Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses [ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_1459 - ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: Jan. 4, 2017 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: July 19, 2017 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: Aug. 20, 2019 (inactive)
- Reduced pressure on forest resources by improved thermal insulation in private houses: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Zevarshoev Rustam
Retail Cooperative "Zindagi"
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
1.5 ແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ອ້າງອີງເຖີງແນວທາງ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ໄດ້ເຮັດເປັນເອກະສານທີ່ໃຊ້ WOCAT)
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
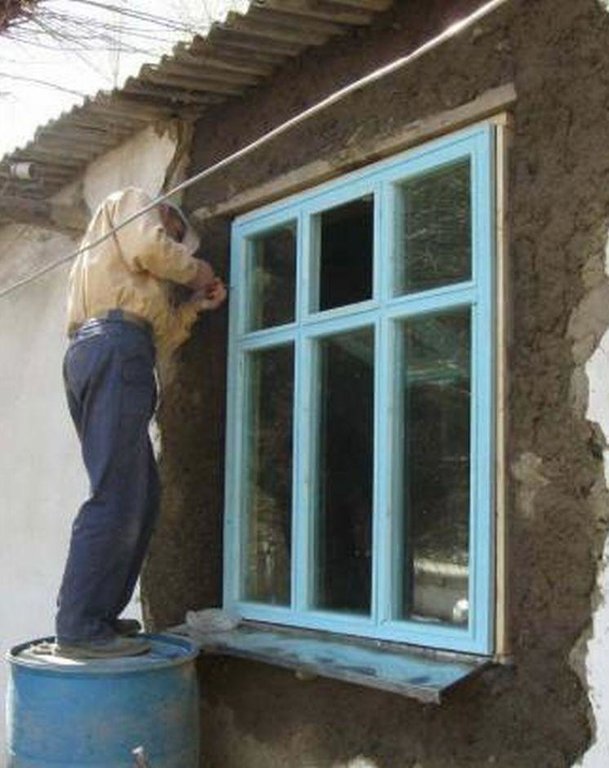
Thermal insulation of private houses with energy efficient products to reduce the fuel-wood demand and pressures on the natural environment.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
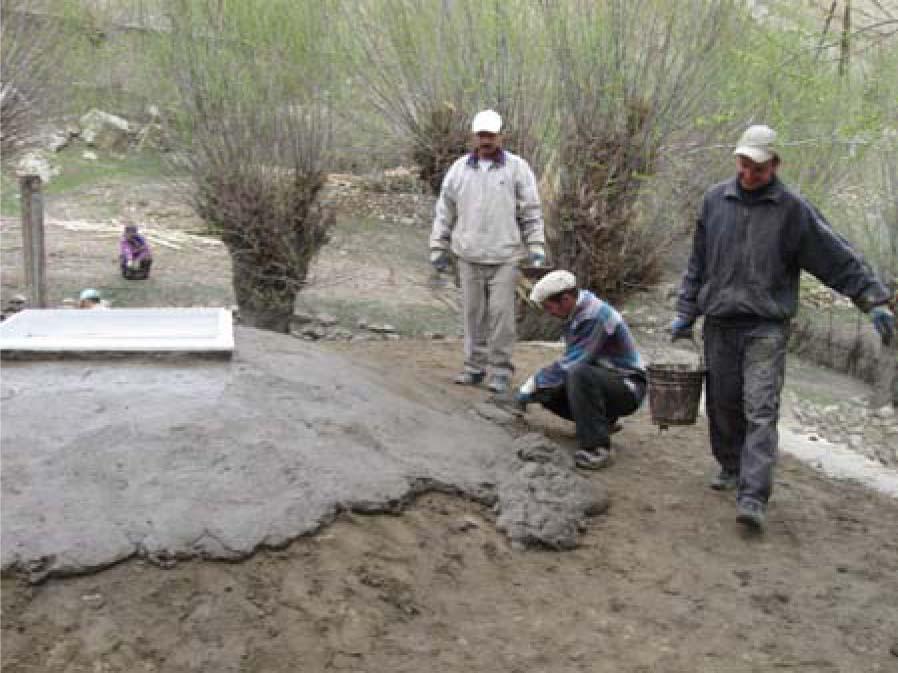
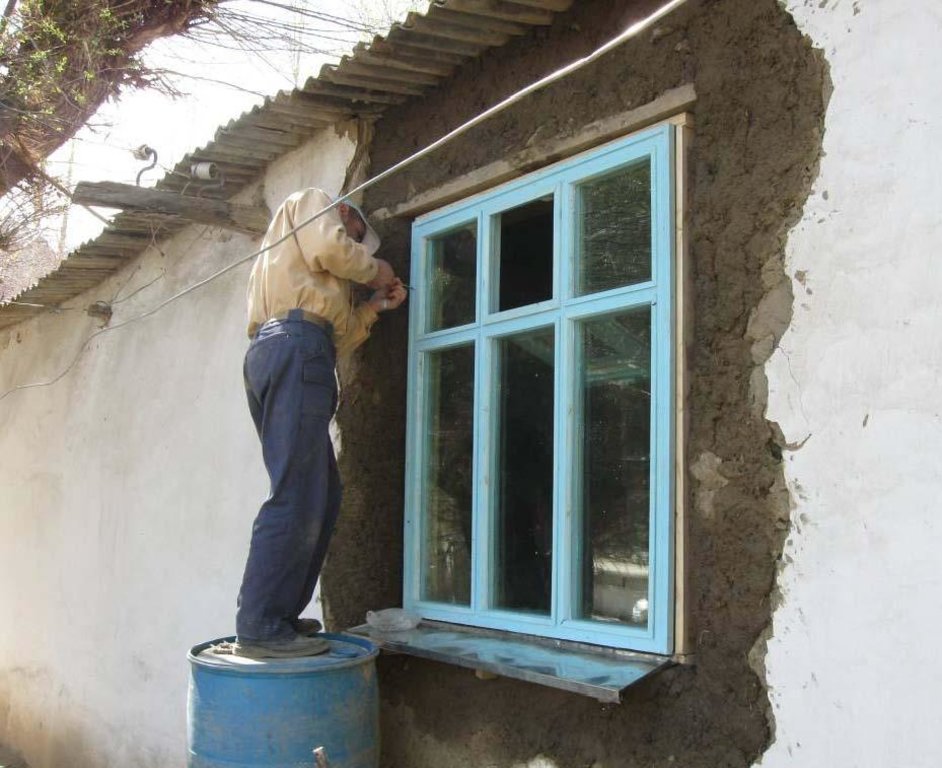
Well insulated doors and windows are installed together with thermal insulation of the ceilings and floors in houses in the remote villages of the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region. Improved quality windows and doors, as well as improved thermal insulation of the houses contribute to retain the heat inside, which is one of the main problems in many of these traditionally built houses. The quality of the materials used to produce the products as well as the quality of the product itself and its installation process are ensured through using locally trained craftsmen. Local available organic materials such as sawdust, straw, water plants, leaves and others can be used as thermal insulation material for walls, floors and ceilings. The materials should be dry and free of insects. The local labour market plays a crucial role in the technical accurate performance of the thermal insulation measures. Therefore the local labour market has to be analysed and training needs for the craftsmen have to be defined, e.g. for producing double-glazed windows and improved doors, as well as insulating walls, ceilings or floors, and the installation of windows and doors in accordance to the defined and standardised thermal insulation measu
Thermal insulation contributes to the reduction of heat exchange between indoors and outdoors and therefore may have two main effects: Less fuel may be needed to heat the houses, or using the same quantities of fuel the temperature indoors can be significantly increased. A reduction in fuel consumption means a reduction either of financial expenses or of labour, so the saved money or time can be used for other purposes - ideally for making investments and creating additional income sources. Higher and more constant indoor temperatures can contribute to a reduction in health risks and to increased quality of life during the winter period. Going beyond the level of the individual household, a reduction in fuel consumption means less pressure on natural resources: The less firewood that is used for heating, the less trees will be cut down and the less the forests will degrade. Also the less manure that is burnt in the stoves means more of it can be used as fertilizer on the arable land. In this framework many of the economical, social and environmental problems could be mitigated if houses were properly insulated.
A technical assessment of the identified house for thermal insulation is carried out to investigate which materials are used for the construction of the house, and to identify measures and materials that could be used for thermal insulation purposes, in order to be able to offer the most technically appropriate solution, which is adapted to the local cultural and climatic conditions. The organic thermal insulation material should be prepared in advance to make sure it is dry and clean. The designated area whether it is the floor, ceiling or walls should be cleared of furniture and other things items. Electric wires should be safely removed, or covered adequately for safety reasons to prevent fire. In the case of the roof, the insulation material is laid out evenly on the surface to a thickness of 15-20 cm depending on the type of organic material which is used. The lime is then spread out over the organic insulation material. For 1 m2 about 1-1.5kg of lime is required. The material is thoroughly tamped down to reduce subsidence of the protective cover, which will be put over the insulation material. A mixture of clay, straw and water is prepared to form a substance with a solid consistency to prevent the surface from cracking when it dries. This clay and straw mixture is then spread evenly on the surface about 4-6 cm thick, ensuring that the whole insulation material is covered. The surface should dry in 24 hours after which some cracks might appear and if this happens then a liquid mixture of clay and sand is used to flatten the area left to dry again. The same process is applied to the floors, and the more complex roof thermal insulation materials where roof felt is used as a basis for the organic insulation material as it is moisture proof. The windows and doors as well as these insulated areas in the house should be properly maintained. It should be ensures that there are no leaks in the roof so that the ceiling insulation is kept dry.
Riparian forests in the Western parts of Gorno-Badakhshan and Teresken shrubs on the high plains in the Eastern parts are almost completely destroyed due to their excessive use as a fuel for heating and cooking, and their overuse as areas for pastures. Manure, as one important natural fertilizer for agriculture, is no longer available in large quantities and so the fertility of soil has decreased. In the Eastern Pamirs, although the area is scarcely populated, Teresken shrubs have been used excessively as a fuel and are no longer found within 70km around the only major settlement of Murgab, which has resulted in massive soil erosion and degradation of pastures in this area. The situation is worsened by the fact that the local, mostly traditionally built houses are poorly insulated, low quality doors and windows do not preserve the heat inside during severe cold temperatures. Constant heating is thus necessary meaning households burn large amount of natural fuel resources to keep their houses warm. The thermal insulation technology should contribute to ease the pressure on the natural resources in the GBAO area and allow natural regeneration of forests and Teresken shrubs.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຕາຈິກິສະຕານ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tajikistan, Gorno Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (GBAO)
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Roshtkala, Shugnan, Murgab and Ishkashim
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 100-1,000 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology was implemented in several regions of GBAO.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The technology was developed and introduced through GIZ project. Gradually Retail Cooperative "Zindagi", established by GIZ is taking the project over.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- (ເຄິ່ງ) ປ່າໄມ້ທໍາມະຊາດ / ປ່າປູກໄມ້
(ເຄີ່ງ) ປ່າທໍາມະຊາດ / ປ່າປູກ: ລະບຸປະເພດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ:
- ການຄັດເລືອກຕັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງ
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ໝາກໄມ້ ແລະ ແກ່ນຖົ່ວ
- ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
- ພະລັງງານ: ທໍ່, ສາຍໄຟຟ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to a shortage of energy sources, wood, teresken and manure are extensively used for heating private houses; natural resources are therefore severely overused, which has resulted in degraded land, destroyed forests and lack of natural fertilizer for agriculture; poor thermal insulation of houses also leads to increased demand for fuel.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Unable to heat their houses properly during cold winters; shortage of fuel for cooking and heating; during cold winters, fire wood becomes so scarce that even fruit trees are cut down.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?

ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານ, ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ປະສິດທິພາບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການນຳໃຊ້ພະລັງງານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V5: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S11: ອື່ນໆ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Exploiting forest resources for heating and cooking.), poverty / wealth (Most people can't afford to buy other fuel such as coal or gas.), Lack of finances
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Extremely cold winters force people to cut down excessive amounts of wood for fuel), change of seasonal rainfall (Less precipitation), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy periods of rainfall), population pressure (Population growth leads to increasing demand for wood for fuel.), Destroyed infrastructure
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
This diagram with photos shows the different thermal insulation measures.
Location: Ishkashim. Ishkashim, GBAO, Tajikisatan
Date: 26-02-2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Increased technical knowledge)
Technical knowledge required for craftsmen: high (Increased skills in producing well insulated doors and windows.)
Technical knowledge required for construction workers: high (Advanced skills in installation of thermal insulation products.)
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), Reduced heat loss from houses, Reduced fuel consumption
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use practices / intensity level
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Tajikistan
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
somoni
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4.6
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of window 1.40x1.30 | Any time |
| 2. | Installation of door 2.00x0.90 | |
| 3. | Thermal insulation |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | labour | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | door | ha | 1.0 | 133.0 | 133.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | window | ha | 1.0 | 126.0 | 126.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Isolation material | ha | 1.0 | 126.0 | 126.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 402.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 87.39 | |||||
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The labour costs are indicated for installation of one window/door. With regards to the thermal insulation the labour costs are higher, so they are calculated per square metre of the area where thermal insulation will be applied.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The costs for the installation of windows and doors depends on their size and also whether additional work has to be done to fit the door or window hatch to the required size. With regards to the thermal insulation the costs are estimated based of the size of the area in square metres, whether it is the floor, ceiling or wall.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
In Murghab District annual rainfall is below 200mm. Around Khorog annual rainfall is 480mm.
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
Thermal climate class: temperate, boreal
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3% (If creditworthy, they can participate through micro-loans schemes.).
Off-farm income specification: The majority of households rely heavily on remittances from Russia.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Save money from buying fuel and electricity
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Income of craftsmen increased.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Less time needed for fire wood collection
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Warmer houses reduce health risks.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Improved knowledge on energy efficiency and insulation measures.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Opportunity to improve living conditions and save money.
contribution to human well-being
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In general, people save money on energy sources and spend less time collecting wood and animal dung from the field. Houses are warmer, which can be beneficial for the family's health.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Up to 45% less wood used for fuel.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In Murghab District teresken used as fire wood is the main fodder for wild animals (e.g. deer, gazelles)
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Protection of riparian forests.
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Protection of riparian forests.
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ລົມ ທີ່ພັດເອົາຕະກອນ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
| Extreme cold temperatures | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
168 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The households take a micro loan with an affordable low interest rate to install thermal insulation products. The micro loan is not provided in the form of cash, but in kind, i.e. the products and installation.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: When one household installs quality windows or doors or has its house insulated, the effects are visible not only to that given household but also to neighbours and other visitors. As a result the number of people interested in installing such technology to their homes is increasing.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Costs of firewood reduced |
| Warm and comfortable houses |
| Reduced workload |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| If implemented on a larger scale can prevent overuse of natural resources for fuel. |
| Incentives in form of micro loans to make the technology more accessible to local people. |
| Reduced workload and costs spent on buying fuel. |
| Imported timber used to produce doors and windows. |
| More fertilizer available. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Lack of skilled craftsmen | Improved professional craftsmen education through training courses. |
| Lack of modern equipment to produce wooden products | Financial support to supply the local craftsmen with modern equipment to further improve the quality of the products and increase the rate the production process. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
24/01/2011
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ