Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production [ຟີລິປິນ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
"Tipid Saka"
technologies_1021 - ຟີລິປິນ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
Jasper Manalo
Monsanto Philippines
ຟີລິປິນ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Edicer Ocampo Jr
FSSRI, http://www.uplb.edu.ph/research/research-centers
ຟີລິປິນ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los (Farming Systems and Soil Resources Institute, University of the Philippines Los) - ຟີລິປິນຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Monsanto Philippines Inc. - ຟີລິປິນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
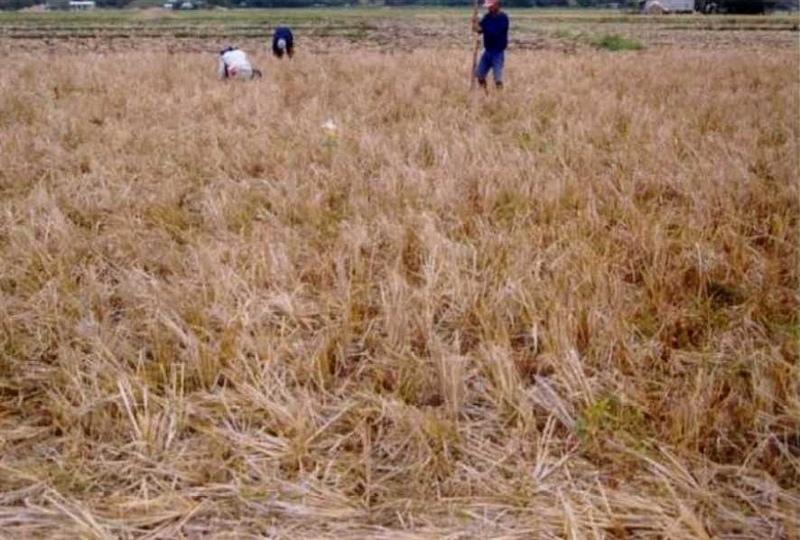
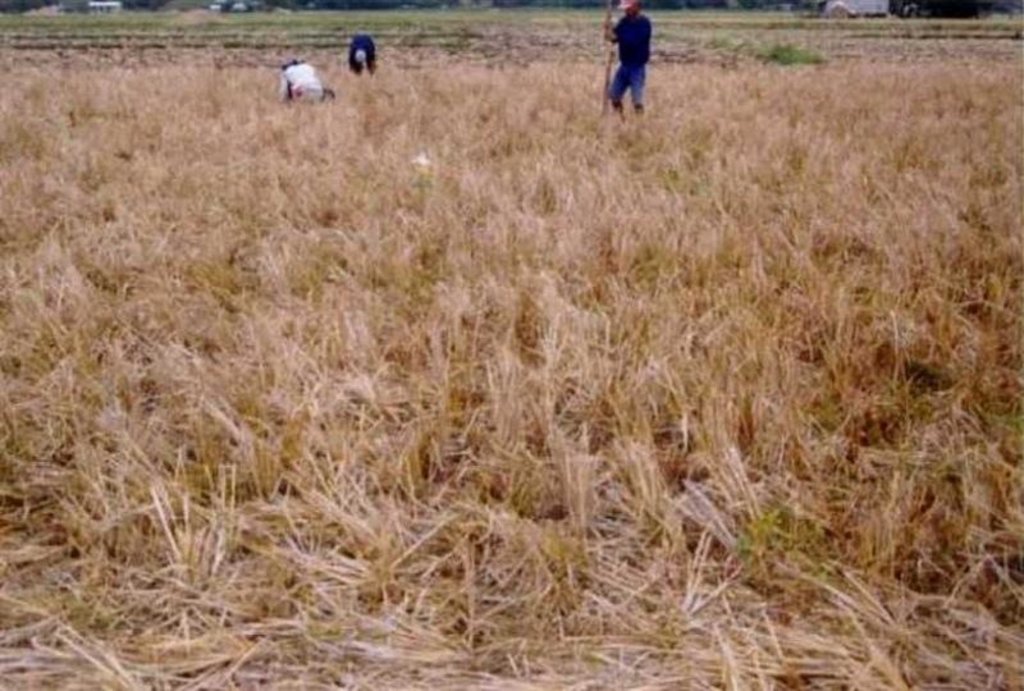
Conservation Tillage Technology (Zero Tillage) or "Tipid Saka" - A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Brief Description about Conservation Tillage Technology
Conservation tillage is the practice of planting seeds through the stubble of last season’s crop, rather than plowing and disking the field. The stubble protects topsoil against loss to wind and rain and reduces chemical run-off to streams. By not plowing, farmers also conserve soil moisture, which can reduce irrigation demands. Farmers can save fuel by reducing the number of farm machinery passes across their fields. In simple terms, Conservation Tillage can be said to lie along a continuum of two other techniques:
Minimum Tillage - mouldboard plowing is replaced by light tillage with tined implements, with or without a low toxicity non-residual herbicide to eliminate both perennial and annual weeds. 30% or more of the soil surface is kept covered by soil residues until final seedbed preparation. Conventional planting equipment can normally be used. Zero Tillage - planting is normally conducted without any preparatory tillage, or seedbed preparation. Normally, this technique requires specialized machinery for planting which can displace residues from the previous crop. A low toxicity non-residual herbicide application is recommended where growing weeds are present. There are numerous potential advantages of conservation tillage:
Farming Benefits
For farmers the primary benefits of CT, achieved with any loss of yields, include:
- More sustainable farming due to dramatic reductions in soil erosion caused by water or wind
- More efficient conservation and utilization of water under dryland conditions
- Improved energy efficiency as a result of reduced fuel requirements associated with fewer field operations
- Greater crop and farm profitability through reduced direct and indirect costs for chemicals, fuel and labor.
Environmental Benefits
At the same time, CT offers a number of significant benefits to the environment, these include:
- Greater biodiversity than with standard cultivation practices where the surface has no crop residues
- Reduces the build-up of soil sediments in reservoirs, drainage, ditches, etc. caused by soil erosion
- Less pollution of drinking water sources caused by run-off of soil, fertilizers and pesticides
- Reduced CO2 emissions due to increased soil organic matter level
Furthermore, crops grown without tillage use water more efficiently, the water-holding capacity of the soil increases, and water losses from runoff and evaporation are reduced. For crops grown without irrigation in drought-prone soils, this more efficient water use can translate into higher yields. In addition, soil organic matter and populations of beneficial insects are maintained, soil and nutrients are less likely to be lost from the field and less time and labor is required to prepare the field for planting. In general, the greatest advantages of reduced tillage are realized on soils prone to erosion and drought. Also achieved are greater water-stability of surface soil aggregates, higher microbial activity and earthworm populations and higher total carbon. Soil loss is less from sprinkler irrigation than in the plow treatment.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຟີລິປິນ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Laguna
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
San Jose, Abra de Ilog, Sta. Cruz, Sablayan
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ກະຈາຍໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເນື້ອທີ່ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມ (ເປັນ ກິໂລຕາແມັດ):
100.0
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 100-1,000 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
"Tipid Saka" is being practiced by farmers in the sites of San Jose, Mindoro Occidental since the dry season cropping (1999-2000) with the entry of UPLB Corn project and Monsanto Philippines, Inc.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 km2.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Although the technology has long been practiced by farmers particularly in the upland areas, zero tillage practices for corn production after rice was introduced in the SWC sites of Mindoro Occidental by the UPLB Corn project through the "Tipid Saka technology of Mosanto Philippines, Inc.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ
- ຕົ້ນຢາສູບ
- ຜັກ-ອື່ນໆ
- rice
ການປູກພືດທີ່ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກໄມ້, ອື່ນໆ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major cash crop: rice, corn
Major food crop: rice, vegetables
Other: fruits, tobacco
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Continuous salinization due to intrusion of salt water and soil fertility decline. Loss of topsoil by water erosion seriously affects soil productivity, degrades water quality and causes costly sedimentation problems.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain and increase crop yield.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Generally, first crop of rice is planted in early part of June nad harvest in mid October. Followed by green corn and/or vegetables in November and harvested in February. Yellow corn is planted in December and harvested in March to April.
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated is common but less used than rainfed
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຊົນລະປະທານ (ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ, ລະບາຍ)
- cost reduction
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
A3: ລະບົບການໄຖແຕກຕ່າງກັນ:
A 3.1: ບໍ່ມີການໄຖ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Ha: aridification
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
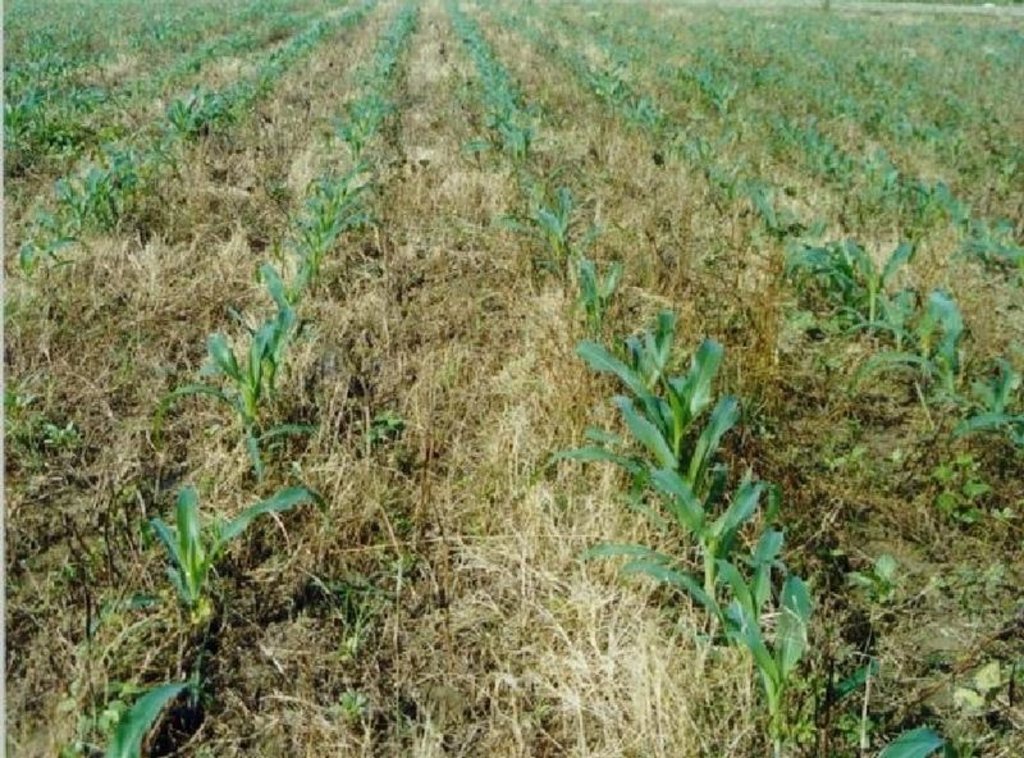
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residues, rice stubbles
Remarks: crop residues serve as mulching materials once killed by POWER herbicide
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: application of POWER herbicide 7-10 days after irrigation
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
5.00
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour vouluntarily and paid | ha | 1.0 | 147.6 | 147.6 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | post harvest | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | seed | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | BIO-N | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | man person days | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | marketing: transportation | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | marketing: packaging | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 541.2 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 541.2 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st side dressing, Release of trichogramma | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 2. | 2nd side dressing, Off-barring and hilling-up | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 3. | Detasseling | late vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 4. | Spray POWER herbicide, Planting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Retouch application of POWER herbicide, Replanting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: plow, harrow, hand tractor
Per hectare of land
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Land cultivation- zero tillage offset the costs incurred during land preparation. Labor costs for hand tractor and carabao-drawn plows are substituted by costs of spraying POWER herbicide which is significantly less expensive
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
450.00
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Landfroms: Area has generally flat topography located along wide plains.
Slopes: Small isoloated areas have slope of 0-2%
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil texture is medium andtextural analysis of samples show that the soils are silt loam.
Soil feritlity is low and the areas have high potential soil salinity problem.
The soil water storage has a capcity of 53.66% to 77.53%.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ສັດລາກແກ່
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 15% of the land.
5% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, plumbing, business, offer of labor services to neighbors
Market orientation of production system: mixed (subsistence and commercia (Corn)l: Sold to feed millers, surplus is kept for next cropping.
Level of mechanisation: Rich farmers can afford to rent trators but Carabao-drawn plow is still dominant among averaged income farmers.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
2-5 ha also common but lowest ranked
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
input constraints
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການລະບາຍນໍ້າ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
10
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຄວາມຮູນແຮງ ຂອງລົມ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
soil fertility
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 11-50%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
300 households
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
300 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Multinational company such as Monsanto Philippines, Inc. Continuously disseminate the technology through promotion of POWER herbicide
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improved production efficiency |
| Increase soil water storage |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction and flooding |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Labios, R.V. Et al. 200-2002," Conservation Tillage Practices in Corn Production After Rice: A Case in San Jose, Mindoro Occidenta"l. Pamhplet published by UPLB, DA-BAR, and National Corn RDE Network. P33
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Labios, R.V., Robles, A.Y., Javier, P.A., Garcia, M.U., Gonzales, P.G., Luis, E.M., Labios, J.D., Medina, C.M., Valencia, G.Z., Tamisin, L.L., Ocampo, E.P. Jr., Miciano, D.M. 1999. Annual Report. Enhancing Adaptation and Utilization of Location Sp
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Manalo, J.O. 2000. Tipid Saka Technology. Monsanto Philippines, Inc. 7th Floor Ayala Life FGU Center, Madrigal Business Park, Alabang, Muntinlupa City.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ