Geocoding of Million Fruit Trees for Monitoring and Tracking [ບູຕານ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Nima Dolma Tamang
- ບັນນາທິການ: Haka Drukpa
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Not Applicable (NA)
technologies_6829 - ບູຕານ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
Agriculture Extension Officer:
Penjor Thuji
Geog Renewable Natural Resources (RNR) Center, Agriculture Office, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
ບູຕານ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - ບູຕານ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology enables remote monitoring of the growth and development of fruit trees ensuring the sustainable use of land and its resources. Further, the technology aids in the success of the Million Fruit Tree Plantation Project reducing the risk of converting cultivable land to fallow.
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Geocoding of fruit trees allows remote monitoring and progress tracking of the growth of seedlings. The Smart App MoDA (Mobile Operation and Data Acquisition) is used in geocoding.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດທົ່ວໄປທີ່ກ່ຽວກັບຮູບພາບ:
The Photo does not directly depicts the technology described here.
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ບູຕານ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Thimphu Dzongkhag
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The geocoding of fruits are in the land users field. Therefore, the area does not fall under any of the protected area or national parks.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸປີ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
2022
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The geocoding of the million fruit trees in the country was initiated as per the directives of His Majesty the 5th King of Bhutan where all the saplings are funded by the Royal Government of Bhutan. Plantation and geocoding were done by the Desuups (Desuup is the highest form of the voluntary act in Bhutan. They wear orange uniforms and are also known as the Guardians of Peace).
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ເຂົ້າໄຮ່
ລະບົບການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ:
ເຂົ້ານາ-ເຂົ້າສາລີ
- Apple
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Paddy in summer is followed by winter wheat or vegetables
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
They intercrop vegetables with lugumes.
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The land used for paddy cultivation is used for planting vegetables such as potatoes.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການປັບປຸງແນວພັນພືດ / ແນວພັນສັດ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology aids in maintaining land cover by ensuring vegetative coverage of the land in which geocoding enhances easy management and improved health of the fruit trees such as apples, dragon fruit, banana, areca nut, kiwi, avocado and others.
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Fruit tree plantations will potentially prevent land degradation in the long term by giving cover and strengthening soil structure by its roots.
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
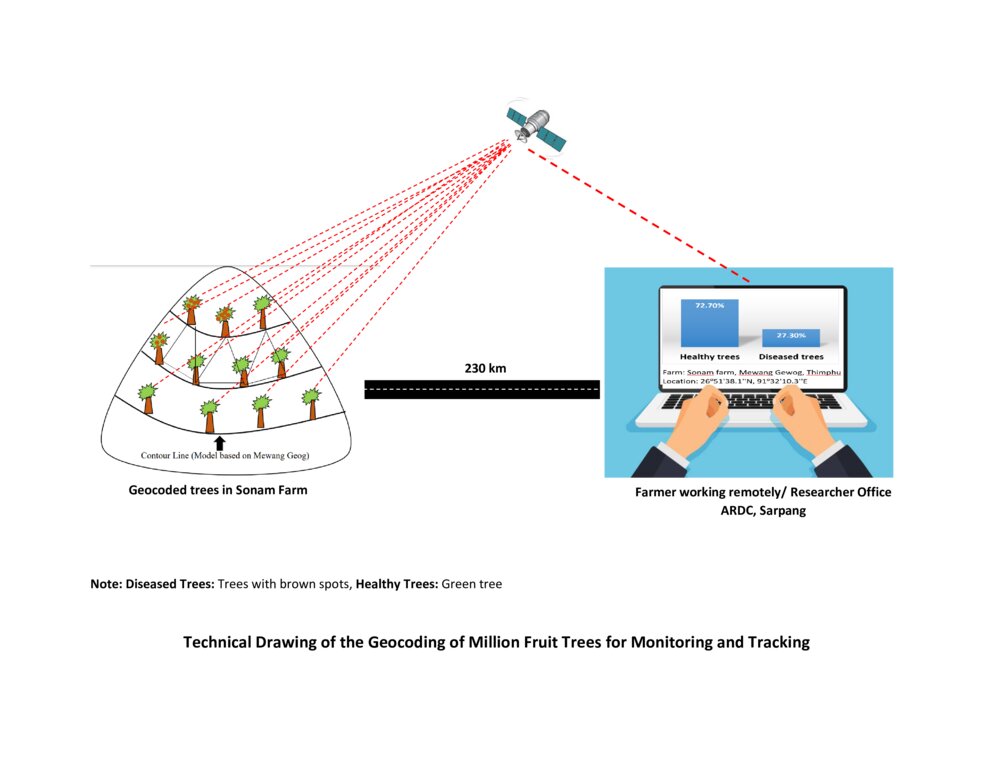
The technical drawing represents the general method of million fruit tree plantation and geocoding done on each tree. It depicts how geocoding enables the researcher or farmer to remotely check the health of the trees using satellite data. ARDC stands for Agriculture Research and Development Center.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Nima Dolma Tamang, Singye Dorji, Tshering Gyeltshen
ວັນທີ:
07/07/2023
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
No of Seedlings
ກໍານົດຂະຫນາດຂອງຫົວນ໋ວຍ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
8000 seedlings (Only in Mewang Geog)
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
82.62
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
800
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting between Gewog leaders and land users | NA |
| 2. | Identified a village for planation | NA |
| 3. | Identified households that wanted the seedings and number of seedlings | NA |
| 4. | Site identification | NA |
| 5. | Orchard layout | NA |
| 6. | Pit digging | NA |
| 7. | Plantation | March- April |
| 8. | Basin making | After planation |
| 9. | Geocoding | After one month of orchard establishment |
| 10. | Growth Tracking | After every six months |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The above information is limited to only Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag.
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6.0 | |||
| ແຮງງານ | Farmers | Person-days | 10.0 | 800.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Shovel | No. | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| ອຸປະກອນ | crow-bar | No. | 5.0 | 100.0 | ||
| ອຸປະກອນ | Spade | No. | 20.0 | 100.0 | ||
| ອຸປະກອນ | GPS remote | No | 6.0 | 12000.0 | 72000.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6.0 | 15000.0 | 90000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Apple | No. | 3500.0 | 70.0 | 245000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Walnut | No. | 1000.0 | 120.0 | 120000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Almond | No. | 500.0 | 120.0 | 60000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Peach | No. | 1000.0 | 70.0 | 70000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Pear | No. | 2000.0 | 70.0 | 140000.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16.0 | 1600.0 | 25600.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 830600.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 10053.26 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
Almost all the cost were covered by the Million Fruit Tree Project of Desuung National Service and Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock jointly.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The total cost calculated is for planting and geocoding. The actual costs borne by land users are very minimal. The only cost the land users have to bear is labour cost and fertilizer cost. The high cost of the project is contributed mainly by seedling cost, GPS remote, tablets and mobile phones which was used during the marking position of fruit trees.
Cost for shovel spade and crowbar is not included as they are available at the farm and are reused.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Twice a year |
| 2. | Fertillizer application | Twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | Once a week |
| 4. | Replacement of dead plants | After 6 months from plantation |
| 5. | Growth tracking | After every six month |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The information obtained are through verbal communication with the Agriculture Extension Officer of Mewang Gewog.
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4.0 | 1600.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| ແຮງງານ | Geocoding | per plant | 8000.0 | |||
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Replacement of plants | per plant | 10.0 | 70.0 | 700.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 7100.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 85.94 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The geocoding was done by the Desuung volunteers. so, the exact costs cannot be deduced.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Most important factors affecting the costs are seedling and labour cost.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
2076.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
The rainfall data for Mewang Gewog is not available. The provided data is for Thimphu Dzongkhag as Mewang Gewog is under Thimphu Dzongkhag (Gewog is one of the geographic units below Dzongkhag). Thimphu falls under a temperate region and experiences minimal rainfall compared to the other parts of Bhutan. Thimphu had the wettest month in July with 497 mm and experienced the least rainfall in December with 5 mm.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
National Center for Hydrology and Metoerology, Thimphu.
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
There are six Agro-ecological Zones (AEZ) in Bhutan and the current place of study falls under warm temperate zone which occurs between 1,800 – 2,500 m. Rainfall is low but the temperature is moderately warm in summer with frost in winter.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ລັກສະນະສວດ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
The area was characterized by a steep valley near the river with minimal slope as the valley widened.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
The availability of water in Mewang Gewog was a concern since a decade ago. Irrigation water was not enough for every farmers which resulted in delayed paddy plantation.
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
The species of flora and fauna diversity cannot be quantified under "high" as per the field observation. The area was surrounded by coniferous forest which generally has low biodiversity.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
The majority of the land users who were part of the Geocoding of million fruit plantation had already established apple orchards.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
An average land holding capacity for Bhutanese household as per the Land Act is 3 acres. The land holding that exceeds 3 acres are categorized in large scale in Bhutanese context.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
Internet:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຕໍ່ຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
ຄວາມຕ້ອງການ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
It adds to farmers sources of income other than vegetable and dairy product sale.
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
ໂອກາດ ໃນການພັກຜ່ອນຢ່ອນໃຈ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
ຊະນິດທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
ການຄວບຄຸມສັດຕູພືດ / ພະຍາດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງດິນ / ຊາກສະລະຫະພັງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
ຄວາມຮູນແຮງ ຂອງລົມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
ການປ່ຽນແປງ ອາກາດ ໃນວົງແຄບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ | |
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູຮ້ອນ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ລະດູຮ້ອນ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພາຍຸລູກເຫັບທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງຊີວະພາບ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍາດລະບາດ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology copes very well with gradual climate change because it sends rapid messages to farmers on actions to take (e.g., concerning pests and diseases). In a way it’s a form of early warning systems (EWS).
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Although the initial establishment of the orchard is costly considering the labour charge, it is expected to have positive income and impact once the fruit trees start bearing.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- > 50%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
Total 8000 fruit trees are planted in the five Chiwogs (third level administrative division under Gewog) under Mewang Gewog.
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Almost all those who adopted the technology are funded by the government.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| 1. Precision Mapping: Geocoding allows for accurate mapping and identification of fruit trees. By assigning specific geographic coordinates to each tree, it becomes easier to locate and monitor individual trees or orchards. |
| 2. Efficient Resource Allocation: Geocoding helps optimize resource allocation by providing information on tree density and distribution. Land users can identify areas with high fruit tree concentrations and strategically allocate resources such as labour, water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. |
| 3. Data-driven Decision Making: Geocoded data on fruit trees can be analyzed to gain insights into their distribution patterns, growth rates, and health status. This information enables land users, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding fruit tree cultivation, pest control, and disease management. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| 1. Conservation and Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data aids in the conservation and analysis of biodiversity. By mapping the locations of different fruit tree species, experts can assess the distribution and abundance of specific varieties, identify endangered local or traditional landraces varieties, and develop strategies for their preservation. |
| 2. Targeted Marketing and Distribution: Geocoded fruit tree data facilitates targeted marketing and distribution strategies. By understanding the location of fruit trees and their yields, producers can identify potential markets and plan transportation logistics more effectively, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery to consumers. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Geocoding large numbers of fruit trees can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, particularly when manual processes are involved. It may require extensive fieldwork and manual data entry, making it impractical or costly for large-scale fruit tree inventories. | |
| Privacy Concerns: Geocoding fruit trees raises privacy concerns, particularly when tree locations are associated with specific individuals or properties. Care must be taken to ensure that privacy is respected and sensitive information is appropriately handled | An updated and secured security-protected website can be used. |
| Lack of knowledge of geocoding by the farmers. | Provide awareness trainings |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The higher expense of the geocoding in terms of labour cost for geo-coding | Train land users on geocoding, instead of using trained professionals. |
| Difficult to constantly update information on time. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
The information documented was from the field visit to orchards near the RNR center.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
The information collected are from first-hand interview with the Agriculture Extension Officer who was engaged fully during the implementation of the technology.
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
07/07/2023
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
De-suung National Service (DNS). (n.d.). Million Fruit Trees Plantation
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://desuung.org.bt/25978-2/#:~:text=In%20order%20to%20monitor%20the,from%20the%20date%20of%20plantation.
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched
URL:
http://www.bbs.bt/news/?p=166763
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Kuensel. (2022). Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched. Thimphu.
URL:
Website: https://kuenselonline.com/414000-fruit-trees-planted-in-45-days/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Geocoding of trees from street addresses and street-level images
URL:
https://www.fs.usda.gov/psw/publications/vandoorn/psw_2020_vandoorn001_laumer.pdf
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ