Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Daler Domullojonov
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Пуркунии селрохахо
technologies_1450 - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Barotov Bahrom
Welthungerhilfe
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Ashurov Bakhtiyor
Welthungerhilfe
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Reclamation and infilling of eroded gullies using barriers of willow branches and live mulberry cuttings to trap loess soil from surface water runoff.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
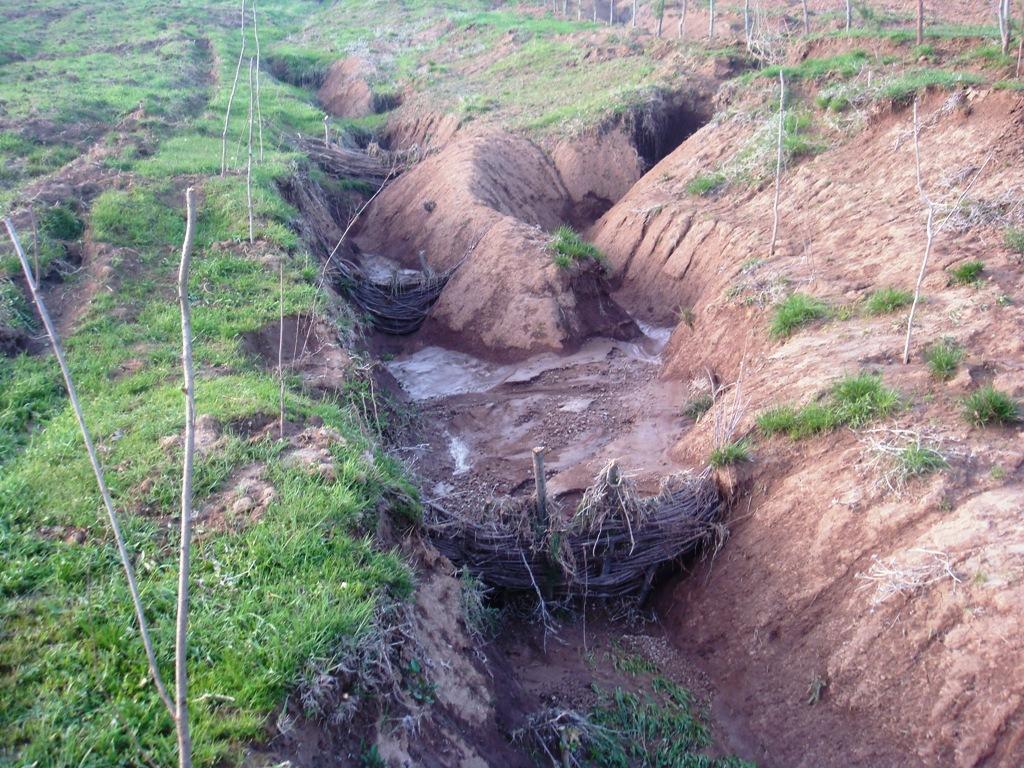
Due to many different factors and mechanisms, soil erosion is at an advanced stage in many of the hilly and mountainous parts of Tajikistan. After disrupting the soil cover in steep areas, starting the process of soil detachment and transportation water runoff gets concentrated into specific areas. As a result, rills develop on the steep areas, and eventually enlarge into gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, low cost barriers are constructed from flexible living branches of a sprouting variety of tree, such as willow. These branches are placed along the gulley at intervals of 3-10 metres, so that they slow down the flow of surface water and trap the sediment, thus eventually filling in the gulley over a period of several years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The barriers are designed to slowly help infill eroded gullies by trapping the sediment from muddy surface water runoff. This helps prevent further erosion, increases the amount of land available for pasture, and reduces the risk of mud flows or floods further down the slope.
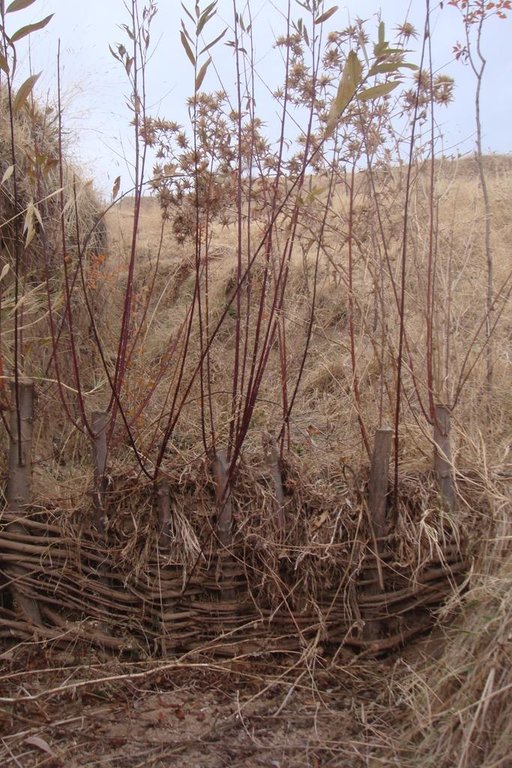
In gullies no wider than 1-2m, live cuttings from local tree varieties with a diameter of 3-5cm and 1 metre in length can be used to establish horizontal woven barriers across the gulley. The barriers are placed at 3-5m intervals along the gulley, starting at the base.
These barriers are constructed from cuttings that are woven in narrow sections with 5-6cm intervals between them. Enforcement and strengthening of these plugs can be achieved through the use of long branches of locally available mulberry. The height of the plug should not exceed 0.5m. The construction activities start in the spring and within several weeks some of the cuttings begin to sprout and grow. To avoid erosion at the sides of the structure, the cut offs are embedded into the sides of the gulley.
Natural / human environment: Gulley plugging is used in pasture land that suffers from overgrazing, deforestation and trampling, which has resulted in the degradation of the soil. Subsequently, the soil has become more vulnerable to the impact of heavy rain in the spring and autumn months, and is prone to erosion from surface water runoff.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tajikistan / Khatlon
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Khovaling / Dorobi
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.017 km2.
Approximately an 800 m long eroded gully was reclaimed.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The technology was developed and promoted using the framework of EC TACIS funded Welthungerhilfe project in Khatlon
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກເບີລີ

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ແບ້
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ
- ແກະ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing on pasture lands, that leads to reduced vegetation cover and deforestation, contributes greatly to the causes of top soil erosion and gulley formation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies are formed after intensive rainfall events. There is nothing in place to stop this erosion.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cows, goats. sheep
Grazingland comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of grazing system comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ແມ່ນ (ກະລຸນາຕື່ມໃສ່ ຄຳຖາມຂ້າງລຸ່ມນີ້ກ່ຽວກັບການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ກ່ອນການທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ)
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກເບີລີ

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: March - June
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ມາດຕະການ ຕັດຂວາງ ກັບຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S6: ແລວກັນເຈື່ອນ, ຮົ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Trees were cut from a steep slope on the side of the hillside.), overgrazing (Freely grazed area, carrying capacity less than animal numbers grazing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More intensive rainfall.), land tenure (Lack of control of livestock grazing activities.), poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Gullies appeared after civil war.)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
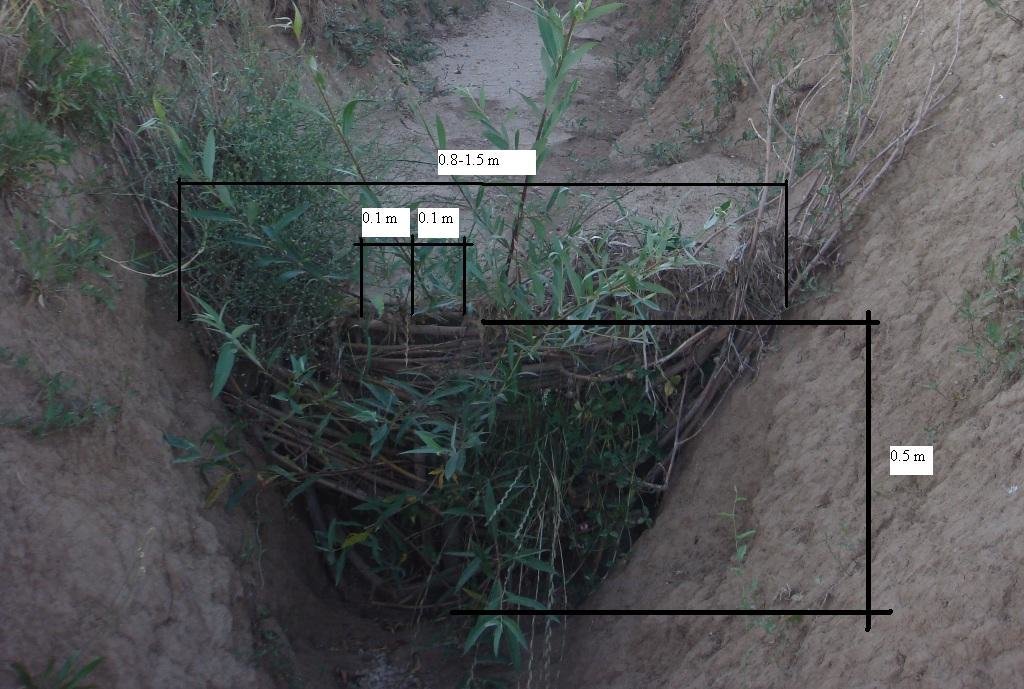
For the plugging of the gully, a low cost and simple barrier was made from locally available fast sprouting species of trees; in this case live willow cuttings were used. In the gully a narrow section was selected, and cuttings (3-5 cm diameter, 1 m length) were placed in a line with 10 cm intervals in between. One third of the cuttings were planted in the gulley, and the rest were used to create a 'wave' wall of flexible branches, which was planted with local mulberry trees (1-1.5 cm diameter). The weaved branches have to be pushed down from the top to make the barrier suitably dense. The ends of the mulberry branches have to be stuck securely to the soil inside the gulley.
Location: Dorobi village. Khovaling / Khatlon / Tajikistan
Date: 2nd July, 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: mulberry
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Construction material (wood): Willow and mulberry branches
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem street, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Tajik Somoni
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4.5
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
5.50 $
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting mulberry in willow wave structure | spring |
| 2. | establishment of barriers in gully bed | once in the beginning |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Planting mulberry | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Establishment of barriers in gully | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 90.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 20.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce structure with additional seedlings when needed | annually |
| 2. | establishment of additional barriers after filling existing barriers with sediments | once per year in beginning of rainy season |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Reinforce structure | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Establishment of additional barriers | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 90.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 20.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The unit cost is for a gulley plug, 1.5 metre wide and around 1m in height.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The materials used to construct the gulley plug are locally available, and are therefore free of charge to the land user. The labour (or time in labour) is the most substantial cost, and this is directly proportional to the number of gulley plugs required to infill the entire eroded gulley. If there is a big sediment load in the surface water runoff it will back fill behind the gulley plugs rapidly and additional barriers will need to be established.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Precipitation is concentrated during the autumn and spring, averaging 1100-1200mm
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Altitudinal zone: 1257 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Average slope 12.6%, max slope 17.2%
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil texture = loess soil
Soil fertility is low due to over use and lack of fallow time.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
> 50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Availability of surface water: In the area around the gulley the land is compacted.
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
20% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The trees can be harvested once the gulley is full of sediment.
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
1.5
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
1.6
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Gully filling can help create new areas of arable land.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
Livelihood and human well-being
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Sediments are trapped
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງດິນ / ຊາກສະລະຫະພັງ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
As a living barrier it needs to grow, and therefore it is sensitive to drought conditions.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- > 50%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
10 households in an area of 1.7 ha
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
|
No training and additional skills are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Broad promotion to other communities with similar climatic conditions and similar issues. |
| It is low cost option. |
| Easy to establish, with a low workload. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Gulley plugs are relatively easy to construct and have a low initial outlay. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be further supported by the strong involvement of local authorities, through the organisation of cross visits, and disseminating ideas between farmers. |
| It is flexible as various varieties of local sprouting trees can be used to build the gulley plug. |
| It can prevent further erosion and expansion of the gulley. It can also increase the amount of land available for pasture activities. |
| Environmentally friendly |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The gulley plug is weak in the beginning as the mulberry trees become more established. It is more susceptible to the impact of heavy rainfall events and concentrated run off down the gulley. | High levels of maintenance in the first initial few seasons. |
| The gulley plug becomes less effective as the gullies become wider and deeper. | Fencing around the gulley. |
| The gulley plug has to be protected from livestock who will eat the vegetation. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Welthungerhilfe projects in Khatlon region, Temurmalik district
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ