Conversion of conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest [ອີສເອວ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Tom Cohen
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
technologies_7674 - ອີສເອວ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Brook Anna
University of Haifa
ອີສເອວ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
ອີສເອວ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
University of Haifa (uhaifa)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This intervention is explicitly designed to reverse and restore previously degraded soils (monoculture exhaustion, fertility decline, low biodiversity).
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Converting conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest-based agroforestry system restores soil health, increases vegetation cover, enhances biodiversity while diversifying production. The intervention improves soil organic matter and ecological resilience through multi-storey planting, reduced soil disturbance, and nature-based land management.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
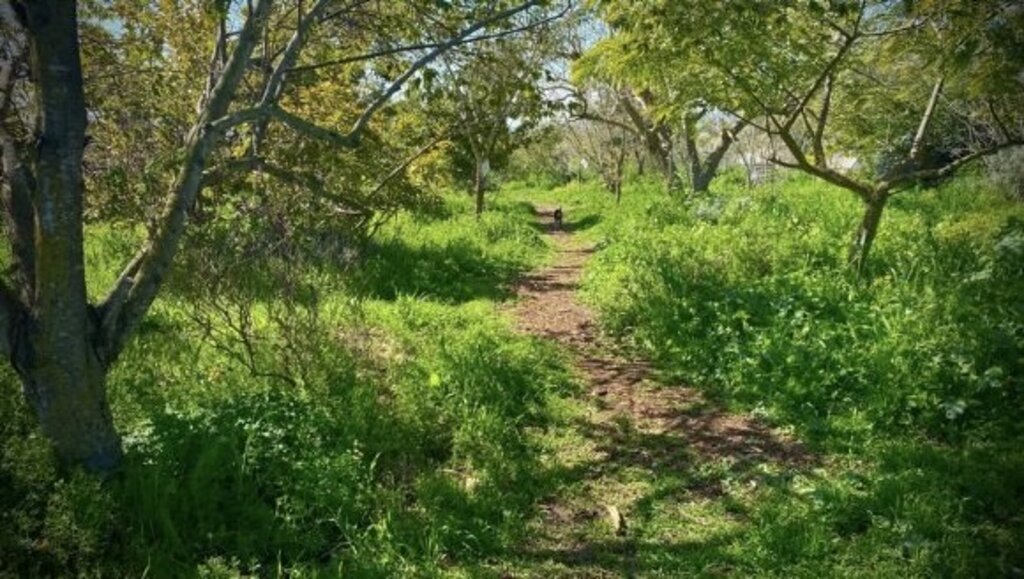
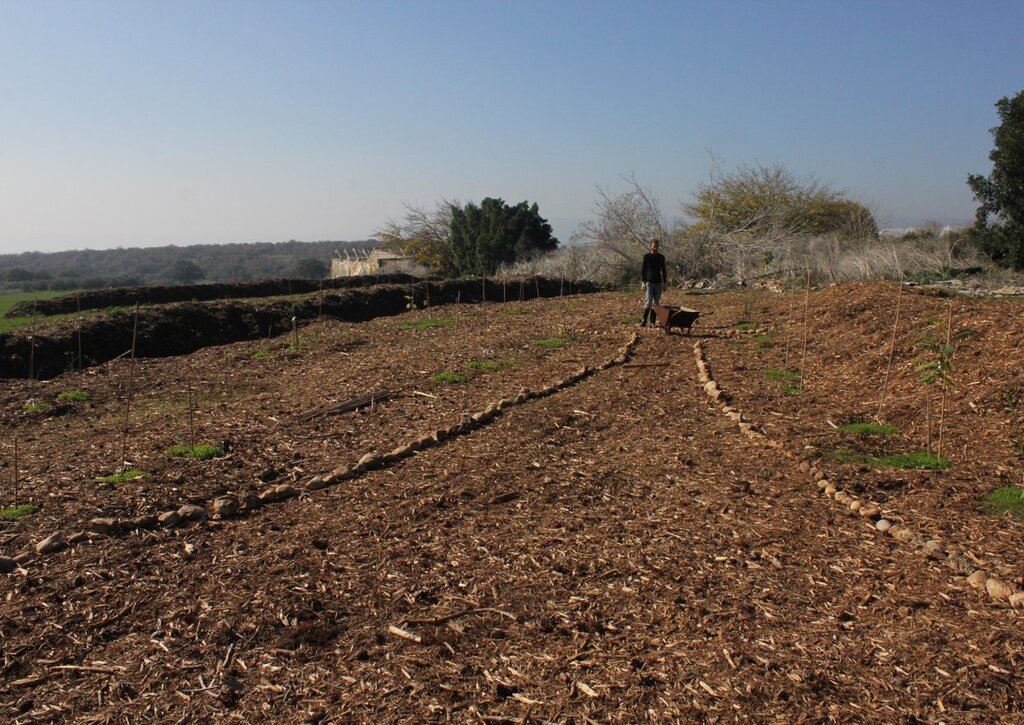
The development of a “food forest” was in response to visible soil degradation caused by years of wheat-based monoculture in Bethlehem of Galilee. The previous land use consisted of annual wheat production, tractor-powered deep ploughing, and routine use of herbicides and pesticides. Over time, these practices depleted soil organic matter, reduced microbial activity, and increased vulnerability to erosion, compaction, and moisture loss. The current food forest, covering approximately 1.5 acres (0.6 hectare), represents a transformative shift from this intensive, extractive system toward a sustainable, perennial, multi-strata agroforestry model.
The primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
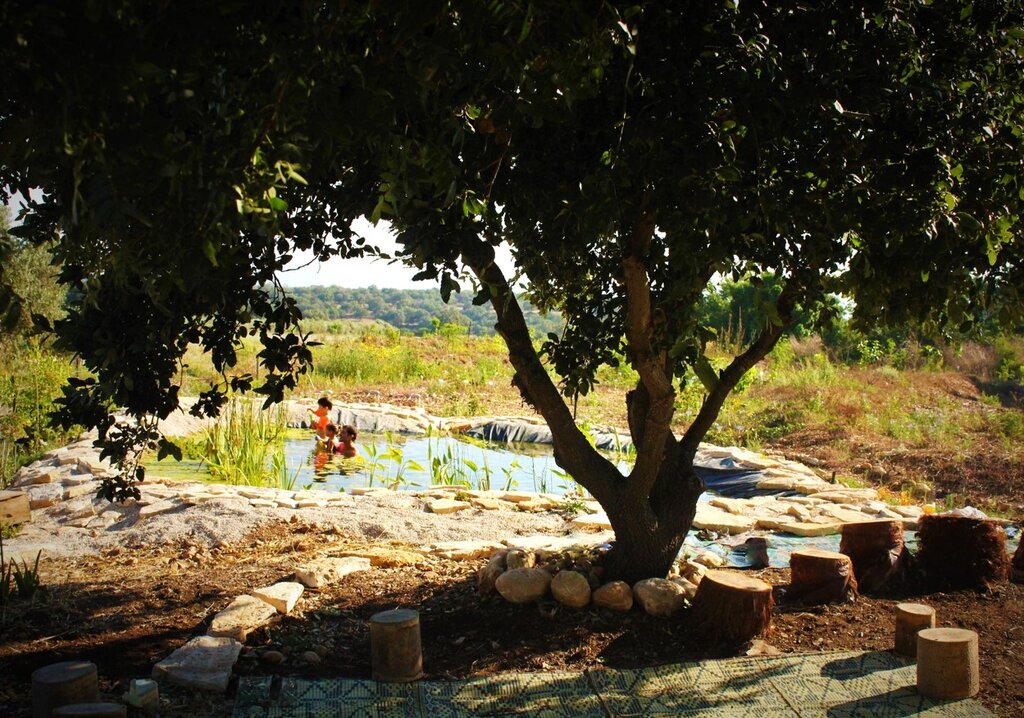
The site has been under continuous restoration for approximately eight years, during which it has gradually developed into a multi-layered food forest. The upper canopy includes species such as ficus, tipa, mulberry, pecan, plane trees, and nitrogen-fixing “ice-cream bean” (Inga edulis), which together generate shade, biomass, and structural diversity. The productive mid-storey contains fruit-bearing species including lemon, plum, pomegranate, avocado, and additional deciduous trees. Beneath these layers, aromatic shrubs such as lavender and rosemary provide perennial cover, habitat complexity, and year-round biomass production. A dedicated lower layer supports seasonal vegetables: carrots, radishes, turnips, lettuces and other greens, interplanted within tree alleys and cultivated using organic methods.
Production follows a diversified model typical of food forests. Tree crops currently yield modest but consistent quantities of lemons, plums, mulberries, pomegranates, and herbs, primarily for consumption by visitors, volunteers, and workers on site rather than large-scale commercial sale. The adjoining vegetable-growing area produces additional crops for small-scale marketing, providing a modest revenue stream while maintaining ecological integrity. As the system is still maturing, productive output is expected to increase over the coming years.
The project is privately managed by a couple in their thirties, who own and oversee all aspects of the site. Labour requirements were most intensive during the establishment phase of planting, mulching, earth-shaping, and infrastructure setup. As the food forest enters a more stable successional stage, labour demands have gradually decreased, with current activities centred on pruning, biomass recycling, vegetable cultivation, and occasional enrichment planting. No chemical inputs are applied at any stage.
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
Overall, this food forest demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for Mediterranean environments, showcasing how degraded wheat monoculture fields can be restored into resilient, biodiverse, and ecologically functional agroforestry systems. The long-term transition highlights substantial gains in soil health, water retention, and landscape diversity, while supporting small-scale production and community-oriented engagement.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອີສເອວ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Galilee
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Bethlehem of Galilee
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ກະຈາຍໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເນື້ອທີ່ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມ (ເປັນ ກິໂລຕາແມັດ):
0.01
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸປີ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
2017
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The landowners developed the site as part of a holistic environmental vision and continue to refine it through ongoing learning, experimentation, and renewal. They actively initiate collaborations with research institutions in Israel and abroad to support long-term monitoring of the site and to advance the food-forest practice within a scientific and evidence-based framework.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວແປກ
- ພືດທີ່ເປັນຢາ / ກິ່ນຫອມ / ພືດປາດແມງໄມ້ ແລະ ສະຫມຸນໄພ
- ຜັກ-ຜັກໃບ( ຜັກສະລັດ, ຜັກກະລຳ, ຜັກຫົມ, ອື່ນໆ)
- ຜັກ-ຜັກໃຫ້ຫົົວ ( ກາລົດ, ຜັກບົ່ວຫົວໃຫ່ຍ, ຜັກກາດຫວານ, ອື່ນໆ)
ການປູກພືດທີ່ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກອາໂວກາໂດ
- ໝາກນາວ
- ໝາກເດືອຍ
- ຫມາກໄມ້ນ້ອຍ (ຫມາກໂປມ, ໝາກຊາລີ, ໝາກຈອງ, ແລະອື່ນໆ)
- stone fruits (peach, apricot, cherry, plum, etc)
- ຕົ້ນຖົ່ວ ( ຖົ່ວເບຣຊິນ. ພິສຕາຄິໂອ. ວໍນັດ. ອ່າວມ້ອນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ)
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 3
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Up to three for the fastest growing crops
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
The whole farm forest embodies intercropping throughout its multi-strata structure
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Various annual crops as described above - and an adaptive succession strategy

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ
ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປູກປ່າ: ລະບຸ ຕົ້ນກຳເນີດ ແລະ ອົງປະກອບ ຂອງສາຍພັນ:
- ແນວພັນປະສົມ
ປະເພດຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປ່າທີ່ປູກ:
- ການປູກໄມ້ ໃນປ່າໄມ້ເຂດໜາວ
- Ficus, Tipu (Tipuana tipu), Plane tree (Platanus spp.), Sissoo (Dalbergia sissoo), Ice-cream bean
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ທີ່ຖືກລະບຸຢູ່ຂ້າງເທິງ ເປັນປ່າຜັດປ່ຽນໃບ ຫລື ປ່າດົງດິບ?
- ປະສົມປ່າປ່ຽນໃບ / ປ່າດົງດິບ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ໝາກໄມ້ ແລະ ແກ່ນຖົ່ວ
- ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ປ່າໄມ້ອື່ນໆ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
- ນັນທະນາການ / ການທ່ອງທ່ຽວ
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ແມ່ນ (ກະລຸນາຕື່ມໃສ່ ຄຳຖາມຂ້າງລຸ່ມນີ້ກ່ຽວກັບການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ກ່ອນການທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ)
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ - ເຂົ້າສາລີ
ລະບົບການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ:
ເຂົ້າສາລີ ຫຼື ພືດຫມູນວຽນຄ້າຍຄືກັນກັບ ຫຍ້າ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Occasionally (see above)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
- M5: ການຄວບຄຸມ / ການປ່ຽນແປງຂອງອົງປະກອບຂອງຊະນິດ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
- Cs: ການເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດດິນເຄັມ / ເປັນດ່າງ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
- Pi: ເນື້ອດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ
- Ps: ຊຸດຂອງດິນອົງຄະທາດ, ການຕັ້ງຖິ່ນຖານຂອງດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
For this pilot, the technology primarily addresses soil degradation (chemical + physical + biological) that resulted from long-term monoculture and herbicide-based management.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
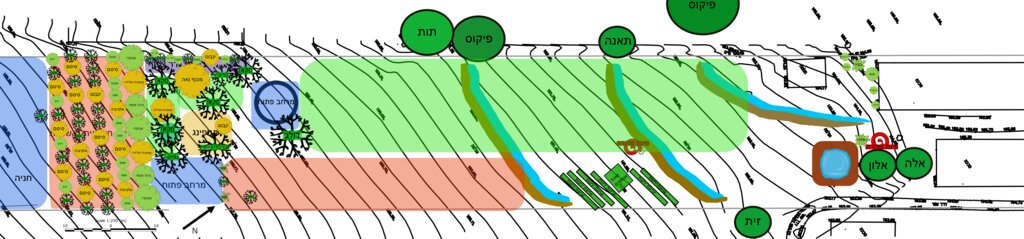
The general site plan (above) illustrates the full spatial organization of the food forest, structured into clearly defined functional zones that together create a balanced ecological and productive landscape (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). The outer perimeter consists of a protective tree belt designed to provide wind buffering, habitat continuity, and microclimate regulation. Inside this perimeter lies a series of densely planted clusters of mixed-species trees and support plants, forming the core forested zones of the design. These clusters contain a combination of canopy species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing support species, and understory elements arranged to promote ecological interactions and long-term resilience. Several open areas are intentionally integrated throughout the site, providing space for circulation, light penetration, future expansion, and community activities. The plan also includes a designated agricultural strip for annual vegetable production, strategically placed to benefit from the moderated microclimate created by the surrounding tree layers. Additional functional elements such as a compost area, shaded seating or gathering points, and access paths appear throughout the design, supporting both maintenance and educational use. Overall, the plan demonstrates a holistic integration of productive, ecological, and social spaces, emphasizing diversity, spatial layering, and regenerative land-use principles.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Nitzan Betzer
ວັນທີ:
01/06/2017
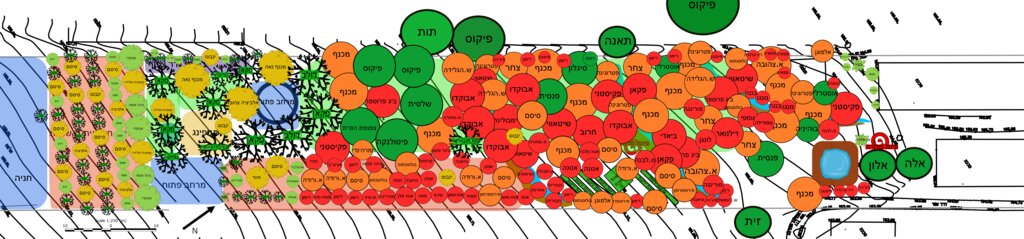
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
The planting plan (below) illustrates the full structural design of the food forest, showing a diverse mixture of perennial species arranged according to ecological function and spatial layout (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). Each color on the map represents a different botanical or functional category. The green circles indicate the major canopy and shade-providing trees that form the upper layer of the system. The red circles mark the fruit-bearing species distributed across the plot, including pomegranate, avocado, fig, loquat, mango, mulberry and others, representing the primary productive component of the mid-storey. The orange circles correspond to nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs, strategically positioned to enrich soil fertility and support surrounding species through natural nutrient cycling. The yellow circles mark ornamental or habitat-supporting species that enhance biodiversity, microclimate regulation and ecological resilience. Together, these categories create a multi-layered mosaic in which canopy, fruit, support species and habitat elements interweave across the site. The design also includes designated open areas, compost space, perimeter rows and an agricultural strip for annual vegetables, demonstrating an intentional balance between ecological restoration, food production and functional zoning.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Nitzan Betzer
ວັນທີ:
01/06/2017
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
1.5 acres
ຖ້ານໍາໃຊ້ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ເນື້ອທີ່ຕາມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ໃຫ້ປ່ຽບເປັນ 1 ເຮັກຕາ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: 1 ເຮັກຕາ = 4 ໄລ່ ): 1 ເຮັກຕາ = :
1 acre = 0.4 hectares
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
158.2
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial site assessment and mapping of soil condition and exposure | Late winter / early spring |
| 2. | Discontinuation of tillage and herbicide applications | Immediately prior to establishment |
| 3. | Soil preparation without deep tillage (light loosening, mulching base layer) | Early spring |
| 4. | Planting of trees in primary layout (skeleton layer) | Spring |
| 5. | Planting of shrubs and understory companion species | Late spring / early summer |
| 6. | Installation of organic mulch cover to protect soil and retain moisture | After planting (early summer) |
| 7. | Enrichment planting / filling gaps with additional groundcover species | Late summer / following spring |
| 8. | Protection of young trees/shrubs if needed (guards, shading, temporary watering) | First growing season |
| 9. | Establishment of biomass cycling (chop-and-drop, composting on-site) | After vegetation takes root |
| 10. | Transition into maintenance phase (reduced intervention, natural succession) | Once canopy begins forming |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Manual labour | Person-days | 139.0 | 158.2 | 21989.8 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools and maintenance equipment | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tractor (for construction) | 1.0 | 7200.0 | 7200.0 | 100.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings, cuttings, and seeds | 1.0 | 14000.0 | 14000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost | 1.0 | 10500.0 | 10500.0 | 100.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Irrigation system | 1.0 | 14500.0 | 14500.0 | 100.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Pruned biomass mulch | 1.0 | 6500.0 | 6500.0 | 100.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 79689.8 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 79689.8 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
Land user bore all costs: but note the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
No chemical fertilizers or pesticides are used; fertilization is based solely on compost
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching with organic biomass (leaf litter, pruning residues, woodchips, etc.) | 2–3 times per year, mainly after rainy season and mid-summer |
| 2. | Selective pruning of trees and shrubs to maintain structure and light balance | Annually / as needed (late winter or autumn) |
| 3. | Enrichment planting and succession planting of understorey species | Seasonally, as ecosystem matures or gaps appear |
| 4. | Weeding by ecological suppression (groundcover strengthening) rather than removal | Continuous, low-intensity maintenance |
| 5. | Soil moisture conservation (biomass renewal / occasional supportive watering in drought years) | Seasonally during dry periods (as needed) |
| 6. | Monitoring soil condition and vegetation health | Ongoing, at least once per season |
| 7. | Replacement of failed or weak young plants | Annually during early growth seasons |
| 8. | Maintenance of biodiversity guilds / companion planting structure | Continuous, adaptive to natural succession |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Manual labour | Person-days | 110.0 | 158.2 | 17402.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Equipment renewal and maintenance | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Cuttings and seeds | 1.0 | 4000.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ອື່ນໆ | Water bills | 1.0 | 5500.0 | 5500.0 | 100.0 | |
| ອື່ນໆ | Products selling kits | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 33902.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 33902.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The establishment costs refer to the initial food forest area of approximately 1.5 acres, while the annual maintenance costs refer to the forest in its current state, covering about 3 acres. Land user bore all costs: but note that the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The most significant cost factor, both during establishment and ongoing maintenance, is labour. All work is carried out manually using hand tools, and apart from the initial establishment phase, no heavy machinery is used
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
The climatic information for the food forest site was obtained from two sources: official data provided by the Israel Meteorological Service (IMS) and on-site measurements collected through a dedicated rain gauge installed as part of the research infrastructure. Together, these sources provide accurate local rainfall and climate monitoring for the plot.
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ທັງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ແລະ ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
Both species diversity and habitat diversity have transformed due to the establishment of the food forest, and are now both high. This is a very agrobiodiverse system.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The land user manages approximately 2–5 hectares in total, of which a portion is undergoing transition into a food forest system; this is considered small-scale in the local agricultural context
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Agricultural input expenses are very limited in this system. Since the site operates as a food forest rather than a conventional agricultural plot, nearly no external inputs are purchased. The management relies on ecological processes, on-site biomass, mulching, and manual care. Inputs are therefore minimal and do not reflect commercial-scale agricultural expenditure.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The plot was originally managed as a monoculture field that depended economically on agricultural production. Today, the food forest operates on a completely different model: its income is derived primarily from research activities, educational programs, workshops, and community engagement. Economic sustainability is no longer based on agricultural yield, as crop production is not the financial foundation of the site anymore.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ກາລະໂອກາດ ທາງດ້ານວັດທະນະທໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest contributes significantly to cultural opportunities in the area. It serves as a community-oriented space that hosts educational events, workshops, volunteer activities, and gatherings focused on sustainability and ecological awareness. The site fosters cultural exchange, strengthens community cohesion, and provides a shared environment for learning, creativity, and connection to nature.
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Note: The food forest strengthens community institutions by collaborating with local educational programs, volunteer groups, and research initiatives. It provides a stable platform for schools, community organizations, and environmental groups to conduct activities, thereby reinforcing their role in community life and expanding their capacity for outreach and engagement.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest contributes to improved SLM and land-degradation knowledge by serving as a living demonstration site where restoration practices can be observed, tested, and monitored over time. It provides real-world evidence on soil recovery, biodiversity enhancement, and regenerative management, supporting both scientific research and practical learning for land users, students, and professionals.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest reduces surface runoff through continuous vegetative cover, increased soil organic matter, and improved infiltration. The multi-layered perennial structure slows water movement, stabilizes the soil, and enhances water absorption, thereby decreasing erosion risk and minimizing overland flow during rainfall events.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest reduces soil surface evaporation through dense vegetative cover, shading from the multi-layered canopy, and increased soil organic matter. Mulching and groundcover plants further protect the soil surface, lowering temperatures at ground level and limiting direct exposure to sun and wind, which significantly decreases soil surface evaporative water loss.
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest increases soil moisture by improving infiltration, enhancing organic matter content, and maintaining continuous groundcover. The multi-layered canopy moderates temperature and reduces evaporation, while mulch and living groundcovers retain water in the upper soil layers. Together, these features create a cooler, moister soil environment that supports long-term ecological function.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest improves ground cover through the establishment of multi-layered perennial vegetation, including trees, shrubs, and living groundcovers. Mulch application and natural leaf litter further protect the soil surface, ensuring year-round coverage that reduces erosion, enhances soil health, and supports ecological stability.
ດິນເປັນຜົງ / ການຈັບໂຕຂອງດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ທີ່ມີການຈັບໂຕກັນເປັນກ້ອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest reduces soil crusting and surface sealing by increasing organic matter, maintaining continuous vegetative cover, and enhancing biological activity in the upper soil layers. Leaf litter, mulch, and root penetration prevent the formation of hard surface layers, while improved soil structure allows better infiltration and aeration, minimizing the risk of crust development.
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest enhances nutrient cycling and soil nutrient recharge through continuous biomass production, leaf litter accumulation, and root turnover. Nitrogen-fixing species, mulch, and on-site organic matter decomposition replenish soil nutrients naturally, while diverse plant strata promote active microbial communities that accelerate nutrient transformation and availability.
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest increases soil organic matter and below-ground carbon through continuous inputs of leaf litter, root biomass, and decomposing mulch. The perennial, multi-layered vegetation system supports sustained carbon incorporation into the soil, while reduced disturbance and enhanced microbial activity further promote long-term carbon storage and soil organic matter accumulation.
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest substantially increases vegetation cover by establishing multiple perennial layers - canopy trees, mid-storey species, shrubs, and groundcovers - that provide continuous, year-round biomass. This expanded plant cover protects the soil, supports ecological processes, and creates a more resilient and biodiverse landscape compared to the former monoculture field.
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest increases above-ground biomass and carbon storage through the establishment of diverse perennial vegetation, including canopy trees, fruit species, shrubs, and herbaceous layers. As these plants grow, they accumulate significant living biomass, sequester carbon, and contribute to long-term ecological stability through continuous organic matter production and structural complexity.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest greatly increases plant diversity by integrating a wide range of tree species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing plants, shrubs, herbs, and groundcovers. This multi-strata design replaces the former single-crop system with a complex, species-rich community that enhances ecological resilience, supports wildlife, and promotes functional biodiversity across the site.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest increases habitat diversity by creating a multi-layered structure that supports varied ecological niches. The combination of canopy trees, understory species, shrubs, groundcovers, open areas, and water features provides habitats for a wide range of insects, birds, and small wildlife. This structural and functional diversity replaces the uniform habitat of the former monoculture and greatly enhances overall ecosystem complexity.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The food forest helps reduce carbon and greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing external inputs, eliminating chemical fertilizers, and avoiding soil disturbance that would otherwise release stored carbon. The perennial vegetation continuously sequesters carbon in both biomass and soil, while the system’s low-energy, regenerative management reduces emissions associated with conventional agricultural practices.
ລະບຸ ການປະເມີນຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ສະຖານທີ່ (ການວັດແທກ):
The assessment of on-site impacts combines both social-cultural learning processes and quantitative biophysical measurements. On the social, cultural, and economic side, the site hosts workshops, guided learning sessions, and community activities designed to understand the meaning, role, and value of the food forest for local stakeholders. These engagements provide qualitative insights into cultural benefits, community strengthening, and the educational function of the place. For the more tangible biophysical parameters – soil health, vegetation condition, biodiversity, and ecological recovery – the monitoring relies on analytical laboratory tests and systematic long-term sampling. Soil samples collected at different stages of the establishment process were analyzed for organic matter, nutrients, structure, and biological activity, providing a clear picture of soil improvement over time. In addition, the site is monitored through remote-sensing-based indicators developed in collaboration with the University of Haifa, which track temporal changes in vegetation cover, biomass, soil moisture proxies, and overall ecological function. Together, these qualitative and quantitative assessments offer a comprehensive understanding of the site’s development, documenting both the ecological restoration underway and the parallel social and educational impacts generated by the food forest.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Using IPCC Tier-1 methods (2006 Guidelines with the 2019 Refinement), we estimate annual removals from (i) mineral soil organic carbon (SOC) gains after conversion from tilled wheat to multistrata agroforestry, and (ii) incremental woody biomass growth. Mediterranean evidence suggests SOC increases on managed woody systems of ~0.2–1.0 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, while biomass increments in multistrata/silvo-arable agroforestry typically add ~0.8–2.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ in the establishment decades; together this yields ~1.0–3.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, i.e., ≈ 3.7–13 tCO₂e ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ (3.67 conversion). For reporting we adopt the conservative lower bound until our paired soil cores (baseline vs. years 2/5/8) and tree allometry—supported by Sentinel-2 time-series—finish quantifying site-specific change. Sources: IPCC 2006/2019 AFOLU guidance; AR6 WGIII (AFOLU); Mediterranean meta-analyses of SOC/biomass in woody systems and agroforestry.
ກໍານົດ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບທາງນອກ (ການວັດແທກ):
Off-site impacts were assessed through a combination of qualitative and quantitative indicators that capture how the food-forest system influences the surrounding landscape and community beyond the plot boundaries. Hydrological effects were inferred from reduced surface runoff and improved infiltration within the site, which collectively lower downstream sedimentation and erosion risks; these implications were evaluated using rainfall records, soil-moisture trends, and comparison of runoff behavior between the restored area and adjacent conventionally managed fields. Vegetation development and canopy expansion – monitored through Sentinel-2 time-series and UAV imagery – provide additional evidence of landscape-scale improvements such as enhanced microclimatic buffering and habitat connectivity. Social and cultural off-site impacts were evaluated through participation in workshops, educational programs, and community events, which extend ecological knowledge and stewardship beyond the site itself. Together, these measurements and observations offer a coherent picture of how the food forest contributes to broader environmental and community benefits outside its physical boundaries.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ປານກາງ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ປານກາງ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ຄື້ນຄວາມອົບອຸ່ນ | ດີ |
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The slightly negative short-term balance does not reflect external subsidies but rather the intentional design and purpose of the site. The food forest is not a commercial enterprise and was never intended to generate profit from agricultural production. Its primary function is research, education, and community engagement, and therefore its revenues come from workshops, collaborations, and research grants rather than crop sales. The short-term financial deficit simply reflects the fact that the landowners invest in a long-term ecological and educational project whose value is measured in environmental and social outcomes rather than immediate economic returns. It should not be interpreted as dependence on agricultural subsidies or market-based support.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
One household: 1.5 acres
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ລະບຸແມ່ນເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງ ທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດມີການປັບຕົວ:
- ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The design and composition of the food forest are continuously adapted as the system matures and as new insights emerge from ongoing learning by the landowners and collaborating researchers. Species selection, spatial arrangement, and management practices have been refined over time in response to observed ecological dynamics - such as canopy development, soil improvement, microclimatic changes, and species performance. Additional trees, shrubs, and groundcovers have been introduced to enhance diversity, strengthen ecological functions, and address emerging needs such as shade regulation, soil enrichment, or habitat creation. This adaptive approach reflects the core principle of the technology: the food forest is a living system that evolves through observation, experimentation, and evidence-based adjustments informed by both practical experience and scientific collaboration.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Restores soil fertility and structure without relying on chemicals and reduces weed pressure naturally through permanent groundcover |
| Improves moisture retention and reduces drought stress over time and supports biodiversity and creates a healthier farm ecosystem |
| Transformational: turns degraded land into a productive long-term asset |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for restoring degraded agricultural soils in Mediterranean climates |
| Increases soil organic matter and biological activity, improving long-term soil function and carbon sequestration |
| Serves as a living demonstration site with high educational and upscaling potential for regenerative farming in the region |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Slow establishment phase before benefits become visible | Patience + phased planting; choose fast-growing pioneer species to accelerate canopy formation |
| Requires knowledge and ecological management skills | Ongoing guidance from experts / capacity building / training |
| Young plants vulnerable to drought during first summers | Supplemental irrigation in the first years and thicker mulching to reduce evaporation |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Long ecological recovery timeline before system reaches full functionality | Use succession planning and pioneer/perennial nurse species to accelerate canopy closure and soil regeneration |
| Success depends on appropriate species selection for local microclimate and soil | Improve site-specific design using adaptive planting trials, monitoring, and locally adapted cultivars |
| Knowledge-intensive management compared to conventional systems | Provide technical training, extension support, and farmer-to-farmer learning |
| Restoration outcomes may vary with drought years and extreme heat events | Increase biomass cover, soil shading, and water retention strategies in early establishment years |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Field visits and surveys were conducted once every season on-site with the primary land user (one key informant), supplemented by technical assessments from the research team
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
One-on-one interviews were conducted with the primary land user (one key informant) at least once a year, focusing on management decisions, perceived benefits and challenges, and changes observed since the start of the transition
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
The expert input was provided by specialists involved in the University of Haifa restoration pilot
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Zbedat, G., & Brook, A. (2025). Land Restoration Effectiveness Assessed by Satellite-Based Remote Sensing Technologies as A New Monitoring Approach. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 48, 149-155.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Google Scholar
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
T. A. Cohen, A. Brook and G. Zbedat, "Long-Term Land Restoration Assessment Using Remote Sensing in Mediterranean Ecosystems," 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Padua, Italy, 2024, pp. 179-183, doi: 10.1109/MetroAgriFor63043.2024.10948855.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Google Scholar
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
React4Med site
URL:
https://react4med.eu
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest Collection
URL:
https://haifa.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/discovery/collectionDiscovery?vid=972HAI_MAIN:HAU&inst=972HAI_MAIN&collectionId=81263109080002791
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ