Agroforestry parkland [ຊີນີໂກ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Julie Zähringer
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1167 - ຊີນີໂກ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ສະວິດເຊີແລນຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
CSE (CSE) - ຊີນີໂກ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
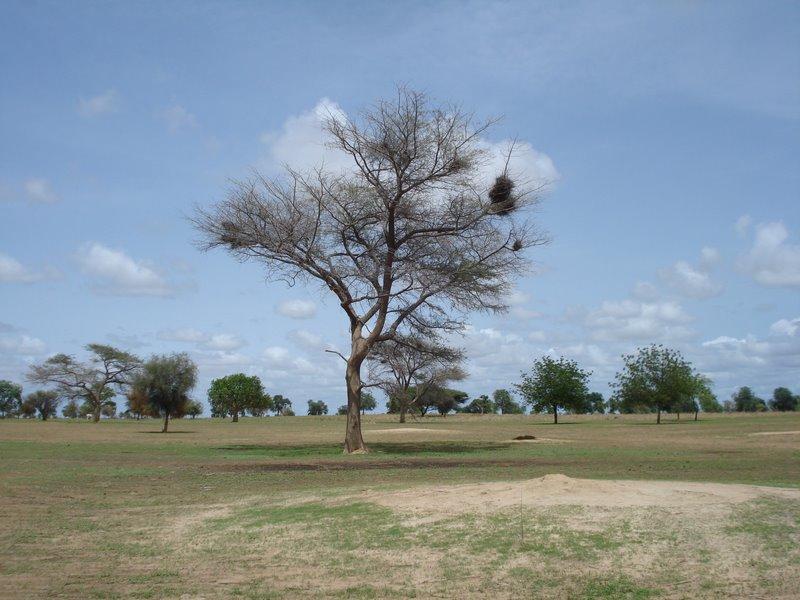
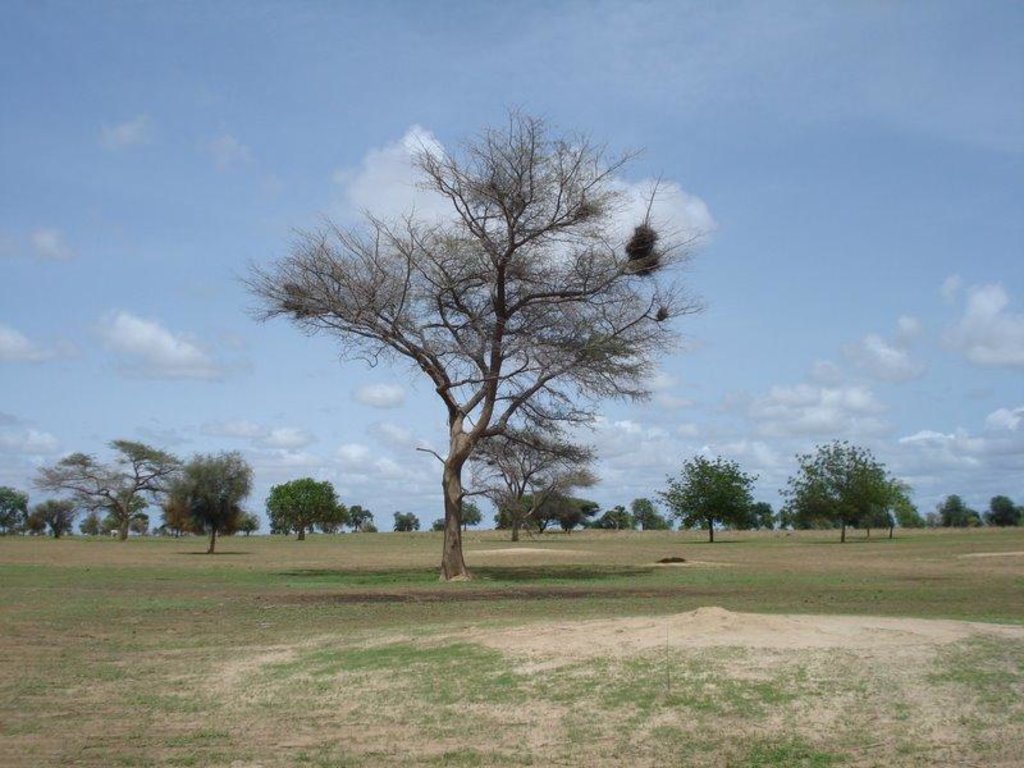
A traditional agroforestry parkland with scattered trees beneficial for soil properties (e.g. Faidherbia albida) or providing food for human beings and cattle (e.g. Sclerocarya birrea)
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Between scattered trees of which some were carefully selected for their positive influence on soil properties, either millet (Pennisetum typhoides), groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) or watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) are grown in rotation. The dominant tree species are Faidherbia albida (syn. Acacia albida), Sclerocarya birrea, Sterculia setigera and Combretum glutinosum. Some of the species were introduced from elsewhere and planted by land users when they settled in the area. Other species regenerated naturally in the fields and were protected till they reached mature age. F. albida sheds it's leaves at the beginning of the rainy season increasing soil nutrient stock for the cultivation period and reducing competition with crops for light. Sclerocarya birrea is widely appreciated by cattle for it's nutritious fruits. Cattle resting in the shade of the large trees provide free organic manure. Mulching and manure application are common means to improve soil organic matter and nutrient content in this remote area where access to inorganic fertilizers is very limited due to inaccessibility.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objectives of this parkland system are to enhance crop production through improvement of soil properties with the help of trees, the provision of supplementary food for cattle in the form of fruits and the availability of certain plants (or parts of them) for traditional medicine.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology has a long tradition in more southern regions of Sénégal and was brought to the Ferlo by Wolof people that moved to this zone in the search for cultivable area. Knowledge is transferred from parents to their children. Except for the purchase of seeds for cultivation of the fields there is no financial inputs required for this system.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. Rainfed agriculture under agroforestry parkland in a belt around the main village is the main landuse type in the area. In a second circle, extensive pastoralism is practiced and forest resources are being exploited. Presence of insects and wild animals (monkeys, warthogs) damaging cultures and the lack of sufficient rainfall are main constraints mentioned by landusers in the area. Degradation of vegetation cover is widespread. The bare soils are prone to wind erosion, a common phenomenon in the area, carrying away the arable soil horizon and causing a decline in soil fertility. In general, the local population has signaled a decline of land degradation due to the widely practiced tradition of SLM technologies.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຊີນີໂກ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Louga
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Linguère / Barkédji
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 0.1-1 ກມ 2
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
introduced from the more southern parts of Sénégal by Wolof farmers
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ເຂົ້າຟາງ
- ພືດປະເພດເມັດໃຫ້ນ້ຳມັນ-ຖົ່ວດິນ
- ຜັກ-ໝາກໂມ, ໝາກອື, ໝາກບວບ ຫຼື ໝາກນ້ຳ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul-Oct
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major cash crop: Millet, groundnut, watermelon
Major food crop: Millet, groundnut, watermelon
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): deforestation, wind erosion causing loss of topsoil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): rain insufficience and presence of insect pests
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການປັບປຸງແນວພັນພືດ / ແນວພັນສັດ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (due to domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (oversized herds of cattle), droughts, population pressure, poverty / wealth (poverty)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mulching
Material/ species: plant residues after harvest
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure from cattle faeces
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 8
Trees/ shrubs species: Faidherbia albida, Sclerocarya birrea, Sterculia setigera, Piliostigma reticulata, Balanties aegypti
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selection or planting of trees | |
| 2. | removal of unwanted tree species |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds | 1.0 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 100.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1.68 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 1.68 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Lifespan of the product: 1 season (120 days)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | application of manure and mulching | |
| 2. | sowing of millet / groundnut | june |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
No cost is involved with organic manure as it can be obtained by giving nomadic Fula herders the right to let their cattle rest in the shade under the trees or feed on plant residues
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
300-400 mm during one rainy season / length of dry period: 9 months
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage / infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: High
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
30% of the land users are average wealthy.
70% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: livestock raising
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (by horse)
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
fruits of Sclerocarya birrea
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
because of availability of plants used in traditional medicine
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
mulching
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
mulching
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
litterfall, organic manure
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
16
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology is already being practiced by the whole population of this village
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
|
increased crop production How can they be sustained / enhanced? protect trees in fields |
|
increased availability of fruits for humans and cattle How can they be sustained / enhanced? protection of trees producing fruits appreciated by humans or cattle |
|
increased availability of plant products used in traditional medicine How can they be sustained / enhanced? protection of trees providing these products |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
increase of soil fertility and organic matter through trees How can they be sustained / enhanced? encourage further plantation or natural regeneration of tree species beneficial for soil properties |
| no costs involved with maintenance of technology |
|
carbon storage below and aboveground How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree density |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| loss of cultivable area due to trees in field |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| natural regeneration practically absent, continuity of parkland threatened | tree planting or assisted natural regeneration if present |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ