Small Irrigation System for Highland Rice Terraces [ໄທ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Pitayakon Limtong
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
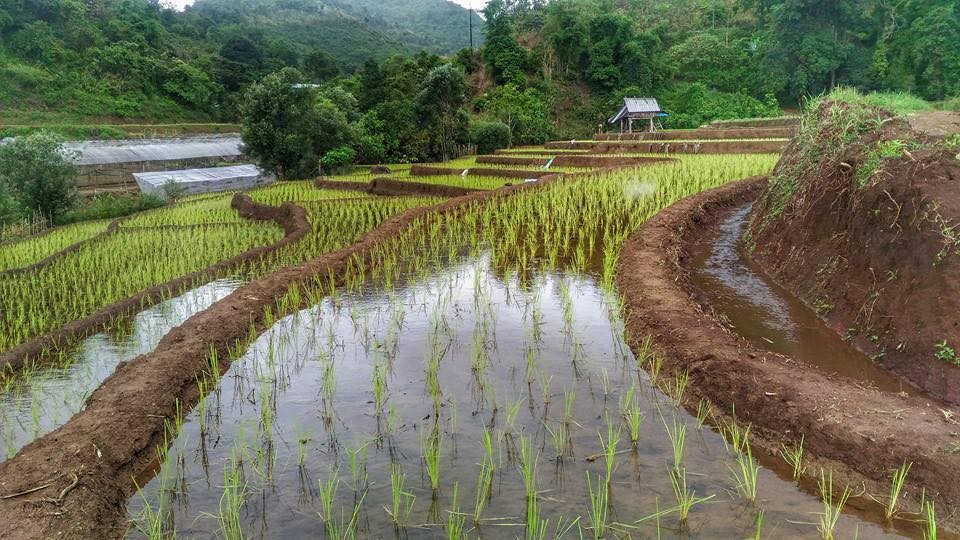
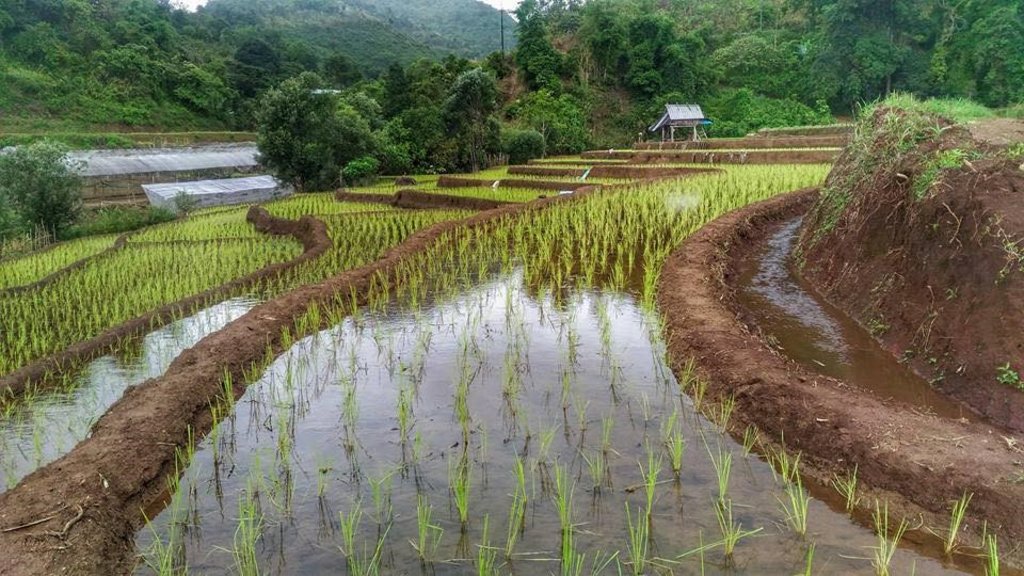
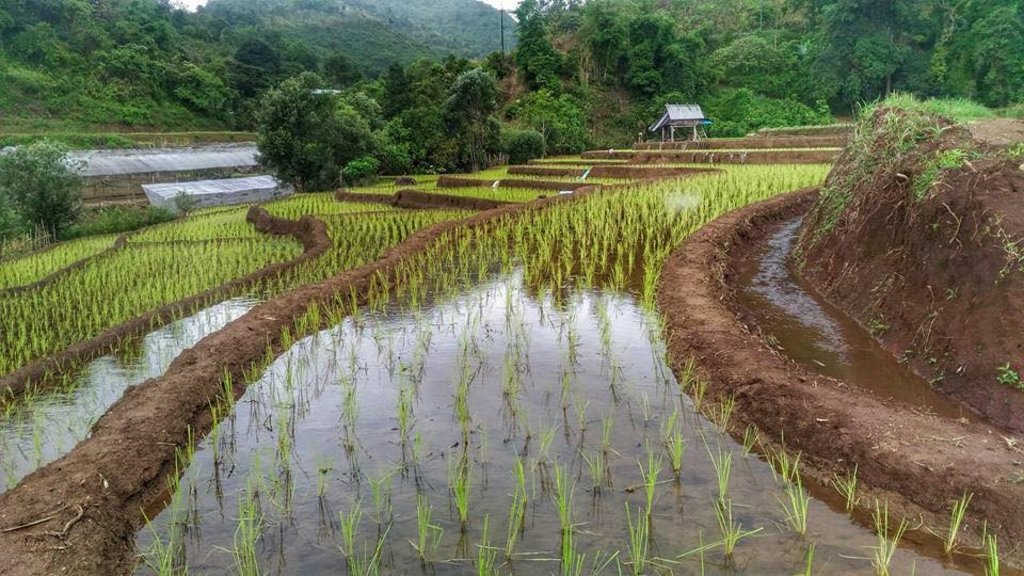
Checkdam for highland rice terrace
technologies_4114 - ໄທ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Srisomkhew Sasirin
662 579 1409 / 669 8269 6410
sasirin0928@gmail.com / sasirin0928@gmail.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
ໄທ
SLM Consultant:
Limtong Pitayakon
66 89 444 6599
pitaya@ldd.go.th / pitaya49@msn.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
ໄທ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Kayanyaiyie Mr.Vitoon
668 7188 0798
Soil Doctor Volunteer
Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
ໄທ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Kongvili Mr.Boonpan
668 4740 1550
47 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
ໄທ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
khangJing Mr.Suchat
668 3660 0272
1/2 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
ໄທ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
KangJing Mr.Somnuek
668 8764 1683
Village Headman
1 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
ໄທ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - ໄທ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
11/09/2018
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Water supply systems in the high landscape rice terraces can prevent land degradation and also land users can utilize this area for producing rice in limited agricultural land. Because this system slows down the water flow, it reduces soil erosion into water courses and controls the amount of water that flows from the forest upstream to the rice terraces. This system increases water available to the rice terraces and improves the utilization of water, thus maximizing benefits for growth and yield of rice.
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds upstream to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
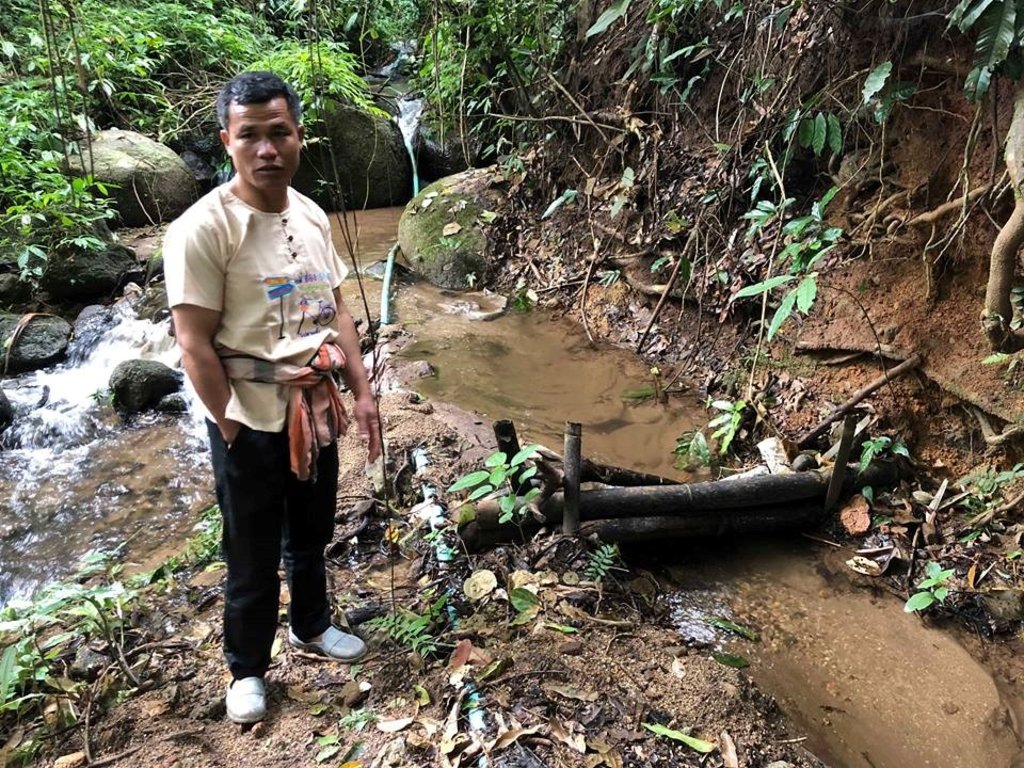
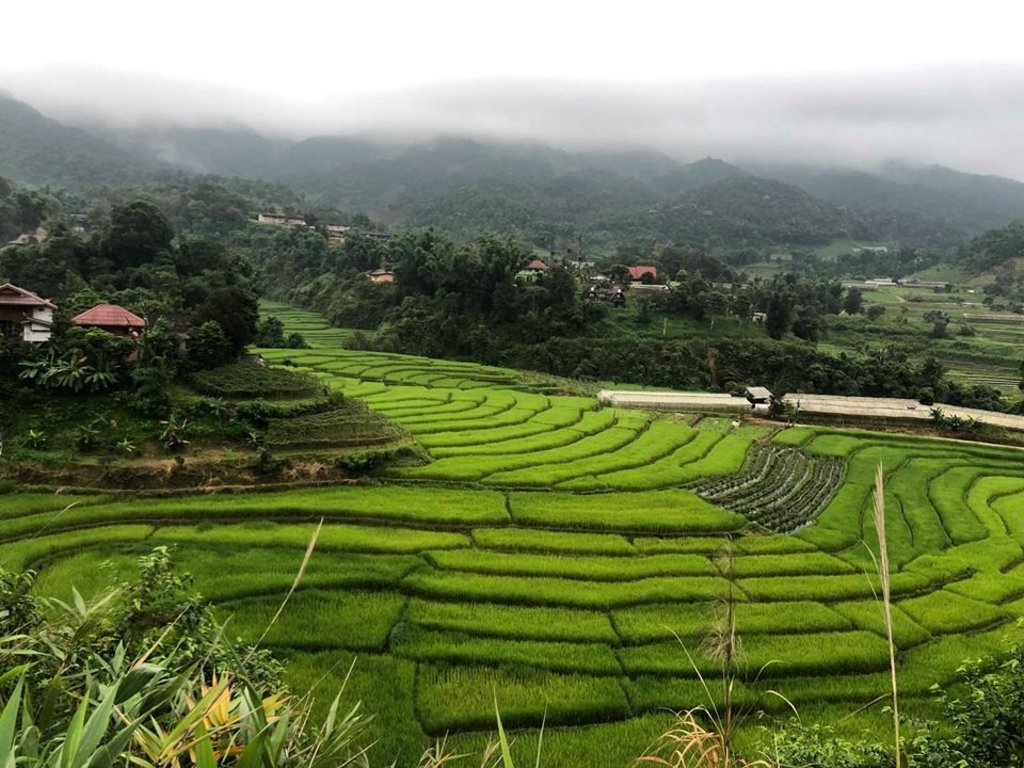
The topography of this mountainous area, Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, is complex. The height ranges from 994 -1,100 m above sea level (m asl). The main river is Mae La Noi. The climate is cool all year round. The annual average temperature is 25 degrees Celsius (⁰C), maximum temperature is 37⁰C in April, and minimum temperature is 8⁰C during December. The annual average rainfall is 1,500 mm and lasts from June to October. The number of households is 147, with total population of approx 763, 400 (Mae La Noi Royal Project Development Center, 2561). An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream areas to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus. The steps of preparation are as follows. 1. Site selection: Rice terraces should be on suitable slopes, not more than 60 degrees, otherwise it will be difficult to excavate the slope and rice fields become very narrow. 2. Reshaping and leveling the slope: The sloping land for rice terrace should be reshaped and levelled by either manpower or mechanical means. The terraces can extend up to 50 m long, be as little as 1 m wide and 0.5 m deep, depending on the slope. The leveling of soil surface in the plot is done by releasing water into that plot and adjust the soil surface until a good level is attained. 3. Soil improvement: Generally, soil structure and fertility in the plots is very low because of reshaping and leveling. It is therefore necessary to restore and improve by application of organic matter, compost, animal manure, legumes, etc. Soil pH must be adjusted, and nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium should be added based on soil analytical results. 4. Rice cultivation: In the first years of cultivation, the terraces may not store water at the desired level, so rice is planted in small holes. Normally, farmers plant rice seedlings (3-5 seedlings per hole) at a spacing of 20 x 20 cm. 5. Fertilizer application: In this highland area focus should be on organic fertilizers to reduce costs, because people can find materials locally such as animal manure and plant residues. 6. Water supply system: Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weirs to release suitable amount of water through a small water channel to rice terraces. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year. 7. Disease and insect control: Most rice varieties are native, so they have high resistance. But there could be some disease/insect outbreaks; they have to be protected according to instructions. The submerged condition in the paddy field can help control weeds, but some labour is still needed. 8. Maintenance: For small dams or weirs, small water channels and terraces, it is necessary to restore and maintain twice a year, i.e. before and after harvest.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.4 ວິດີໂອ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ວັນທີ:
11/09/2018
ສະຖານທີ່:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
ຊື່ຂອງຜູ້ຖ່າຍວີດີໂອ:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
ວັນທີ:
21/03/2018
ສະຖານທີ່:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
ວັນທີ:
11/09/2018
ສະຖານທີ່:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
ຊື່ຂອງຜູ້ຖ່າຍວີດີໂອ:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ໄທ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດຫຼັກ (ທີ່ສາມາດສ້າງລັບຮັບ ເປັນເງິນສົດ ແລະ ເປັນພືດສະບຽງອາຫານ):
Paddy rice and vegetables such as chili, cabbage

ທິດທາງໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າ, ດິນທາມ
- ທໍ່ລະບາຍນໍ້າ, ທິດທາງນໍ້າ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
Small dams or weirs with small water channels to supply/distribute water to rice terraces.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Farmers in the area will grow rice in the rainy season for household consumption. The duration of cultivation until harvesting is about 6 months. In the dry season, the farms are converted to several kind of vegetables under support by the Royal Project Foundation.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The system of water supply of this technology distributes water resources from forest upstream to the rice terrace.
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 3
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Paddy rice once a year and vegetables 1-2 crops a year
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ມາດຕະການ ຕັດຂວາງ ກັບຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
- ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງນໍ້າ ແລະ ການລະບາຍ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This water system covered around 200 households, each household covers an area of 0.5 hectare.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S1: ພັກຄັນໃດ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M7: ອື່ນໆ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
ວັນທີ:
25/09/2018
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
The irrigation water distribution system for highland rice terraces by farmers in the village is suitable for highland, sloping agriculture, with slopes ranging from 5-60 degrees. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream zone to the agricultural land through the consensus of community members. Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weir which are used to divert and release suitable amount of water through small water channels to rice terraces. The terraces can extend up to 50m long, 1m (or more) wide and 0.5m deep, depending on the degree of the slope. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year.
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
0.48 hectare for each farmer
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Baht (THB)
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
32.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
300
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | prepare small dam and water canal | ໂຄງສ້າງ | in the first year |
| 2. | prepare terraces and land leveling | ໂຄງສ້າງ | in the first year |
| 3. | cultivation | ໂຄງສ້າງ | before rainny season |
| 4. | soil improvement | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after preparing and cultivating the soil |
| 5. | rice planting | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | rainy season |
| 6. | fertilizer application | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after planting |
| 7. | irrigation | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after planting |
| 8. | disease, pest and weed control | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | after planting |
| 9. | havesting | ພືດ | when rice grains are mature |
| 10. | None | None |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ແຕກຍ່ອຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງຕາຕະລາງລຸ່ມນີ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ ສາມາດ ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນ ມູນຄ່າທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
98100.0
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | prepare dam and canal | 7x10 | 70.0 | 300.0 | 21000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | planting | 7x1 | 7.0 | 300.0 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | maintainance | 20x2 | 40.0 | 300.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | harvesting | 20x7 | 140.0 | 300.0 | 42000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | tractor | set | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | fuel | liter | 20.0 | 30.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | rice seed | bag | 3.0 | 100.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | chili seed | plant | 5000.0 | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | fertilizer 21-0-0 | bag | 3.0 | 400.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | fertilizer 15-15-15 | bag | 3.0 | 700.0 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | fertilizer 16-20-0 | bag | 3.0 | 600.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | animal manure | bag | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 98100.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Labour of small and canal preparation was paid in the first year, after that paid for maintain all of these structuer.
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | restoration and maintain dam, canal and terrace | ໂຄງສ້າງ | 2 times a year |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງຕາຕະລາງລຸ່ມນີ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເຖິງ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນ ມູນຄ່າທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
1800.0
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | restoring and maintaining the dam, water canal and terraces | 2dx3m | 6.0 | 300.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1800.0 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
Land user spend their money for 100% of costs
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The most important factors that affect the costs is the labour factor, where farmers need to hire labourers for rice cultivation such as planting, fertilizer application, maintaining the system and harvesting, including, the excavation and restoration of the small dam, water channels and terraces.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1500.00
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ລັກສະນະສວດ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ສູງ (> 3 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງພືດ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ນໍ້າດື່ມ ມີຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ນໍ້າ
ກາລະໂອກາດ ທາງດ້ານວັດທະນະທໍາ
ໂອກາດ ໃນການພັກຜ່ອນຢ່ອນໃຈ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ການລະບາຍນໍ້າ
ຊັ້ນນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ / ນໍ້າ
ດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ການທັບຖົມຂອງດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ດິນສົ້ມ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຊະນິດທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ມົນລະພິດ ທາງນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ປານກາງ | ||
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູຮ້ອນ | ບໍ່ດີ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ປານກາງ |
| ພາຍຸເມກທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ປານກາງ |
| ພາຍຸລູກເຫັບທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ປານກາງ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄຟໄໝ້ປ່າ | ປານກາງ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງຊີວະພາບ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍາດລະບາດ | ບໍ່ດີຈັກຢ່າງ |
| ແມງໄມ້ / ການລະບາດຂອງພະຍາດ | ບໍ່ດີຈັກຢ່າງ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼາຍກ່ວາ 50 %
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 90-100%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| The villagers are self-reliant by living in balance between demand and supply to meet their own needs. So every household will grow rice for their consumption and solve some problems in water management of these rice terraces by their community. |
| Villagers have knowledge and technology of water management and systematically and continuously transfer to other land users from generation to generation, causing a connection between kinship and community. There are groups to solve the main problems of the community. |
| Villagers have a stable and strong mental state with the hard thinking to fight the obstacle in the way of living, to achieve a more prosperous life. Individual communities have strength in self-reliance, and also have strong mind in learning, having virtue and rationality in thinking and decision-making. |
| They have the ability to promote agriculture with natural resources and ecological tourism and develop the communication system for visitors to access the local information and facilities. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| The selection of appropriate technology can solve the problem of soil degradation, reduce soil erosion and manage adequate water supply to agricultural area for the whole year. |
| The villagers have to rely and trust on each other with high willingness to share their knowledge and experience. |
| Communities have the ability to use existing natural resources in maximizing benefits, and at the same time they try to conserve and prevent soil degradation in this area. |
| Community networking allows them to conduct activities to achieve self-reliance. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Land users’ lack of ownership of the land that cannot be legally owned by individuals, as the area is located in a preserved forest. The villagers therefore might be afraid to move out of the area in the future. | The community leaders and villagers need to solve this problem, one thing being that they should ask the government to help. |
| Lack of opportunities for children to have education caused by the poverty of their parents. | Schools in the area have increased educational opportunities for poor children by sponsoring underprivileged children. |
| Lack of social and health welfare because this area is far from the city. Villagers will not be able to reach the hospital in time in the case of emergency. | Villagers take the right treatment from the gold card or project 30 baht free treatment of all diseases for emergency situations. |
| Lack the coverage of energy and communication system in this area. Some areas still lack electricity, telephone and internet facilities. | Some villagers purchased and installed solar panels for their own use. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The villagers lack the ownership of the land, which located in the conserved forest. That means they do not have right to hold the land. | The government has a policy to solve these problems, and at the same time serve and arrange this preserved forest as natural resource. |
| Lack of educational opportunities, The study site is located in a remote area. Children living there lack opportunities in education. | The government has a policy to give underprivileged children equal education to children. |
| Villagers lack social and health welfare because of the remoteness of the place that they live. It is difficult to access medical treatment and hospital. | The government has set up and supported the budget to develop district health promotion hospitals in the sub-district level. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
7.3 ສາມາດເຊື່ອມໂຍງ ຂໍ້ມູນຂ່າວສານ ໄດ້ໂດຍຜ່ານການອອນລາຍ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Ecological tourism of Mae La Noi Development Center, Royal Project
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=818zn7JMKsU
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Mae La Noi Royal Project Foundation
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M8pFfl18fC8
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/interest510.htm
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
History of Mae La Noi Development Center
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/rypmaenoi.htm
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Mae La Noi Project for tourism of beautiful paddy rice terrace
URL:
https://mgronline.com/travel/detail/9590000106920
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://royalprojectthailand.com/maelanoi
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Rice terrace in highland
URL:
http://www.ricethailand.go.th/rkb/management/index.php
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ