Controlling invasive species by physical removal and crop cultivation through open fallow irrigation [ເຄັນຢາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Beatrice Otieno
- ບັນນາທິການ: Urs Baumgartner, Christian Hergarten
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Rene Eschen
Cut, Burn, Uproot and Cultivate
technologies_3444 - ເຄັນຢາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
14/03/2018
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Cultivation through irrigation in Perkerra scheme begun in 1954, three decades before the introduction of Prosopis in Baringo. Despite the rapid and widespread expansion of the invasive species, it is evident that cultivated areas under the scheme are free from Prosopis, unlike their surrounding neighborhoods which are heavily invaded and rendered unproductive. This is an indication of its sustainability to control Prosopis spread to irrigated land.
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
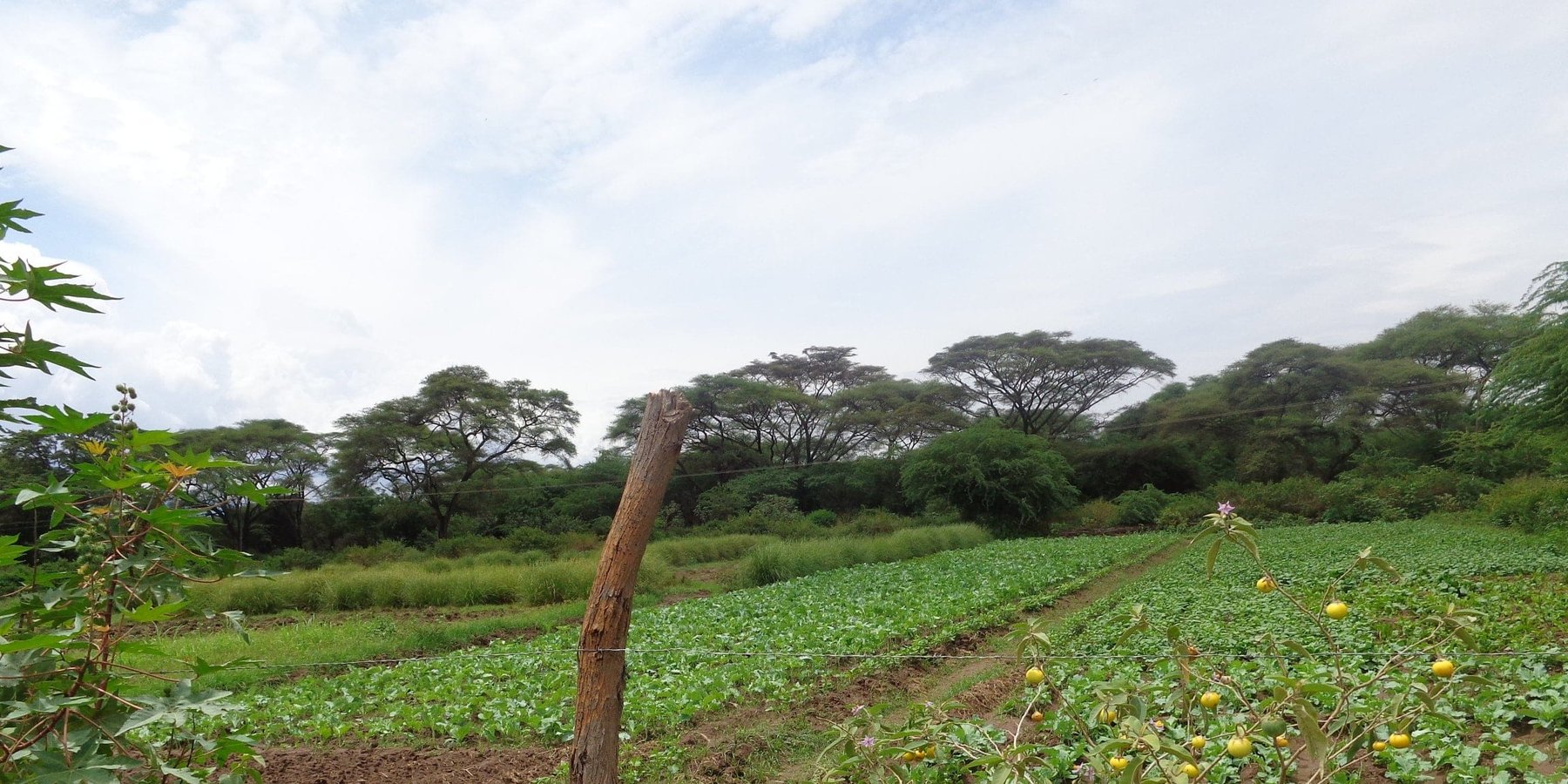
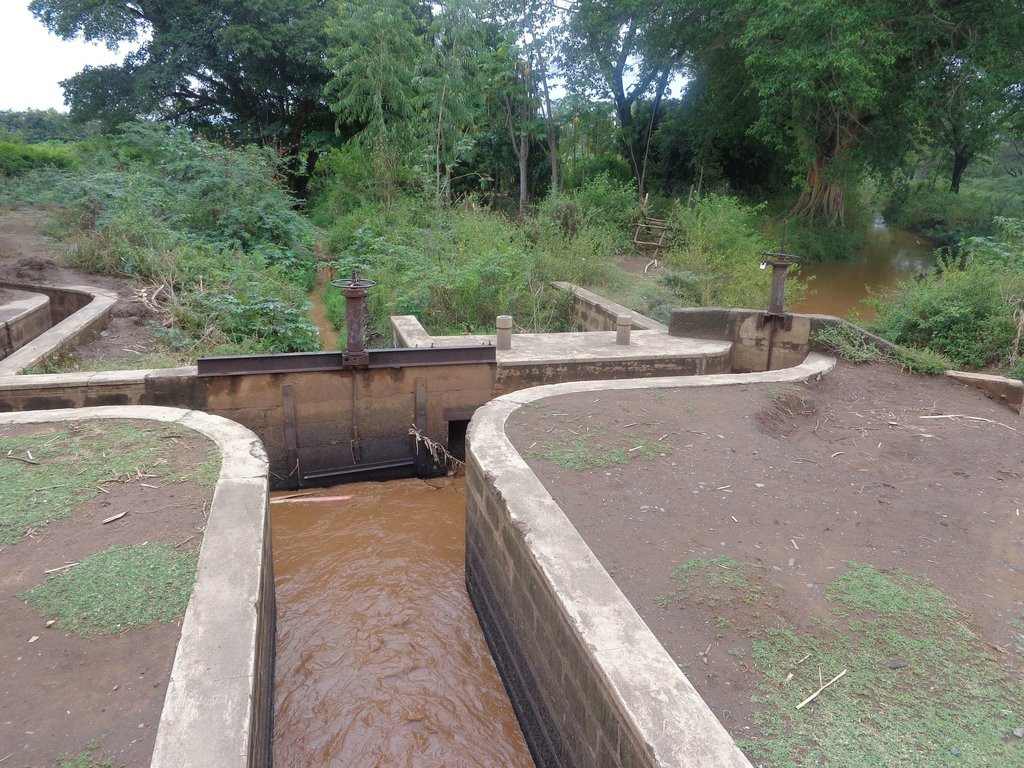
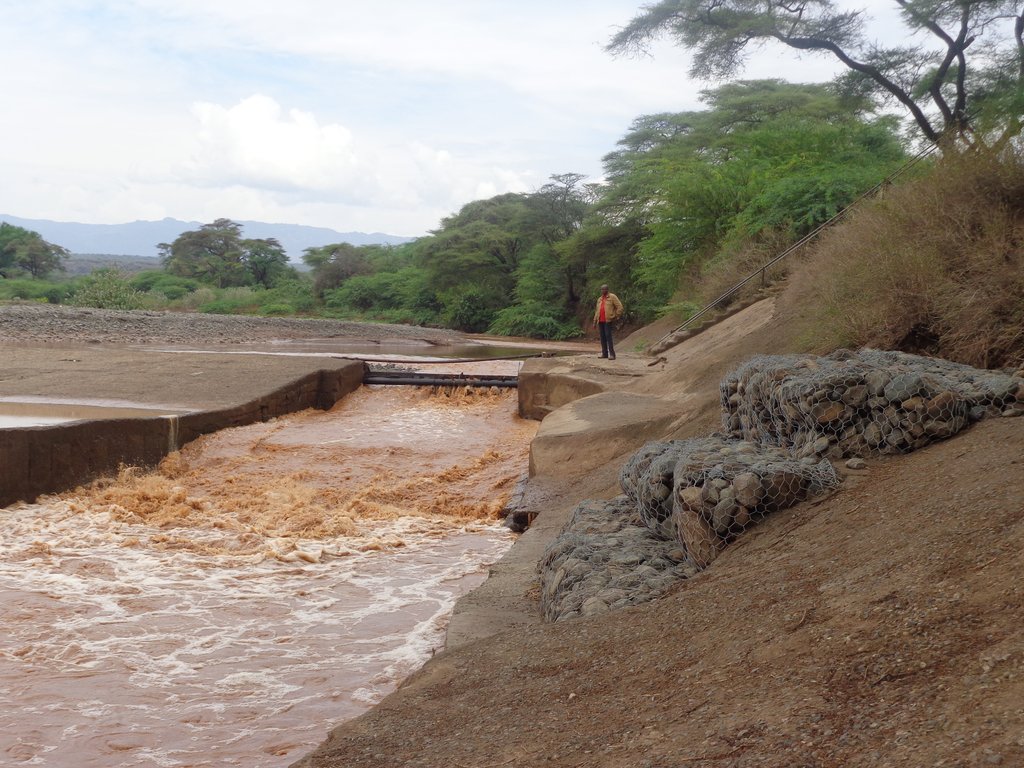
This is an open-furrow system consisting barriers constructed along a water source such as a river to direct water through a conveyance system by gravity into feeder channels to cultivated land. It is a simple method entailing control of water flow rate and direction to improve water utilization efficiency and enhance productivity of land.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Perkerra irrigation scheme was constructed by the colonial government in 1945 to ensure efficient water utilization, enhance soil productivity and food security. It is an open-furrow system consisting barriers constructed along a water source such as a river to direct water through a conveyance system by gravity into feeder channels to cultivated land. Water control system is constructed between the conveyance and the feeder channels to control the direction and speed of the water.
This technology is suitable on fairly flat, irrigable land with reliable water sources for irrigation. Consideration of population structure is crucial in ascertaining the availability labor force in farmlands. Depending on the size and market orientation of the production system, a stable market is also an important consideration.
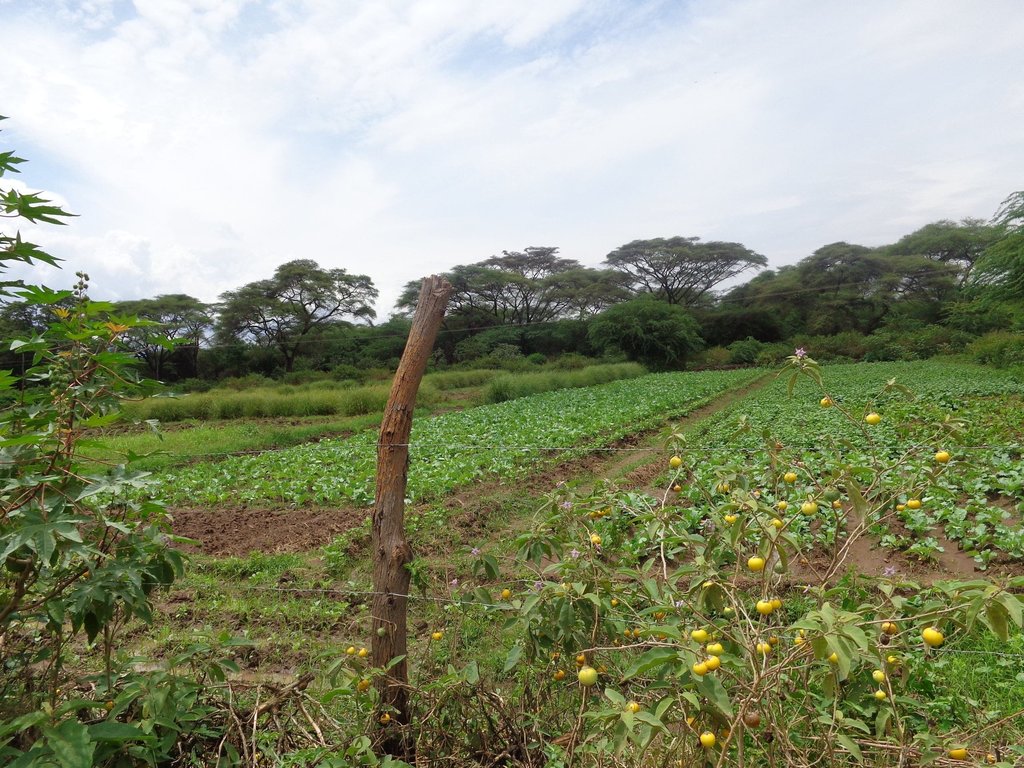
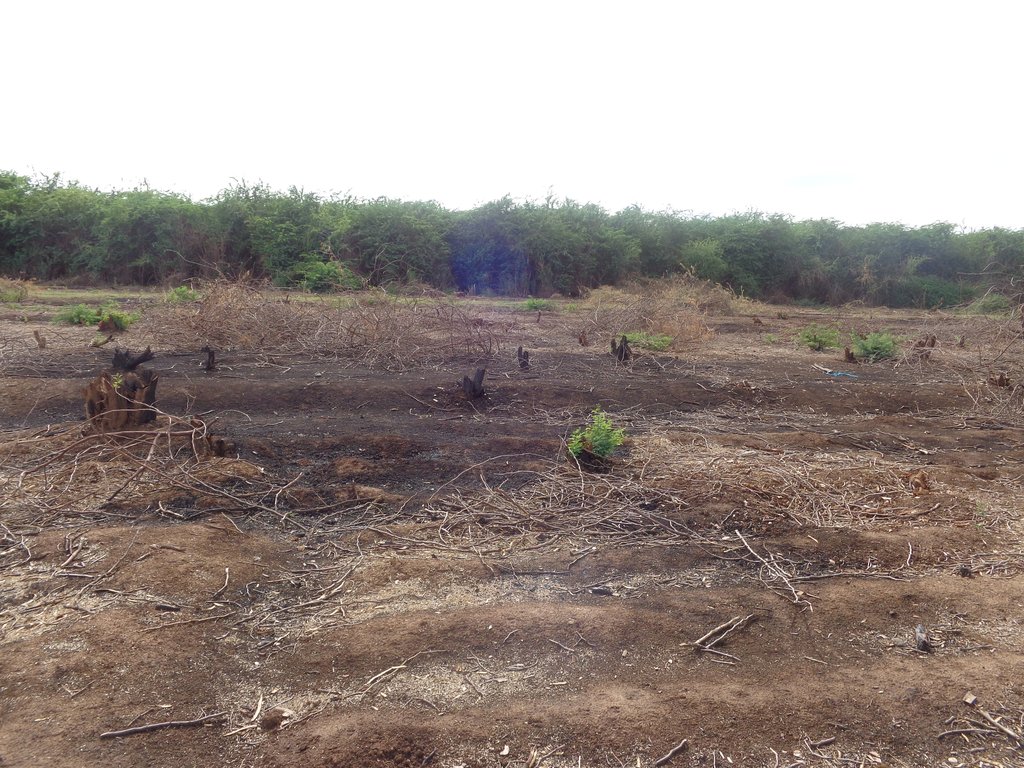
Irrigated farming in the scheme is carried out in 3 seasons a year due to availability of reliable water from the permanent Perkerra River. This also ensures that land is never left idle for re-invasion of Prosopis. Activities commence with land clearance conducted at the beginning of every planting season. Prosopis on invaded farmlands are manually cut, burnt and uprooted to minimize chances of the invasive tree from coppicing. The uprooted trunk is utilized in charcoal production for commercial purposes while the small branches are used as firewood for domestic cooking.
The cleared land is then ploughed using a tractor to break the soil structure and provide a fine tilth for planting. This is followed by mechanized ridging to create channels and buffer furrows to convey and retain water long enough to be infiltrated into the soil. Seeds are then sown, a joint activity carried out through farmers’ cooperation. The scheme was originally specialized for bulb onions plantation but has transformed into more diversified food crops for subsistence and commercial purposes. Crops under contractual farming are seed maize, rice, sunflower, green grams, pepper and cow peas while surplus crops under irrigation include tomatoes, vegetables, water melons, subsistence maize crops and commercial fruit trees. In addition, availability of assured market and payment has made the scheme popular for seed maize cultivation. Ongoing experimental research on a variety sweet potatoes to reduce overdependence on maize crops have also shown promising results and are likely to be recommended for implementation. During planting seasons, fallow periods are replaced by rotational cropping and crop diversification. This improves soil structure by alternating deep and shallow-rooted crops. Replacement of the crop during rotation disrupts the life cycle of disease causing organisms, thus controlling pests and diseases as well as improving crop productivity. Consequently, there is minimal application of chemical pesticides, hence reduced chances of pollution.
The irrigated cultivation has improved the welfare of the community by diversifying their sources of livelihood from pastoralism, enhancing food security, eradication of poverty and improving infrastructure such as access roads to the farms. It is a major source of income, directly supporting 1,625 farm households earning an approximate total net income of Ksh. 148, 192,259 Million (Perkerra scheme brief prepared by the National Irrigation board, 2017). Each household is assigned between 0.5 to 4 acres of land. This range might however be narrowed in the near future due to the increasing population in demand for the fixed land resource. The other option under consideration is to reclaim more invaded land and expand the scheme. The challenge facing this approach and is yet to be addressed is limited water resources to sustain the expansion. Lack of suitable market for non-contractual crops as well as poor pricing due to monopolization by contracting institutions is also a great setback to this technology. A good example is the abandonment of pawpaw production by farmers due to marketing problems.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເຄັນຢາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Baringo County
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Marigat sub-couty
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The scheme was established during the colonial period through local detainees in Marigat. This followed a feasibility study pointing to the suitability of the IIchamus plain for agricultute,
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ປະສົມປະສານ (ການປູກພືດ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້), ລວມທັງ ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
Contracted crops: Seed maize, green grams, sunflower
Surplus crops: tomatoes, vegetables, assorted fruit and tree seedlings, pepper

ທິດທາງໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າ, ດິນທາມ
- ທໍ່ລະບາຍນໍ້າ, ທິດທາງນໍ້າ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ໃນເວລາ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ແມ່ນໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າ ດິນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຄີຍເປັນດິນປະເພດໃດ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
IIchamus plain was initially a pastoral land for grazing. Being a state owned land with no one held responsible for its management, the land was poorly managed by the society.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Channeling of irrigation water into farms is restricted to dry seasons and temporarily halted during the rainy season.
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 3
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
The irrigation scheme is subjected to continuous cultivation with contracted crops planted in 2 seasons and a surplus crop on a third season in a year. Crop rotation and diversification is practiced to improve soil productivity, control pests, reduce soil erosion and enhance soil structure.
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ລະບົບການປູກພືດໝູນວຽນ (ການປູກພືດໝູນວຽນ, ປ່າເລົ່າ, ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່)
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຊົນລະປະທານ (ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ, ລະບາຍ)
- ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງນໍ້າ ແລະ ການລະບາຍ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ືື ຢ່າງສະໜ່ຳສະເໝີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ ໂດຍການຄາດຄະເນ:
- > 10,000 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology are specifically applied along the irrigation scheme with sufficient water for irrigation
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A5: ການຈັດການ ແລະ ການປັບປຸງແກ່ນເມັດພັນ ແລະ ແນວພັນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V3: ການຈັດການປູກພືດ
- V4: ການປູກທົດແທນ / ກຳຈັດສາຍພັນ ທີ່ຮຸກຮາມ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S2: ຄັນຄຸ, ແຄມຕາຝັ່ງ
- S5: ເຂື່ອນໄຟຟ້າ, ຝາຍເກັບນໍ້າ, ອ່າງ, ໜອງ
- S7: ອຸປະກອນເກັບຮັກສາ, ສະໜອງນ້ຳ, ຊົນລະປະທານ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- M4: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ໄລຍະເວລາ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
- M5: ການຄວບຄຸມ / ການປ່ຽນແປງຂອງອົງປະກອບຂອງຊະນິດ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
- Cs: ການເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດດິນເຄັມ / ເປັນດ່າງ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bp: ສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ພະຍາດເພີ່ມຂື້ນ, ສູນເສຍນັກລ່າ ແມງໄມ້ທີ່ໃຊ້ປາບສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ພະຍາດຂອງພືດ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
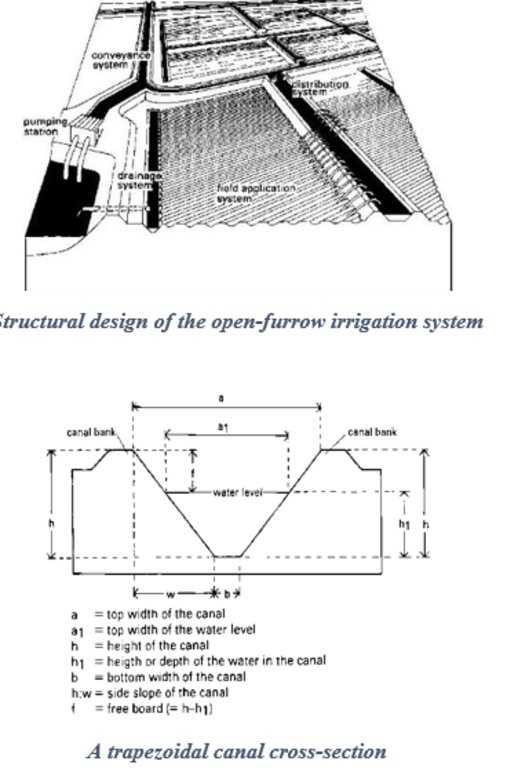
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
The intake structure convey water from the main water source to the irrigation system. It may consist of a water pump or a barrier designed for this purpose. The water is directed to a conveyance system of open canals which control the flow and direction of water to different field application and distribution systems. The canals depth (h) is preferred to exceed the expected maximum water level (h){h>h1} of water within the irrigation system to minimize bank overflow. The side slope is a ratio of the vertical height to the horizontal canal width (h:w). They are fitted with water measurement, erosion and distribution control structures to regulate accurate distribution of water to the farms with minimum siltation of the banks. The water is then distributed to field ditches which transfer it to the irrigated farm. These are narrow waterways dug along the farms with checks across their lengths to hold and raise the upstream water levels long enough before releasing it to the next segment of the field ditch. This is meant to increase the rate of water infiltration into the soil.
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
hactares
ລະບຸປະລິມານ, ຄວາມຍາວ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ (ຖ້າຫາກວ່າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
1
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
KES
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
100.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
500
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct gravity intake system | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Once during establishment |
| 2. | Excavation of water canals | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Once during establishment |
| 3. | Establishment of water control structures | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Once during establishment |
| 4. | Land preparation ( Clearance and partitioning) | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Once during establishment |
| 5. | Construction of a suitable road network | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Once during establishment |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Activities involved are the construction of a gravity intake system, excavation of water canals, construction of a suitable road network and water control structures. Prior considerations are reliable water source, availability of irrigable land and labor for cultivation.
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ແຕກຍ່ອຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງຕາຕະລາງລຸ່ມນີ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ ສາມາດ ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນ ມູນຄ່າທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
600000000.0
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The initial establishment and construction of the irrigation infrastructure is often conducted by the national government due to associated high costs approximated by key informants to be Ksh, 600, 000,000 (600,000 USD). This is however an initial, one off expenditure that are non-recurrent.
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing land | ພືດ | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 2. | Ploughing | ພືດ | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 3. | Ridging/Cutting furrows | ໂຄງສ້າງ | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 4. | De-silting of canals | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 5. | Planting | ພືດ | 3 times a year. |
| 6. | first irrigation | ໂຄງສ້າງ | 3 times a year after planting (3 to 5 days per season) |
| 7. | Pest control | ພືດ | Whenever applicable |
| 8. | Weeding | ພືດ | Once every season |
| 9. | Second irrigation | ໂຄງສ້າງ | 10 to 12 (each time withinn 3 to 4 days) per planting season. |
| 10. | Top dressing ( Apply fertilizer) | ພືດ | Once every season |
| 11. | Harvesting | ພືດ | Once every season |
| 12. | Shelling | ພືດ | Once every season |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Maintenance activities mentioned above are dependent on the status of an individual's farm, availability of resources and the purpose for cultivation. Farm produce cultivated under contracted terms will however need to follow strict procedures for them to meet the minimum requirements.
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Land clearance | Man-hour | 540.0 | 120.0 | 64800.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Partitioning | Man-hour | 180.0 | 100.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Planting | Man-hour | 90.0 | 100.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Ploughing tractor | Hours | 18.0 | 420.0 | 7560.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Ridging tractor | Hours | 18.0 | 420.0 | 7560.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds and seedlings | Kg | 75.0 | 150.0 | 11250.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Channeling water for irrigation | Season | 3.0 | 2000.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Fertilizer | Kg | 150.0 | 50.0 | 7500.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 131670.0 | |||||
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Size of land
Disease and pest outbreak
Crop variety as contracted crops minimum requirements which may be costly to meet
Occurrence of rainy seasons especially during harvesting which affect the drying cost and output of produce. Seed maize, for example, may not meet the required moisture content when aired during the rainy season hence lowering the net income from them.
Condition of the farm e.g invasion level by Prosopis
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
671.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Rainfall is characterized by seasonal and annual fluctuations
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
The area is in a semi-arid zone with temperatures ranging between 16 to 36 degrees, averagely 24.6 degrees, accompanied by high evaporation rates of up to 6mm. It experiences an average rainfall of 671 mm annually which are very erratic.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
The technology is applied in relatively flat land to increase water retention long enough to be infiltrated into the soil
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Clay soil with alkaline pH of 7.5 , rich in calcium phosphate but low in organic matter
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
Prosopis has heavily invaded the land, encroaching agro-pastoral land and outcompeting native species leading to degradation of native species and habitats.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມ (ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ / ເປັນສິນຄ້າ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Current land allocated by the government for the practice is an estimate of 1,800 ha. Pressure due to population increase has however triggered plans for future expansion.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The scheme is state owned , leased to the community who nominate a 7 member advisory committee tasked with all land administration aspects ranging from land adjudication, allocation, succession and dispute management as well as set laws guiding water utilization and conservation.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
567 ha
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
1,745 ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
the area developed for furrow irrigation has increased by 1,178 ha between 1958 when the operations begun to date. This is more than twice the initial land size allocated and utilized for irrigation purposes.
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Development of the technology has transformed it from an open access to an organized communal tenure system with communally-designed restrictions to its access, utilization and management.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນໍ້າ ສໍາລັບລ້ຽງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There are chances of water pollution when contaminated irrigation water flows back to the animal watering points.
ຄວາມຕ້ອງການ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The progressive increase of area under cultivation as well as prolonged dry seasons over the years have culminated into increased water consumption hence a high demand for the same.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Net income of 148 192 259 million Kenya shillings
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Farming activities have diversified and increased income sources to the community who depended mainly on pastoralism. This has been enhanced by a wide variety of crops being cultivated through irrigation.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Farming activities (tedious cutting, burning and uprooting of Prosopis in invaded farms, ploughing, weeding and harvesting) are all physical activities that increase the workload of the communities involved.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ສາຍພັນຕ່າງຖີ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Irrigated land has to undergo clearance of all Invasive species, in this case, Prosopis during land preparation activities. This is carried out through a cut-burn-uproot approach to minimize chances of their proliferation. Any re-growing invasive plant is uprooted before maturity to prevent further competition for water and nutrient with cultivated crops. Chances of re-invasion are also minimized as land is never left idle for colonization by Prosopis. This has greatly decreased invasive cover on irrigated land.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Drought related impacts such as malnutrition, famine and death have been reduced by irrigation practices which increases food insecurity independent of the season.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Diversion of water into open channels for irrigation reduce the downstream flow for offsite usage downstream.
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Potential flood water are diverted to farms hence reducing downstream flooding. However, this impact may not be significant during heavy downpours where diversion valves are closed to prevent unnecessary water logging on farmlands.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ / ລະດູຝົນ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ປານກາງ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງຊີວະພາບ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍາດລະບາດ | ບໍ່ດີຈັກຢ່າງ |
| ແມງໄມ້ / ການລະບາດຂອງພະຍາດ | ບໍ່ດີຈັກຢ່າງ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
Direct beneficiaries of the technologies are about 13,000 people. However, indirect beneficiaries from the transportation and sale of the produce may double this number
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 90-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
All operation are carried out at the full expense of the land users. Credits advanced to them have to be repaid with at least 11% interest
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ລະບຸແມ່ນເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃດທີ່ໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງ ທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດມີການປັບຕົວ:
- ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ຮ້າຍແຮງ
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Water conveyance along the furrows to the farms is halted during heavy downpour to minimize water logging.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| A source of finance to land users through sale of their produce. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Continuous farming activities have ensured that land is constantly managed, limiting the proliferation of Prosopis weeds which have adverse impacts to the ecosystem and livelihoods. |
| Improved human welfare by enhancing their financial stability. An extension of this is indirect benefit through employment creation to farm laborers, merchants and buyers of the fresh and healthy farm produce. |
| Increased food security |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Poor market prices for their produce. | They feel they have no option due to inadequate knowledge and access to other available markets |
| Pests and disease out break such as the fall armyworm. | Advisory services are offered by research institutions to stakeholders on how to manage and control pests. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Monopoly of the market by the contracting institutions may lead to poor pricing or tight minimum requirements such as the quality of output leading to losses. | Diversification of market to tighten competition that may offer better prices to farmers. |
| High chances of water pollution by chemicals and fertilizers that may be washed away by the running water | Minimize application of chemicals as possible accompanied by integrated nutrient management practices. |
| Post harvest losses when supply exceeds demand | Proper timing of planting season whereby harvesting coincides with seasons of shortage and scarcity to maximize returns. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
2
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
2
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
2
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Brouwer, C., Goffeau, A., and Heibloem, M. (1985): Irrigation Water Management: Training Manual No. 1
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://www.fao.org/docrep/r4082e/r4082e00.htm#Contents
7.3 ສາມາດເຊື່ອມໂຍງ ຂໍ້ມູນຂ່າວສານ ໄດ້ໂດຍຜ່ານການອອນລາຍ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Perkerra Irrigation scheme Brief
URL:
https://www.nib.or.ke/projects/public-irrigation-schemes/perkerra-irrigation-scheme
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
The 9 Benefits of Crop Rotation to the Environment
URL:
http://richmondvale.org/crop-rotation/
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ