Minimum tillage in Mediterranean vineyards [ປໍຕູໂກລ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Carla Ferreira
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Minimum tillage
technologies_2879 - ປໍຕູໂກລ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Centro de Estudos de Rescursos Naturais, Ambiente e Sociedade (CERNAS) - ປໍຕູໂກລ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
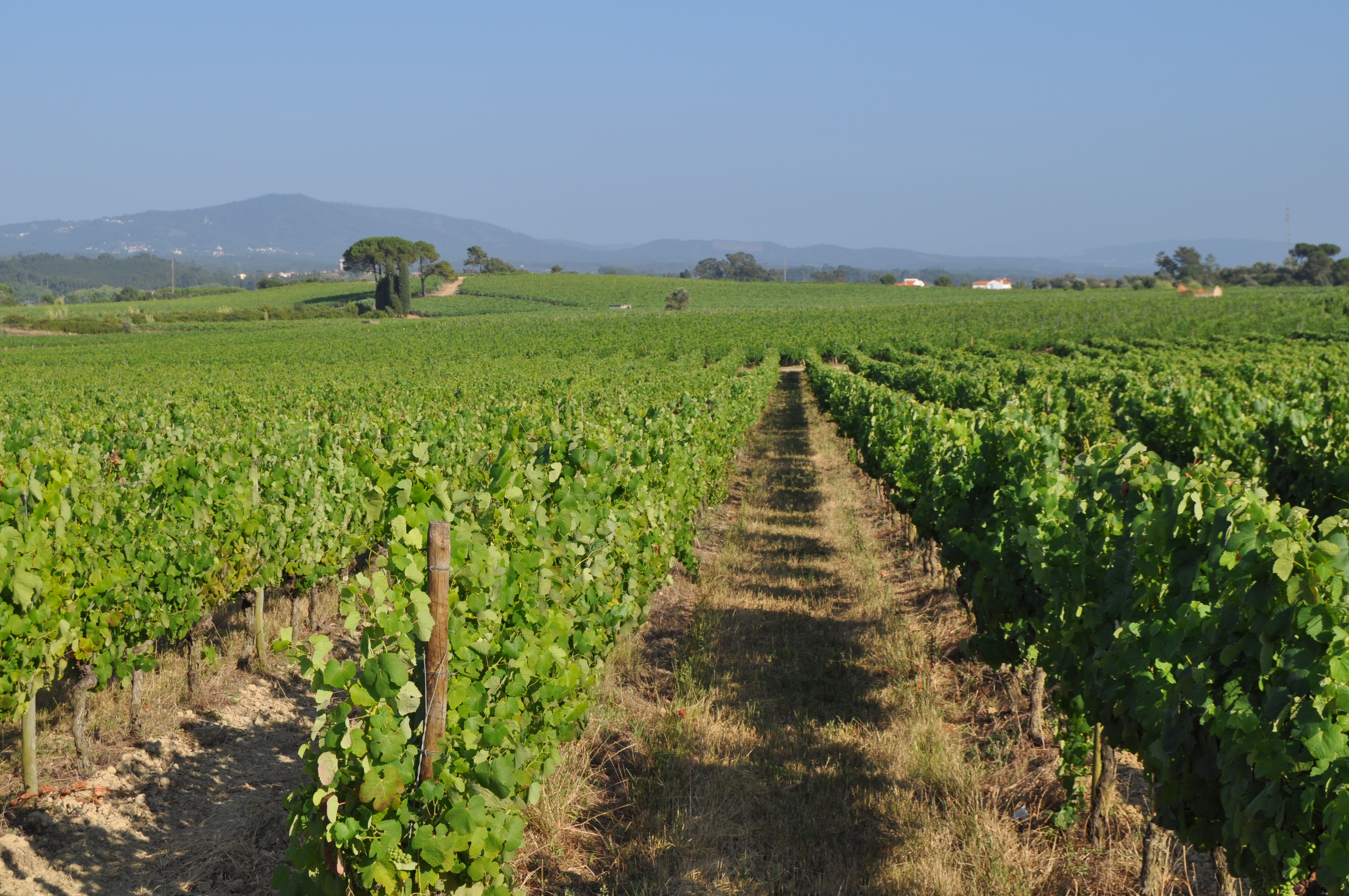
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in alternated inter-row zone, to promote soil decompation and maintain partial vegetation cover.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Portugal is one of the larger wine producers in Europe, with vineyard area covering 27% of permanent crops. Vineyards play an important role in the Portuguese economy, not only due to the impact of wine industry but also the important cultural heritage and great influence on tourism sector. There are thirteen specialized wine regions in the country, from which we highlight Bairrada region, located in central mainland, where minimum tillage is becoming popular. Bairrada has a Mediterranean climate, characterized by a long dry summer, although the strong influence of the Atlantic Ocean. Vineyard is the most relevant crop in Bairrada. In this region, farmland is mostly cultivated by landowners, comprising small winegrowers (5-10ha), most of them members of local farmers associations, as well as large producers (100-500ha) with a relevant position in the world wine market.
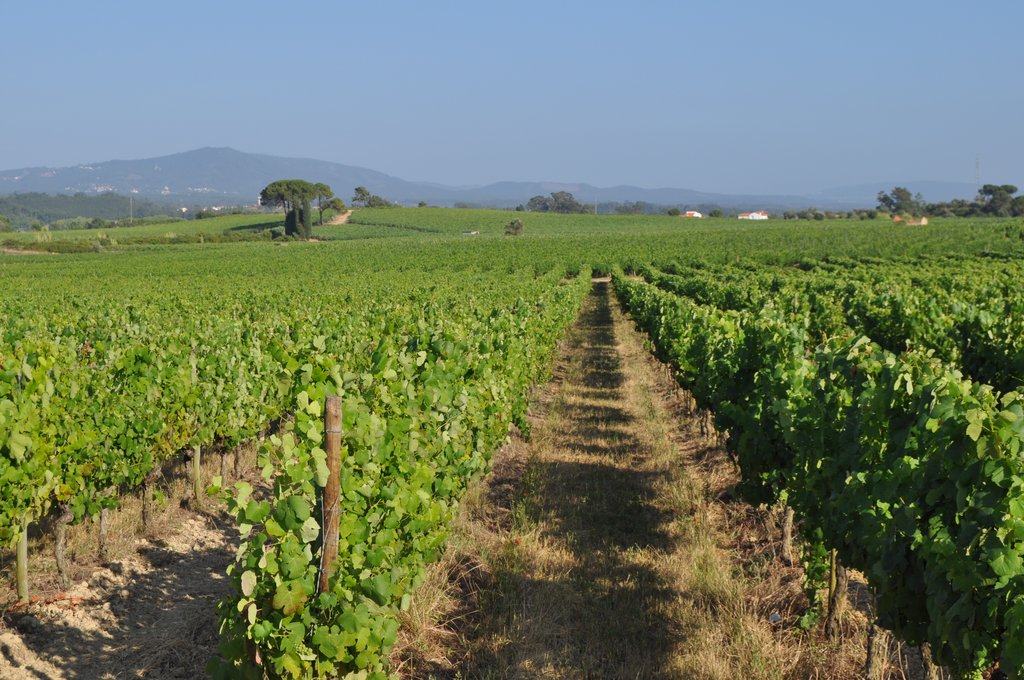
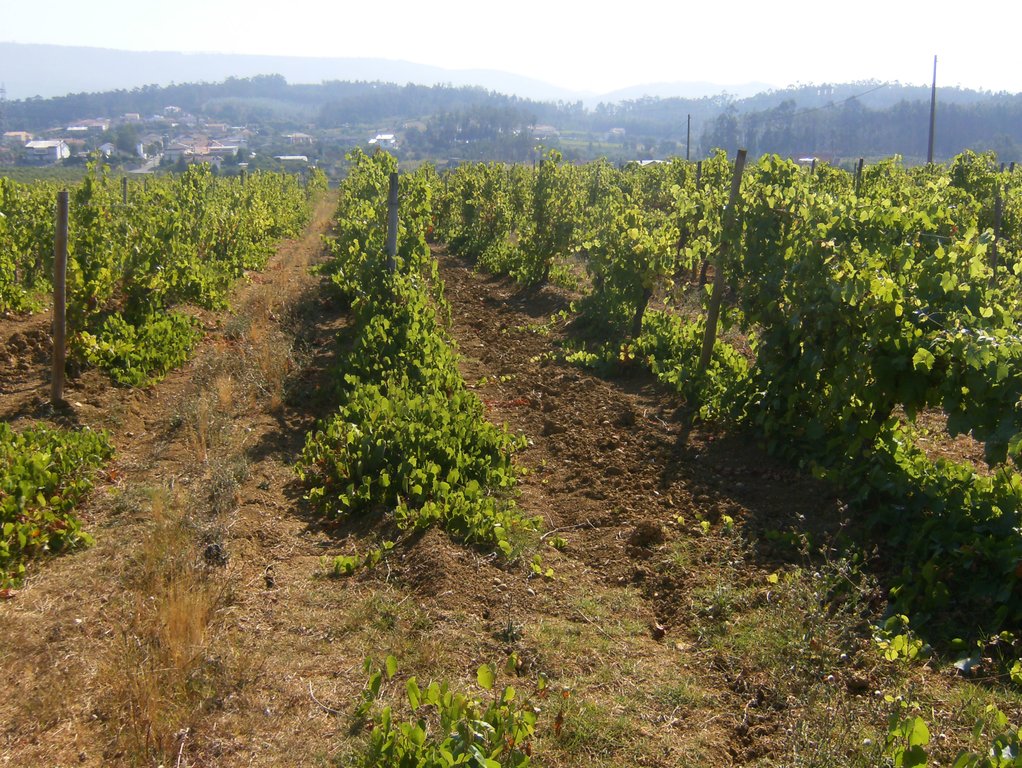
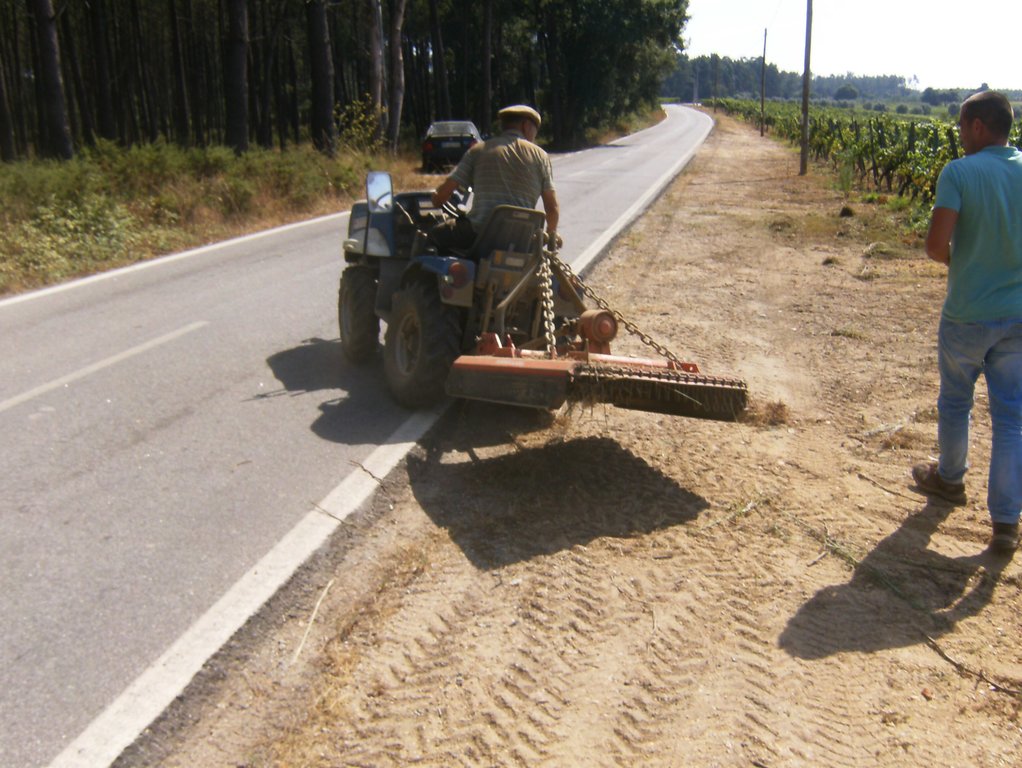
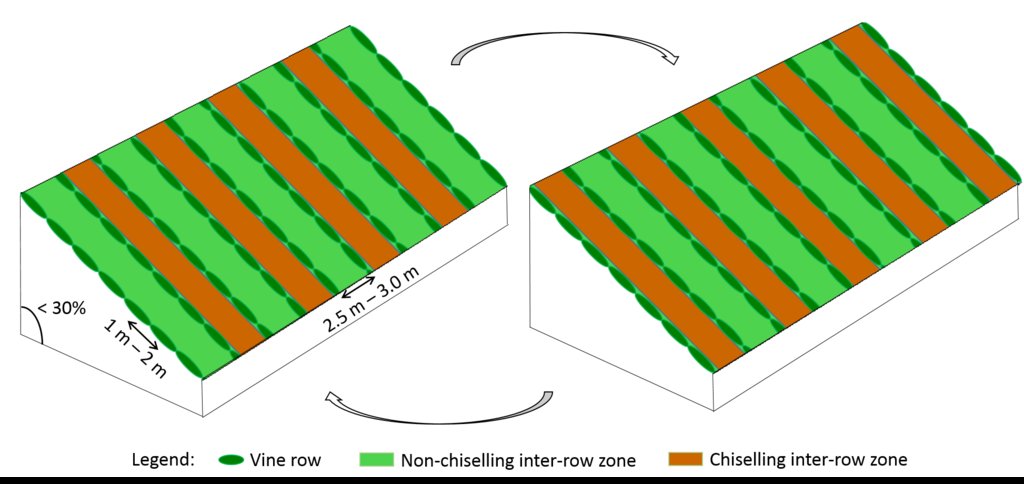
In vineyards, tillage is performed to promote de-compaction of the typical medium/fine soils and weeds control. In Bairrada wine region, soil tillage is usually performed twice per year – in autumn and spring, depending on weather conditions. Tillage is performed with a ripper and disc arrow (10-15cm), since mechanized vineyards require vines arranged according to horizontal wire bundles. However, tillage activities favour soil degradation, namely due to soil erosion and increasing mineralization of organic matter. In order to mitigate land degradation, minimum tillage of inter-row zone was adopted. No tillage is not applied by the farmers due to the need to de-compact the soil, favoured by the relatively high clay content. The minimum tillage is performed in alternated inter-rows, to keep vegetation cover in part of the vineyard. Tillage inter-row switch every time, so that each inter-row is not tilled more than once per year. Weeds control in the non-tilled inter-rows is performed using a rotary brush mower. In the plant zone, weeds are controlled with herbicides, applied twice per year: autumn-winter (before vine plant winding) and spring-summer (during vegetative growth). During the hot dry summer, weeds are naturally controlled due to water-stress. Mechanical intervention is also performed for pest and disease control, generally applied as preventive measures. Phytosanitary treatments are performed upon receipt of notices from Regional Directorate of Agriculture or technicians from local farmers association. These notices also include recommendations about the type of products and the application rate. In the majority of the Region, pruning and harvesting is performed manually. Pruning residues are typically mowed and left at the soil surface.
The adoption of minimum tillage was triggered by governmental subsidies. Farmers recognize the impact of this technology on the environment, namely on preventing soil degradation and enhancing biodiversity. However, soil compaction and water competition between vegetation cover and vines (over the summer) are major concerns.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ປໍຕູໂກລ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Bairrada, Central Region
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 100-1,000 ກມ 2
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- motivated by financial support from the government
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Technical recommendations provided by technicians of farmers associations.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດທີ່ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກລະແຊ້ງ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
One harvesting per year
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Vineyard
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
A3: ລະບົບການໄຖແຕກຕ່າງກັນ:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in the inter-row zone, in alternated lines switching between chiselling activities (10-15cm), usually performed in autumn and spring. There is no specific technical recommendations.
Vines are disposed horizontally, supported by wire or cord sustained by wood or metal support. Planting compass varies with soil fertility, type of wine, as well as expected quantity and quality of production, and desired height of the edges. Typically, distance between vine plants within each row ranges from 1m to 2m, and the inter-rows distance from 2.5m to 3.0m, leading to densities of 1000-3000 vines/ha. Generally vineyards are installed on natural surface profile for slopes lower than 30%, and in terraces for hillslopes of 30-50%. Vine plantation is forbidden for slopes greater than 50%.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Carla Ferreira
ວັນທີ:
26/06/2017
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
1 ha per year
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
euro
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.86615
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
30
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chiselling of alternated inter-row zone | Autumn/Spring |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control in alternated inter-row | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chemical control of weeds in plant zone | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸປະກອນ | Chisel | Equipment | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Rotary brush mower | Equipment | 1.0 | 1600.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Sprayer | Equipment | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 5100.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 5888.13 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
Young farmers (<40 years old) may submit agricultural projects for partial government funding.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The costs provided do not include the tractor aquisition costs.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeds control with herbicides (in vine rows) | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chiselling (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | For chiselling activities | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | For mechanical weed control | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | For spraying of herbicides | Person-days | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tractor with chisel | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tractor with rotary brush mower | 2.0 | 145.0 | 290.0 | 100.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tractor with spraying system | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Herbicides | Litres | 6.0 | 12.0 | 72.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 802.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 925.94 | |||||
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Machinery and labor
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1077.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
The climate is Mediterranean but with a significant influence of the Atlantic Ocean. The dry season extends from July to September and the rainiest period extends from November to February.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
10G/01UG from the Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Csb according with Köppen climatic classification.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Óis do Bairro: 5%; São Lourenço: 10%; Estação Vitivinícola: 9%; Quinta do Valdoeiro: 10%; Pocariça: 14%. Altitude ranges from 25m to 55 m a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
There is a lack of studies regarding biodiversity.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
- ຮັ່ງມີ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ການຮ່ວມມື
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Some of the farmers belong to large wine companies, which export the wine to several countries
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
- ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The area of land varies a lot. Individual farmers can have vineyards from 2-15ha, whereas large wine companies own up to 400 ha of vineyards in Bairrada region.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບໍລິສັດ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The state also own some vineyards devoted to research.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There are no measurements.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Although there are no measurements, it is expected less sediment and nutrient export (linked to decreasing runoff), thus less impacts on aquatic ecossystems.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Associated with decreasing chiseling activities
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ໂອກາດ ໃນການພັກຜ່ອນຢ່ອນໃຈ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Vineyards are relevant for tourism, thus, their sustainability is relevant.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Farmers associations provide knowladge and trainning to farmers.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Not measured, but available water in the water cycle is expected.
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There is no data, but decreasing runoff will contribute for lower sediment and nutrient exports, thus, improving water quality.
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There are no measurements, but field studies performed elsewhere report increasing soil moisture due to vegetation cover.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Maintenance of vegetation cover in half of the vineyard inter-rows. However, vegetation cover is limited during dry periods.
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Based on bibliography.
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Although there are no measurements, farmers report that ploughing activities are relevant to reduce soil compaction.
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
According with literature review, minimum tillage decrease the mineralization of organic matter.
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Not measured.
ຊະນິດທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Not measured, but expected given the partia maintenance of vegetation cover.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Decreasing runoff will contribute for decreasing downstream flooding
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less runoff and erosion will decrease downstream siltation.
ມົນລະພິດ ທາງນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less runoff will provide lower sediment and nutrient exports to rivers.
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Lower tractor activities contribute for less greenhouse gases emission.
ກໍານົດ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບທາງນອກ (ການວັດແທກ):
The impacts have not been measured. The response is based on literature review and field observations.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology does not have an impact on climate related issues.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ປານກາງ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 11-50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Less herbicides and ploughing decreases maintenance costs. |
| It allows to reduce herbicide application to control weeds, thus favouring biodiversity. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Minimum tillage is best suited for heavy, compacted and/or poorly drained soils, typical of vineyards. |
| It reduces land degradation, by improving soil structure and vegetation cover, important to reduce soil erosion. |
| Improving soil cover will improve soil moisture and aeration conditions, relevant for crop development and soil biodiversity. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction due to lower ploughing | Improve soil structure |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to maintain inter-row vegetation cover during the dry season | Replace vegetation cover by other materials (e.g. mulching) |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
More than 10 field visits were performed over a three month period.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
Seven
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Two
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
Several
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
01/05/2017
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Biddoccu, M., Ferraris, S., Pitacco, A., Cavallo, E. (2017). Temporal variability of soil management effects on soil hydrological properties, runoff and erosion at the field scale in a hillslope vineyard, North-West Italy. Soil & Tillage Research 165, 46–58.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716301386/1-s2.0-S0167198716301386-main.pdf?_tid=22418bb0-5b58-11e7-980c-00000aab0f6c&acdnat=1498582154_0fb04affbfbcf3f6e729ccdd354527ee
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Byrne, S., Guire, L.M. (2005) Vineyard Floor Management. Final report to Grape and Wine Research & Development Corporation (RT 04/03-1)
URL:
http://www.mvwi.com.au/items/526/Vineyard%20Floor%20Management%20RT%2004%2003%201.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Cruz, A., Botelho, M., Silvestre, J., Castro R. (2012) Soil management: Introduction of tillage in a vineyard with a long-term natural cover. Journal of Viticulture and Enology 27(1), 27-38.
URL:
http://www.scielo.mec.pt/pdf/ctv/v27n1/v27n1a03.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Napoli, M., Marta, A.D., Zanchi, C.A., Orlandini, S. (2017). Assessment of soil and nutrient losses by runoff under different soil management practices in an Italian hilly vineyard. Soil & Tillage Research 168, 71–80.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716302604/1-s2.0-S0167198716302604-main.pdf?_tid=34c1a784-5b58-11e7-8e6a-00000aacb35d&acdnat=1498582186_a97504bbec990b26b9de92901fae9b9b
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Puig-Montserrat, X., Stefanescu, C., Torre, I., Palet, J., Fàbregas, E., Dantart, J., Arrizabalaga, A., Flaquer, C. (2017). Effects of organic and conventional crop management on vineyard biodiversity. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 243, 19–26.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880917301603/1-s2.0-S0167880917301603-main.pdf?_tid=1428ce58-5b58-11e7-a61a-00000aacb361&acdnat=1498582131_0ca1f7a72aa834a0345b38122a2f7a05
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Raclot, D., Bissonnais, Y.L., Louchart, X., Andrieux, P., Moussa, R., Volts, M. (2009). Soil tillage and scale effects on erosion from fields to catchment in a Mediterranean vineyard area. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 134, 201–210.
URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880909002023/1-s2.0-S0167880909002023-main.pdf?_tid=3a75799e-5b58-11e7-8adf-00000aab0f6b&acdnat=1498582195_b808271c0c5bcddc3fa189cccc11fea3
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ