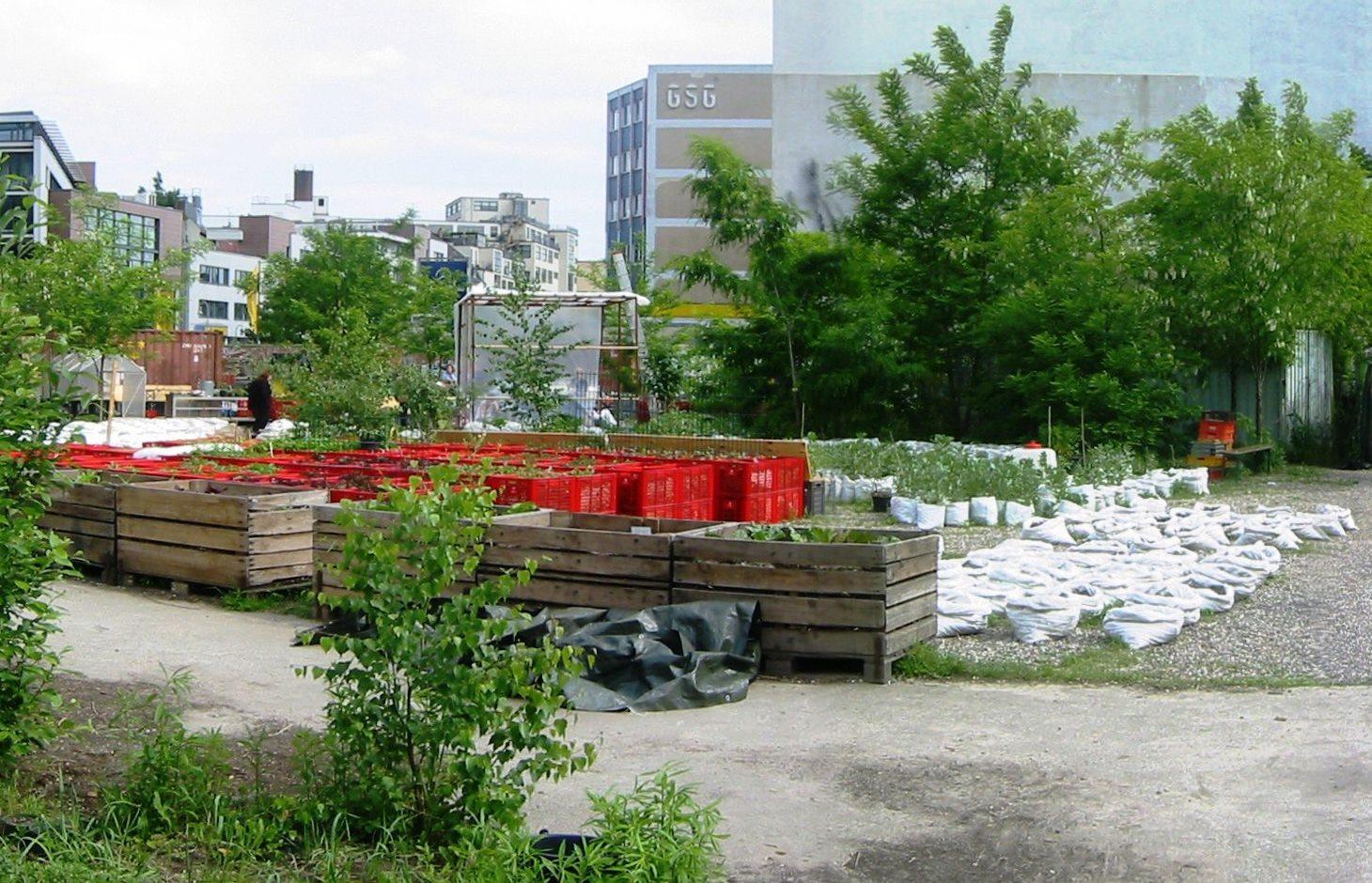
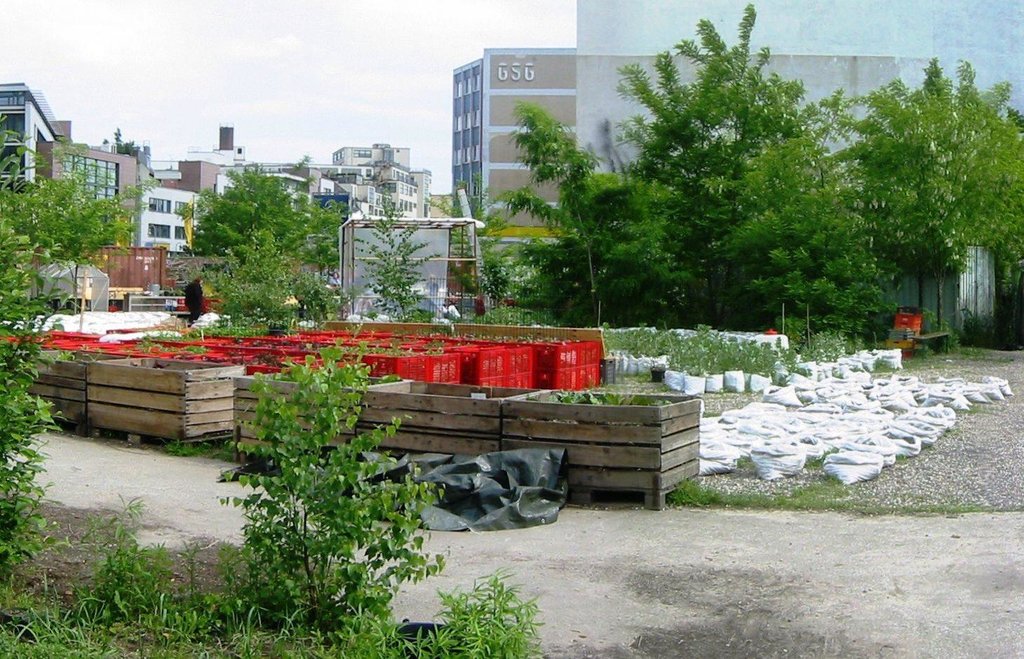
Mobile vegetable cultivation system for urban areas with "baker boxes" as main elements.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
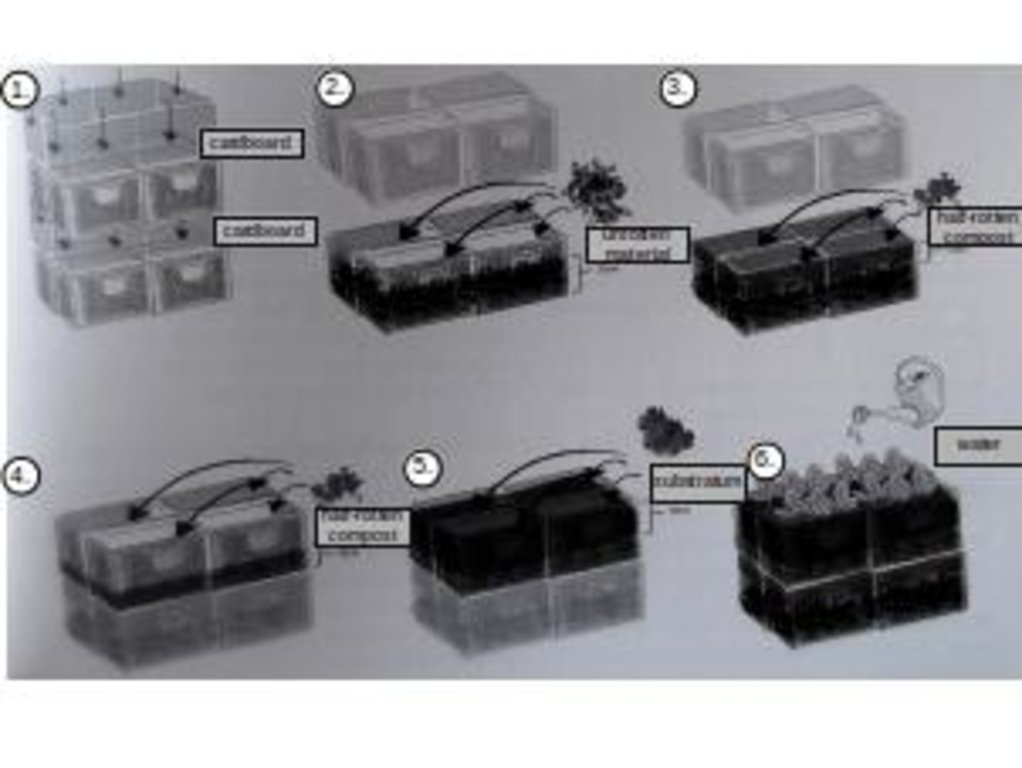
The main technology applied in the urban gardening project "Princess gardens" can be described as mobile vegetable culitivation system based on the use of "baker boxes".
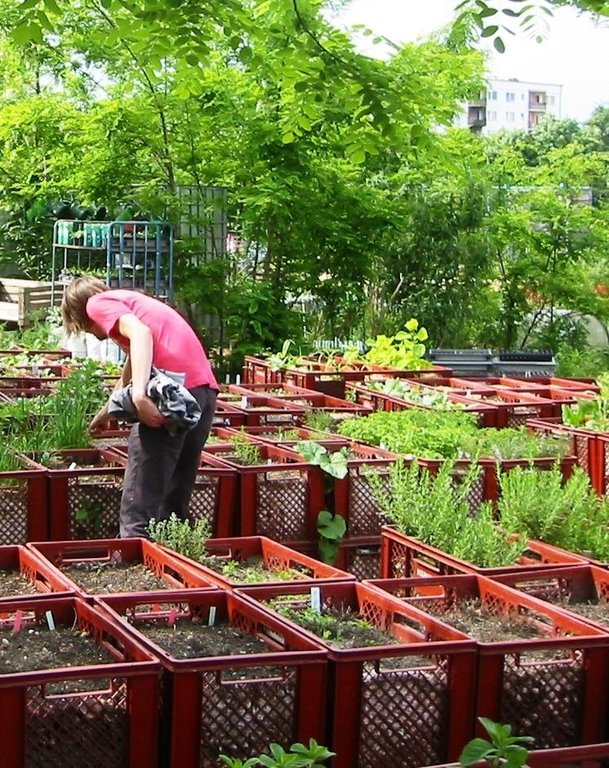
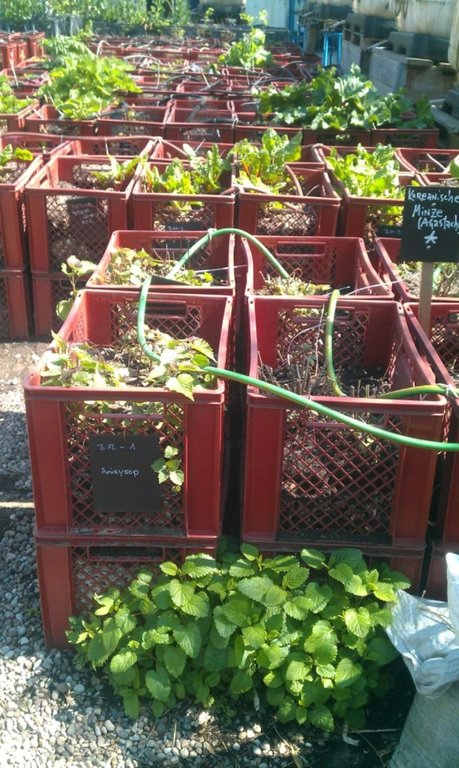
"Baker boxes" are plastic boxes (size: average area of 40 cm x 60 cm x 35 cm) made out of heat-resistant materials, which do not contain softeners. The bottom part as well as the side parts are formed in a grid pattern (holes of 1cm³ size).
For the vegetable production, cultivation units ("box towers" ) are built out of two boxes by placing them on top of each other. The lower box is filled with organic material (composition of the material like in a compost) and the upper box is filled with garden mould (or other earth material suitable for cultivation). To prevent the washing out of earth material through the grid pattern, carton is put on the bottom as well as on the side walls of the upper box.
During a period of time (length can vary from 1 to 3 years) the upper box can be cultivated according to the principles of "good practise" (e.g. crop rotation). During this time, the lower box serves as compost. In the course of each year this box is checked if the ongoing decomposition processes have lead to the creation of free space in the box. In this case, organic material needs to be refilled.
In the end of the 1-3 years-cultivation period the upper box is emptied and the contained earth material can be used for purposes such as landscaping. The box is then filled with organic material and switched with the lower box, which should contain "ready to cultivate"-compost material. The cultivation can then be restarted.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to allow cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils. Through the use of the box towers as cultivation units the roots of the plants never get in touch with the soil. While the main rooting zone is to be found in the upper box, deeper rooting plants can grow down to 70 cm into the lower box without reaching the soil in place.
Another purpose of the technology is to create a mobile cultivation system. If needed, the boxes can be easily moved away even during the vegeation period.
Last but not least, the technology has the purpose to create a space, where knowledge sharing on a practical basis regarding the topics e.g. agriculture, sustainability and health can take place.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the technology first and foremost a sufficient number (depending on the size of the gardening area) of "baker boxes" is needed.
Maintenance activities consist of refilling the lower box with organic material.
This is also true for the required inputs.
Natural / human environment: The environment is strongly influenced by humans, as the first urban structures in this area already were established about 200 years ago. Regarding the topic soil this led to the conversion of the natural soils in place to Technosols.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຢຍລະມັນ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Berlin
Map
×3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
- ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ອາຄານ
- ການຈາລະຈອນ: ຫົນທາງ, ທາງລົດໄຟ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem can be addressed as a lack of cultivation plots within the urban areas. This is due to the fact that the soils are to a great extent sealed or contaminated.
As a result in the urban area there is also a lack of pratical learning areas which relate to the topics agriculture and soils.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As major land use problems the cultivation circumstances are regarded. This inculdes the topics of destroyed natural soil fertility and a lack of water infiltration into the ground.
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 200Longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- Cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,006 m2.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S11: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M6: ການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ (ຂີ້ເຫຍື້ອ, ນໍາໃຊ້ຄືນໃຫມ່ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
Specification of other structural measures: creation of cultivation plots
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pk: ການບັນເທົາ ແລະ ການປົກຄຸມຂອງເປືອກໂລກ
- Pu: ການສູນເສຍ ການທໍາງານ ຂອງຊີວະພາບຜົນຜະລິດ ເນື່ອງຈາກການກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (1 sealing (foundations of buildings were constructed in the area))
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (as a main cause for urbanisation), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (need for public services in the city), governance / institutional (urban planning in the city)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
edited by Peter Kirch on the basis of Daniel Müller/dkmnews in „Prinzessinengärten- Anders gärtnern in der Stadt“, Nomadisch Grün (Hg.),Dumont Buchverlag, Köln, 2012, page. 115
Location: Berlin. Germany
Date: 08.10.2015
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Structural measure: boxes
Spacing between structures (m): various
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,35
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,6
Construction material (other): plastic (food-safe)
Change of land use type: urban area to urban gardening area
Layout change according to natural and human environment: area is limited through infrastructure elements (roads) and buildings.
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Euro
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
0.9
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | putting boxes in place | ໂຄງສ້າງ |
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Costs are affected by the wages for the employees and the rent of the plot
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water sotrage capacity is very low
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Seasonality of water quality and source of pollution: for agricultural use only (rainwater)
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2%
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, very poor
1% of the land users are very rich.
5% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
4% of the land users are poor.
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
100
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
100
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ກາລະໂອກາດ ທາງດ້ານວັດທະນະທໍາ
ໂອກາດ ໃນການພັກຜ່ອນຢ່ອນໃຈ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The "Prinzessinnengarten" is more than just a place to grow vegetables in the city. It is a space for diverse activities. Through the opportunity to contribute and to participate in open workshops, through the garden café and a variety of cultural events, the "Prinzessinnengarten" has become a lively meeting place far beyond the neighborhood.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
An economic analysis is hard to make, as the main goal of the project is not economical profit. In the interviews it was stated, that each year about 50.000 people visit the garden. To have an outreach to such a high number of people with a budget of about 500.000 € is regarded as "benefical" by the project members.
Only looking at the financing part it was stated in the interview that the garden is one of the very few urban gardening projects that can provide for its recurrent costs itself.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Comments on adoption trend: The members of the "Prinzessinnengarten" are supporting other land users to implement urban gardening projects through giving them advise. Up to 100 urban gardening projects were supported this way. The support is often funded by foundations. How to receive such funding is communicated by the Prinzessinnengarten to the ones seeking their advise.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| light and long-lasting production units |
| a great part of the needed material has been recylced |
| standardized format of the production units (fitting even to international cargo norms) |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| mobile, flexible cultivation system |
| allows cultivation on sealed or polluted soils |
| open access technology |
| knowledge sharing as key priority |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| limited productivity | |
| are highly dependent on irrigation, as the boxes dry-out fast (high evaporation/ surface area) | |
| Soil can be easily lost/washed out throught the grid pattern (especially in the long term, when the erosion measures are reduced (decomposition of carton) | |
| The spacing in between the boxes serves as habitat for snails. | |
| The carton sometimes rots away in the course of the cultivation period. This leads to a loss of soil material out of the boxes. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| dependent on a high supply of "baker boxes" | |
| dependent on external inputs (especially organic material) | |
| allows only for hand labour |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Urban Gardening. Über die Rückkehr der Gärten in die Stadt. Christa Müller, 2011.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
ISBN 3-86581-244-9
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Prinzessinnengärten. Anders gärtnern in der Stadt. Marco Clausen, 2012
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
DuMont,ISBN 3-8321-9436-3
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ