Pond Sand Filter (PSF) with Raised Embankment [ບັງລາເດດ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: John Brogan
- ບັນນາທິການ: Shahid Kamal, Md. Rahmatullah Faruque
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Alexandra Gavilano, Hanspeter Liniger, Nicole Harari, Deborah Niggli
FILTER
technologies_550 - ບັງລາເດດ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - ສະວິດເຊີແລນ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
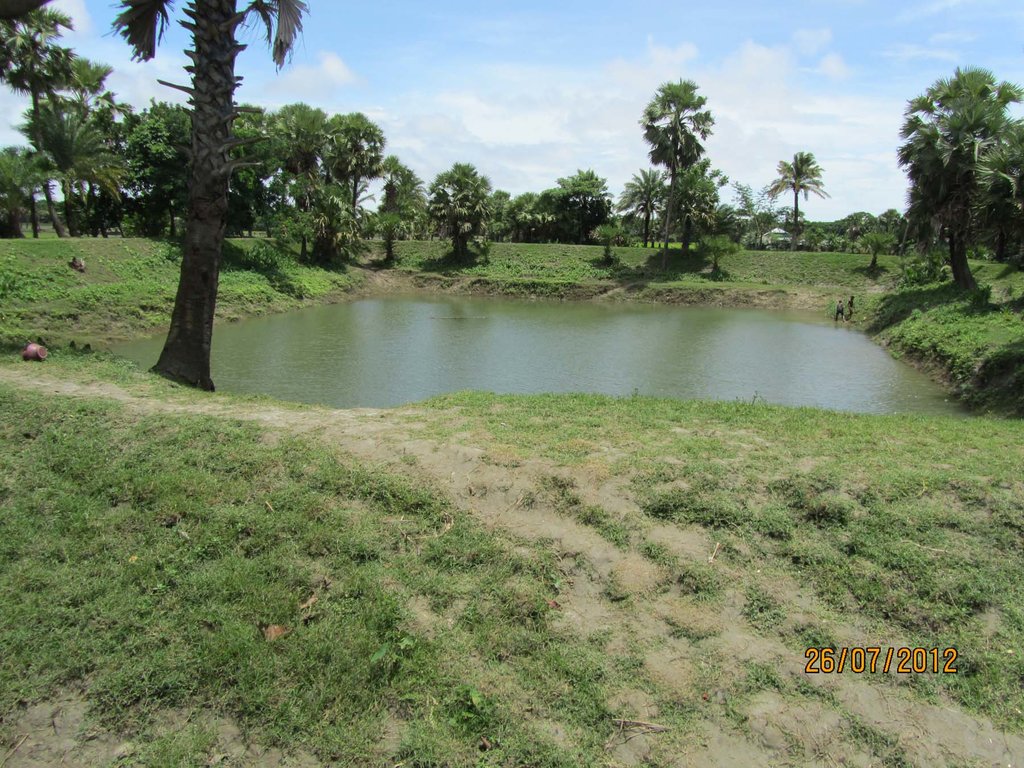
The combination of pond sand filters (PSF) and raised pond embankments protect drinking water sources and increase the resilience to flood and tidal surge events in low-lying coastal areas.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
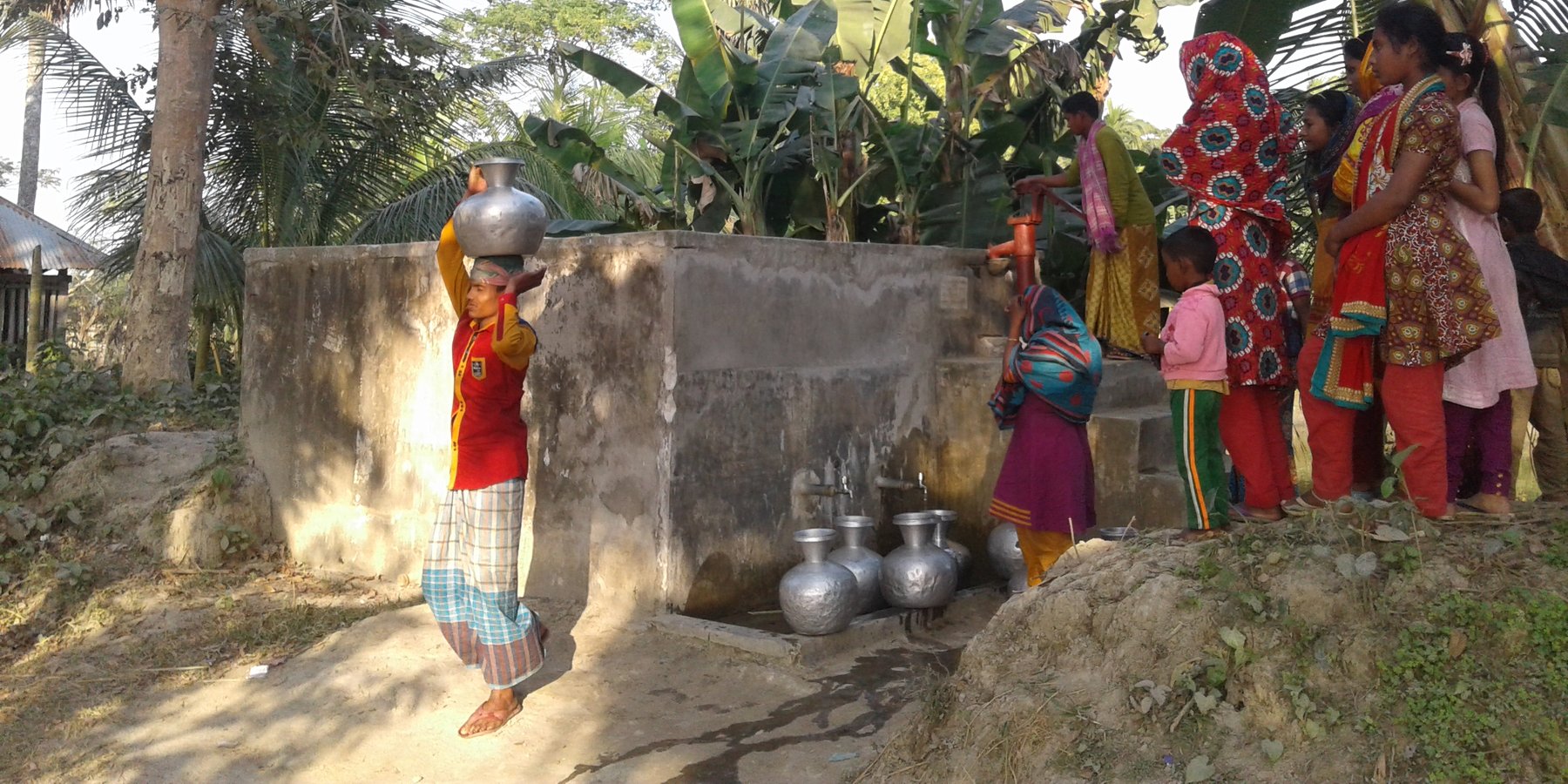
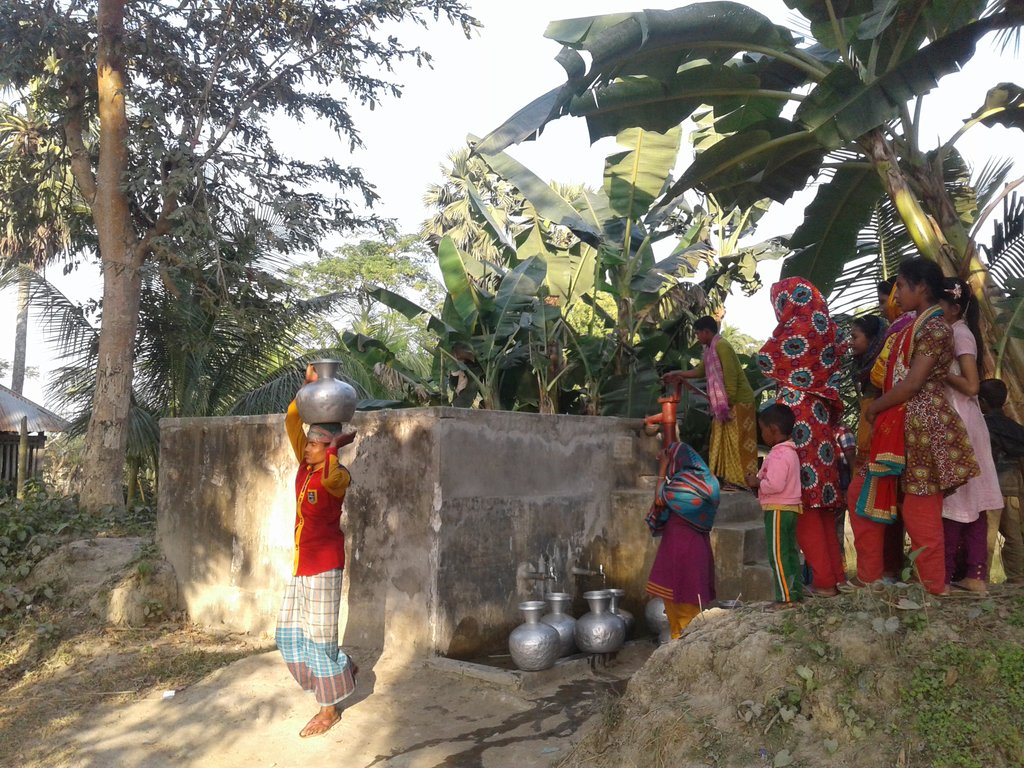
Coastal areas along the Bay of Bengal experience extreme seasonal variance in the presence of surface water including flooding, tidal surge, and drought. Many families living in these rural communities construct small ponds to ensure water availability for a variety of uses, such as washing, bathing, fish farming and animal watering as well as domestic use. Some families build larger ponds that are open to the use of all community members; whereby water is carried by women and children to households. Use of pond surface water may last up to several months during the year depending on the location, seasonal weather patterns, geologic conditions, capacity of the pond and user habits. Residents rely on ponds as a source of drinking water during the dry season when household rainwater harvesting techniques are no longer viable, making treatment essential.
Pond sand filters (PSF) is acentralised or semi-centralised water treatment technology often employed in many coastal areas where surface water is the only option due to saline aquifers and lack of resources for more robust, safely managed community water supply systems. The technology uses slow-sand filtration to remove turbidity (sediments) and pathogenic organisms whereby freshwater flows through layers of sand and gravel populated by a thin layer of microorganisms and treatment happens through physical and biological processes. Due to resource constraints, the number of PSF serving as water sources is usually limited. The technology considerably reduces the risk of infection with enteric pathogens. In conjunction with PSF, safe water transport (covered and cleaned containers) and household water treatment systems (chemical or additional filtration devices) are essential.
As stated in the Sustainable Sanitation and Water Management Toolbox (SSWM) slow sand filtration systems are characterised by a high reliability and rather low lifecycle costs. Moreover, neither construction nor operation and maintenance require more than basic skills. Hence, slow sand filtration is a promising filtration method for small to medium-sized, rural communities with a fairly good quality of the initial surface water source. As stated by the the World Health Organisation, slow sand filtration provides a simple but highly effective and considerably cheap tool that can contribute to a sustainable water management system.
Once a SSF facility is built, only clean sand is required for occasional replacement. The sand layers are put in gradually according to their grain sizes: rather coarse grains at the bottom and fine grains at the top. The sand-bed is usually covered with one meter of supernatant water (LOGSDON 2003). As the process of biological filtration requires a fair amount of time in order to improve effectiveness of water treatment, SSFs usually operate at slow flow rates between 0.1 – 0.3 m3/h per square metre of surface (WHO n.y.). The water thus remains in the space above the medium for several hours and larger particles are allowed to separate and settle. It then passes through the sand-bed where it goes through a number of purification processes (HUISMAN 1974).
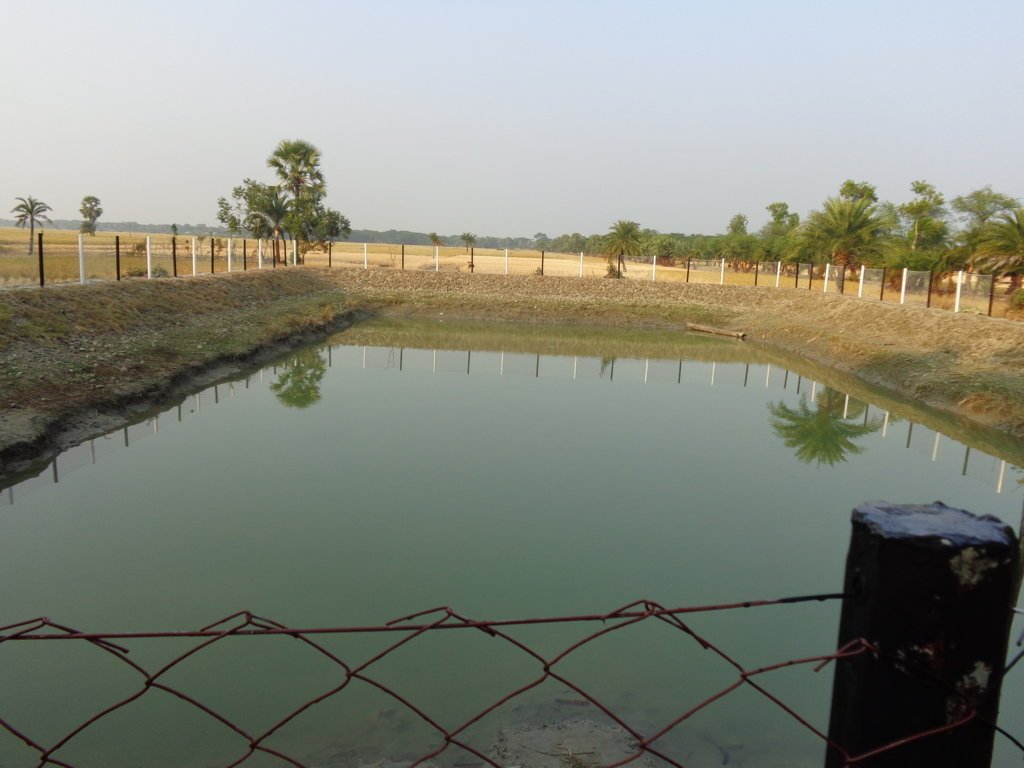
Due to the risk of inland flooding and (seawater) tidal surges from offshore storms, communities build earthen embankments around the ponds to prevent contamination. Local authorities and community members must be involved in the design height of the embankment—which should be equivalent to the highest pre-recorded flood level. In the geo-referenced area (Patharghata) this is equivalent to the tidal surge of Cyclone Sidr (2007). Constructed roadways are often a good reference point. In southern Bangladesh , rural roadways are built to at a ten-year flood return period, so exceeding this height according to the means of the community and/or project is recommended.
Pond embankments are best raised with soil preferably of a clayey nature. The final covering layer must be rich in clay. Embankments should be planted with native grasses and flora that have strong root systems to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion during the rainy season and in cases of tidal surge due to storms. In Bangladesh, the native kolmi (Ipomoea) has proven effective. Community members have also planted crops on the embankments, such as banana trees, medicinal plants and even small garden trenches in the middle of the slope. Beyond structural support, the horticulture helps diversify nutrition and can provide a source of income for maintaining the pond sand filter.
Fences should be installed to prevent animals from entering ponds reserved for drinking water. Community members must guarantee that the ponds selected for PSF construction shall not be used for purposes such as: washing, bathing, fish farming (natural fish however can be allowed), direct cattle access washing and watering. Furthermore:
•Fertilizers and other chemicals shall never be allowed to go into the pond.
•The flow of any polluting materials in the vicinity of the pond shall always be directed away from the pond.
•Latrines, cowsheds, garbage dumps, graveyards, fuel outlets and similar polluting structures shall not be constructed within a distance of 30 meters from the pond.
•Duck or poultry rearing hanging sheds shall never be constructed over the pond.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
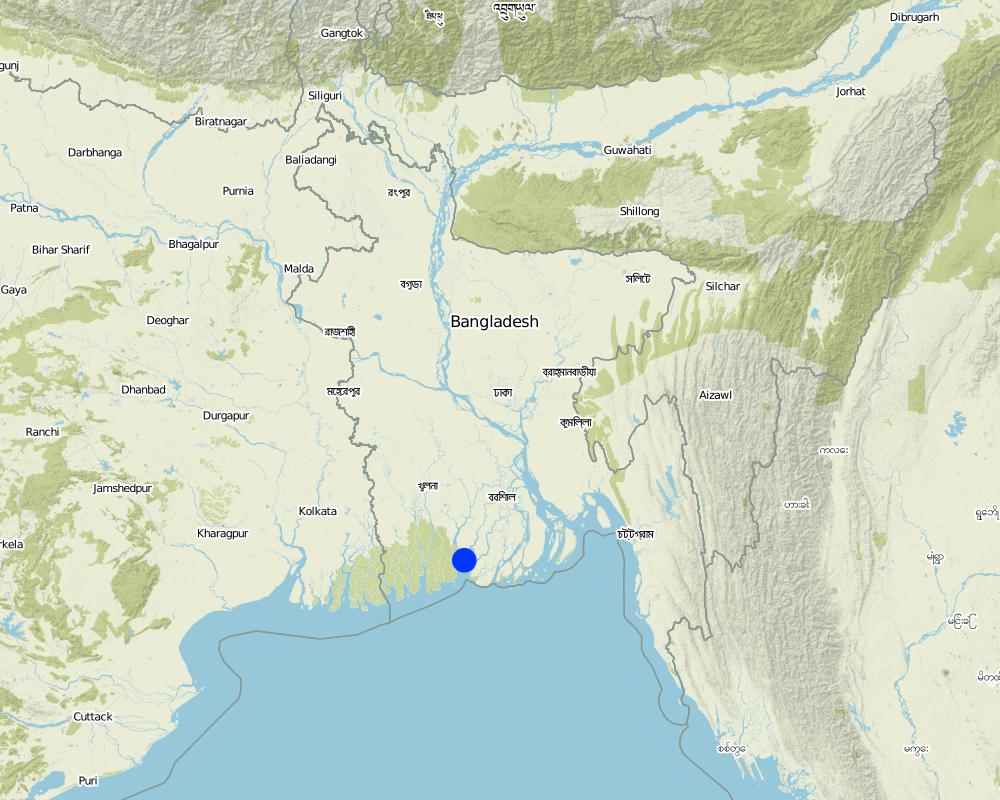
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ບັງລາເດດ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Patharghata, Barguna district in coastal region
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Baratangra, Ward:4, Union: Patharghata Union Parishad
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This technology may be applied to selected ponds within a community.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ພືດທີ່ເປັນຢາ / ກິ່ນຫອມ / ພືດປາດແມງໄມ້ ແລະ ສະຫມຸນໄພ
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ກ້ວຍ/ກວ້ຍຂຽວ/ໄຍຕົ້ນກ້ວຍ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ (ນ້ຳຈາກພຸ, ແມ່ນໍ້າ, ທະເລສາບ, ທະເລ)
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S2: ຄັນຄຸ, ແຄມຕາຝັ່ງ
- S5: ເຂື່ອນໄຟຟ້າ, ຝາຍເກັບນໍ້າ, ອ່າງ, ໜອງ
- S7: ອຸປະກອນເກັບຮັກສາ, ສະໜອງນ້ຳ, ຊົນລະປະທານ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Hs: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະລິມານ ນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
- Hp: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Preventing salt water intrusion, the surface water quality and quantity is protected. Turfing and planting the embankment prevents erosion.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ບໍ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
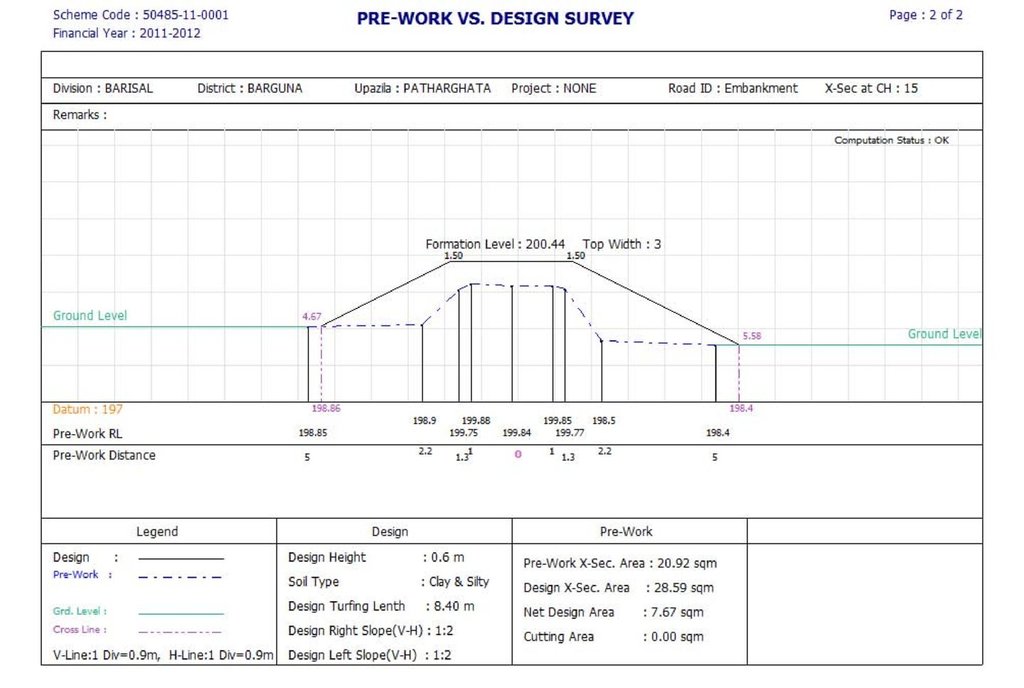
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
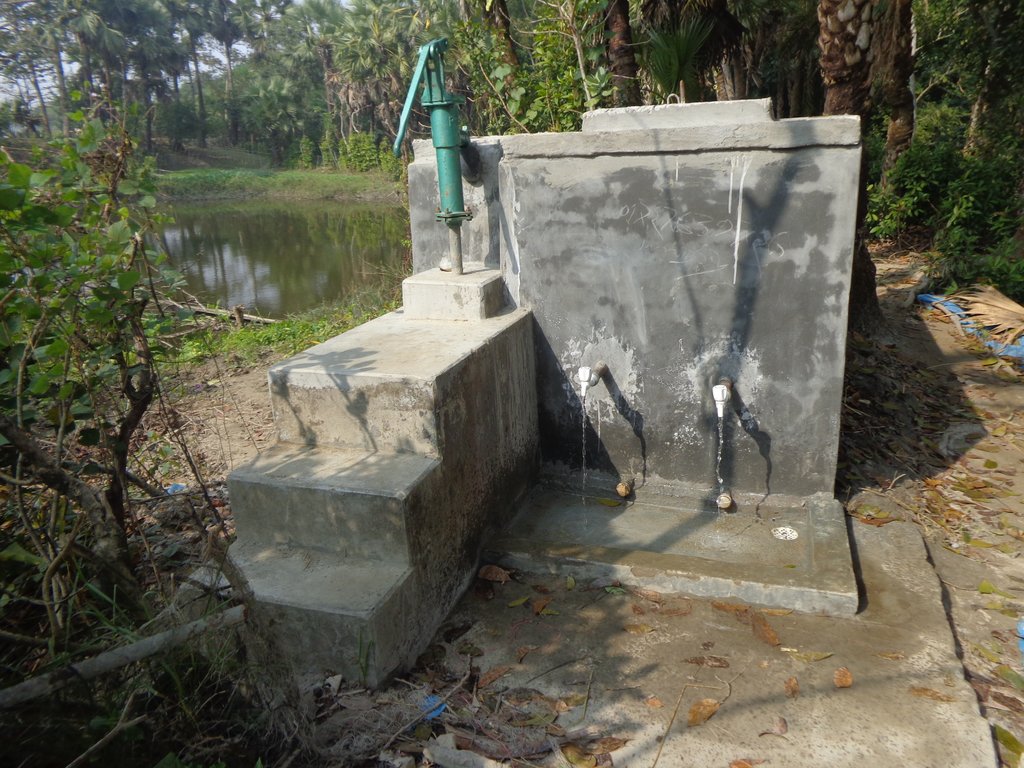
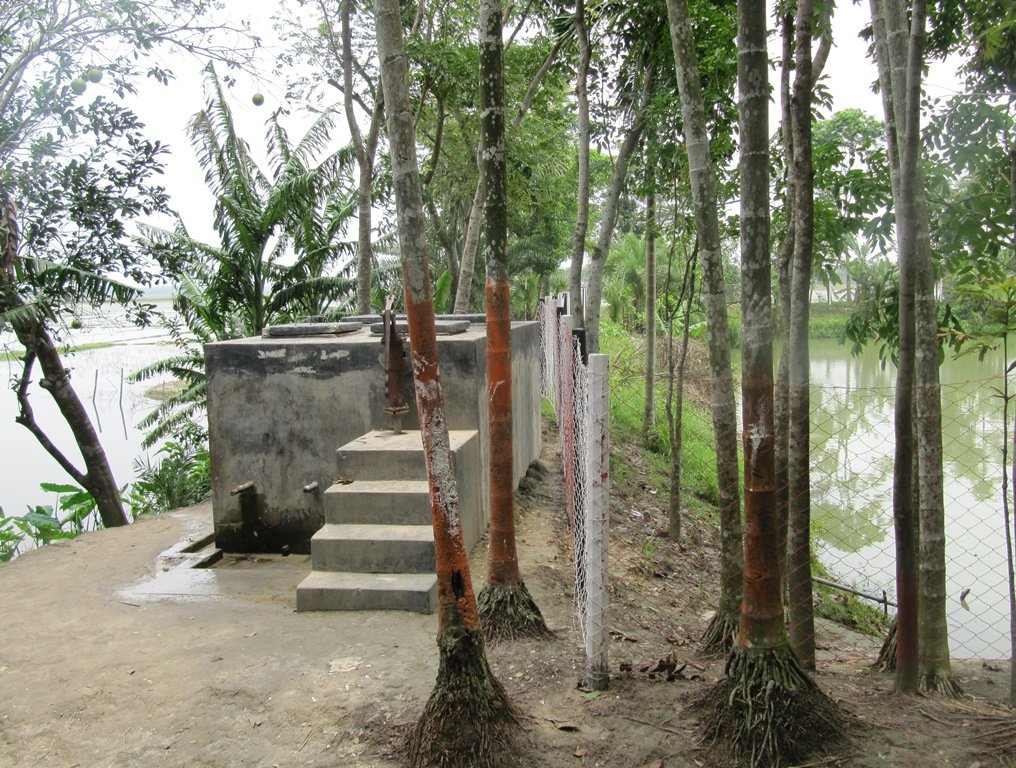
PSF is built on top of the raised embankment as a reinforced concretes structure consisting of a sand filter chamber, filtered water chamber and the sedimentation tank. The height is 4 feet 2 inches; Length-14 feet 5 inches; Width-7 feet. The capacity of PSF is 2500 liters. The construction materials used include include brick, sand, brick chips, cement, galvanized iron pipe, water tap and rebar.
The medium in the filter chamber shall comprise of three layers: 1) filter sand of 2 feet (60 cm) depth placed above 2) a 3” layer of fine gravel and 3) a 3" layer of coarse gravel.
1) The filter sand shall have the following size and grade: (a) Sand grains in the range 0.1 to 1 mm, with (b) effective size ( d10) in the range 0.15 to 0.20; and (c) Uniformity Coefficient ( d60/d10) in the range 1.5 to 2.5. Sieves are used to test sand size and grade.
The "under drainage" bottom gravel layers:
2) Fine gravel: 3” layer ¼” to 1 mm grains (gravel that passes through the ¼” sieve and are retained on 1 mm sieve)
3) Coarse gravel: 3" layer of ½” to ¼” grains (gravel that passes through ½” sieve and are retained on ¼” sieve)
Use different sized sieves made of wire mesh in wooden frame to prepare the media to prepare the two layers of gravel.
Every 5-6 weeks (or when flow rate is limited) cleaning the filter should be performed. Remove the filter aggregate layers, clean the PSF by removing any remaining objects in the three chambers (sand filter chamber, filtered water chamber and the sedimentation tank). Clean these chambers thoroughly using hard brush in necessary. Sequentially clean and replace t the coarse gravel media, then the fine gravel media, and finally the filter sand. For cleaning the gravel and sand place about 1/4th bucket of grave or the sand in plastic bucket (8, 10 or 12 liters, whichever may be convenient), pour about ½ bucket of water and then wash lifting the gravel or the sand from the bottom with hand several times, then decant the water by tilting the bucket. (Only fine particles less than 0.1 mm should be poured out while washing the sand.)
Raised Pond embankments are built with earthworks of clayey soils designed per the maximum flood height. The design depicted in this section is an indication, however the services of a qualified structural/civil engineer will be required. In general building the embankment is raised 0.6m above the maximum flood level is recommended, at a slope of 1:2. From the ground level, the average height of an embankment is two meters, and the average excavation depth is also two meters. All plans for both embankment works and PSF construction were reviewed and approved by the Bangladesh Government Department of Public Health and Engineering.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Terre des hommes
ວັນທີ:
30/06/2016
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
Pond Sand Filter with raised earthen embankment
ກໍານົດຂະຫນາດຂອງຫົວນ໋ວຍ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
2,500 Litres capacity of filter; embankment average of 100 meter perimeter.
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
5 $ per day for labor
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community consultation for Committee Formation | Before onset of rain |
| 2. | Create PSF Users' Committee, agre on user contributions | Before onset of rain |
| 3. | Committee / pond selection approved by local Government | Before onset of rain |
| 4. | Technical orientation to PSF Committee, input on designs | Before onset of rain |
| 5. | Excavation of Pond | Before onset of rain |
| 6. | Embankment Construction | Before onset of rain |
| 7. | PSF Construction | |
| 8. | Fencing | |
| 9. | Turfing and hortiuclutre on the embankment | Before onset of rain |
| 10. | PSF Training on Media Selection and maintenance | Regular intervals throughout the year (every 1-2 months) |
| 11. | Pond embankment maintenance | Before onset of rain |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
In general, the community approach begins with several consultation meetings in the community (inclusive: gender balanced and representative of the diversity makeup of the community) and with municipal authorities. An Outcome Mapping process is initiated to observe signs that a village is prepared and mobilized to receive support for PSF and pond embankment construction. Families must be willing to participate and contribute in the construction and take complete responsibility for operation and routine maintenance.
During the initial phase, a PSF Users’ Committee is formed and approved by the municipal government. Its members make time to participate in trainings on the design, use, maintenance and community organization for managing a PSF. Importantly, the PSF User’s committee must seek public commitments toward the construction costs in cash and/or in kind (labor, construction materials, embankments plants, etc). In Bangladesh this was 10% and usually in kind. Roles and responsibilities of the PSF Users’ Committee:
1)Be responsible for regular operation, maintenance and cleanliness of the pond sand filter;
2)Ensure that the maintenance points for pond water quality is respected per the manual;
3)Advocate for local authorities to conduct regular water quality testing; and to promote household water treatment systems
4)Establish a system of collecting money from users for the regular maintenance;
5)Organize Committee meetings before the start of each season and whenever needed. Similarly if required organize a wider meeting with users in connection with resolving any O&M issues.
6)Care for the tools and other materials that may be purchased for the pond sand filter.
Selection of ponds for PSF construction should be participative with criteria agreed and communicated with the community members and local authorities. The following criteria are suggested based on Terre des hommes’ experience in Bangladesh:
•Ponds that are large enough to retain water throughout the dry season.
•The salinity of the pond water must not exceed 600 ppm at any time of the year.
•While the location of the PSF should be close to a family to ensure its security, it must be as centrally located as possible for ease of access
•Freely accessible to the public; ideally donated for public use.
•Ponds located on higher ground and thus more resistant to flooding / sea water intrusion.
•Space available for raising the embankments around the ponds
•Ponds most accessible to a largest segment of the population during disaster.
•Each PSF should have an effective drainage space and system.
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Pond Excavation and Embankment Raising | Person-days | 180.0 | 5.0 | 900.0 | 10.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Pond Fencing Works | Person-days | 20.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | |
| ແຮງງານ | Masonry | Person-days | 36.0 | 6.25 | 225.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Repairing tools | Set | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tubewell/handpump | Pieces | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 10.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Sanitary Fittings | Set | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Bleaching powder for disinfection | kg | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Lime for cleaning | kg | 50.0 | 0.5 | 25.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | bricks | pieces | 6000.0 | 0.075 | 450.0 | 10.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | cement | 50 Kilo Bags | 50.0 | 5.75 | 287.5 | 10.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | sand | cubic feet | 52.0 | 0.375 | 19.5 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | mild steel round bar | kg | 210.0 | 0.75 | 157.5 | |
| ອື່ນໆ | Materials Transport Cost | Lump Sum | 1.0 | 185.0 | 185.0 | 10.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 2501.5 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 2501.5 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The project requested 10% contribution in kind (materials, transport, labor) from each community. The remaining costs were covered by the project.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The budget is for raising a 100m perimeter length of embankment.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing | Before onset of rains |
| 2. | Cleaning | Before onset of rains |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | two-monthly cleaning of filter materials | Person days | 12.0 | 5.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Seasonal erosion control | Person days | 12.0 | 5.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | bleeching powder | bag | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 130.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 130.0 | |||||
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Comparatively, construction materials costs was reflected as the most expensive consideration.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
www.discoverybangladesh.com
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ທຸກຍາກ / ບໍ່ມີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
groundwater table is salty along the Bay of Bengal, salt water intrusion. Tidal surge following cyclones also creates soil salinity.
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເປັນປົກກະຕິ:
ເລື້ອຍໆ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Embankments provide a modest space for small scale gardening and fruit/medicinal tree cultivation. Such agriculture activities would be protected from tidal surge waters that destroy agriculture in low-lying areas.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Terre des hommes had raised embankments on ten community ponds prior to cyclone Mahasen (2013). Nine of the ten ponds embankments remained intact, preserving valuable fresh water from sea water contamination for drinking after treatment with PSF.
ນໍ້າດື່ມ ມີຄຸນນະພາບ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
>1000 fecal coliform units
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
<10 fecal coliform units
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The PSF water source considerably reduces the risk of infection with enteric pathogens from the pond water. In Terre des hommes’ field experience, although a reduction in presence of fecal coliform (FC) by over 99% is possible, the PSF technology rarely eliminates all FC. A level of 1-10 fecal coliform units (FCU: colonies of E. coli per 100 mL of water) has been achieved, which is equivalent to an intermediate risk, or “probably safe” as defined by WHO. In conjunction with PSF, safe water transport (covered and cleaned containers) and household water treatment systems (chemical or additional filtration devices) are essential.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Users reported a decrease in water borne diseases through use of PSF water compared to surface water.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
During disaster, the use of the PSF increased, with people walking from further distances to take water from the PSF to their homes.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຄື່ນ / ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຊາຍຝັ່ງ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
PSF serves as disaster resilient Technology that helps residents in coastal villages along the Bay of Bengal to cope with the effects of climate change; such as increased incidence and intensity of storms and salt water intrusion.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- > 50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| The Technology is useful for supplying drinking water at household level and supports cultivation of fruit trees, medicinal plants and vegetables at the pond embankment, above the flood line. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| The Technology is conducive for ensuring supply of water for drinking, cooking and irrigation purposes if the community is motivated and understands the impact of PSF when faced with water shortage during dry season and other disaster events. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Every five to six weaks, the PSF filter media needs to be maintained, requiring some training, as well organising labor and collecting petty funds for bleaching powder. | The PSF User's Manual has been translated into local language with images and tips for maintenance. This is distributed following the training. The PSF User's Committee must regularly collect user fees for smooth operations. A bank account promotes transparency. Sale of crops harvested on the embankments can help defray costs of maintenance. |
| Although not laborious, the hand pump requires some degree of force, and the taps are often a target of children's play. | Children should be supervised and small children must not be allowed to operate or play near the pump. Investing in sturdy tap systems is essential. |
| The bio-film will form after seven days of operating the pump. | Users must boil or treat water very carefully in this period. |
| Private owners could lose interest availing their asset for the communty. For example, they may start using the pond for fish farming in order to sustain their livelihoods. | Formal agreements with the municipality about the usage rules for the pond, and public commitments taken by the pond owners are important. Posting signboards that identify the pond as "Drinking Water Only" and specify forbidden activities is also helpful. Owners can take a higher share of crops cultivated on the embankment. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Interviews with six informants
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
Compilation from five documents from past projects.
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
16/08/2016
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
SSWM University Course Module 6: Disaster Situations: Planning and Preparedness Further Resources: Water Purification Slow Sand Filtration, Marco A. Bruni, Dorothee Spuhler (seecon international gmbh), 2012.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://www.sswm.info/sswm-university-course/module-6-disaster-situations-planning-and-preparedness/further-resources-0/slow-sand-filtration
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Pond Sand Filter (PSF) Manual – community operation and maintenance, Laxman Kharal (Terre des hommes), 2012
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Contact: info@tdh.ch
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th Edition, WHO, 2011
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/2011/dwq_guidelines/en/
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ