Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [ເຄັນຢາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Michael Herger
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Hanspeter Liniger, Donia Mühlematter
technologies_2990 - ເຄັນຢາ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 1, 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 22, 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Sept. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Makurian Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: May 9, 2019 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Sepeika Milton
+254 (0) 723870987
olenape@yahoo.com
Makurian Group Ranch
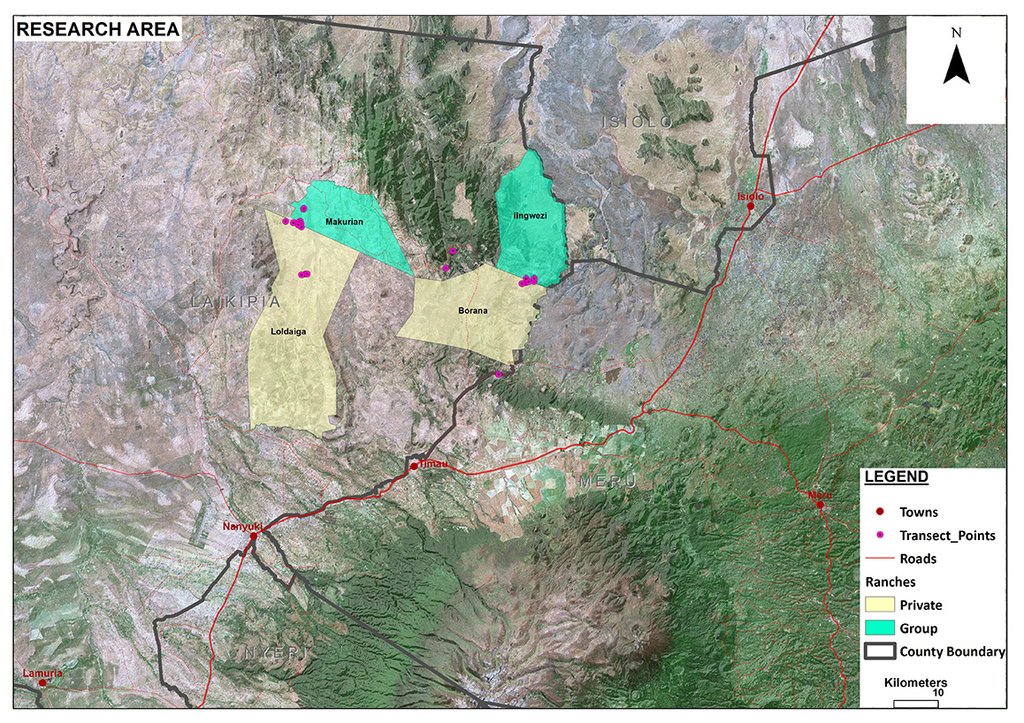
Mukogodo Division, Laikipia North District, Kenya
ເຄັນຢາ
1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
22/01/2017
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Makurian rangeland is in bad condition. The land is largely degraded and dominated by the invasive species "Opuntia". Makurian Group Ranch has abandoned the in 2007 implemented "Holistic Management" principles. However, one has to take into account that Masai pastoralists have historically been squeezed from all sides into smaller areas. Compare Herger (2018).
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
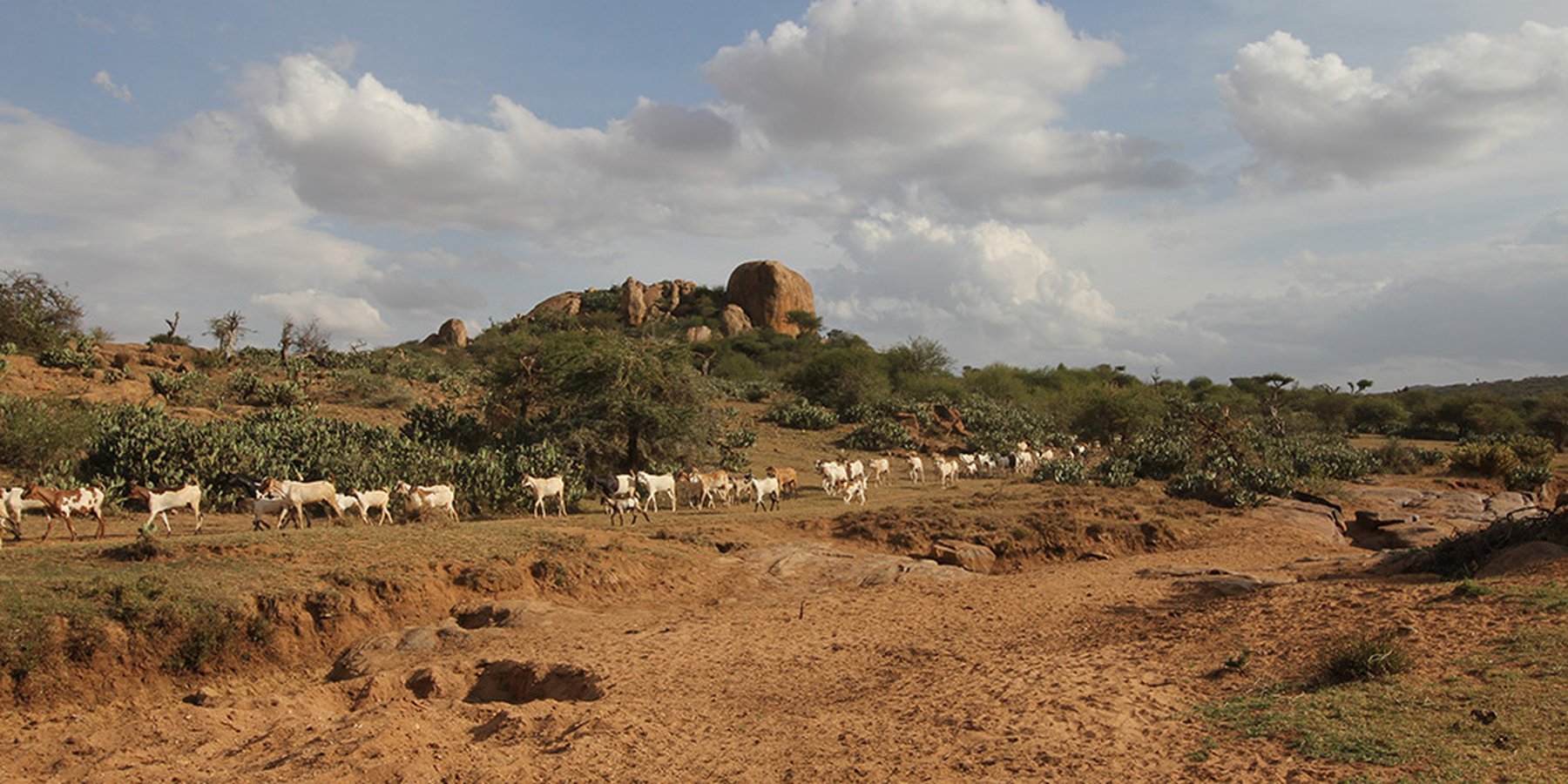
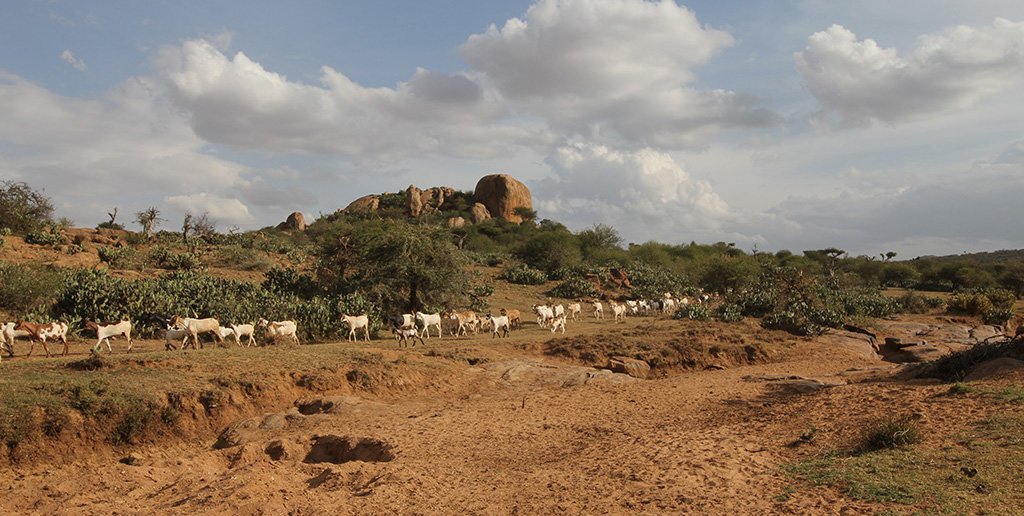
The grazing principles of a Masai group ranch (pastoralists) deal with high numbers of livestock in semi-arid lands with very limited water resources. Makurian has abandoned "Holistic Management" principles and applies a more traditional management system today. There is a grazing plan for the rains, while during the dry season everybody seeks for water and pasture individually. Bare land is recovered by "Boma” technology (strategic corralling of animals overnight) and reseeding. The rangeland is due to high stocking rates severely degraded with lots of erosion, bare ground, and invasive species. High stocking rates have on the one hand historical and political reasons and on the other hand socioeconomic rationales.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
On Makurian Masai Group Ranch, livestock production management is through a combination of traditional livestock keeping practices and newly introduced management principles. Livestock production at Makurian is for subsistence and local use, and has very high cultural significance.
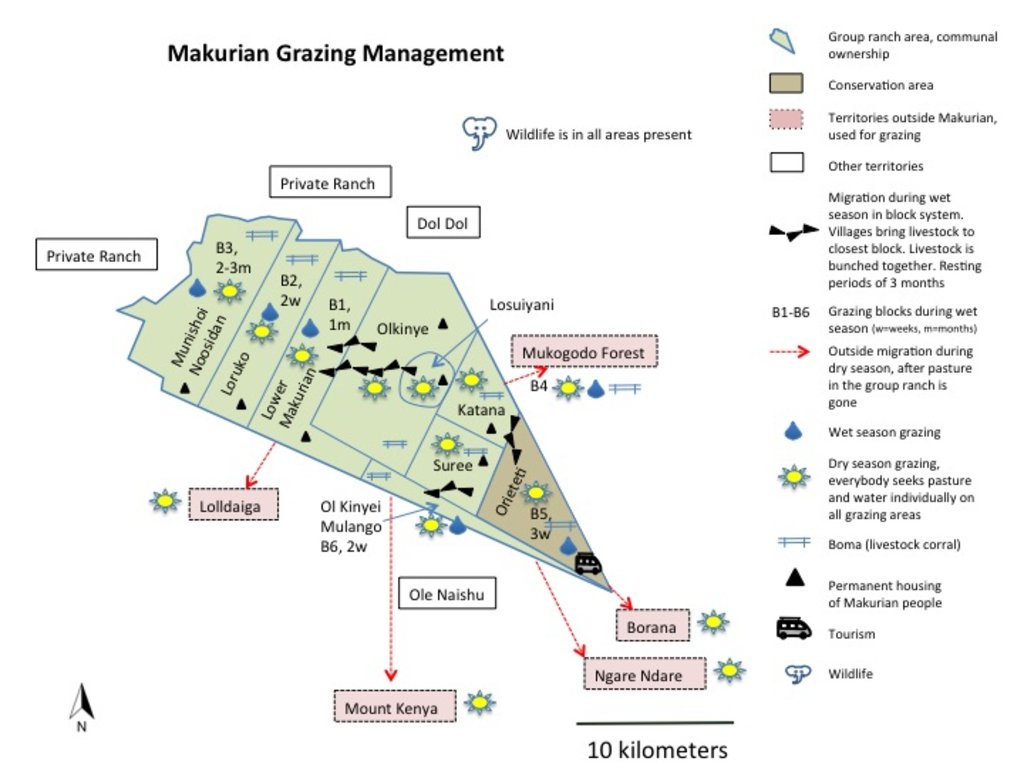
During the wet season, livestock are “bunched” together and rotational grazing in blocks is practiced. The management team (elders) group all livestock from each village (16 villages) and each uses the block next to their village. Livestock are hardly separated (cows, heifers, steers, bulls all herded together).
o Block 1: Lower Makurian - 1 month
o Block 2: Makurian Loruko - 2 weeks (next to Lolldaiga Northern Gate)
o Block 3: Munishoi Noosidan - 2-3 months
o Block 4: Mukogodo Forest - 1-2 months
o Block 5: Orieteti Conservation Area - 3 weeks. Soft grass, runs out quickly.
o Block 6: Ol Kinyei Mulango - 2 weeks. Next to Olenaisho
They apply resting periods of three months after usage (if this rule is broken, the owner is punished by a fine of one livestock unit).
When it becomes dry, everyone is responsible for their own livestock. Owners of livestock want to maintain and decide about their livestock individually, this is why "Holistic Management" and specific grazing plans for the dry season did not work.
In comparison to earlier days when the whole family moved, and livestock was herded by morans (young warriors), they hire external herders nowadays (800 herders in total). Herders seek whatever water and pasture remains on the group ranch, then move on to:
(a) Ngare Ndare forest: 1,000 cattle and 1,000 sheep and goats (shoats) per year on average, for 1-2 months, over an area of 250 km2;
(b) Mukogodo forest: 3,000 cattle and 4,000 shoats per year on average, for 3-4 weeks, over 250 km2, and
(c) Mount Kenya: 12,000 cattle and 5,000 shoats on average per year, for 1-2 months, on an undefined area.
In Mukogodo forest, Makurian Masai have also officially settled, in Ngare Ndare forest on the other hand they graze on the basis of an informal agreement and on Mount Kenya it is not official pasture - but grazing is tolerated). They are also assisted by private ranches to graze during droughts (Lolldaiga and Borana; for every 1,000 units, they usually pay 5 Ksh per cow per month: a token amount). On one private ranch (Borana) they also graze steers and cows for fattening and selling.
Furthermore, Laikipia rangelands support some of the highest densities of wildlife in Kenya, however, group ranches less so than private ranches. The wild herbivore biomass density on group ranches is by Georgiadis et al. (2007) estimated at 205 ha /TLU.
Bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) for the livestock are constructed in traditional style, where animals are kept closely bunched together in enclosures overnight. Bomas are strategically located on denuded land to rehabilitate the land (through dung accumulation and breaking the soil crust by hoof action). Every homestead has one boma (approximately 1,500 in total in the whole Group Ranch). When herders are moving with livestock, temporary bomas are constructed.
Sales are usually need-driven (e.g. for school fees) within a family. They sell to the nearest local markets (in DolDol and Nanyuki) or directly to butchers. Makurian is also part of the "Dung Market" in Mukogodo District, where livestock dung is sold as manure for crop production. Moreover, Makurian makes additional income by harvesting sand and selling it for construction.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຄັນຢາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Laikipia
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Mukogodo Division
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory was implemented in 2007, which was abandoned after a few years. This documentation focuses on the traditional system and new management principles they introduced since then. For Holistic Management see "Il Ngwesi" and "Borana" documentations.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດທໍາມະຊາດ:
- ແບບເຄິ່ງຂັງ / ເຄິ່ງປ່ອຍ
ຊະນິດພັນສັດຕົ້ນຕໍ ແລະ ຜະລິດຕະພັນ:
Livestock: Cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, camels. Meat and milk production (also blood) and as a bank/ value asset. Subsistence and local production. Livestock: 13,500 TLU, Stocking Rate 0.6 ha/TLU calculating the total area used by livestock (78 km2). Pressure on land (including wildlife density of 205 ha/TLU): 0.6 ha/TLU Livestock numbers: 15,000 cattle, 30,000 shoats (ratio goats - sheep 2:1) Livestock fluctuations (per year): -500 cattle sales, -4,000 shoats sales, +100 cattle purchase, +350 shoats purchase, -3,500 shoats slaughtered. +6,000 cattle, + 15,000 shoats due to natural breeding. On average, 2200 steers on Borana rangeland for fattening purpose. During droughts, livestock move to neighbouring private ranches (1,000 cows each on Lolldaiga and Borana on average) Wildlife: Giraffe, antelope/gazelle (e.g. gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle), baboons, zebras, dikdik, hares, elephants, and more.

ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
- ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ອາຄານ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດ:
Villages, bomas, manyattas.
8'000 inhabitans.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງສັດລ້ຽງ (ຖ້າຫາກວ່າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
13’500 TLU, Stocking Rate 0.6 ha/TLU
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງສັດລ້ຽງ ແລະ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- 10-100 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The area size of the group ranch is 68 km2, however, the total area affected by livestock is 78 km2.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
- M4: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ໄລຍະເວລາ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
- Pk: ການບັນເທົາ ແລະ ການປົກຄຸມຂອງເປືອກໂລກ
- Pi: ເນື້ອດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Across the grasslands and rangelands, an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems caused (partly) by livestock production in the research area are: major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species (Makurian is heavily affected by the invasion of Opuntia strica species). The current major problem on rangelands is the invasive species Opuntia stricta, which, however, only could spread that widely because of degraded land in the first place. The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
Herders, animals treatment (for the total area affected by livestock = 78km2)
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- ໂດລາສະຫະລັດ
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
1.5
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grazing planning for bunched animals (livestock from all households) | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | |
| 2. | Hiring herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | unknown |
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | ||
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | ||
| 3. | Planning activites | ||
| 4. | Boma Management (mainly movement of Bomas) |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Herders, watchmen, supervisors | Person-days | 260000.0 | 1.5 | 390000.0 | |
| ແຮງງານ | Engaged population in livestock production | 720000.0 | 1.5 | 1080000.0 | ||
| ອື່ນໆ | Animals treatments | Per TLU | 13500.0 | 3.5 | 47250.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1517250.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Every family hires their own herder during the dry season. The family is staying put. Inhabitants are also considered as labor since they are usually all engaged in livestock production. However, milk and blood production are not considered.
Animal treatments consist of vaccination, spraying (ticks), injections.
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Herders
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
378.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes. Makurian generally drier than Lolldaiga.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Rainfall gauge Lolldaiga Northern Gate (neighbouring ranch)
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol
SOC 0.8 %
pH: 6.4
Clay: 9 %
Silt: 41 %
Sand: 50 %
Fore more data on rangeland health see Herger (2018)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
> 50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
Grassed acacia bushland. Bare land up to 70% during dry season. Loss of (native) vegetation. Invasive species coming in. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Opuntia, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies. Dominant trees: Acacia drepanolobium, Acacia etbaica. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (see Herger 2018).
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ແບບເຄີ່ງຂັງ-ເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມ (ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ / ເປັນສິນຄ້າ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Masai people. 8'000 Masai living in Makurian. Traditional livestyle. Livestock with very high cultural value.
Have been historically "squeezed" from all sides into smaller areas for livestock keeping. Future of pastoralism is in question.
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This applies for households that are staying put. Herders trek livestock on a total area of over 10'000 ha.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Lack of rain. Impact analysis is comparing the current state vs. some 10 years ago when they applied Holistic Management. This is why improvements are indicated according to the land user, even though the land is severely degraded.
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ນໍ້າດື່ມ ມີຄຸນນະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
less salt
ມີນໍ້າ ໃຫ້ສັດລ້ຽງ
ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນໍ້າ ສໍາລັບລ້ຽງສັດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Compared to HM it has decreased, because of higher numbers of livestock it has increased though
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
More traditional knowledge than with Holistic Management
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Other communities
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Opuntia
ຊັ້ນນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ / ນໍ້າ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Opuntia (an invasive cactus) is chasing out native plants and consuming water. Elephants are destroying trees (high density of elephants, Opuntia is additionally attracting elephants)
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Opuntia
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
More wildlife coming in, roaming even in villages. Elephants problematic; breaking fences
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Wildlife numbers are declining drastically. Indigenous vegetation is being driven out by invasive species like Opuntia.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Resilience has worsened
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄໍາເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບ:
All listed impacts are as perceived by land users according to Milton Sepeika, Chief of Makurian. In his opinion, abandoning Holistic Management principles had many advantages. According to him, animal production has increased. Though he recognices the bad condition of the land and poor conditon of livestock. He mainly blames the drought and the Opuntia invasion for these problems. Results from a rangeland health assessment (only ecological conditions) show heavily degraded ecological conditions (dry season up to 70% bare soil, poor soil and vegetation, erosions features, inability of producing annual and perennial grasses after rains etc) (compare Herger 2018). A
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດອື່ນໆ | Greater variation of seasonal rainfall, more intense rainfalls, change in rainfall regimes in general (see Schmocker 2013 and Imfeld 2016). | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ຄື້ນຄວາມອົບອຸ່ນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ລະບຸແມ່ນເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງ ທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດມີການປັບຕົວ:
- ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Masai people have changed their livestock composition towards owning more smallstock (goats and sheep) than cattle. Goats are tolerant to drought, and as browsers they don't need grass. They can be turned into money much quicker than a cow in times of need. Their faster reproductive cycle means they can rebuild numbers faster than cattle after losses through drought.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Everybody makes their own decision about their livestock (during the dry season). Owners stay in charge. |
| Grazing principles and plans lead to community control. |
| Traditional knowledge |
| Fewer costs |
| Less of effort (during the dry season no bunching of animals) |
| Fewer trees cut. During Holistic Management times many trees had to be cut to create two big bomas every month. |
| Can enrich land, livestock is tilling ground (seeds don't go away - kept in ground due to "tilling") |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Brings in conflicts. If you start to protect and maintain your grass, thieves come in. | |
| Spread of diseases when animals from different places with different diseases are brought together during the wet season |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Makurian (mostly next to Lolldaiga Northern Gate) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
Several meetings with chief, rangeland specialist and botanist of Makurian.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Imfeld, N. (2016). Modeling Seasonal and Annual Precipitation using long-term Climate Records and Topography. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Online
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
University of Bern
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Georgiadis, N.J., Olivero, I.N., Romanach, S.S. (2007). Savanna herbivore dynamics in a livestock-dominated landscape: I. Dependence on land use, rainfall, density, and time. Biology Conservation 137(3): 461-472.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Online
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ