Organic Agriculture with Reduced Tillage [ຢູເຄນ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Natalia Prozorova
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Organic Agriculture
technologies_7440 - ຢູເຄນ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Prozorova Natalia
National Scientific Center «Institute for SoilScience and Agrochemistry Research, named after O.N. Sokolovsky»
ຢູເຄນ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Delft University of Technology (TU Delft)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
This organic agriculture technology combines reduced tillage with organic farming practices to enhance soil health, increase carbon sequestration, and maintain sustainable agricultural productivity.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
This example of organic agriculture is applied primarily in the central Poltava region of Ukraine, which is characterized by undulating plains within the Poltava Plateau. The region’s fertile chernozem soils provide an ideal environment for sustainable farming practices. These soils are predominantly deep, medium-humus, medium-loam chernozems, known for their agronomically favourable physical and chemical properties, including high organic carbon content (around 3% in the upper layer) and excellent water retention capacity. The natural fertility of these soils, combined with their relatively high nitrogen and exchangeable potassium content, underpins their suitability for organic farming.
Organic agriculture in this context combines two land management technologies (LMTs): reduced tillage and organic farming. Reduced tillage minimizes soil disturbance, which preserves soil structure and reduces erosion, while organic farming eliminates synthetic inputs and relies on crop rotations, organic fertilizers, and biological pest control to maintain soil health and ecosystem balance. The purpose of these practices is to enhance soil carbon sequestration, mitigate climate change impacts, and support sustainable agricultural productivity.
Farming is certified as a producer of organic plant products in accordance with the standards equivalent to Council Resolutions (EU) 834/2007 and 889/2008.
Under this system, shallow tillage is carried out to a depth of 4–6 cm, which helps preserve the natural structure and capillarity of the soil. It employs Horsch cultivators of the "Agrosoyuz," "Scorpion," and "Quant" models. The enterprise also extensively uses disc harrows from the French manufacturer Grégoire Besson, such as the DXRV and DXRV-HD models, which are employed for green manure incorporation. These tools operate at a precisely determined depth, regardless of the micro-relief of the field. Thus, PE "Agroecology" does not use ploughs for inversion tillage but instead prioritizes shallow tillage with cultivators and disc harrows.
The main crops grown include winter wheat, soy, corn, sunflower, and perennial herbs such as sainfoin. The combination of these crops supports soil fertility and biodiversity while maintaining agricultural productivity. Land Mitigation Technology (LMT) refers to practices and technologies designed to reduce or offset the environmental impact of land use activities. It includes strategies for restoring degraded ecosystems, preventing soil erosion, conserving biodiversity, and managing resources sustainably. LMT is often applied in agriculture, construction, and land development to balance development needs with environmental protection.
Key activities to establish and maintain the technology include transitioning from conventional to organic farming practices, adapting tillage methods to reduced-intensity operations, and maintaining organic soil fertility through natural inputs. These activities require significant initial effort and investment, including soil testing for nutrient content and organic carbon stocks, stakeholder engagement for field planning, and long-term monitoring of soil health indicators. The establishment process also involves collaboration with scientific institutions, such as ISSAR and Bioclear Earth, to ensure effective implementation and validation of the technology.
The primary benefits of this technology include improved soil structure, increased biodiversity, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and enhanced carbon sequestration. The technology has demonstrated the potential to sequester up to 0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, with minimal yield trade-offs. Additionally, the resilience of the chernozem soils supports similar crop yields in both organic and conventional systems, thanks to their natural fertility and lower input rates in conventional agriculture. Farmers particularly value the long-term sustainability and ecological benefits of organic farming.
Land users face challenges with this technology. Transitioning to organic farming can result in temporary yield reductions, requiring adaptation in farm management practices. Furthermore, reduced tillage demands specific equipment and techniques, which may present a financial barrier for some farmers. The implementation of organic farming also requires significant effort in pest and weed management due to the absence of chemical inputs.
Overall, this form of organic agriculture represents a promising approach to sustainable farming in Ukraine, particularly in the fertile Chernozem region. Its ability to enhance carbon sequestration while maintaining comparable yields to conventional systems highlights its potential to contribute to climate mitigation and soil restoration goals. Further research and field validation are needed to refine the understanding of its impacts and optimize its implementation.
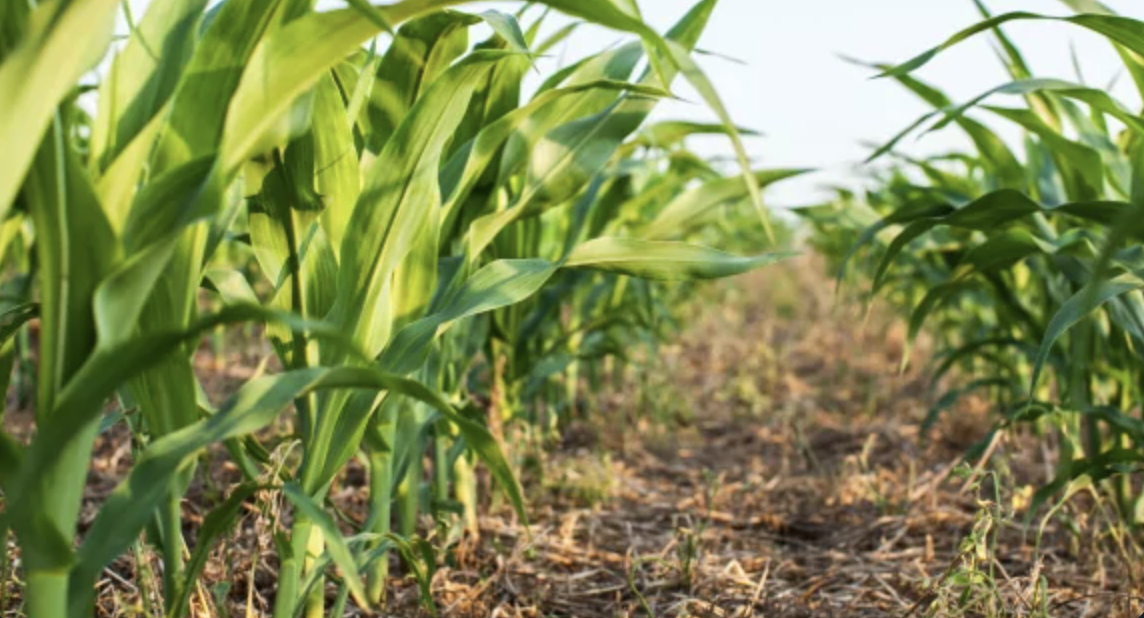
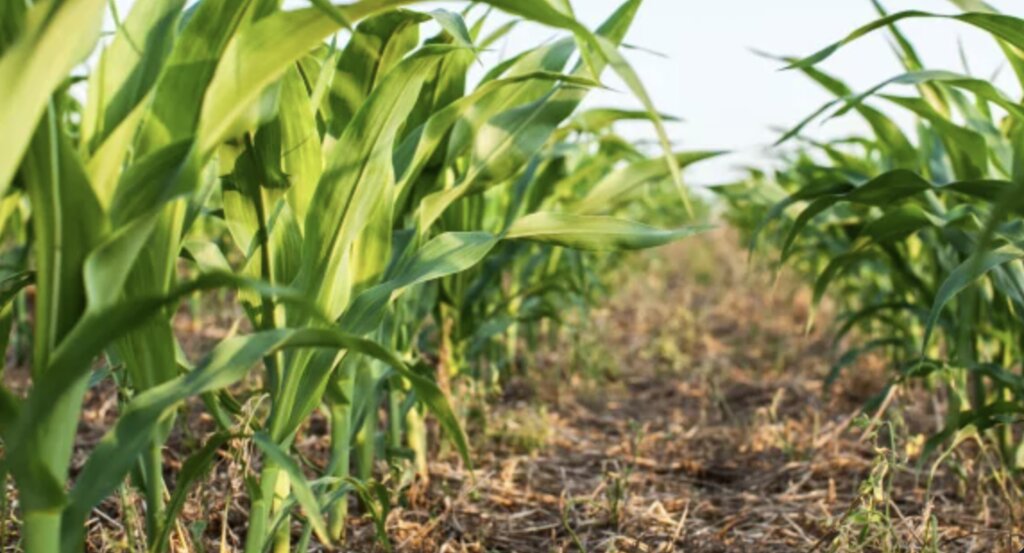
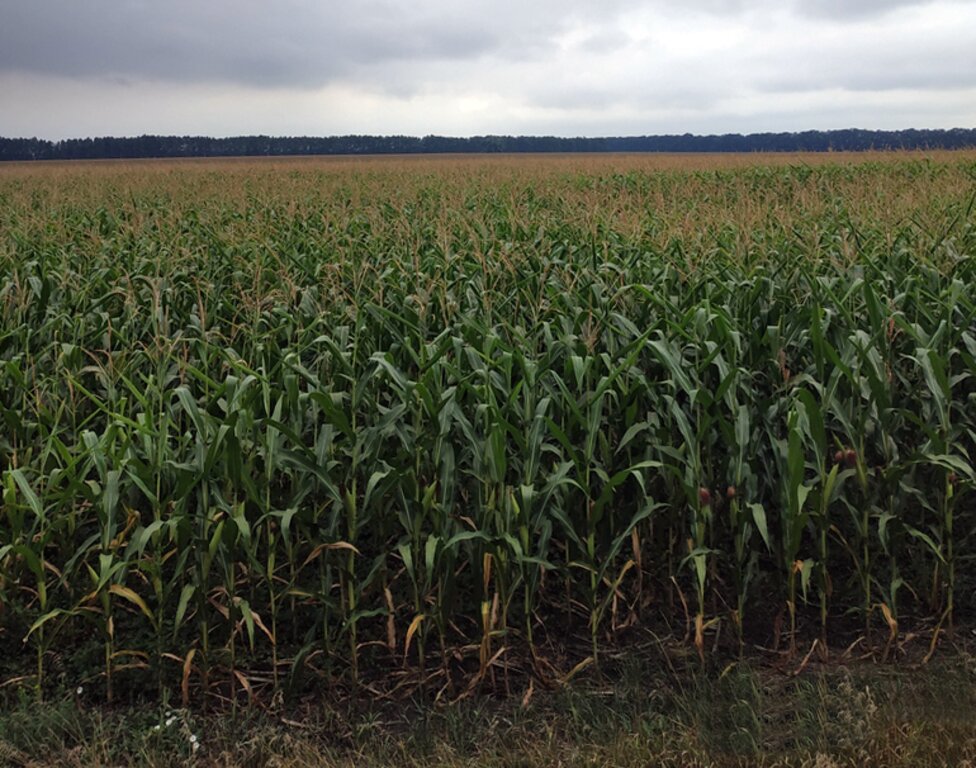
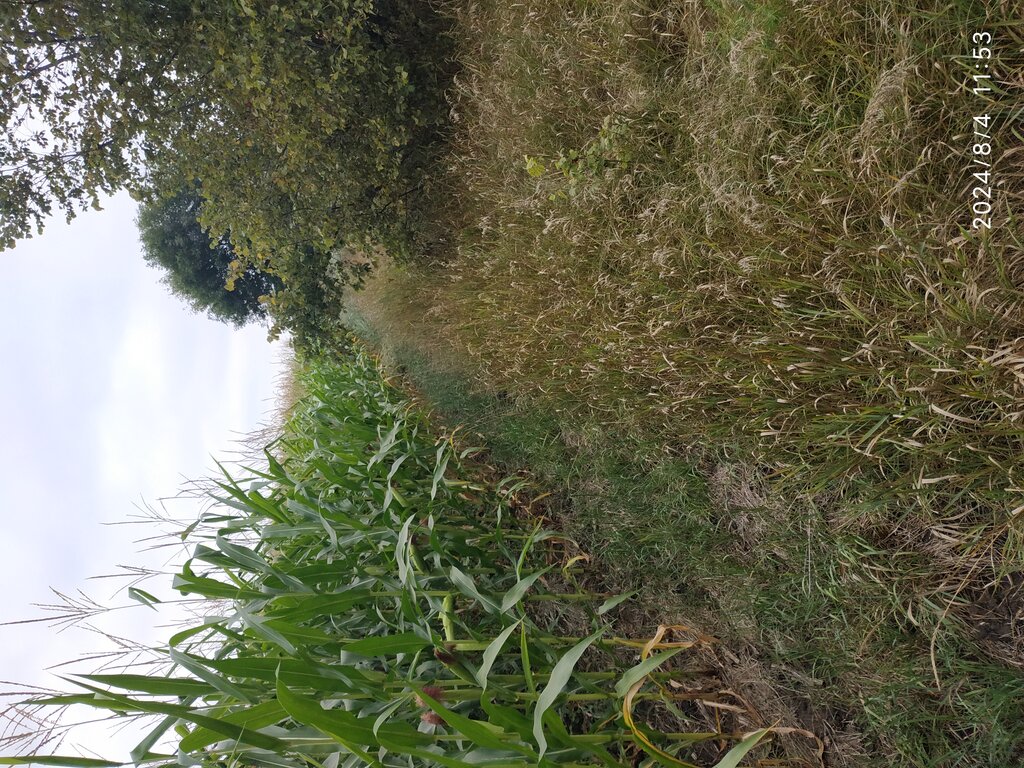
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດທົ່ວໄປທີ່ກ່ຽວກັບຮູບພາບ:
The photos provide a detailed view of the agricultural practices in the field, highlighting the healthy state of the maize crops in central Ukraine. These images capture the natural environment where organic farming techniques are being applied, showcasing the crops' growth, the quality of the soil, and the overall ecological balance. The close-up shots emphasize the care taken to maintain soil health and biodiversity, aligning with the principles of organic farming. The visuals also illustrate the sustainable land management practices that promote environmental stewardship and high agricultural yields.
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ຢູເຄນ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Poltava region, Shishaky area
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Poltava region on the left bank of the river Psyol, in 20 km from urban-type settlement Shishaky and in 80 km to the regional center Poltava
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 1,000-10,000 ກມ 2
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- 10-50 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
- chernozem productivity assessment between conventional and traditional agriculture
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- Perennial herbs
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- cereals - buckwheat
- ທັນຍາພືດ - ເຂົ້າສາລີ (ລະດູ ໜາວ)
ລະບົບການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ:
ເຂົ້າສາລີ ຫຼື ພືດຫມູນວຽນຄ້າຍຄືກັນກັບ ຫຍ້າ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Spring/Summer Season; Autumn/Winter Season
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
Intercropping involves a combination of perennial herbs (such as sainfoin) with annual crops like buckwheat or sunflower. This practice helps optimize resource use, improve soil fertility, and enhance field biodiversity.
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The crop rotation system includes a diverse mix of:
Annual crops: Buckwheat, winter wheat, soya, corn, and sunflower.
Perennial crops: Sainfoin, spelt, and other forage herbs.
This rotation is designed to Maintain soil fertility, Reduce the risk of pests and diseases, Optimize nutrient use, and Support sustainable farming practices. The rotation is adapted to the specific soil and climatic conditions of the region to ensure long-term productivity and environmental health.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ບໍ່ (ຕໍ່ເໜືອງກັບ ຄຳຖາມ 3.4)
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
- ການຈັດການອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນປະສົມປະສານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Some water and wind erosion (but almost no erosion at all)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The organic agriculture system in Poltava prevents land degradation through sustainable practices, including:
Reduced tillage: Maintains soil structure and minimizes erosion.
Use of mulch: Organic mulch, such as crop residues, is applied to protect the soil from wind erosion, conserve moisture, and reduce surface runoff.
Crop rotation and intercropping: These practices improve soil health, reduce nutrient depletion, and promote biodiversity.
Green manure incorporation: Enhances soil organic matter and strengthens soil resilience against degradation.
This proactive approach ensures that the fertile chernozem soils remain productive and sustainable for future generations while reducing the risks of erosion and nutrient loss.
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Dimensions of Structures or Vegetative Elements:
Raised Beds/Planting Rows: Typically range from 10–30 cm in height and 30–60 cm in width, depending on crop and soil type.
Plant Spacing: Varies by crop; cereals (e.g., wheat, barley) are spaced 20–30 cm apart, while row crops (e.g., sunflower, corn) are spaced 50–80 cm apart. Cover crops are planted more densely, up to 200 plants/m².
Vertical and Lateral Gradients:
Contour Planting and Terraces: Applied in areas with slopes of 5–15°. Terraces or contour planting are spaced at 5–20 meters vertically to reduce erosion and enhance soil stability. The lateral gradient is maintained at ≤1% through contour plowing or vegetation strips, following natural land contours.
Slope Adjustment:
Before and After Technology Implementation: Initial slopes (5–15°) are slightly leveled or terraced, reducing slope gradients to improve soil stability and prevent erosion.
Machinery for Reduced Tillage:
The technology employs Horsch cultivators (e.g., AgroSoyuz, Scorpion, Quant) and disc harrows from Gregoire Besson (DXRV and DXRV-HD models). These tools are precisely calibrated to a shallow tillage depth of 4–6 cm, ensuring minimal soil disturbance.
These machines operate efficiently, incorporating green manure while preserving the soil's natural structure and capillarity. They eliminate the need for plowing, which is traditionally associated with significant soil disruption.
Species Used and Plant Densities:
Legumes: Clover, vetch, sainfoin.
Cereals: Winter wheat, barley, spelt.
Row Crops: Sunflower, corn.
Cover Crops: High-density planting up to 200 plants/m² for effective soil coverage and nutrient cycling.
Plant Densities: 150,000–200,000 plants/ha for cereals and legumes; 30,000–50,000 plants/ha for row crops.
Materials Used:
Construction materials include loamy soil, organic mulches, compost, and locally sourced biomass.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Larisya Shedei
ວັນທີ:
12/04/2023
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
7000 ha, it represents a large typical farm in Ukraine. It’s also a convenient size for scaling up agricultural solutions or technologies.
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
depending on local conditions and the type of labor required (e.g., general farm work vs. skilled machinery operation)
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil testing (chemical & biological) | Pre-season |
| 2. | Transition planning (certification) | Pre-season (2-3 months before planting) |
| 3. | Cover crop seeds (e.g., clover, vetch) | Pre-season (1-2 months before planting) |
| 4. | Compost/organic amendments | Pre-planting (2-3 weeks before planting) |
| 5. | Reduced tillage equipment upgrade | Pre-season (1 month before planting) |
| 6. | Labor for initial setup (e.g., planting cover crops) | Pre-season (1–2 weeks before planting) |
| 7. | Miscellaneous inputs (mulches, fencing, etc.) | Pre-season (1–2 weeks before planting) |
| 8. | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | Annual (pre-planting) |
| 9. | Cover crop replanting | Annual (during planting season) |
| 10. | Reduced tillage operations | Annual (during planting season) |
| 11. | Organic pest and weed management | Annual (growing season) |
| 12. | Labor for maintenance activities | Annual (during planting season) |
| 13. | Miscellaneous (repairs, small inputs) | Annual (as needed throughout the year) |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Establishment costings include the first year of operations
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Consulting fees, planning materials | session | 10.0 | 2500.0 | 25000.0 | 50.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Labor for planting cover crops | Day | 4200.0 | 50.0 | 210000.0 | 20.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Labor for weeding, pest management, maintenance | Day | 4200.0 | 50.0 | 210000.0 | 15.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Equipment rental or purchase | machine | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Reduced tillage equipment use | ha | 7000.0 | 150.0 | 1050000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Cover Crop Seeds (e.g., clover, vetch) | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 25.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Replanting of cover crops | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 20.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost/Organic Amendments | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 35.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Organic fertilizers | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 25.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Organic pest control (biocontrols, organic pesticides) | liter | 35000.0 | 30.0 | 1050000.0 | 25.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Mulches, fencing | unit | 7000.0 | 2.5 | 17500.0 | 15.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Soil Testing (chemical & biological) | test | 7000.0 | 20.0 | 140000.0 | 30.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Small repairs, inputs like mulches | unit | 7000.0 | 2.5 | 17500.0 | 10.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 4705000.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 4705000.0 | |||||
ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ໄຈ້ແຍກຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນຕາຕະລາງຂ້າງເທິງ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນຂອງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງຫມົດ ຂອງການສ້າງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
4705000.0
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The land user is responsible for 60% of the total costs, The remaining 40% could be covered by government subsidies, agriculture support programs, or sponsorships from private companies involved in the agritech or sustainable farming sectors.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cover crop replanting | Annually (during planting season) |
| 2. | Reduced tillage operations | Annually (during planting season) |
| 3. | Organic pest and weed management | Annually (growing season) |
| 4. | Labor for maintenance activities | Annually (during planting season) |
| 5. | Miscellaneous repairs and small inputs | As needed throughout the year |
| 6. | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | Annually (pre-planting) |
| 7. | Soil health monitoring (e.g., soil testing) | Every 2-3 years (or as needed) |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Organic pest and weed management | ha | 1000.0 | 50.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Labor for maintenance activities | day | 7000.0 | 50.0 | 350000.0 | 80.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Reduced tillage operations | Equipment | 1.0 | 200000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Cover crop replanting | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Miscellaneous repairs & small inputs | Unit | 70000.0 | 2.5 | 175000.0 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Soil health monitoring (soil testing) | test | 7000.0 | 20.0 | 140000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1895000.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 1895000.0 | |||||
ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ໄຈ້ແຍກຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນຕາຕະລາງຂ້າງເທິງ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນຂອງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງຫມົດ ຂອງການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
1895000.0
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
remaining costs covering by government programs, investors, depending on the context and support mechanisms available.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
For Soil Health Monitoring, the cost is distributed over 2-3 years (based on testing frequency).
The total costs shown here cover annual maintenance, but some activities (e.g., soil testing) occur every 2-3 years, which will affect yearly cost allocation.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The costs of implementing and maintaining organic agriculture combined with reduced tillage as a land management technology are influenced by a combination of local factors, including labor, equipment, inputs, land conditions, certification, environmental factors, and scale of operation. Understanding these factors helps in estimating costs more accurately and planning for efficient resource use.
1. Initial Soil Testing and Amendments: Costs are influenced by the condition of Chernozem soils and the need for specific amendments to support organic farming practices.
Labor for Establishment and Maintenance: Seasonal labor demand for planting cover crops, applying organic fertilizers, and managing pests affects overall costs.
2. Specialized Equipment: Upgrading or accessing reduced tillage equipment tailored to this technology adds to establishment expenses.
3. Certification Requirements: Transitioning to certified organic farming involves costs for documentation, inspections, and compliance with standards.
4. Material Inputs: Price and availability of cover crop seeds, compost, and organic pest control products impact both establishment and recurrent costs.
5. Weather-Driven Costs: Unpredictable weather can lead to increased use of inputs like organic pest management and irrigation.
6. External Support: Grants, subsidies, or cost-sharing arrangements can reduce the burden on land users but are variable depending on donor or government programs.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
500.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Selyaninov’s Hydro-Thermal Coefficient 0.81-1.05, precipitation XI-III 140-150
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Cold period 120-133 days, assimilation of precipitation in the cold period 47%
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ສູງ (> 3 %)
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Typical chernozem medium-, low-humus (Haplic Chernozem)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
< 5 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ທັງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ແລະ ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບໍລິສັດ
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Crop yields increased by ~60% due to improved soil fertility and organic farming practices.
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
Enhanced marketability of products due to organic certification
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increased awareness and adoption of sustainable practices in the local community.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Improved organic matter content (+50%) and reduced soil compaction.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Carbon sequestration potential of 0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ observed
ລະບຸ ການປະເມີນຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ສະຖານທີ່ (ການວັດແທກ):
Soil organic matter measured at 5.5% after implementation, compared to 3.6% previously.
Water infiltration tests showed a 30% improvement over two seasons.
Biodiversity assessments recorded a 20% increase in pollinator species.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Reduced erosion and runoff benefit adjacent landowners
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Net GHG reduction due to carbon sequestration and reduced fertilizer use (0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹)
ກໍານົດ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບທາງນອກ (ການວັດແທກ):
Carbon footprint analysis identified a positive balance through sequestration and input optimization.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| Soil degradation | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Land users have observed a significant increase in extreme heat and drought events over the past decade, which have directly impacted crop yields and soil health. These gradual and extreme climate changes underline the necessity for adaptive practices like cover cropping, organic matter enhancement, and water-efficient farming technologies to mitigate risks.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- > 50%
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Most adopters implemented the technology spontaneously, driven by its potential to enhance soil health, reduce input costs, and improve long-term productivity. Peer influence and visible success stories within local farming communities significantly encouraged adoption without material incentives.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Land users see the technology as a sustainable solution that improves soil health, reduces input costs in the long term, and offers potential market advantages through organic certification, leading to higher-value crops and improved land productivity. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| From the key resource person’s perspective, the technology promotes long-term environmental sustainability, increases resilience to climate change, and contributes to carbon sequestration, while aligning with broader policy goals for sustainable agriculture and reduced environmental impact. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Initial high costs: The transition to organic agriculture and reduced tillage involves significant upfront investment in equipment, labor, and materials. | Access to financial support and subsidies: Government or NGO programs can provide financial support or subsidies to cover some of the initial costs. |
| Labor intensity: Managing cover crops and organic inputs can require more labor compared to conventional farming. | Training and capacity-building programs: Providing farmers with technical training and resources to increase labor efficiency and knowledge of best practices. |
| Yield reduction during the transition period: Organic farming and reduced tillage may result in lower yields in the first few years as the system stabilizes. | Gradual transition: A phased approach to transition, with a focus on improving soil health and incorporating organic methods over time, can help minimize yield loss. |
| Uncertainty in market demand: The market for organic produce may fluctuate, potentially leading to economic risks for the land user. | Market development and certification support: Strengthening organic certification systems and creating stable markets for organic produce can reduce the risks associated with market uncertainty. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Conducted surveys with 25 informants, including farmers and local community members, to gather practical insights and observations on the technology's implementation and impacts.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
Held structured interviews with two big farm owners actively using the technology to understand their experiences, challenges, and benefits observed.
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
19/03/2024
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Practices for Ukrainian Agriculture, ISSAR Team, 2022, 978-1234567890
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://issar.com.ua/shop/
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Carbon Sequestration through Organic Farming in Chernozem Soils, Dr. O. Ivanov, NSC ISSAR, 2021, 978-9876543210
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Publication portal, https://issar.com.ua/shop/
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Impact Assessment of Climate-Resilient Agricultural Technologies, M. Kuznetsov, NSC ISSAR, 2023, 978-5432167890
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Publication portal, https://issar.com.ua/shop/
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
National Scientific Center "Institute for Soil Science and Agrochemistry Research" (NSC ISSAR) Official Website
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Sustainable Land Management Practices in Ukraine
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/sustainable-land-management
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Organic Farming Transition Guidelines
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/organic-farming-guidelines
7.4 ຄຳຄິດຄຳເຫັນທົ່ວໄປ
The questionnaire and database provide a valuable platform for documenting technologies, but integrating more dynamic features and ensuring accessibility will further strengthen its utility for land users, researchers, and policymakers.
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ