Rubagano rooftop rainwater harvesting system (with concrete/brick tank) [ອູເຈນດາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Wilson Bamwerinde
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okwombeka tanka z'amaizi ahamaju (Runyankore)
technologies_1595 - ອູເຈນດາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
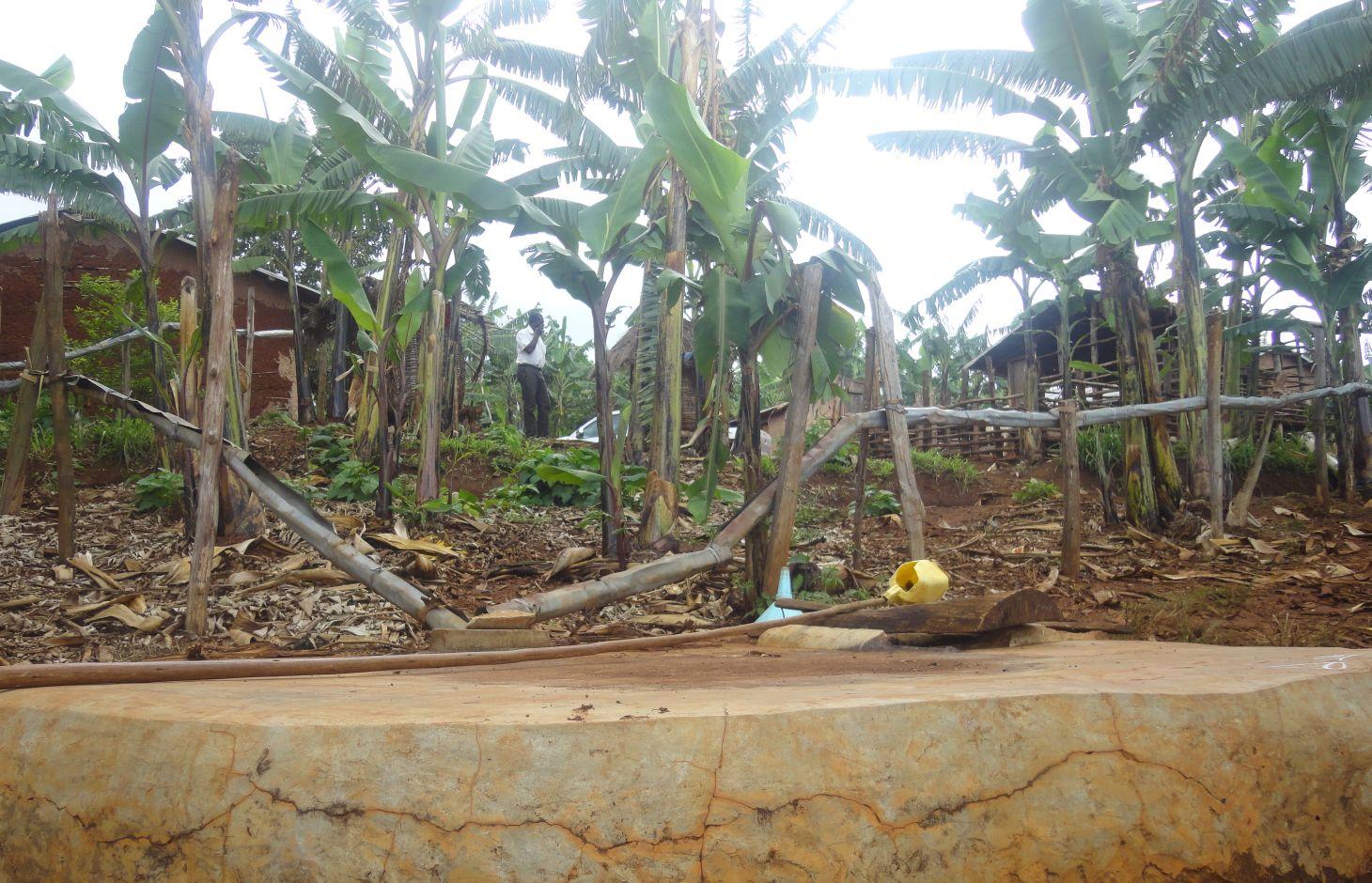
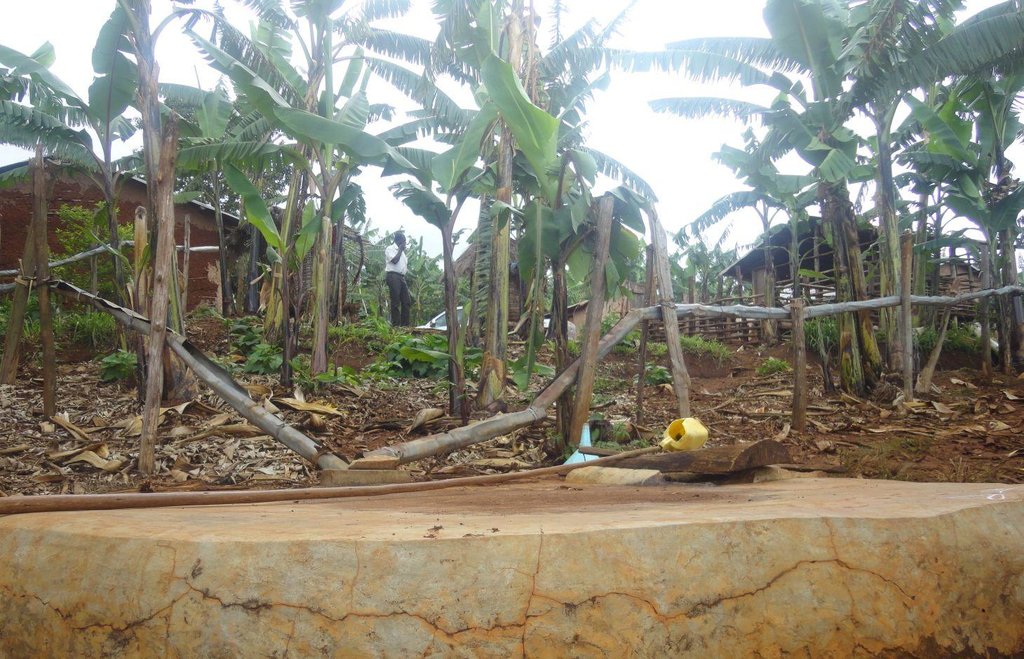
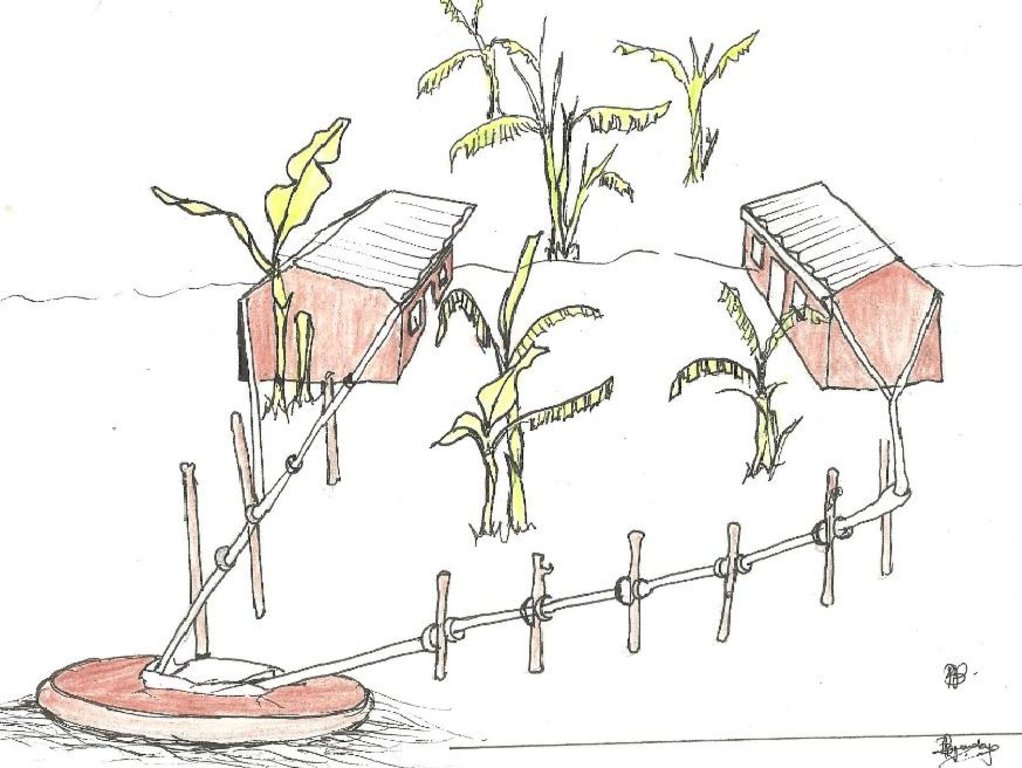
Rain-water from all corrugated iron roof structures in one compound is harvested and stored in underground tanks.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Despite high precipitation (>1200 mm), Rubagano still experiences water shortage. It is hilly, with steep (>30%) to very steep (>58%) slopes. Rain water runs off to the valleys below, causing erosion and damaging infrastructure such as roads along its course. There is little rain water infiltration and the ground water level low. The few boreholes that government constructed in the area are often dry. Therefore women and children normally walk distances of up to 4 km to fetch water which, in many cases, is actually runoff dammed behind a concrete wall built across an open rock patch. To alleviate water scarcity, farmers have been mobilized by Kagera TAMP project to harvest the rain water from their own roofs. Because water sources are far from most households, rooftop water harvesting has a very high utility for the farmers. Adoption is high.
Purpose of the Technology: The primary goal of the technology is to increase household water availability. It also reduces runoff, produces water for the tree nursery and backyard gardens..
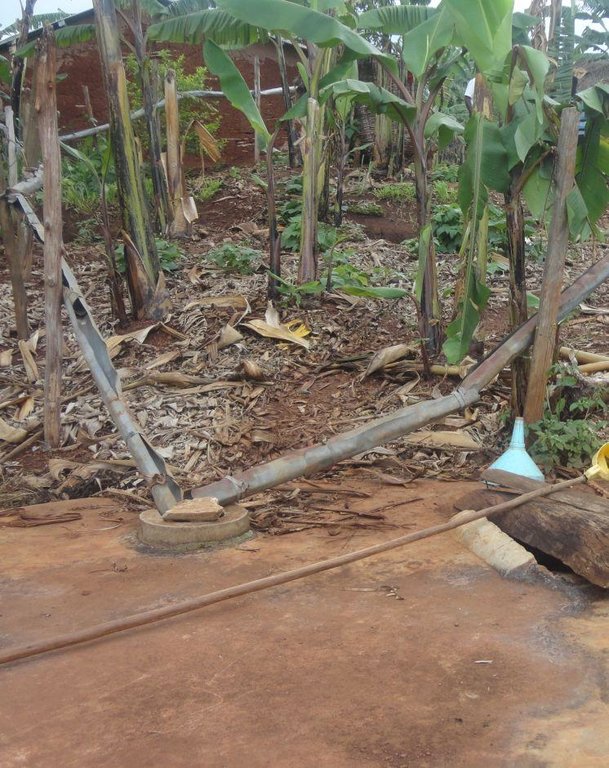
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Requirements for harvesting water on an iron roof are water collection gutters and an underground tank. Rain falling on the roof flows into collection gutters constructed around the roof which angle gently away from the house and end at one or more underground tanks. Excavation and construction of the storage tank is costly and requires well qualified artisans. These are trained locally and are available within the community to minimize costs. The underground tank is constructed by excavating the ground between 3.0 m and 3.5 m deep and 2.0 m to 2.5 m diameter. Thus, a small tank will have a capacity of 38,000 litres (38 cubic metres). The bottom and walls of the pit is then built up throughout with brick and mortar. The top is a concrete slab with 2 openings of 0.3 m diameter, one connected to the gutters and the other through which a plastic container is lowered to fetch water. Though establishment costs appear high for farmers, the longer term benefits outweigh the original cost. Once established the maintenance costs are limited to periodic cleaning.
Natural / human environment: Heavy rainstorms may blow the gutters out of position.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອູເຈນດາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Uganda
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Mbarara District (Rubagano, Mwizi)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.85203 30.62232; -0.85850 30.62204; -0.85792 30.62021
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.001 km2.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ກ້ວຍ/ກວ້ຍຂຽວ/ໄຍຕົ້ນກ້ວຍ
ການປູກພືດທີ່ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ກາເຟ, ປູກຢູ່ພື້ນທີ່ເປີດ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: February to May

ທິດທາງໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າ, ດິນທາມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of vegetation, soil erosion and very low ground water level. Difficulty in finding access to water for domestic use, livestock and crop irrigation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Women and children walk very long distances in search of water from permanent natural wells.
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S5: ເຂື່ອນໄຟຟ້າ, ຝາຍເກັບນໍ້າ, ອ່າງ, ໜອງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Hs: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະລິມານ ນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
- Hp: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Removal of vegetation cover), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Forests harvested for fuel wood, charcoal, agriculture etc.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep slopes increase the speed of runoff and soil erosion)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change effects of human activity), droughts (Longer dry spells as a result of climatic changes), poverty / wealth (Cannot afford manure or fertilizers to make soil more productive so forest is cut to create more agricultural land)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Details of rainwater harvesting system: roof catchment, gutters and underground storage tank
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi Sub-county, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 18 December 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Artisan's work once the land user has decided on the size of the water tank required)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water spreading
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): d=3.0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): r=2.0
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): n/a
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 38m3
Catchment area: 900 m2m2
Beneficial area: 900 m2m2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.1
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kabale, Uganda
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
UGX
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
2500.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
10.00
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tank construction | Throughout the year |
| 2. | Procurement and raising of collection gutters | Throughout the year |
| 3. | Wooden poles | Throughout the year |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Bricks | ha | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Cement | ha | 1.0 | 420.0 | 420.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Sand | ha | 1.0 | 160.0 | 160.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1526.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 0.61 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tank maintenance (above ground) | Once a year |
| 2. | Gutter replacement | Twice a year |
| 3. | Wooden poles | Twice a year |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Bricks | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Cement | ha | 1.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Sand | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 216.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 0.09 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: Pick-axe, hand hoe, panga
The calculations were done for a 38.0 cubic meter tank constructed in September 2013
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Skilled labor for the construction of the underground tank
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Average annual rainfall for Rubagano is >1200 mm
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l (Ranked 1, rubagano has an average altitude of 1700 m a.s.l) and 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (ranked 2)
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
> 50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 65% of the land (Have an iron roof house, some livestock and land for cultivation).
4% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Similar statistics for all types of land users as far as off-farm income is concerned
Level of mechanization: Manual work (All land is cultivated manually)
Market orientation of production system: Mixed (ranked 1, most farmers cultivate banana plantations for subsistence and commercial use) and subsistence (ranked 2, a few farmers cultivate for subsisce)
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຕໍ່ຜົນຜະລິດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Women and children
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Women and children no longer have to walk long distances in search of water.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
E.g. Roads
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ (ແມ່ນໍ້າ) ນໍ້າຖ້ວມ | ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄລຍະເວລາການຂະຫຍາຍຕົວຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology may appear expensive to the farmer at the time of establishment but it is cost-effective in the long-term.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
25
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 51-90%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Regardless of the high costs involved, improved water security has encouraged farmers to adapt the technology.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Makes water for drinking and domestic use more readily available to the household How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption and maintenance through farmer-to-farmer information |
|
Saves women and children from walking long distances in search of clean water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Empower women and children to demand and obtain rooftop water harvesting at home |
|
Rooftop harvested water is cleaner than trapped runoff used by many members of the community How can they be sustained / enhanced? Help households to acquire materials for rooftop water harvesting |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Technology is expensive to establish | Support government and private sector to subsidize tanking systems for farmers |
| Requires technical expertise especially in concrete preparation to prevent cracks and leakages | Ensure farmers who express the need to adapt get access to construction technicians |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ