Mulch-till [ສະໂນວາເນຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Gregor Kramberger
- ບັນນາທິການ: Matjaz Glavan
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Konzervirajoča obdelava tal (mulch-till)
technologies_6241 - ສະໂນວາເນຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Curk Miha
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
ສະໂນວາເນຍ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Cvejic Rozalija
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
ສະໂນວາເນຍ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Ropič Andrej
Farmer
ສະໂນວາເນຍ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - ສະໂນວາເນຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Mulch-till is a method of farming that does not utilise a plough, and thus the soil is not turned over. Furthermore, at least 30% of the cultivated area remains covered with organic residues left over from the previous crop. There are multiple benefits to the soil and carbon dioxide emissions are reduced.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
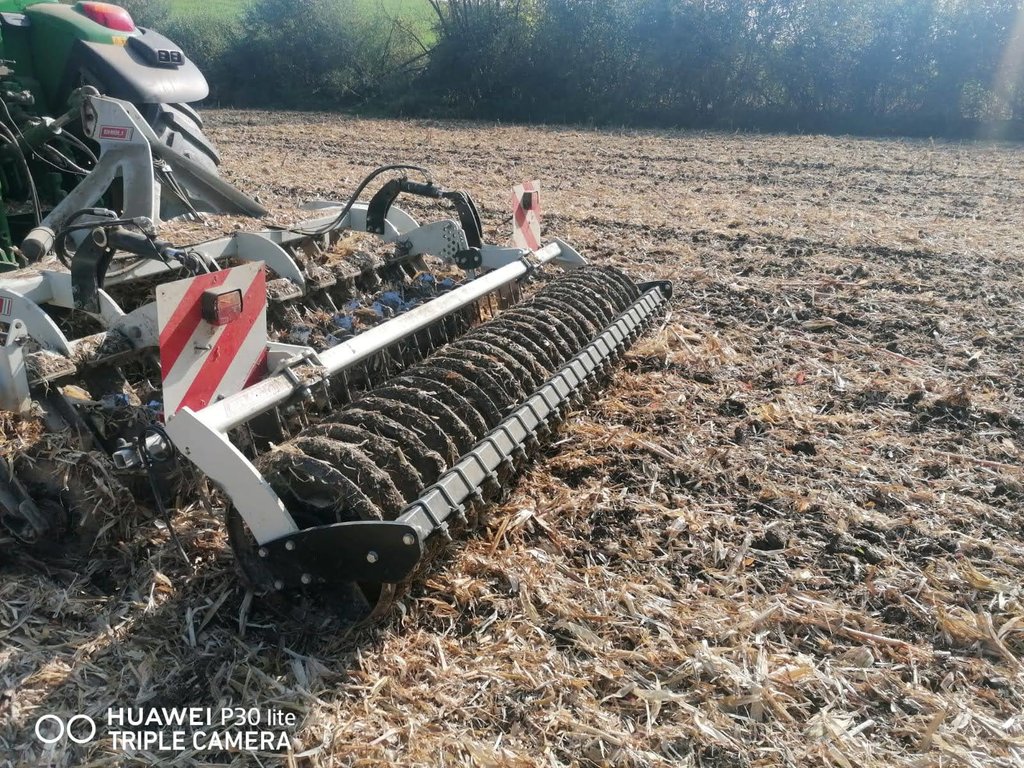
ການພັນລະນາ:
Mulch-till (also called “conservation agriculture” or “minimum tillage”) is a method of land management with modified, less intensive tillage, where land is covered with plant residues year-round (at least 30% cover) or grass, energy consumption is reduced, and there is less trampling/ compaction of the soil because of fewer machine passes and the protected surface. Under mulch-till, special agricultural machinery and attachments are required. Disc harrows and chisel ploughs are used to loosen the soil, and direct drills are employed for seeding. Ploughs are not used and the soil is not inverted. This method of tillage is intended to maintain soil structure, build up humus, improve nutrient supply and soil moisture, increase soil microbiological activity and also to prevent soil erosion. Mulch-till reduces the number of work operations on the cultivated area. Because the soil is disturbed less, this minimises the exposure of soil organic matter to the air, and therefore decreases the formation and release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
The debate over whether ploughing is still necessary has been going on for quite some time. Both mulch-till and ploughing have their advantages as well as disadvantages. Research shows that mulch-till reduces soil erosion and compaction, and this has a significant impact on soil fertility. On the other hand, ploughing better inhibits the spread of weeds and certain types of diseases and pests.
Mulch-till requires complete replacement of machines/tools, and this is a considerable initial investment. Regular annual maintenance of the equipment is needed also. Mulch-till provides full benefits after a number of years, through making sure that minimal soil inversion and organic soil coverage is guaranteed. It also requires good planning of crop rotation, the use of a special seed drill and employment of herbicides after emergence (or surface hoeing). Users mention one advantage being the low costs for tillage, which is less expensive than ploughing, and the reduction of soil erosion on sloping terrain. However, they do not like the high investment for equipment, possible lost of yields and increase in weeds: all tend to arise at the beginning of implementation. Knowledge and experience are required, as the technology is quite demanding, so there are chances of failure.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດທົ່ວໄປທີ່ກ່ຽວກັບຮູບພາບ:
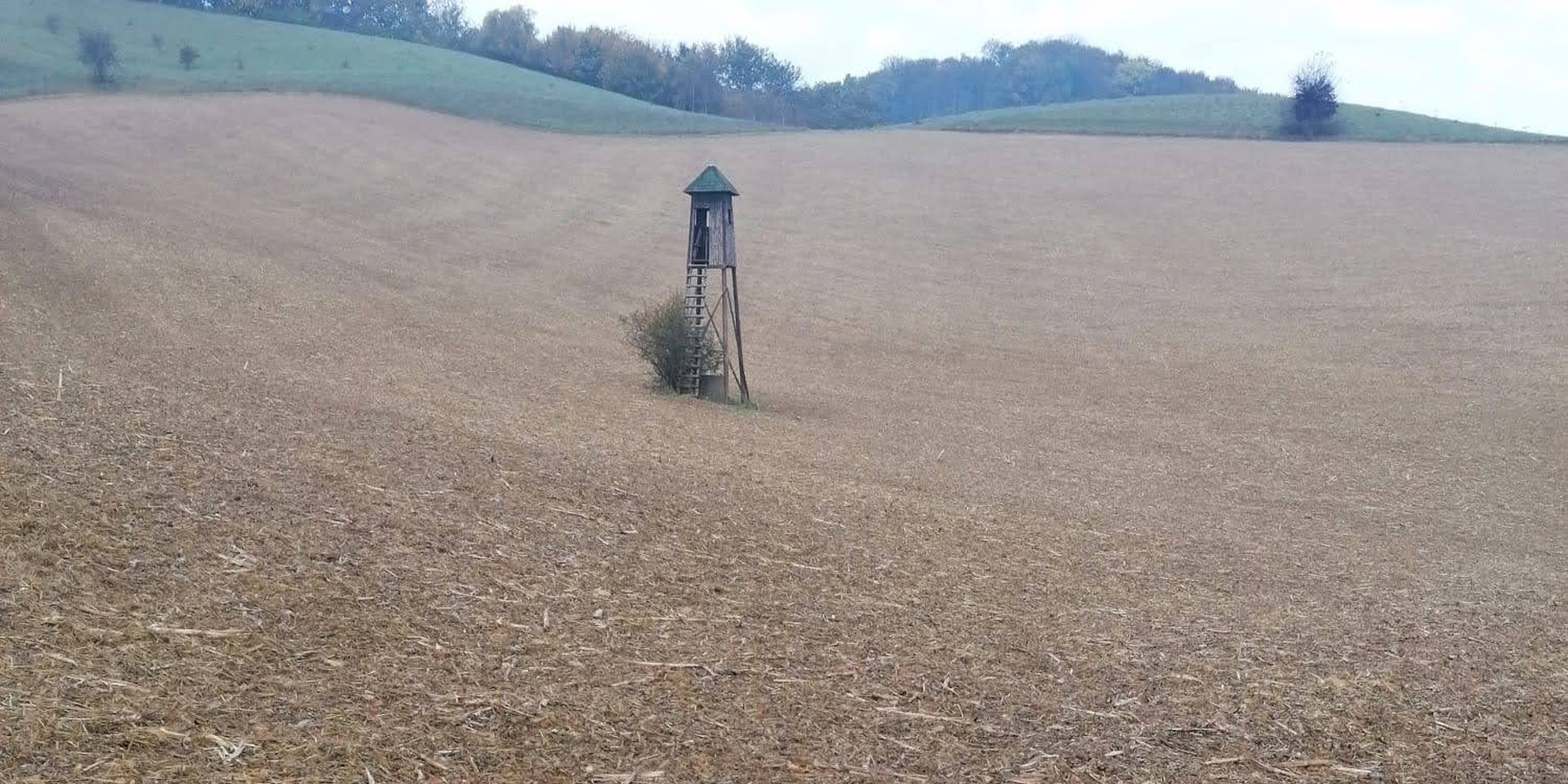
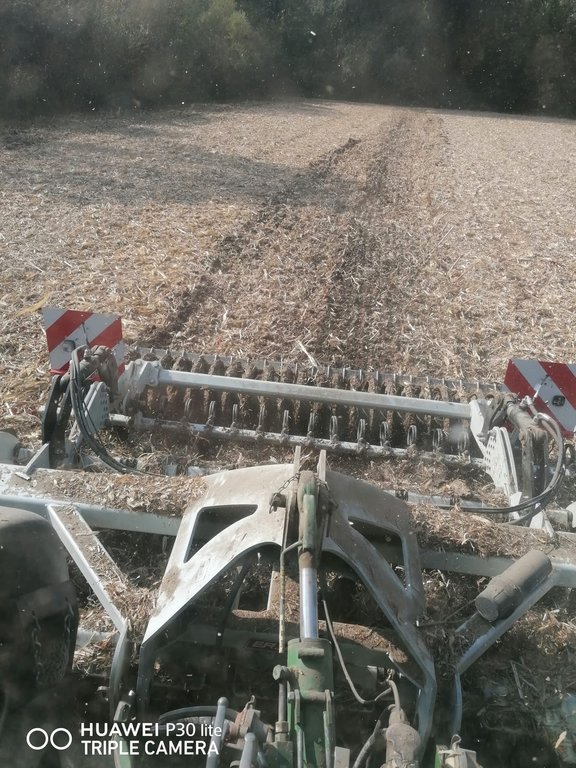
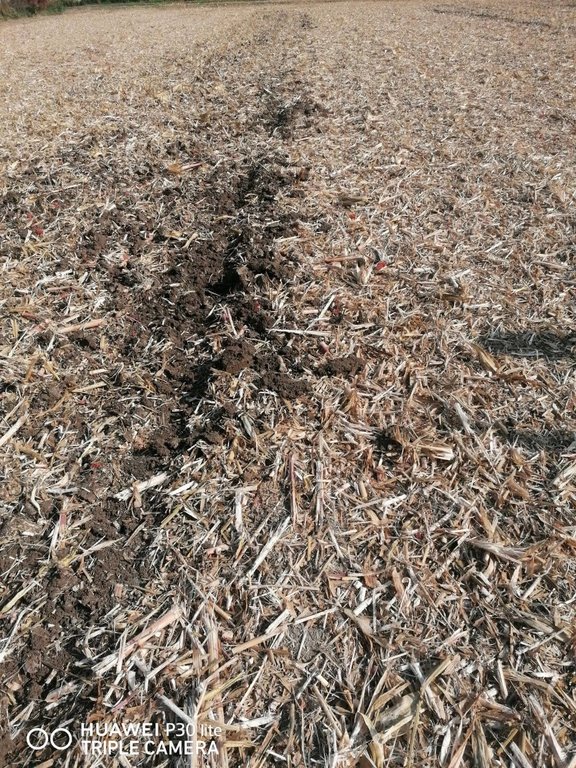
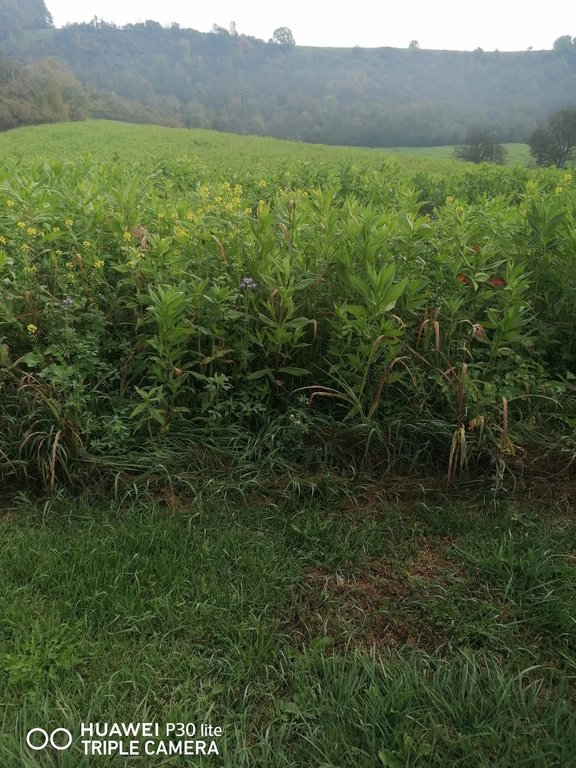
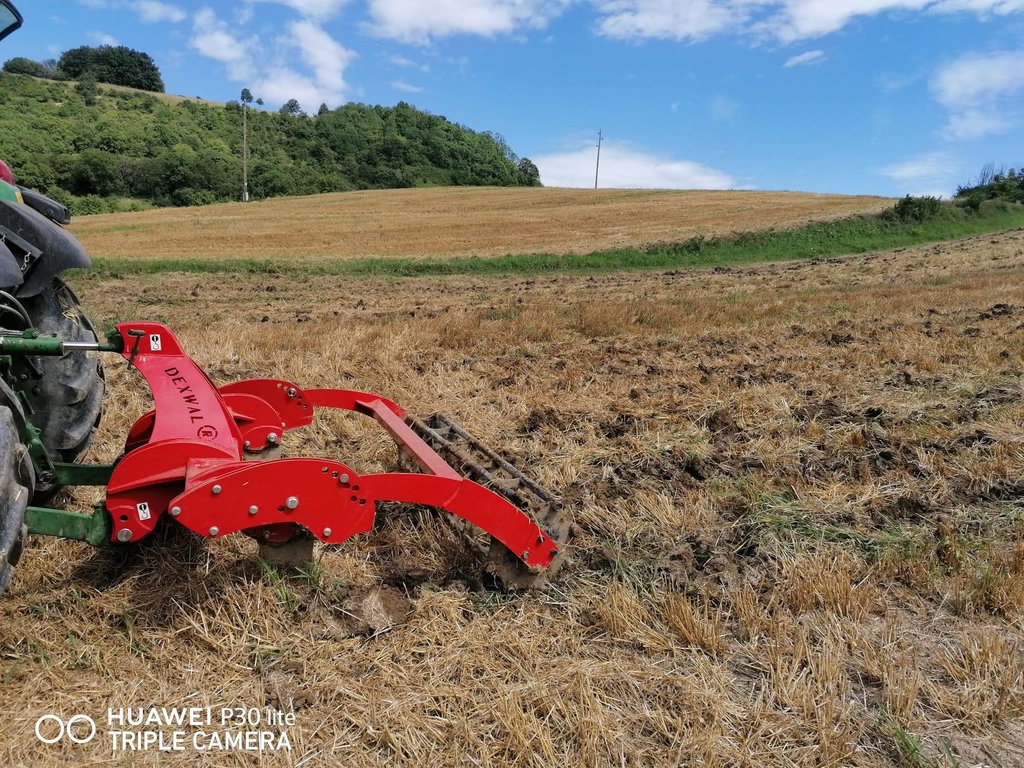
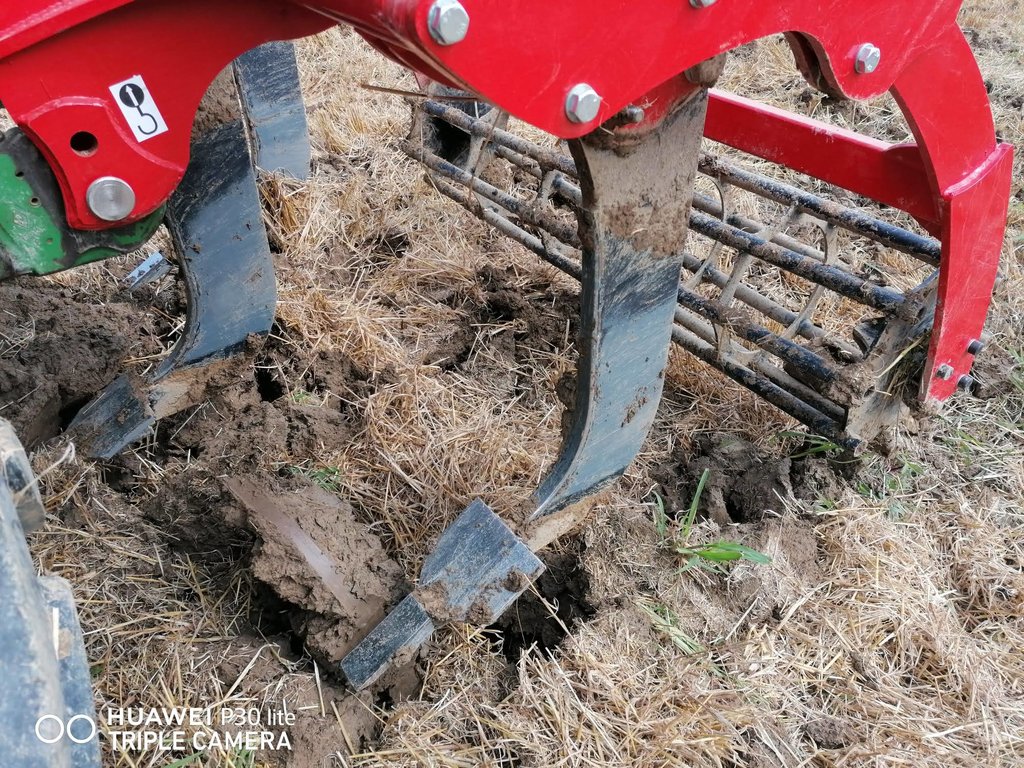
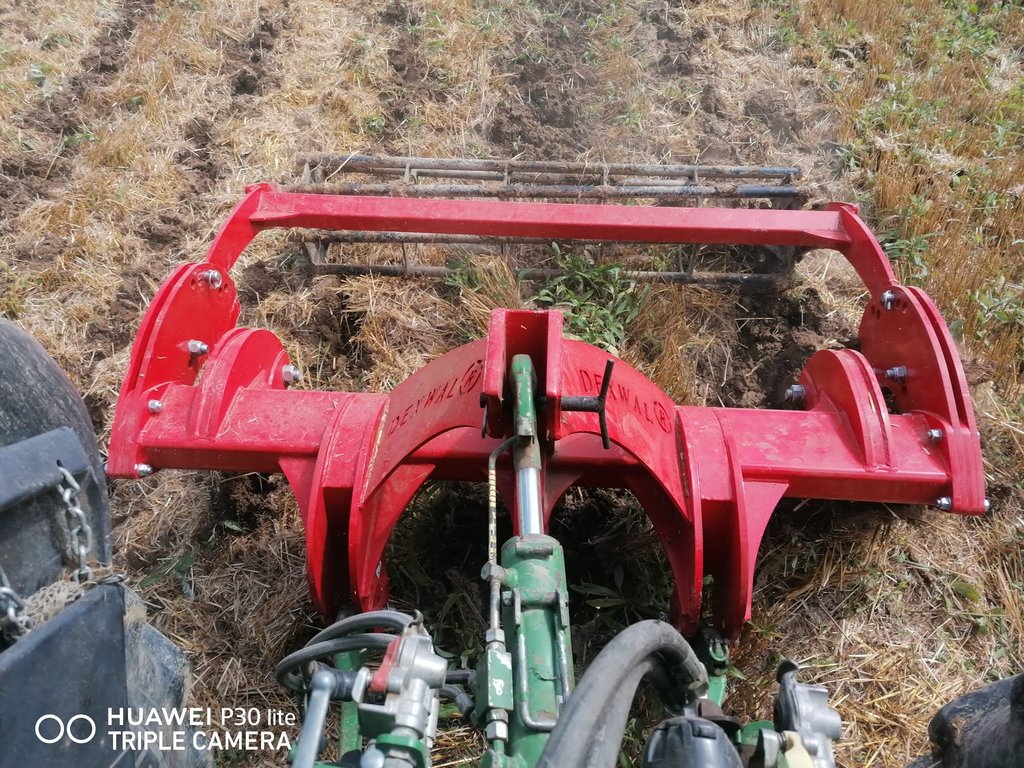
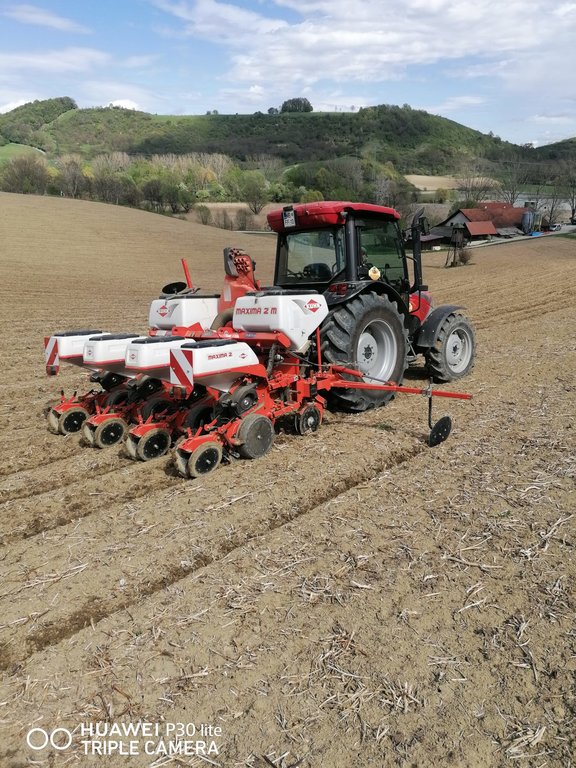
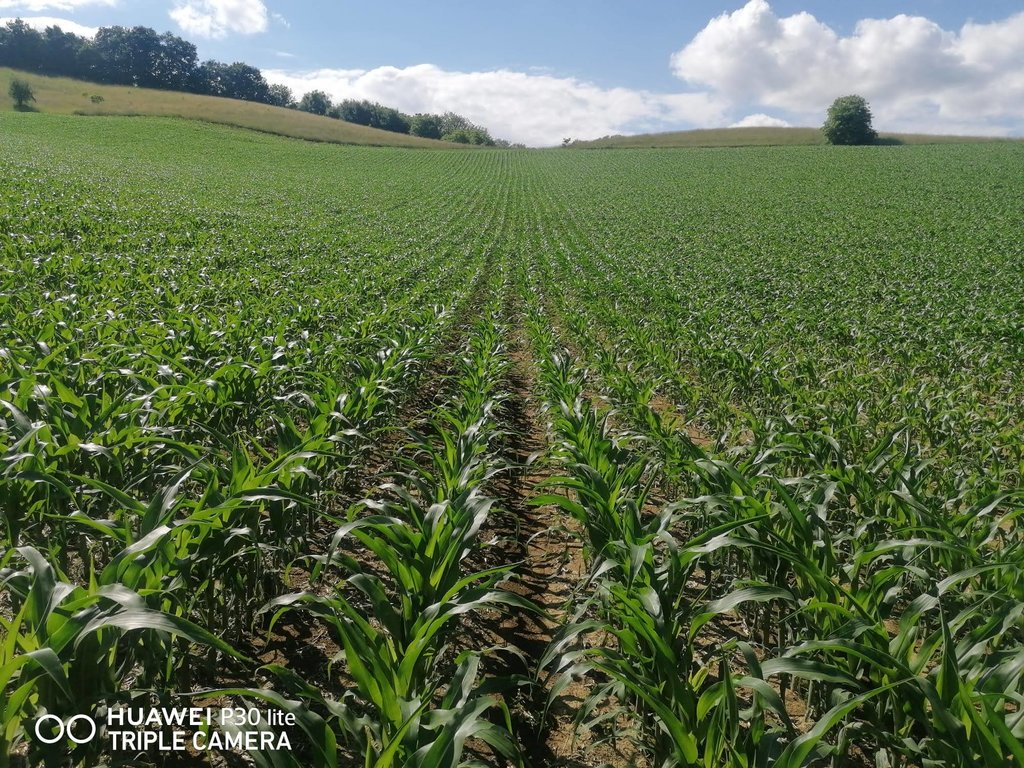
Mulch tillage technique and sowing of maize at the Ropič farm.
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ສະໂນວາເນຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Jareninski dol, Pernica
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Vosek
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸປີ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
2020
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
A few years ago, the farmer transitioned from traditional plowing to a mulch-tillage technique and has been using this method since 2020. In 2021, the farmer sought assistance from a consulting service to connect with the Biotechnical faculty in Ljubljana. Tests were conducted to assess the impact of conservation tillage. Following the positive results, the farmer has continued collaborating with the Biotechnical faculty and the public advisory service, further experimenting with the technology and maintaining the new cultivation approach. Today, he is one of the prominent advocates of conservation tillage.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ເຂົ້າບາເລ້
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ສາລີ
- ທັນຍາພືດ - ເຂົ້າສາລີ (ລະດູ ໜາວ)
- ພທດອາຫານສັດ- ປະເພດດອກ
- ພືດອາຫານສັດ-ພືດປພະເພດອື່ນໆ
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວປະເພດອື່ນໆ
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວເຫຼືອງ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 1
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Continuously 1 main crop: maize, wheat (winter) or barely (winter) and fodder peas or soy. After the main crop, the rotation includes cover crops (greening) which consist of mixtures of plants such as phacelia, clover, mung bean, etc.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
- ການຈັດການອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນປະສົມປະສານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
- A6: ການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ
A3: ລະບົບການໄຖແຕກຕ່າງກັນ:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6: ລະບຸການຈັດການສິ່ງເສດເຫຼືອ:
A 6.4: ເກັບຮັກສາໄວ້
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Whether it is low-till or conventional tillage depends on the tool use during soil tillage and how we use it. There are many implementation variants of conservation tillage that go by different professional names and definitions. Low-till is defined according to the depth of tillage, the intensity of soil layer mixing, the coverage of soil surface with harvest (organic) residues or intermediate tillage residues, according to the way tools move on the soil and the number of machine operations that are performed individually or combined (basic tillage, soil loosening seedbed preparation, pre-sowing tillage, sowing, ...). We focus on one version of low-till that we estimate has the greatest chances of being established in a short time in the case study area, which is so called »mulch-till«. We will concentrate on the term »mulch-till« which we define as a medium deep (10 cm) conservation tillage technique using chisel plow in combination with disk harrow. The coverage of the soil surface with residues must be at least 30% or higher. In addition, a special seeder is required to carry out "mulch" sowing (with moving parts). The success of mulch-till also depends on the combination with other implemented measures like crop rotation, cover crops, etc.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Bodenbear beitung und Bestellung
ວັນທີ:
2015
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
1 ha
ຖ້ານໍາໃຊ້ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ເນື້ອທີ່ຕາມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ໃຫ້ປ່ຽບເປັນ 1 ເຮັກຕາ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: 1 ເຮັກຕາ = 4 ໄລ່ ): 1 ເຮັກຕາ = :
1 ha = 10,000 m2
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
EUR
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.97
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
90.90
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of 2-row disc harrow | 1st year |
| 2. | Purchase deep chisel plow | 1st year |
| 3. | Purchase pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow | 1st year |
| 4. | Purchase pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements | 1st year |
| 5. | Purchase cover crop seed drill | 1st year |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Tractor should also be considered as part of the investment in implementing the mulch-till technology. The required tractor for operating Mulch-till is at least 110 HP. Let's assume a tractor with four-wheel drive, 95–125 kW (129–170 HP), with an investment cost of 66,400 €. Its usage should be economically justified for the entire farm (used for all farm tasks).
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸປະກອນ | Purchase of 2-row disc harrow | piece | 29.7 | 404.0404 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Purchase deep chisel plow | piece | 29.7 | 101.0101 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow | piece | 29.7 | 909.0909 | 27000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements | piece | 29.7 | 572.3905 | 17000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Cover crop seed drill | piece | 29.7 | 151.5151 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 63500.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 65463.92 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The estimated lifespan of the equipment represents only an illustrative measure in terms of total hours, hectares, or machine work until its obsolescence. This data is not considered in the cost calculation. It is generally not economically viable to use a machine until its complete obsolescence, as it may become technologically outdated or require excessive investment for restoration compared to its economic usage. It is more sensible to use the machine's depreciation period. The average depreciation value is determined based on the average annual usage of the machine. The depreciation period for attachments is 12 years.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor operation and maintanance | It is used for all operations related to the technology (without cover crop seed drill operation).. |
| 2. | Deep chisel plow operation and maintanance | 1 time per 5 years, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 1.0 h/ha. |
| 3. | 2-row disc harrow operation and maintanance | 2 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 0.8 h/ha. |
| 4. | Pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements operation and maintanance | 1 times per year, on 50 % of all cultivated field surfaces (14.85 ha), 1.3 h/ha. |
| 5. | Cover crop seed drill operation and maintanance | 1 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha), 0.8 h/ha (combined with harrow). |
| 6. | Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow operation and maintanance | 1 times per year, on 50 % of all cultivated field surfaces (14,85 ha), 1.4 h/ha. |
| 7. | Purchase cover crop seed mixture Fruh | 1 time per year, on all cultivated field surfaces (29,7 ha). |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Tractor operation | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 18.144 | 538.88 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Machine maintenance | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 2.88 | 85.54 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of tractor operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 122.598 | 3641.16 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of deep chisel plow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 4.36 | 129.49 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of 2-row disc harrow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 30.432 | 903.83 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of pneumatic precision planter with rotating elements operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 14.85 | 29.744 | 441.7 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of cover crop seed drill operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 2.872 | 85.3 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Machine avarage total costs of Pneumatic seed drill combined with rotary harrow operation and maintanance | EUR/ha | 14.85 | 52.416 | 778.38 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Cover crop mixture Fruh | EUR/ha | 29.7 | 66.768 | 1983.01 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 8587.29 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 8852.88 | |||||
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
It very much depends on the type of soil, what is the structure of the soil. In addition, the planning of the crop rotation and cover crops also affect the costs. As a result, weed development and subsequent herbicide use may be different.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1015.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
The most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are June and August, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Jareninski vrh (1981 – 2010)
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Mean annual temperature in year 2014 Jareninski vrh is 11,9°C.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ລັກສະນະກີ່ວ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
There are depressions, settlements are in the valley, concave type.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາພຽງຢ່າງດຽງ (ຊົນລະປະທານ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ເປັນປົກກະຕິ:
ຕອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Hydromelioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດກາງ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
based on national legal system
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Some farmers report a slight drop in yield in first years after the implementation of the measure, but the farmer in the case study location didn't notice any difference in yield.
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຕໍ່ຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Reduced risk, but with the wrong approach it can increase. For example, reduced risk due to unfavorable weather conditions, increased risk due to the possibility of weed development.
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Simplified soil tillage technology.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Reduced costs due to lower energy (fuel) consumption.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Fewer hours dedicated for tillage.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Facilitated production with lower costs, motivation to do business in agriculture.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ການທັບຖົມຂອງດິນ
ດິນເປັນຜົງ / ການຈັບໂຕຂອງດິນ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ທີ່ມີການຈັບໂຕກັນເປັນກ້ອນ
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ສາຍພັນຕ່າງຖີ່ນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Cover crops act as hiding places for various animals.
ຊະນິດທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Plants attract pollinators.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Surface cover with plants.
ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ກ່ຽວກັບພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ ສາທາລະນະ / ເອກກະຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The soil is not carried into ditches and ponds.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ຄື້ນຄວາມອົບອຸ່ນ | ດີ |
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ດິນເຈື່ອນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງລົບເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The initial establishment and investment costs for implementing the technology are high, and in the short term, the benefits may not be very noticeable or even negative compared to conservative technology. However, the long-term benefits are more significant and positive. While there are recurring costs involved, such as maintenance expenses, they are considerably lower compared to the initial investment costs. The technology requires substantial upfront investment in equipment, which can initially outweigh the immediate returns. It takes time for the technology to mature and for the full benefits to be realized. As the system becomes established and optimized, the positive outcomes become more apparent over the long run. Additionally, the lower costs mentioned refer to the ongoing maintenance and operational expenses required to sustain the technology (machines), which are generally lower than the initial investment costs. These costs are often outweighed by the benefits gained from improved efficiency, reduced resource consumption, and other long-term advantages. Therefore, while the short-term returns may not be overwhelmingly positive, the investment in the technology pays off over time, with greater benefits and lower operational costs.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸແຈ້ງ):
added equipment/mechanization attachments to facilitate technology implementation, improved technology implementation with knowledge and experience
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Added cover crop seed drill. more emphasis on cover crop.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Less depression, erosion and soil leaching. |
| Cost and time (fewer passes, machine hours, less machine power required). |
| Care for nature, sustain natural resources. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| In the long term it enables the achievement of better soil conditions, in terms of appropriate ratios of water, air, nutrients, organic matter, microbial activity, pH, microbial activity, pH and other factors of soil fertility. |
| Compaction and drying of the top layer of the soil is significantly less frequent and as a result losses of young plants are therefore smaller. |
| It reduces the potential for soil erosion. A major threat to soil fertility is erosion processes (wind, water and other erosion), where the most fertile surface layers of the soil are carried away to other parts of the ecosystem that are not intended for food production. |
| It brings advantages in terms of energy consumption and the possibility of carrying out production tasks in a shorter time and in difficult weather conditions. Conservation tillage tools typically operate in a shallower soil layer and mix less soil mass, it enables the use of tools with larger working widths and thus less unproductive driving in the field. |
| Benefits in terms of reduced transfer of phytopharmaceuticals and nutrients excess from the cultivation area to water and other ecosystems. |
| Reduced tillage improves soil quality, reduces nutrient leaching and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Benefits in terms of bioavailability and nutrient uptake efficiency. |
| Benefits in terms of greater adaptability of crops to extreme weather events. |
| Benefits in terms of maintaining the overall biological diversity of the agricultural landscape and soil. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| A big investment in machinery. | It is possible to start gradually with cheaper and simpler machines (also home-made). |
| Adaptation of crop protection. | Implementing integrated pest management (IPM). |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| An increase in the occurrence of certain types of weeds and a high dependence on certain types of herbicides. Some studies show that the introduction of conservation tillage slightly increases losses from certain diseases and pests. | For successful weed control, it is important to have a varied crop rotation, frequent sowing of cover crops and intercrops, and that the weeds never leave uncontrolled development on the stubble. The variegated crop rotation is meant as an obstacle that interrupts the development cycle of diseases and pests. How we handle harvest residues is also important. The more finely they are chopped by combines, mulchers or tools for vertical tillage before sowing, the faster they decompose and the worse the chances of harmful organisms developing on them. An evenly distributed mulch of harvest residues should remain, which prevents the emergence of new waves of weeds. These additional measures, together with mechanical weed control with new types of tools, allow limiting the weed population to a level that can be controlled with a limited range of herbicides. |
| Investment costs in machines designed for the method of soil cultivation can be very high. An important obstacle in the introduction of conservation tillage is the large investments in new machinery... The value of purchasing these tools can well exceed the amount of 100,000 euros for an individual farm, which is a practically unfeasible investment for small farms. | Small farms can take the transition to conservation farming only with the help of hired machinery services from neighbouring large farms that have been able to invest in new equipment. The subsidization of the purchase of machinery and also the economic legal status of the farm in terms of VAT calculation play an important role. |
| It is necessary to replace all the tools used by farmers according to the old methods of tillage. It is necessary to purchase adapted cultivators, harrows, looseners and especially seeder drills. | Increase in the supply of relatively inexpensive machines from manufacturers from Eastern Europe and Turkey, which can increase the availability of this equipment to smaller farms. |
| In the first years of the transition period, there may be a significant reduction in yields and poor financial results. There is a yield reduction and financial stress during the transition period to the new system. The transition from conventional cultivation to conservation tillage is usually difficult and risky. | Growers must be financially strong in order to make the transition, and the areas under alternative cultivation systems must increase gradually when they really master the new cultivation technique. Good financial support during the transition period is very important for small farms with weak investment assets. Targeted education and training is necessary, as technological errors due to lack of knowledge regarding the implementation of conservation cultivation in different soil types can be economically very fatal. |
| A small increase in the seeding rate (10 to 15 %) is often recommended to compensate for losses caused by diseases and pests at the time of plant emergence. | A necessary cost that must be accepted (higher sowing rate for the main crops and additional crops – cover crops) for the successful implementation of the measure. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
1 farmer (Andrej Ropič)
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3 (Biotechnical Faculty; Matjaž Glavan, Miha Curk, and Rozalija Cvejič)
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
2 (we utilized the following documents: "ANALYSIS OF ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF ALTERNATIVE AGRONOMIC PRACTICE (AAP) ON VVO" by Črtomir Rozman, Karmen Pažek, Mario Lešnik, and "Bodenbearbeitung und Bestellung Definition von Bodenbearbeitungs- und Bestellsystemen" (translated to English as "Tillage and cultivation Definition of tillage and cultivation systems") by Dr. Joachim Bischoff et al.)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
17/01/2023
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Visit to the farm and farmer interview. A working group was established, where we met 2 times to review and respond to the questionnaire.
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
TJ Townsend, SJ Ramsden, P Wilson. Analysing reduced tillage practices within a bio-economic modelling framework. Agricultural Systems 146 (2016) 91–102.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
ScienceDirect
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
E Houshyar, MJ SheikhDavoodi, M Almassi, H Bahrami, H Azadi, M Omidi, G Sayyad, F Witlox. Silage corn production in conventional and conservation tillage systems. Part I: Sustainability analysis using combination of GIS/AHP and multi-fuzzy modeling. Ecological Indicators 39 (2014) 102–114.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
ScienceDirect
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
C Rozman, K Pažek, M Lešnik. Analiza ekonomske ucinkovitosti alternativne agronomske prakse (AAP) na VVO. Univerza v Mariboru, Fakulteta za kmetijstvo in biosistemske vede, 2018.
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjNtpH7peD8AhWFzaQKHdPXBM4QFnoECAYQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.kgzs-ms.si%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2018%2F07%2FD.T3.3.1-Study-final-May-2018.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3qni6nXmwUM25mhI0FwPln
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Mimalna obdelava tal – praktični primeri na naših kmetijah (žipo, ropic, horvat)
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwiZ6smRpuD8AhWrsaQKHcRSBoMQFnoECAkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.kmetijski-zavod.si%2FPortals%2F0%2Flombergarjevi%2FMinimalna%2520obdelava%2520tal%2520%25E2%2580%2593%2520prakti%25C4%258Dni%2520primeri%2520na%2520na%25C5%25A1ih%2520kmetijah%2520%5BSamodejno%2520shranjeno%5D.pdf%3Fver%3D2021-12-13-094249-623&usg=AOvVaw1jtWGuL4ovgrvC0rvqm1iS
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ