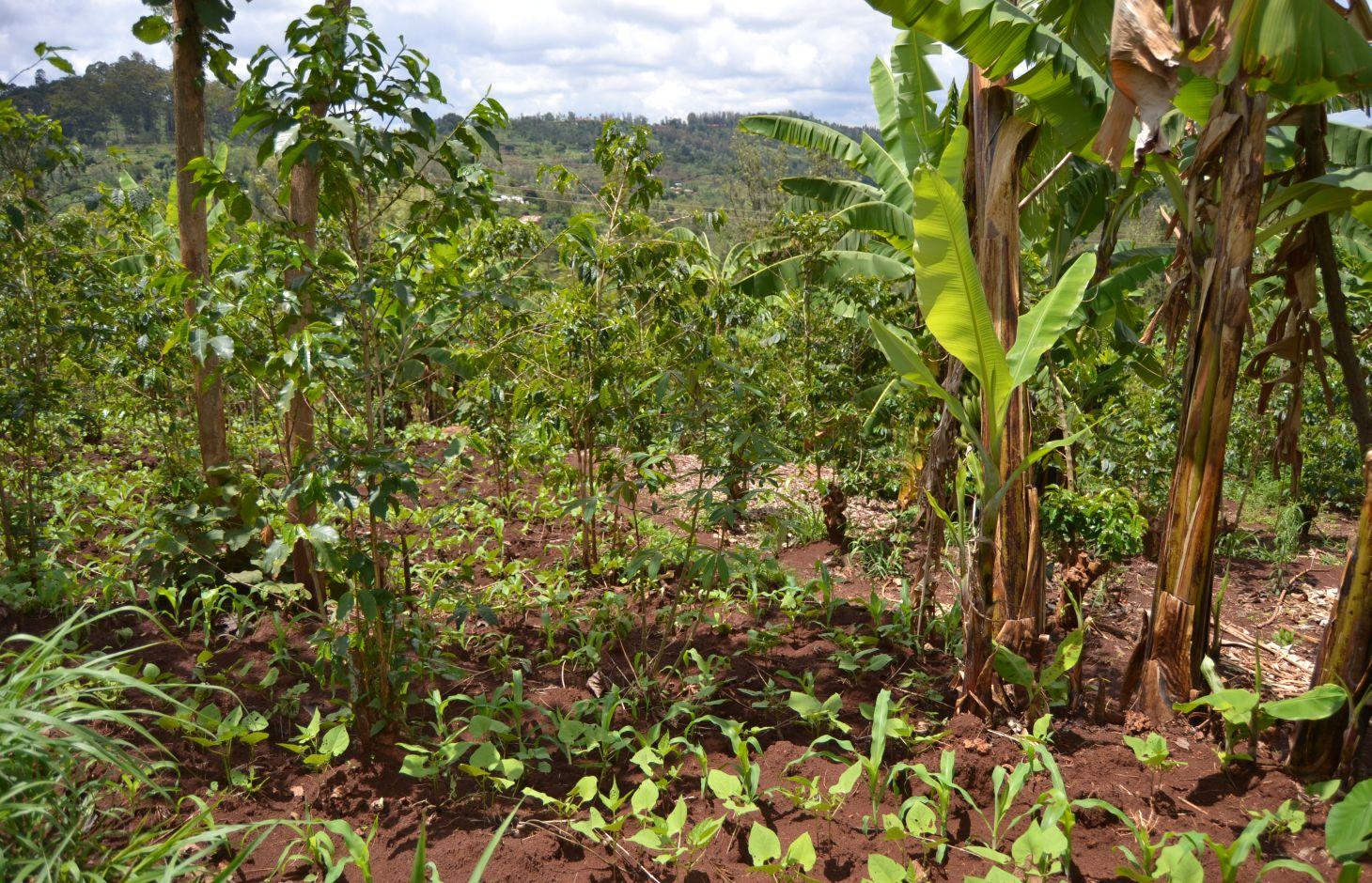
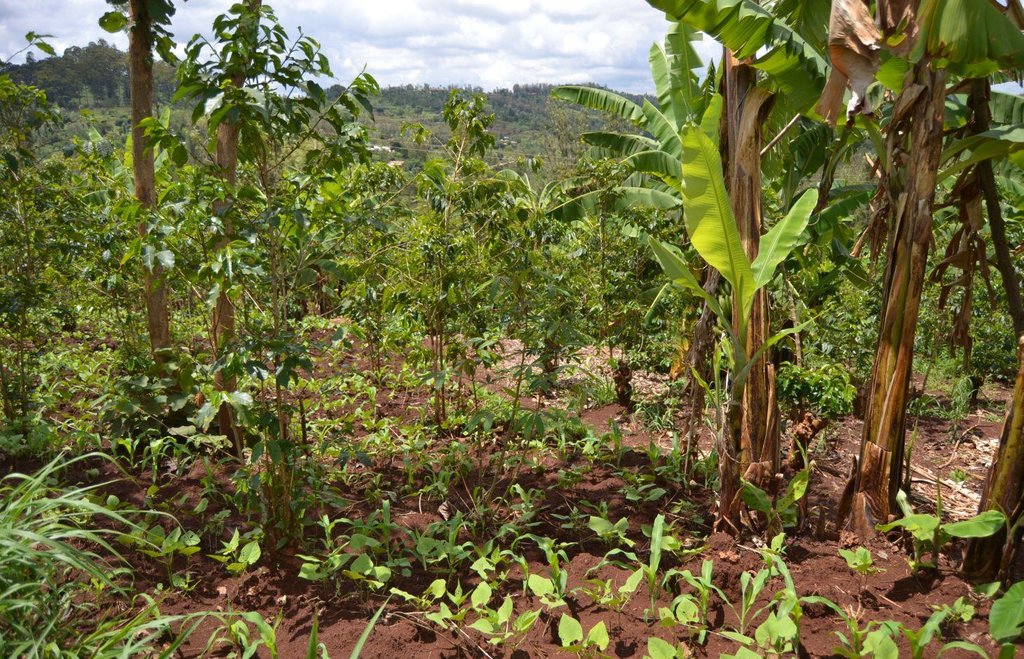
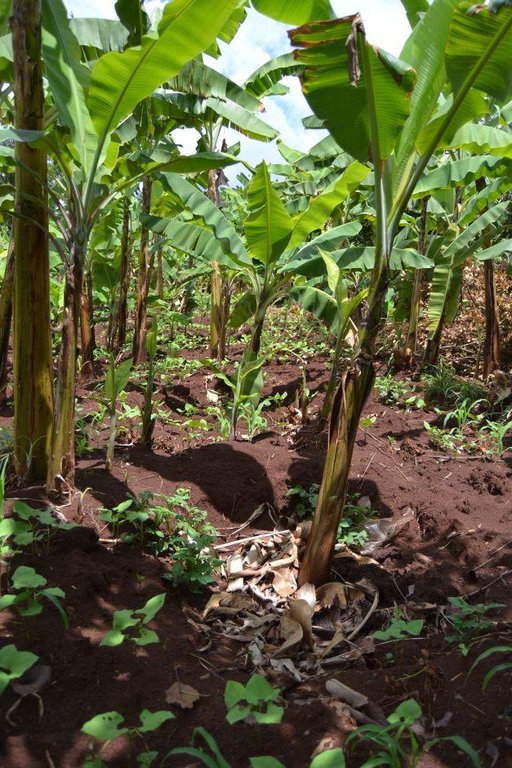
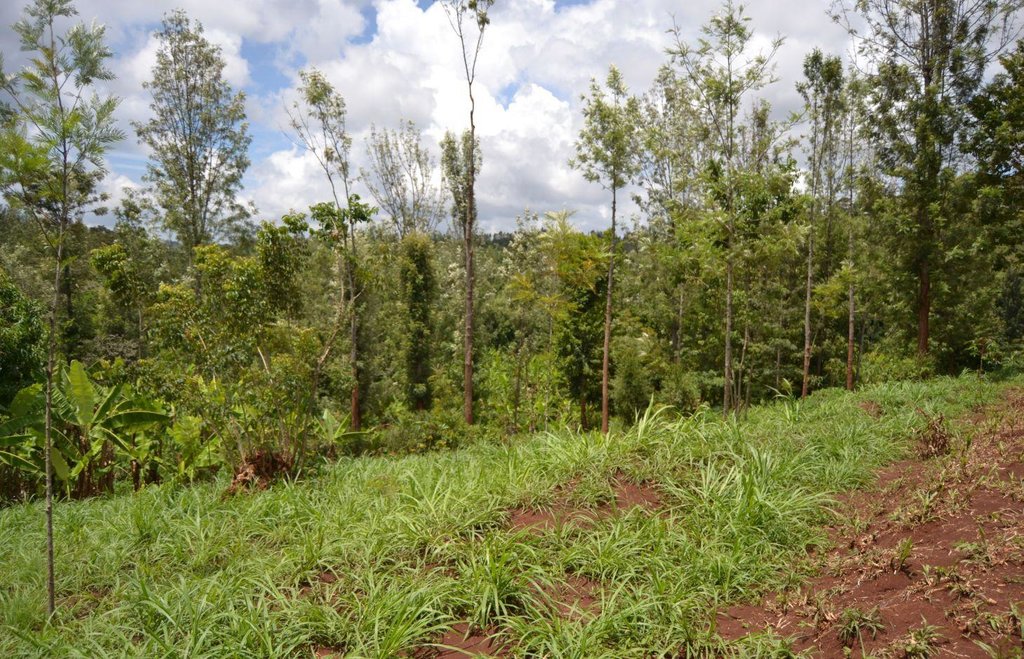
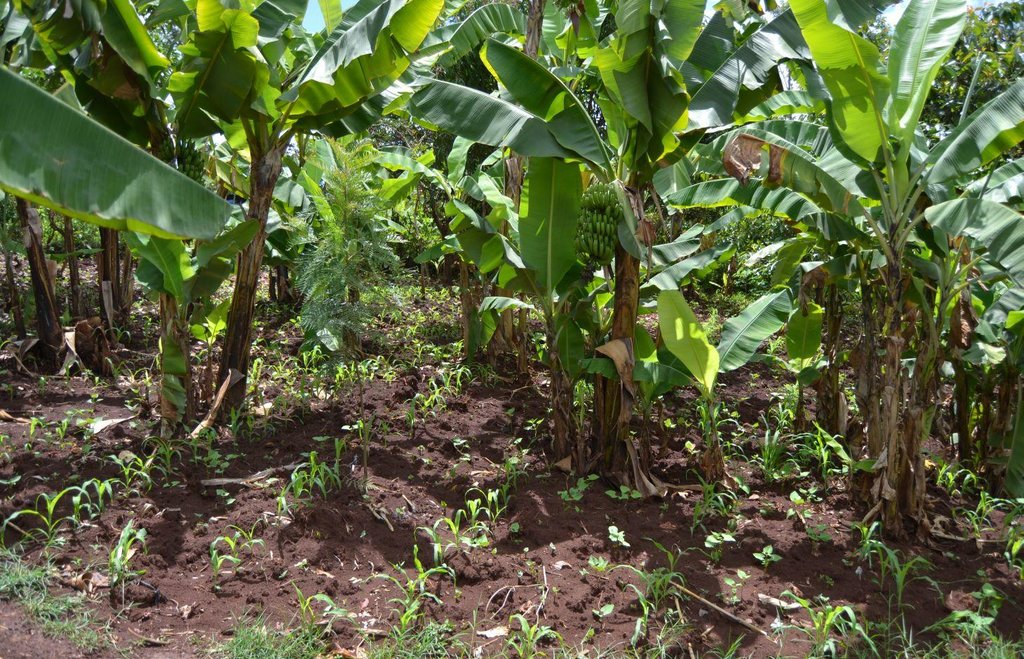
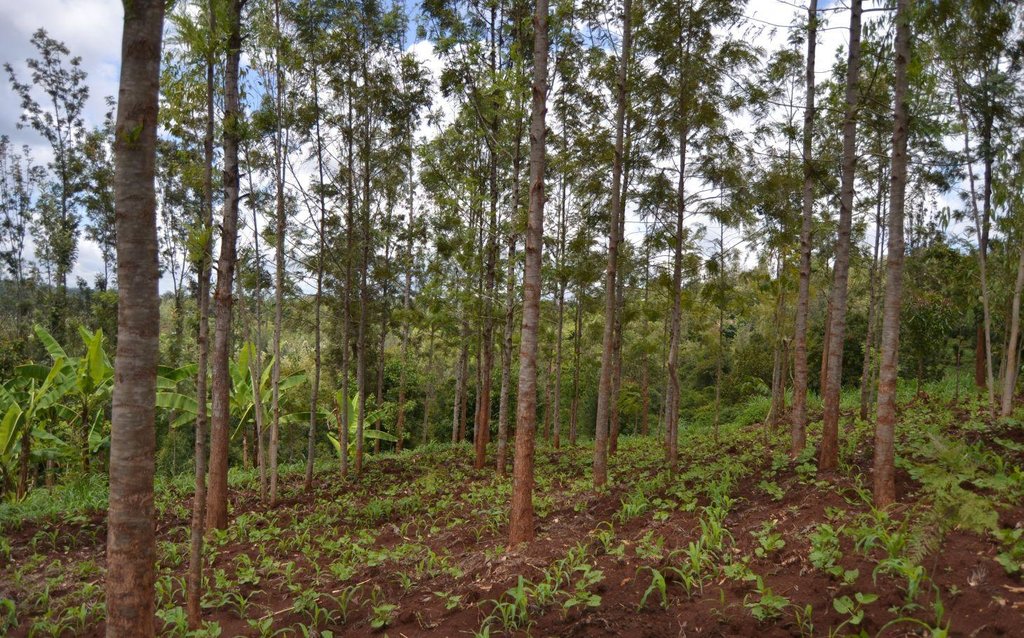
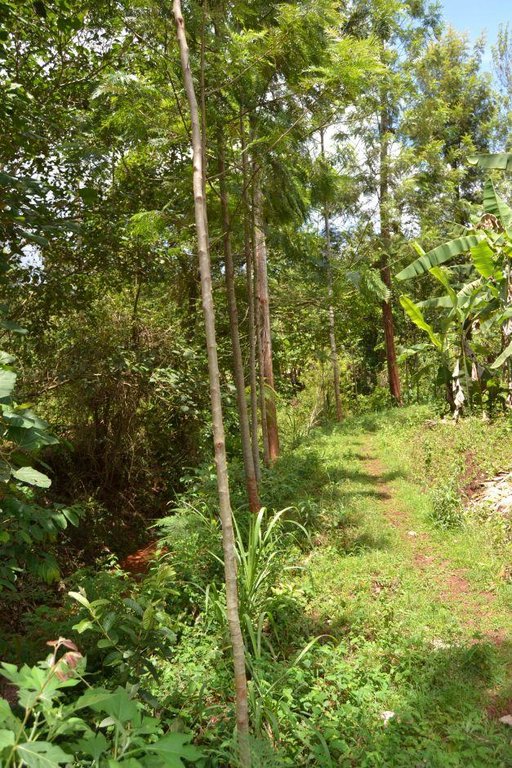
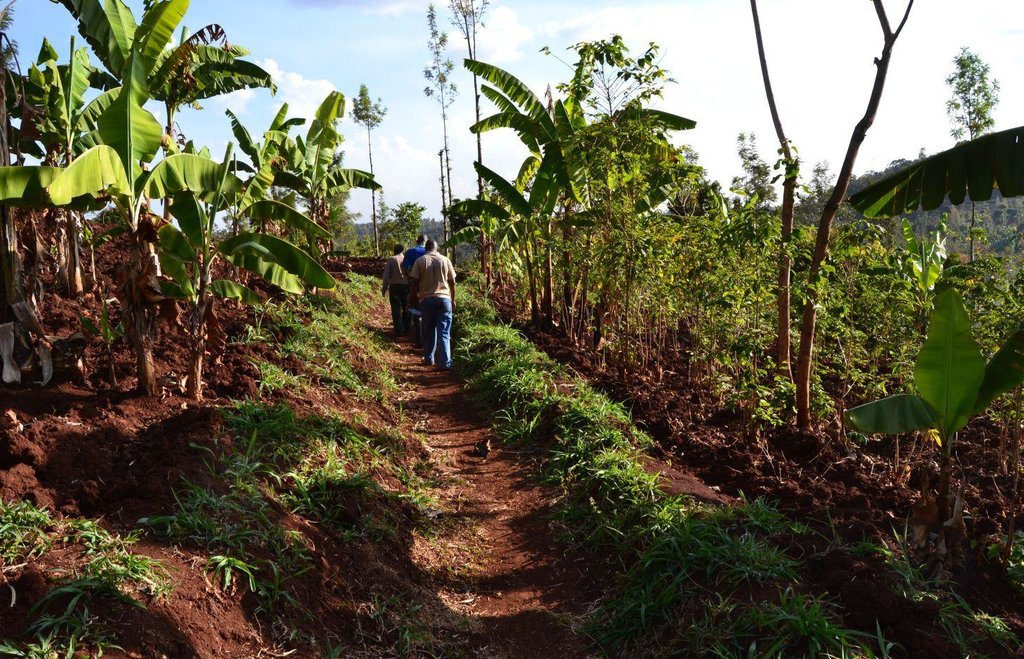
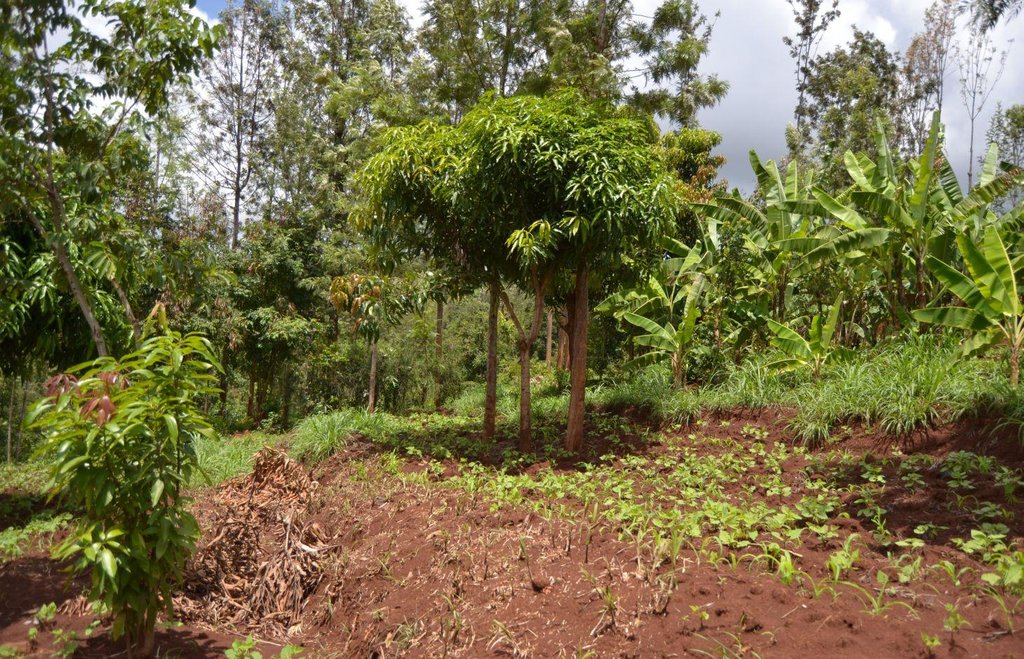
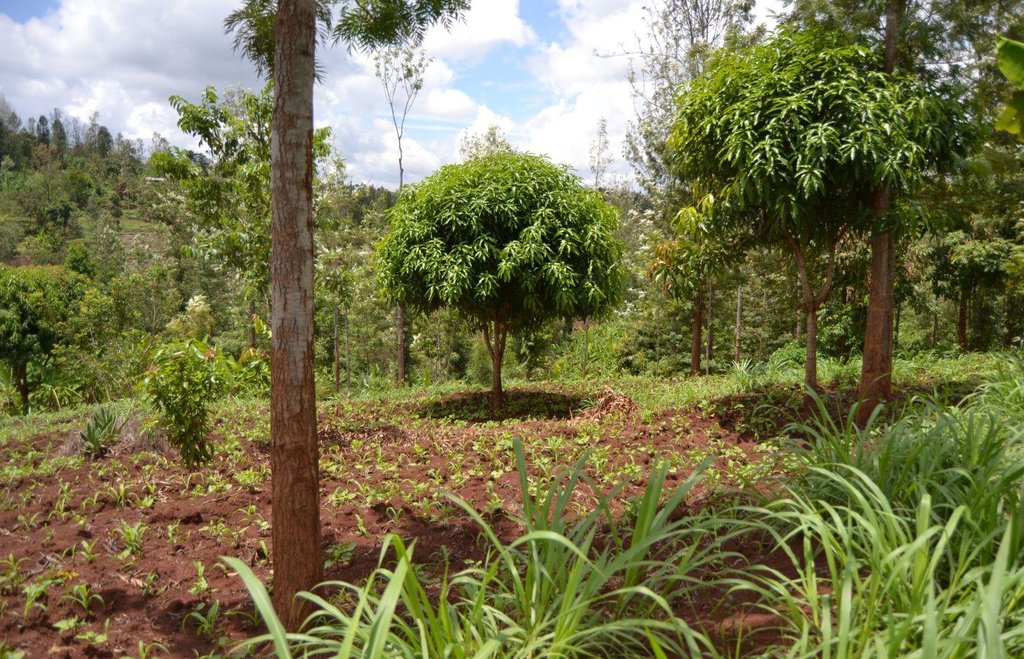
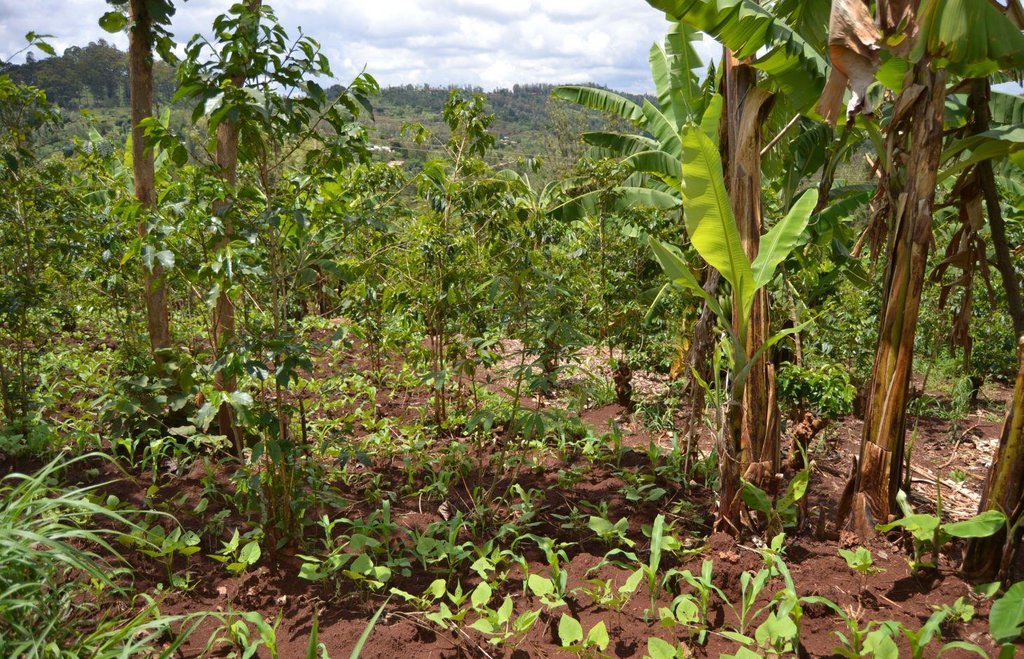
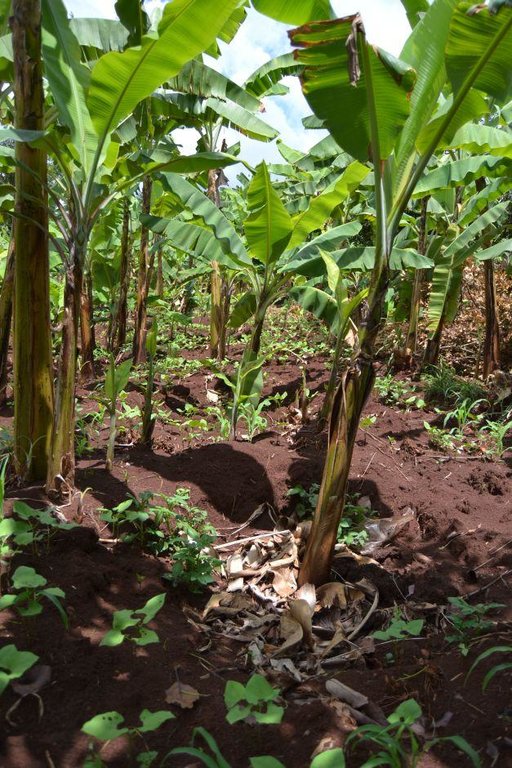
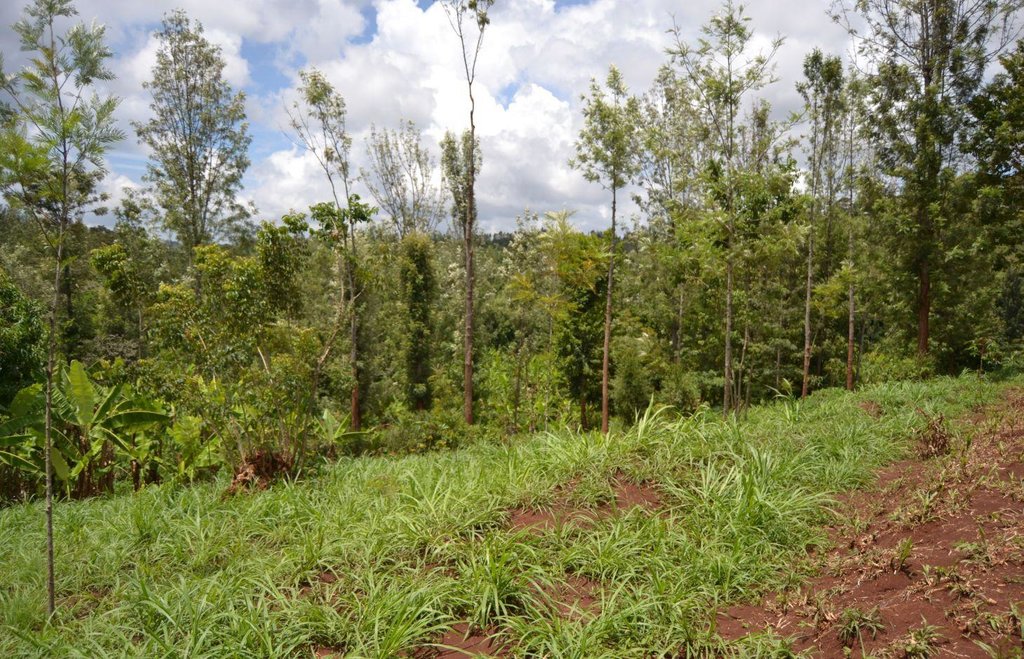
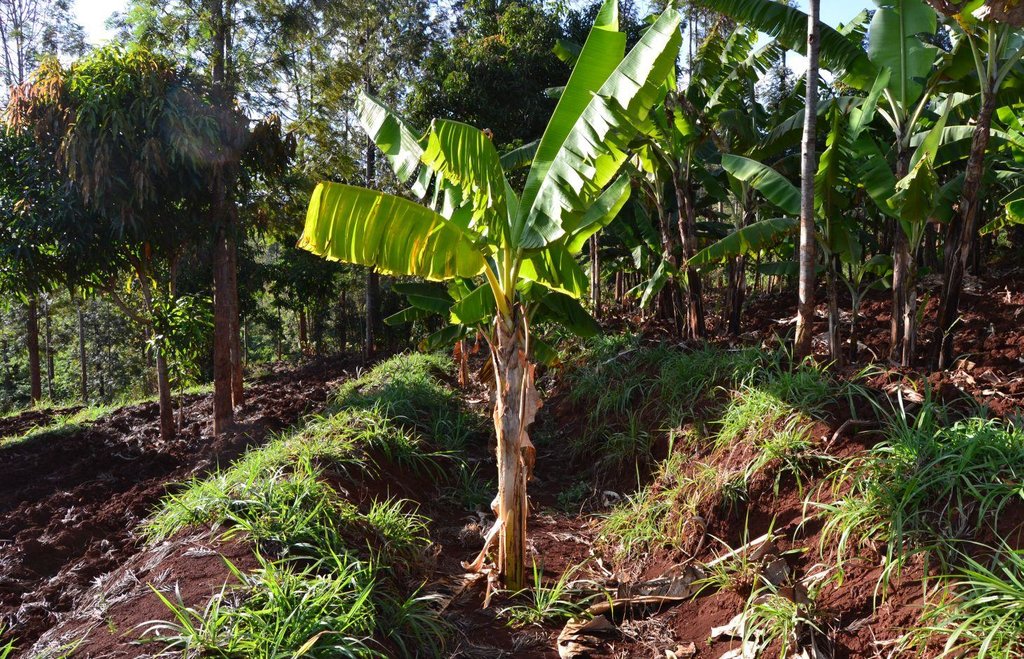
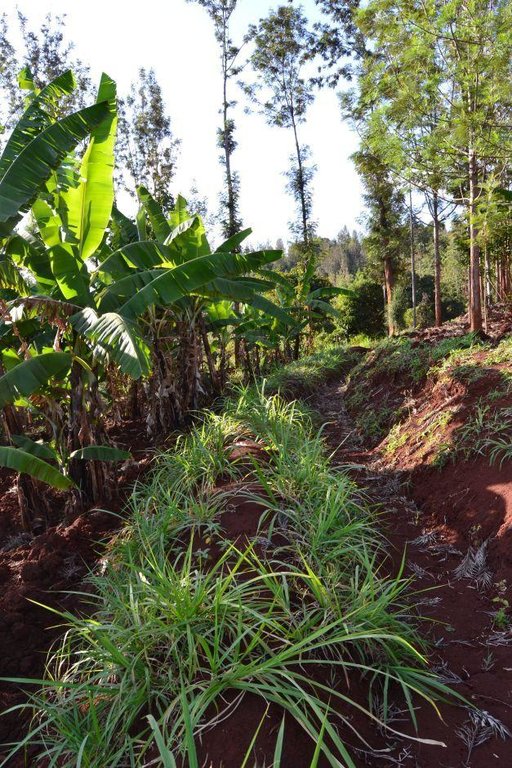
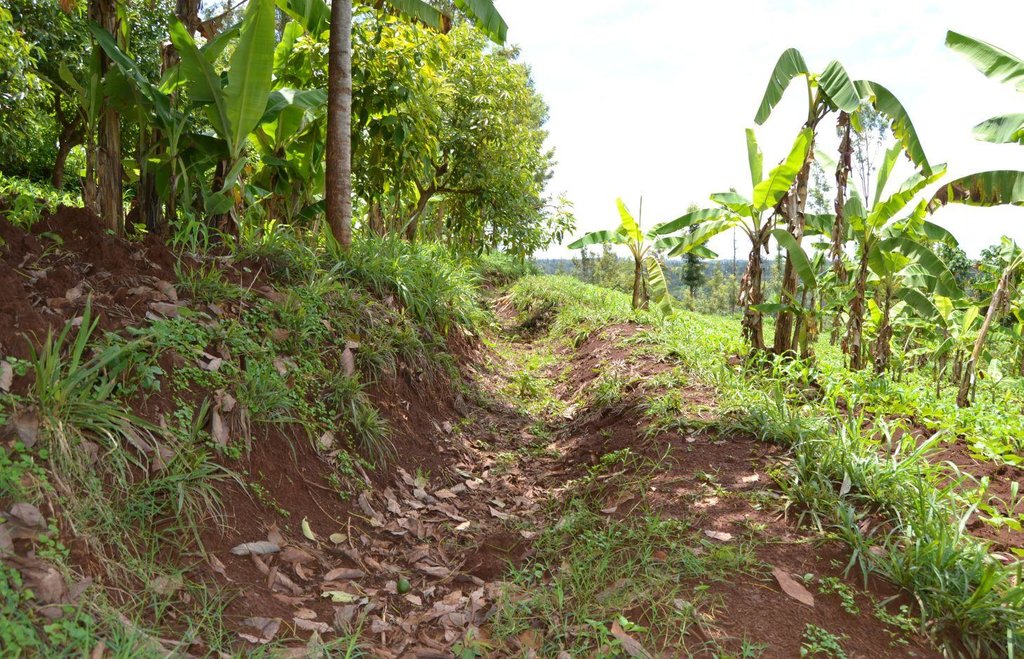
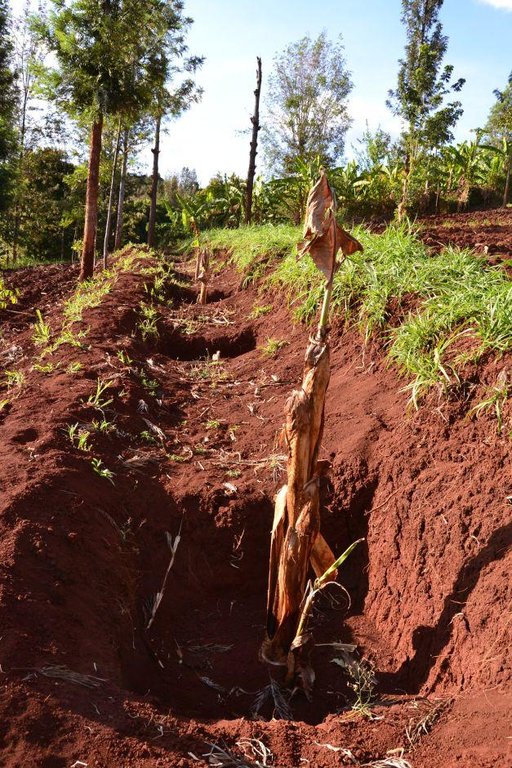
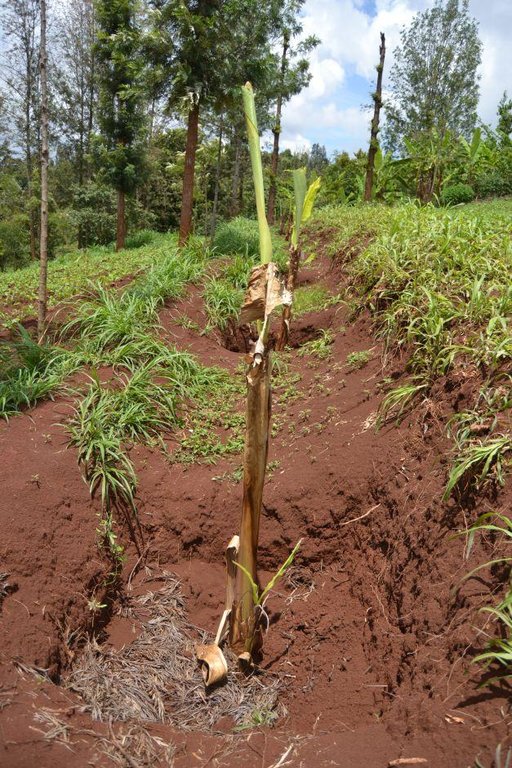
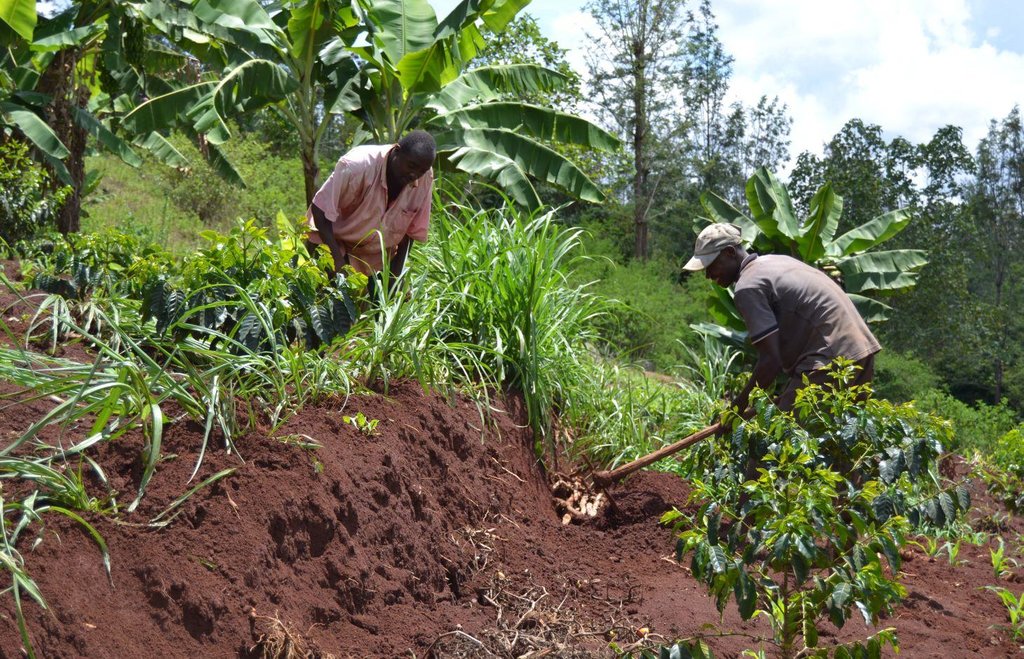
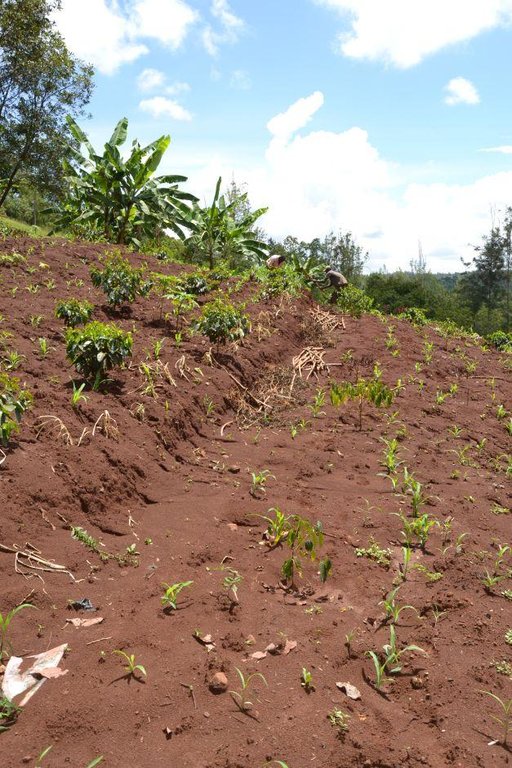
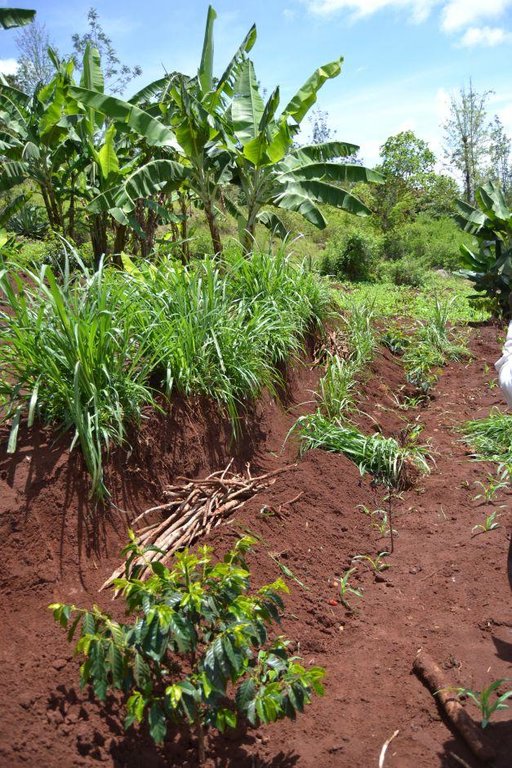
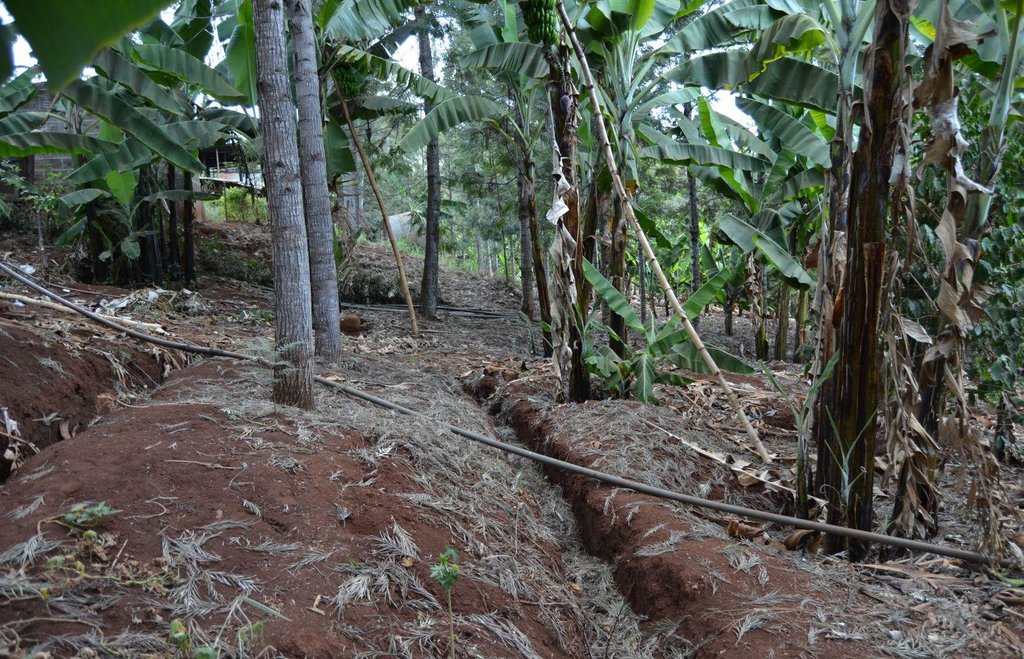
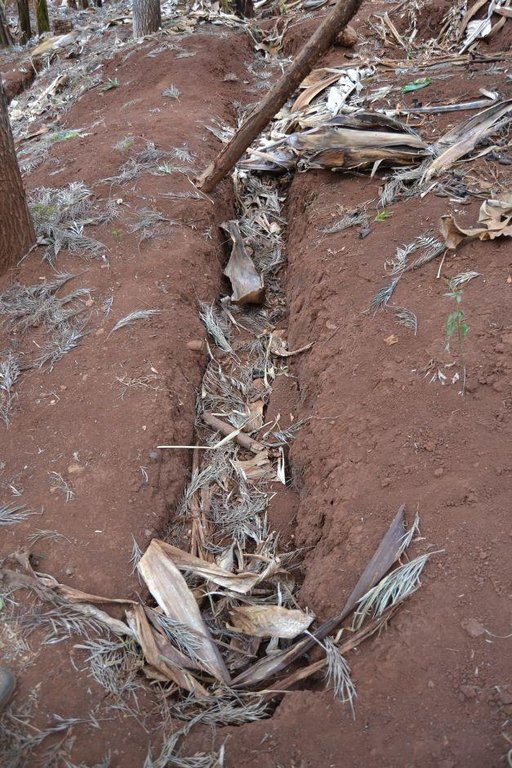
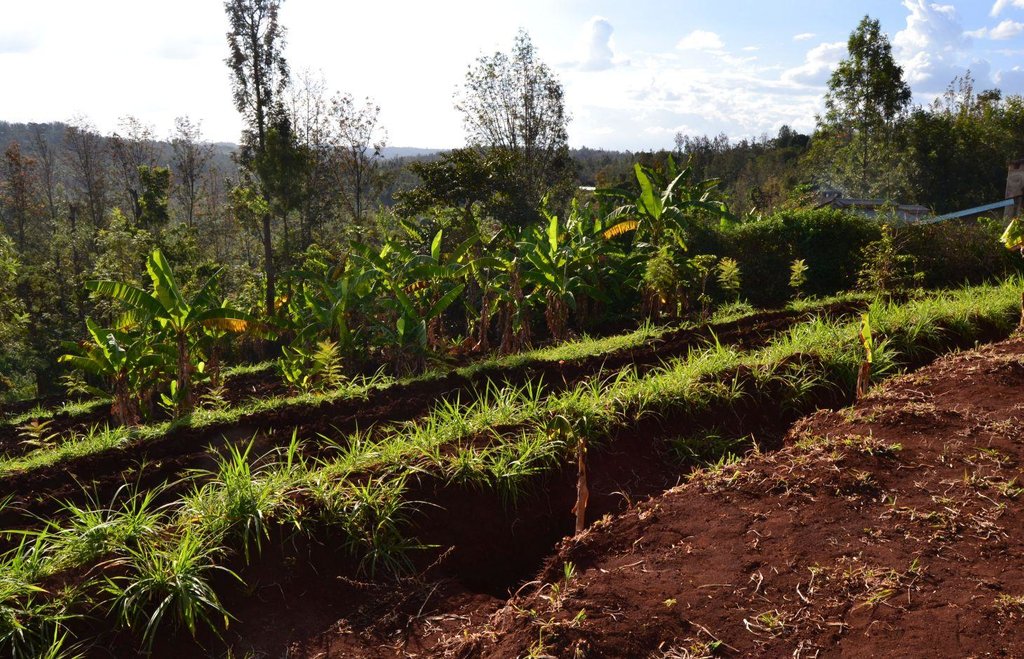
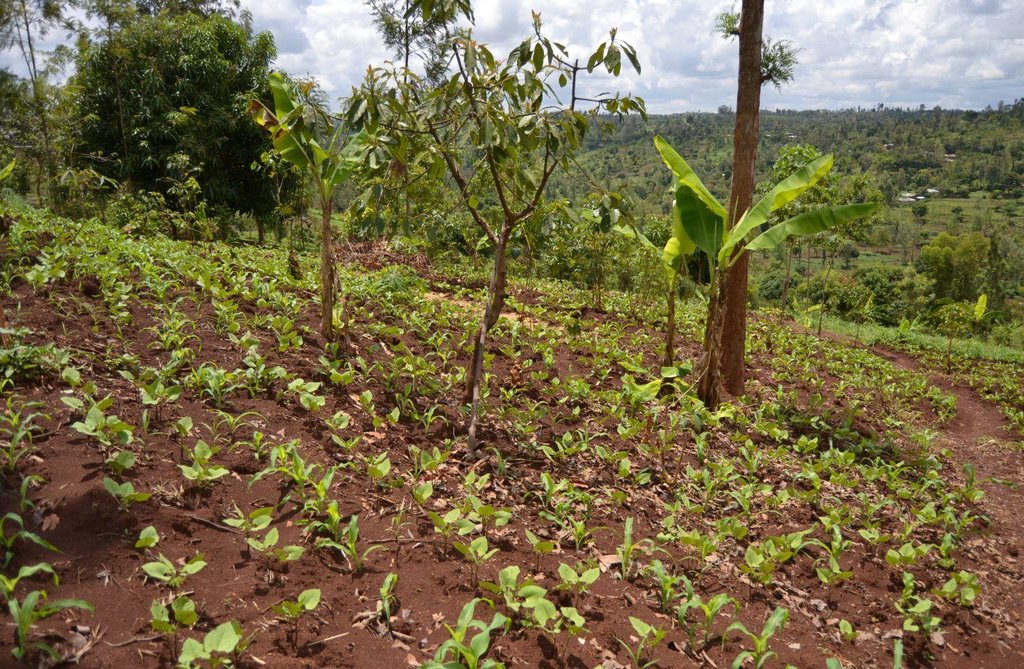
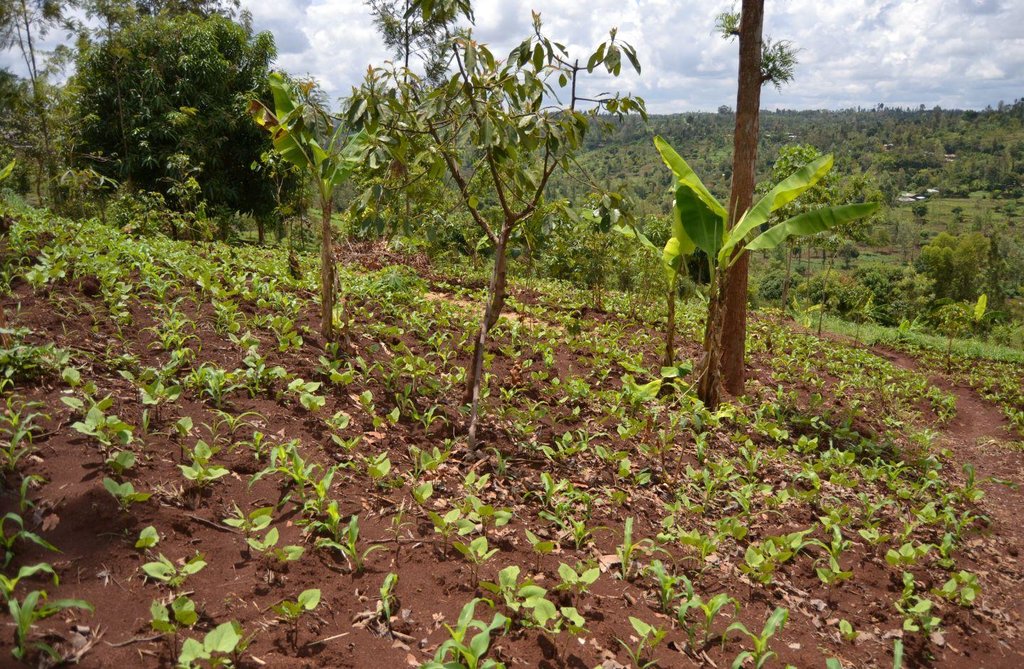
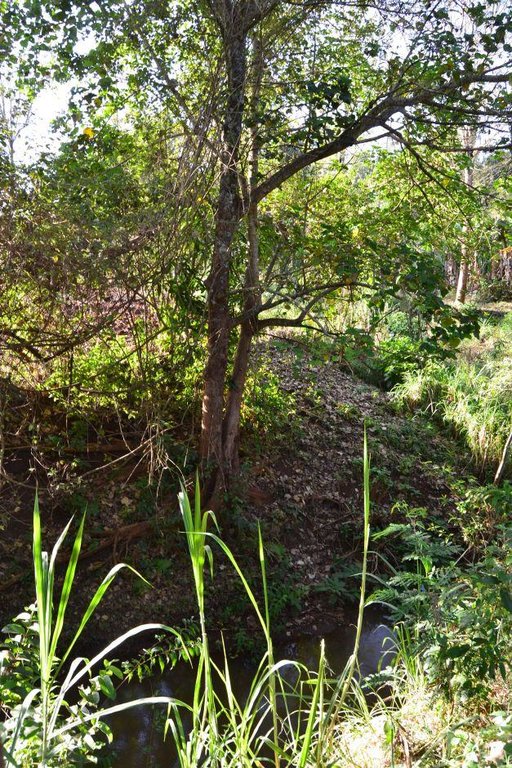
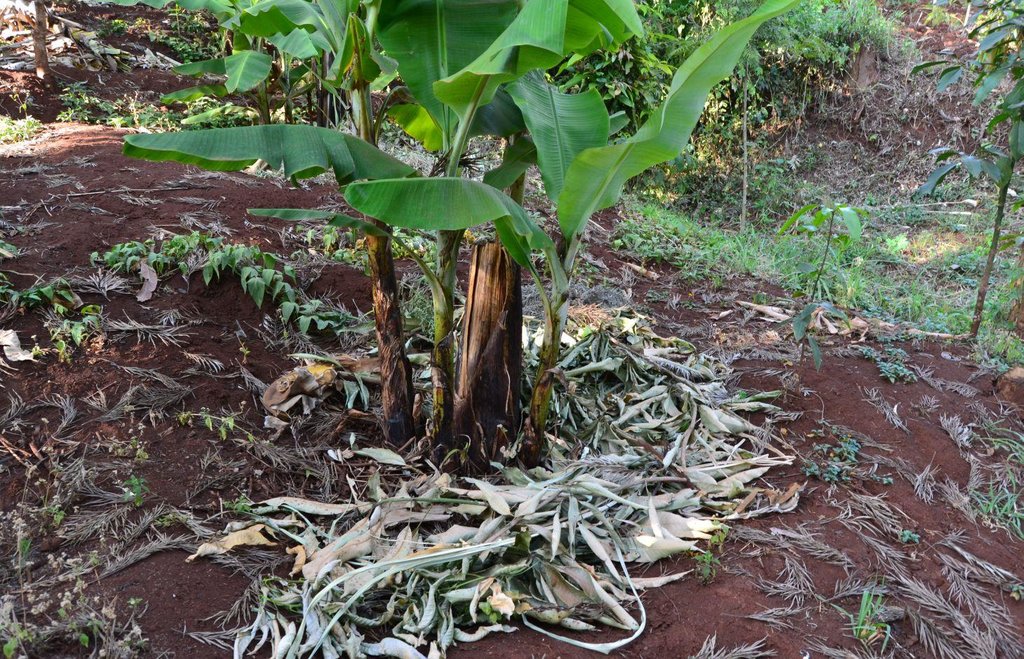
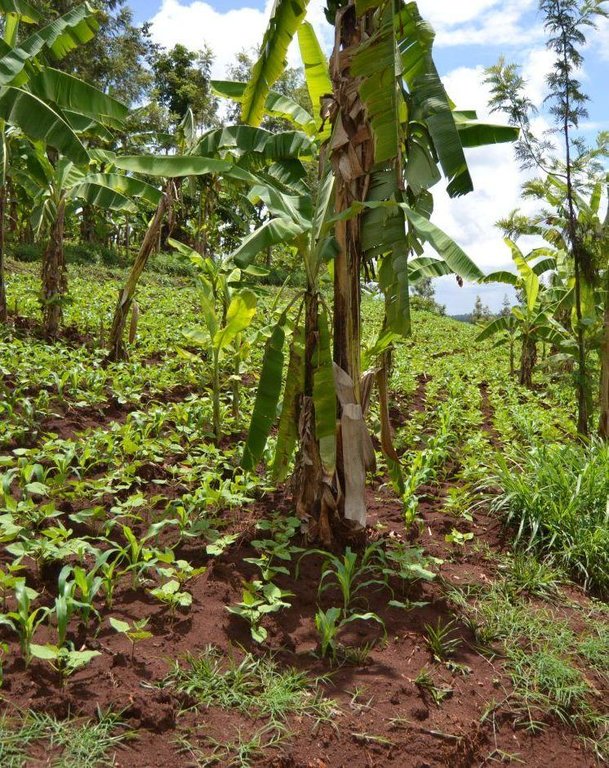
Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips. [ເຄັນຢາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Laura D'Aietti
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1159 - ເຄັນຢາ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: Dec. 29, 2016 (inactive)
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: June 5, 2017 (inactive)
- Agroforestry land use in bench terraces with cut-off and infiltration ditches and Napier grass strips.: May 3, 2019 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
F. K. Nyamu Jospeh
WRUA Sabasaba
ເຄັນຢາ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
02/11/2012
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
A combination of agricultural (e.g. intercropping, mulching, minimum tillage), vegetative (e.g. Napier grass strips, trees planting) and structural (e.g. ditches, bench terracing) measures which aim to maximise the overall yield in a sustainable manner (e.g. reduction of soil erosion and increasing the soil quality).
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
The land of the farmer is of 3 acres: 2 acres to plant maize (Zea mays) intercropped with beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) in combination with several trees species: Mangoes, Avocadoes, Bananas, Grevillea and Makadamia and half acre for coffee plantation with Bananas and half with Napier grass production for fodder (to feed cows). To increase and fasten the grass growth, manure is applied twice a year, before the rainy season (around February and September), while mulching is practiced under Banana trees every season. Minimum tillage is applied to reduce soil disturbance and to increase water use efficiency by minimizing direct evaporation, increasing infiltration and water recharge (Liniger, 1991) especially during dry seasons, which results in better crop yields.
For timber production Grevillea trees are planted scattered overall the land and on the edge of the river for demarcation (environmental role in stabilizing the soil against erosive forces).
Concerning the structural measures, the farmer constructed has built 14 bench terraces, six of them were designed to plant cash crops (coffee); each terrace is characterized by a ditch to cut off the drainage and collect water and nutrients; they are also used as paths to facilitate transportation and farm operations. Ditches are both drainage and infiltration types and are excavated along the contour.
Purpose of the Technology: Beans and maize are cultivated for home consumption but partially (about 20%-4 bags of maize and half bag of beans) also for commercial purposes. Coffee is harvested twice a year, with a production of about 500 kg per season; the coffee is sold at 45 Kenyan Shillings (KSh) per kg (SL-28-arabica varieties). Indeed, the farmer is interested in cultivating the certified and improved variety called Ruiru 11 which is generally disease resistant, easy to maintain (less expensive) with a modest risk of pests (according to the farmer). Grevillea timber is sold twice a year, only trees of 1.5 feet in diameter (about 45 cm), at about 80 KSh per feet. Beside the commercial role of Grevillea, when sufficiently grown these trees lead to a reduction of the wind speed, protect the intercrops and provide mulching material to be used over banana trees. The deep roots of mature Grevillea are not in competition with the crops for soil and water, instead they enhance infiltration (Otengi, 2007). Makadamia will be used to produce cooking oil, while bananas, avocados and mangoes are fruits collected for the local markets. Napier grass is cultivated to stabilize the ditches and for fodder production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There is a high initial input (mainly labour) needed to create ditches and terraces and for planting crops is required. The vegetative and structural measures require a labour intensive management during the year, for example maintenance is necessary after each rainy season to repair ditches and to rebuild terraces (e.g. because of the accumulation of soil and organic matter in the pits and ditches). Concerning Napier grass, labour is employed regularly for weed control, to cut grass for fodder and every three seasons to replace and replant the grass because it becomes less productive. Concerning trees, in the Agroforestry systems, canopies of Mango and Avocado trees shade the soil reducing evapotranspiration and therefore improving soil water storage. On the other hand, regular pruning is needed when the shadow effect obstructs photosynthesis and therefore growth of the crops planted below (maize and beans). Pruning of branches is carried out also for firewood. Furthermore, a common practice is Grevillea root pruning to conserve soil moisture (Otengi, 2007) and to reduce competition for nutrients during the growing season. Indeed, the farmer explained how superficial roots may interfere with the Banana root system and to cut them he has created small trenches. Harvesting is carried out twice during the year for both cereals and coffee.
Natural / human environment: The area is characterized by rolling to hilly slopes, therefore it is exposed to erosion and land degradation. The combination of trees with mixed crops is adopted to maximise productivity and at the same time to prevent degradation by increasing the vegetative cover.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຄັນຢາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Kenya
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Muthithi location-Kagurumo sublocation-Gatwamikwa village
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The technology has been started by the father of the farmer about 70 years ago. His initiative has been developed and improved over time thanks also to the support of the MoA extension officers.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ຕັດຫຍ້າ ແລະ ຂົນຫຍ້າ / ບໍ່ມີທົ່ງຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດ
ຊະນິດພັນສັດຕົ້ນຕໍ ແລະ ຜະລິດຕະພັນ:
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: fodder for 2 cows, from Napier grass

ປະສົມປະສານ (ການປູກພືດ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້), ລວມທັງ ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and nutrient leaching which could drain into the river (Fig. 17).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The most important limiting factor to the crop and fodder production remains water: not only related to the weather conditions (e.g. shorter and delayed rainy seasons) but due to the lack of a proper irrigation systems, to minimize the water losses and time. Furthermore, soil has been considered 'not good', because does not hold enough water due to the slope of the land.
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ໃນເວລາ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ແມ່ນໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າ ດິນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຄີຍເປັນດິນປະເພດໃດ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Agroforestry
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 122Longest growing period from month to month: from about March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 61Second longest growing period from month to month: from about October to November
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງສັດລ້ຽງ (ຖ້າຫາກວ່າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
< 1 LU/km2
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
About 1.21 ha (3 acres).
The area accounts for the land owned and cultivated by the farmer. According to the interviewee from the Ministry of Agriculture, on average farmers in Saba Saba sub-catchment own 1 acre of land (Elemans, 2011).
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S1: ພັກຄັນໃດ
- S4: ລະດັບຮ່ອງ, ຂຸມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Hp: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Poor vegetation cover, mainly herbaceous), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Land use: cropland), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (From gentle to hilly slope)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Especially during wet seasons: March-June and October-November)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
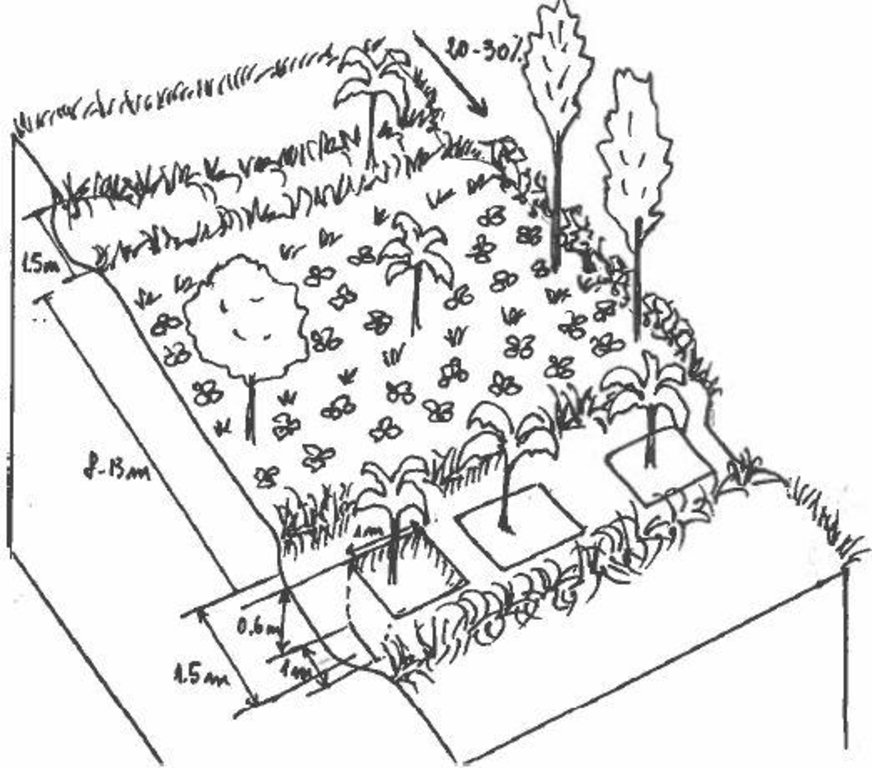
Detailed overview of the Agroforestry system in a bench terrace with infiltration (retention) and cut off (drainage) ditches. Along them, strips of Napier grass on both sides.
Location: Upper Saba saba river. Kagurumo in Muthithi location
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: Organic residues around Banana trees
Quantity/ density: undefined
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 3bags270kg
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Manure from two cows
Quantity/ density: 8 tonnes
Remarks: for 1 year
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 400 grass per2lines strip
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): few cm
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6-1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): about 80
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea, Coffee
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Persea americana, Musa sapientum, Mangifera indica, Macadamia tetraphylla
Grass species: Pennisetum pyramidalis (Napier grass or elephant grass)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 5-8%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 8-13
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6-1
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 8-13
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6-1
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 12-15
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8 (moderate) (Fig.4-7Annex3)%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 25-30%
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Kenyan Schellings
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
85.9
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
2.00
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging holes and planting Coffee seedlings (20 KSh per plant) | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | |
| 2. | Digging holes (1 feet ×1 feet) and planting trees (seedlings)- 4 days ×5 persons at Ksh 200.e.g. the main work consist of digging small pits for bananas (300 plants) | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | |
| 3. | Establishment of the infiltration ditches and cutoff drains (total 5). 3p.d. (200 Ksh *3) each. | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Each season: during dry season |
| 4. | Establishment of the retention ditches with bench terraces (tot.8): 2 p.d., 250 Ksh per day | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Each season: during dry season |
| 5. | Purchase cows | ພືດ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Life span of the cows: Several years
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Digging holes and planting seedlings | person/day | 20.0 | 2.3 | 46.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Infiltration ditches | person/day | 1.0 | 1277.0 | 1277.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Establishment of the infiltration ditches and cutoff drains (total 5) | person/day | 15.0 | 2.333 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | stablishment of the retention ditches with bench terraces (tot.8) | person/day | 16.0 | 2.9375 | 47.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Cow | pieces | 2.0 | 349.0 | 698.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings Mango | pieces | 10.0 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Coffee seedlings | pieces | 250.0 | 0.464 | 116.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings Avocado | pieces | 12.0 | 0.25 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings Macadamia | pieces | 8.0 | 0.25 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Grevillea | pieces | 50.0 | 0.12 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | cows | animal | 2.0 | 349.0 | 698.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 2930.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimum tillage and planting maize and beans | ພືດ | 2 times in a year |
| 2. | Harvesting maize/beans (around Feb/March and Ag/Sept) | ພືດ | 2 times in a year |
| 3. | Feeding cows on daily basis (normally 3 times a day): 200 Ksh is the price of 1 labour to feed the cows with lunch, for 6 days | ພືດ | daily basis |
| 4. | Preparation and application of manure | ພືດ | 2 times in a year |
| 5. | Digging planting holes and planting grass | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | 2 times (because they get 'old') or 1 half year, depending on the conditions |
| 6. | Maintenance of the grass (weed control and cutting Napier grass/repairing and collecting fodder) | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | Every season (March/Sept); cutting Napier: 2times in a season |
| 7. | Clearing the tree for selling timber (the price depends also of the use of the chainsaw (or saw) or not -(considering 4 trees at the time) - with machine operator | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | When in need of cash (not regularly), not less than 5 years after planting |
| 8. | Prepare manure and feeding cows on daily basis (normally 3 times a day): 200 Ksh is the price of 1 labour to feed the cows with lunch, for 6 days (7200 for 6 months) | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | Every season |
| 9. | Pruning branches/roots and let them dry for firewood- (considering 4 trees at the time) 3 persons days- 200Ksh | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | Every 3 seasons (and when shortage of firewood) |
| 10. | Mulching | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | Twice in the year on Bananas |
| 11. | Harvesting coffee | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | Twice in the year |
| 12. | Distribute manure on Napier grass, also in the pits | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | 2 times |
| 13. | Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | ໂຄງສ້າງ | After rains (every season) |
| 14. | Rebuilt repair terraces | ໂຄງສ້າງ | 3 times per year |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Minimum tillage and planting maize and beans | person/days | 15.0 | 1.5333 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Harvesting maize/beans | person/days | 10.0 | 1.2 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Feeding cows and preparing the manure on daily basis | person/days | 312.0 | 0.166666 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Preparation and application of manure | person/days | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds Maize | kg | 10.0 | 2.3 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds Beans | kg | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings grass | per trench | 200.0 | |||
| ອື່ນໆ | Labour: Digging planting holes and planting grass | person/days | 5.0 | 1.8 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Labour: Maintenance of the grass (weed control and cutting Napier grass/repairing and collecting fodder) | person/days | 3.0 | 1.66666 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Labour: Clearing the tree for selling timber (the price depends also of the use of the chainsaw (or saw) or not -(considering 4 trees at the time) - with machine operator | person/days | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Labour: Repairing the ditches and remove excess of soil/leaves accumulated during the rainy season | person/days | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Labour: Rebuilt repair terraces | person/days | 5.0 | 1.8 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 161.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: panga, fork djembe, hoes, shovel, fork djembe, panga, saw, shovels, fork djembe
The costs has been computed during the period of the field visit and include all the costs for the establishment and the maintenance of the different measures (structural, agronomic and vegetative), for 3 acre of land.
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
In the farmer's opinion, the main constrains are the costs carried out to maintain the structural measures described. Water instead become the limiting environmental factor during dry season.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: subtropics. June, July and August
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
> 50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ປະສົມ (ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ / ເປັນສິນຄ້າ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is rich because he owns 3 acre of land and livestock, assets (electricity) which are above the average standards of the community. No family food insecure issues during all year, and he was a teacher.
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Water use rights depend on the use: open access for drinking and domestic uses.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Agroforestry (dispersed trees on cropland) and intercropping: The technology is simple to adopt and provides a sustainable land management with a diversified source of income/ food supply. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Implementation could focus on the increase of species: Jaetzold et al. (1982) underlines the positive impacts of the use of biomass from Mucuna, Crotalaria, Tithonia, Calliandra and Leucanean hedges/trees for soil fertility improvements, increasing grain yields. Crop rotation and leaving crop residues on the ground could further help increasing the production. |
|
Napier grass has been used for different purposes: e.g. ditch stabilization, fodder production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other herbaceous vegetation could also be planted: e.g. Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower),an excellent green manure and medicinal plant. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The amount of work required to carry out all the activities is too much. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The technologies in place require regular maintenance especially during rainy seasons. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Jaetzold R., and Schmidt H., 1983. Farm Management Handbook of Kenya. Natural Conditions and Farm Management Information. Vol. 2.Part B: Central Kenya.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://www2.gtz.de/dokumente/bib/07-1284.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Jaetzold R., Schmidt H., Hornetz B., Shisanya C., 1982. Farm Management Handbook of Kenya. Natural Conditions and Farm Management Information. West Kenya, Subpart A2. Nyanza Province.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://www2.gtz.de/dokumente/bib/07-1284.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Liniger HP (1991). Water conservation for rainfall farming in the semi-arid Footzones northwest of Mt. Kenya (Laikipia highlands). Consequence on the water balance and the soil productivity. Laikipia/Mt. Kenya PaperD-3, Nairobi, Kenya & Bern, Switzerland.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Ouma J. O., Murithi F. M., Mwangi W., Verguijl H., Gethi M., De Groote H., 2002. Adoption of maize seed and fertilizer technologies in Embu District, Kenya. KARI, CYMMIT.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Otengi S. B. B., Stigter C. J., Ng'anga J. K. N. H. Liniger H. P., 2007. Soil moisture and its consequences under different management in a six year old hedged agroforestry demonstration plot in semi-arid Kenya, for two successive contrasting seasons. African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 2(3), pp. 089-104.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Storey P. J., 2002. The conservation and improvement of sloping land. Volume 1: Practical understanding. Chapter 5: Improving the soil management.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ