Improved grazing land management [ອີທິໂອເປຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Daniel Danano
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano, Donia Mühlematter
Gitosh masheshal
technologies_1049 - ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - ອີທິໂອເປຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
01/07/2003
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.5 ອ້າງອີງເຖິງແບບສອບສອບຖາມ (ຫຼາຍ) ທາງດ້ານວິທີການ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
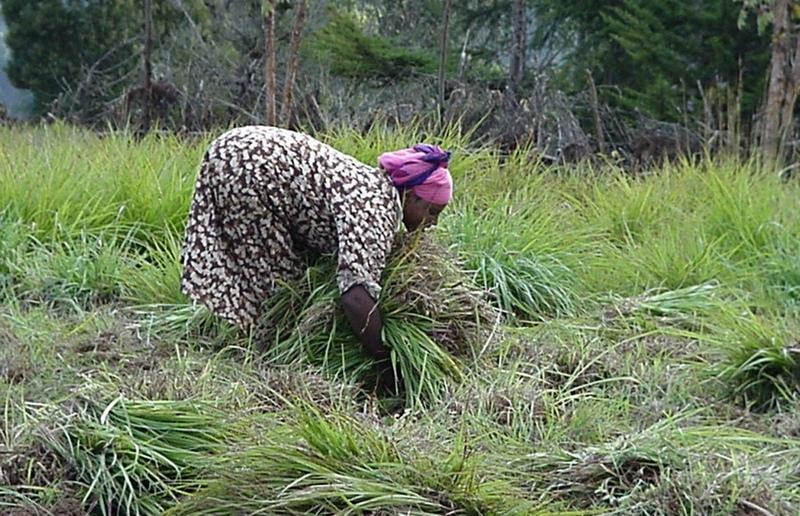
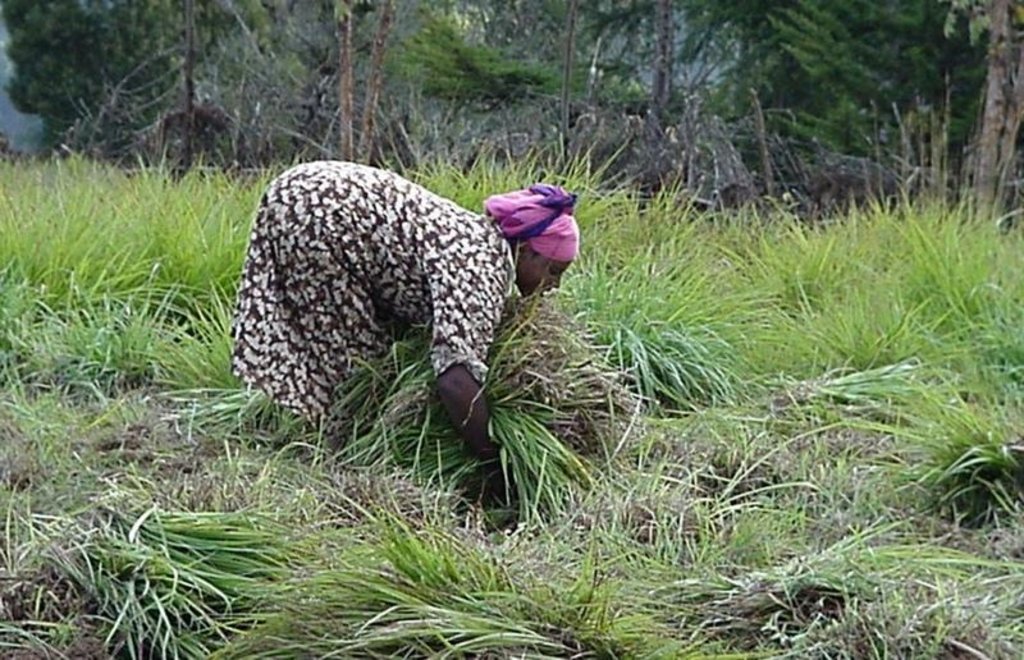
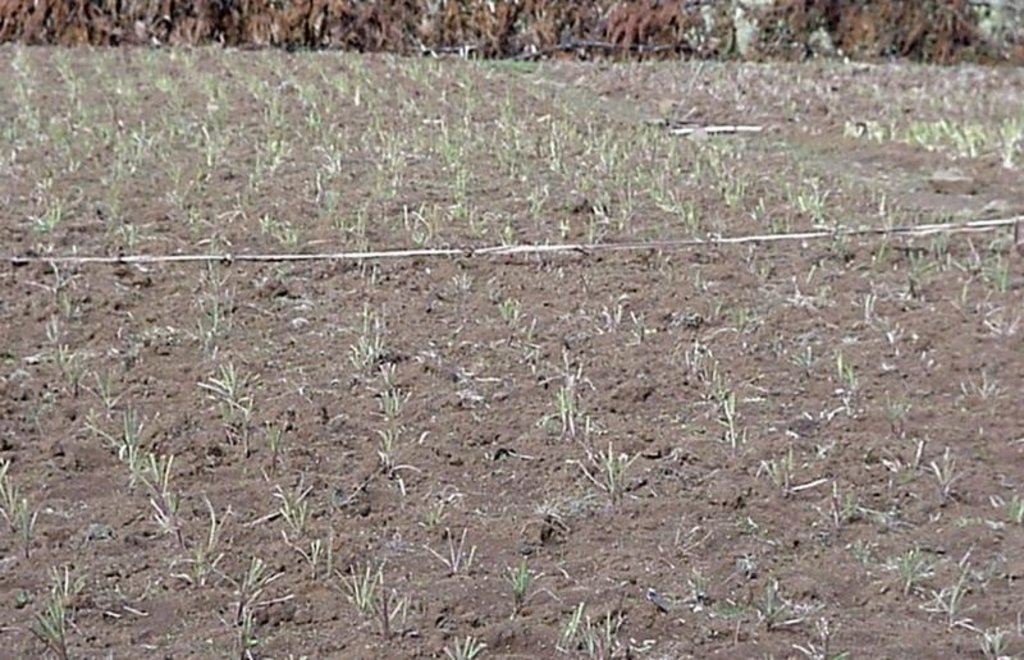
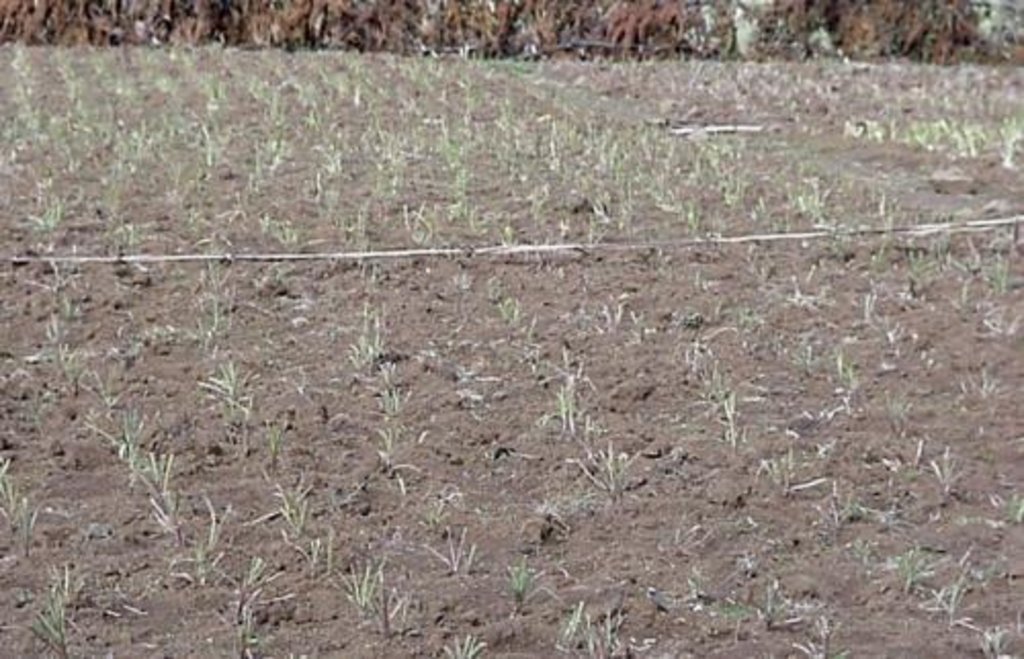
Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands, through planting of improved grass and fodder trees and land subdivision, to improve fodder and consequently livestock production.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
This case study focuses on the highly populated, humid highland regions of Ethiopia that experience serious shortages of pasture. Due to rapid population growth, communal grazing areas are increasingly being converted into cropland. This has led to enormous pressure on the little remaining grazing land, through overstocking of dairy cows and oxen, and thus overgrazing, resulting in considerably decreased productivity.
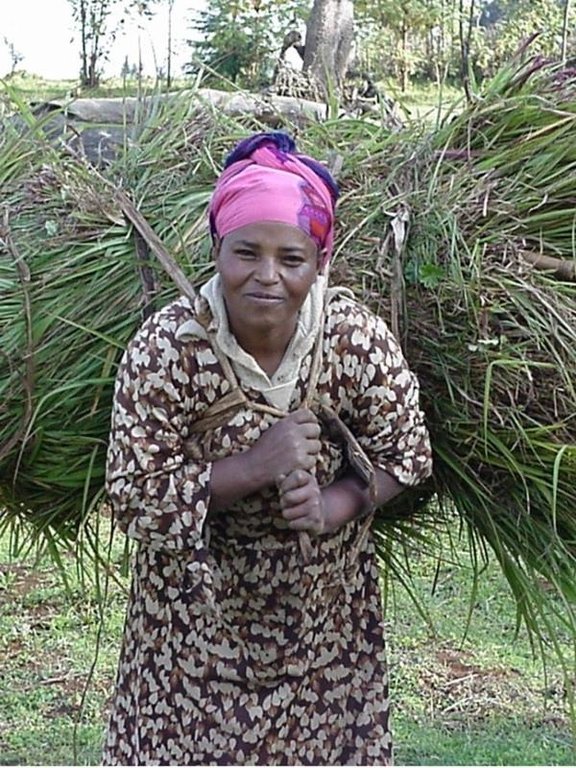
Improved grazing land management is vital to increase food security and alleviate poverty, as well as to bring environmental rewards. To address these problems, the national SWC programme in Ethiopia initiated a grazing land management project over a decade ago. Implementation of the technology includes the initial delineating of the grazing land, and then fencing to exclude open access. This is followed by land preparation, application of compost (and, if necessary, inorganic fertilizers) to improve soil fertility, then planting of improved local and exotic fodder species, including multipurpose shrubs/trees such as Leucaena sp. and Sesbania sp. and the local desho grass (Pennisetum sp.). Desho has a high nutritive value and regular cuts are ensured. It is planted by splits, which have high survival rates and establish better than grasses which are seeded. Other grass seeds, as well as legumes, including alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa) and clovers in some cases, are mixed with fodder tree seeds and then broadcast.
Maintenance activities such as weeding, manuring and replanting ensure proper establishment and persistence. Fodder is cut and carried to stall-fed livestock. Once a year, grass is cut for hay, which is stored to feed animals during the dry season. Experience shows that such grazing land is best managed when individually owned and used. In the study area, the community has distributed small plots (<0.5 ha) of communal grazing land to individual users to develop, manage and use.
The overall purpose of the intervention is to improve the productivity of grazing land and control land degradation through the introduction of productive techniques and improved fodder species, which consequently improve livestock production. Commercialisation of animals and marketing of their products increases the income of farmers. The government provides technical assistance, close follow-up, and some inputs for initial establishment. Land users are trained in compost/ manure application, planting of seeds, splits and seedlings, and general maintenance.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Chencha
Map
×2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ຕັດຫຍ້າ ແລະ ຂົນຫຍ້າ / ບໍ່ມີທົ່ງຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບປຸງ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ຊະນິດພັນສັດຕົ້ນຕໍ ແລະ ຜະລິດຕະພັນ:
before SWC

ປະສົມປະສານ (ການປູກພືດ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້), ລວມທັງ ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
After SWC - cut-and-carry (desho gras (Pennisetum sp.)), legumes (alfalfa, lucerne: Medicago sativa), trees (Leucaena sp, Sesbania sp.)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population growth has resulted in a substantial reduction in land holdings (<0.5 ha per family) and this in turn has led inevitably to encroachment onto communal grazing lands for cultivation. Livestock numbers on the other hand have remained unchanged, and this has led to overstocking of the few areas left. Livestock production, which accounts for 40% of the average household income, is thus reduced and farmers’ income declines correspondingly.
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ໃນເວລາ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ແມ່ນໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າ ດິນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຄີຍເປັນດິນປະເພດໃດ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: March - September
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປິດພື້ນທີ່ (ຢຸດການນໍາໃຊ້, ເພື່ອປູກເປັນປ່າຟື້ນຟູ)
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການປັບປຸງແນວພັນພືດ / ແນວພັນສັດ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
Splits of desho grass (Pennisetum pedecillatum) are plantet in lines, using a hand hoe, after good seedbed preparation. Spacing between grass splits is 10 x 10 cm. The white line is a boundary between two households' plots (width of plot: 15-20 m). Trees are planted at rirregular spacing (around 5 m apart), layout is not specified.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of dispersed runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure, control of concentrated runoff
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: animal manure, leaf litter, wood ash, soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena sp., Sesbania sp.
Grass species: Desho grass (Pennisetumsp.), alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa)
Other type of management: change of intensity level
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delineation of the area to be conserved and establishment of a fence | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | before the onset of rain |
| 2. | Subdivision of communal land into individual plots of 0.3–0.5 ha. | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | |
| 3. | Planting material preparation in nurseries: grass splits (desho) | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | |
| 4. | Good seedbed preparation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | (at the onset of the rains). |
| 5. | Planting of grass splits and tree/shrub species in lines; sowing of grass | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | (early in the rainy season). |
| 6. | Weeding. | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 320.0 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Grass splits (tillers) | ha | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1052.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compost/manure preparation. Material used includes animal manure, | ພືດ | / initial establishment |
| 2. | Compost application | ພືດ | / one month after planting, initial establishment |
| 3. | Cut-and-carry, to stall-fed animals, begins when fodder is ready. | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | (after 2–3 months growth) /2 -4 times |
| 4. | A final cut for hay is taken early in the dry season when the grass has matured well. | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | (end of October) / |
| 5. | Weeding | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | /each year. |
| 6. | Compost/manure application, mixed with soil, during seedbed preparation (only where plants have died and need replacement and fertilisation). | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | |
| 7. | Enrichment planting and gap filling | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | after a year / repeated each year. |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 126.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Seedlings are given by the government for initial establishment. For further extension of area and replanting, the
land users set up their own nurseries. After 2-3 years maintenance costs decrease substantially as the grass cover closes up and maintenance activities such as replanting/enrichment planting and compost application are reduced or cease. The local daily wage is about US$ 0.70 a day, but varies depending on the intensity of the work. In this calculation the standard rate has been applied.
Farmers usually cannot afford fertilizers. Milk production compensates for some of the high investment costs (previously, production was low).
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Local term: wett dega
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and foot slopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 2) and low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Off-farm income specification: source of off-farm income includes petty trade and weaving
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha: Ranked 1
< 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha: Both ranked 2
2-5 ha: Ranked 3
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ບຸກຄົນ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increase in livestock production
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increase in the availability of livestock products on the market
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Decrease in size of grazing plots due to land fragmentation
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Selling animals and their products
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
Dependence on incentives
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Initially high. Incentives such as free seeds, seedlings, tools
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Improvement in household diets (milk)
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increased willingness
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
Sediment transport
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 50 households who accepted the technology in the initial phase, did so with incentives. They were provided with planting materials (seeds, seedlings, grass splits) and hand tools.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The rate of spontaneous adoption is very high. At present over 500 households have taken up the technology and the total area covered is about 20 km2.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Increased national income due to export of animals and their products. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Availability of fodder (grass, hay, shrubs) in sufficient quantities, and all year round How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the area under such development. |
|
Reduction in soil loss and land degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain adequate cover by planting more grass. |
|
Introduction of high yielding species as well as increase in land productivity and livestock production How can they be sustained / enhanced? ntroduce bigger variability of quality species and improve maintenance activities such as weeding and cultivation. |
|
Improved diet: livestock by-products such as milk, butter and cheese are essential food items required by the households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep on increasing/improving quantity/quality of livestock feed. |
|
Increased income through commercialisation and marketing of animals and their by-products. Meets financial needs for paying taxes, school fees, clothes etc. |
| Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands is both a technical and social challenge. Here is a promising example from Ethiopia that is spreading quickly. The key is subdivision of land into individual plots where cut-and-carry of grass and stall-feeding of livestock is practiced. This is only a possible option, however, where rainfall is favourable. land use rights: individual for cropland, open access (unorganised/communally used) for grazing land, except for the case study area where the rights to rehabilitated grazing land are given to individuals |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| At the initial stage of establishment it is very labour intensive | Use of improved land preparation methods such as oxen ploughing. |
| Substantial cash for inputs, particularly seedlings, is required | Produce seedlings of improved species and making compost in backyards. |
| Needs high fertilizer application | Focus more on organic fertilizers. |
| High pressure on remaining grazing areas | Keep animals in stall (stable) or park, at least part of the day and during the night, and introduce cut-and-carry more widely. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Adane Dinku, Chencha Wereda, Natural Resources Management Annual Report,. 2001 and 2002.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ